A change in the temperature regime in four-month-old babies occurs during the activation of the protective functions of the body, which react with such symptoms to infection entering the child’s body. When the temperature of a 4-month-old child rises above 37 degrees, the bacteria begin to die and their reproduction is interrupted. As a result, pathogenic microflora dies out. Heat production in newborns works somewhat differently than in adults, heat production is active, and sweat glands are underdeveloped, so maintaining low-grade fever in infants in the first year of life can be considered normal.
Oral temperature measurement
37.4 for a 4 month old baby
A temperature of 37 4 in a 4-month-old child does not always indicate the presence of pathology or infection. After birth, the baby goes through quite a long path of adaptation to the environment. How long this process will take is an individual question: some children quickly get used to all the new conditions for them, others may suffer from ailments, runny nose, cough, intestinal infection and sleep problems. The children's nervous system is also not formed and will actively develop until the age of 10, so the physical and mental health of the baby undergoes complex transformations.
Important! In the first year of life, according to the vaccination calendar, most infants are vaccinated. As a rule, on the first and second days after, an increase in temperature may be observed - this is the body’s reaction to the introduction of a foreign substance. There is no point in doing anything about it unless the thermometer reads 38-39 degrees.
Temperature measurements can be taken:
- During sleep, these will be the most accurate numbers;
- While awake.
Before and after breastfeeding, after waking up and when overexcited, the indicators will be inflated and inaccurate.
Babies may have a fever in the morning
Normal temperature values
People are used to thinking that 36.6 is the norm and a sign of absolute health. However, a temperature of 37 4 in a 4-month-old baby is not necessarily a sign of the presence of the disease. A child at four months old has normal temperature readings of 37 and 37.2. But these values may not always be constant. At this age, the thermometer can show from 36 to 37.4, and this is the norm for children from birth to one year. The method of measurement and type of thermometers can contribute to different temperature readings.
Non-contact thermometer
37 degrees in a baby in the fourth month of life is considered normal, so it makes no sense to provide any assistance. If the fever begins to rise, antipyretics should be used.
Note! Children under 5 months should only lower their temperature at 38 degrees, and from 6 months - at 38.5. If you begin to reduce the temperature with medication at lower thermometer readings, this can significantly impair the child’s immune health.
When a baby at 38 degrees is cheerful, active, and does not show any signs of illness, then there is no need to panic. First you need to make sure how reliable the thermometer readings are.
Monitoring the baby's temperature
Low-grade fever in children under 1 year of age cannot be considered a decisive reason to consult a doctor. But only if there are no signs of disease. If:
- moodiness increases slightly at 37℃,
- drowsiness appears,
- the child becomes lethargic, eats poorly, does not want to play - even a slight deviation in the thermometer readings adds confidence that it is time to go to the pediatrician or call him at home.
But when the baby is happy and healthy, 37.3 can be an absolutely healthy value for him. This temperature must be monitored by measuring daily in the morning, afternoon and evening at the same time. This may be normal for your child. If you have determined it empirically and now know for sure, then you will easily notice an increase during a cold.

How to make sure there is no overheating? The skin should be soft pink, not red, the body should be warm, not hot, and the arms and legs should be a little cool.
Possible causes of overheating, in addition to excess clothing and an unfavorable microclimate in the room:
- swimming in water with a temperature above normal;
- being in a car in the heat; under no circumstances should you leave a baby alone in a closed car;
- walking outside on a sunny day without a hat;
- sleeping in a stroller in the sun or near a radiator - such overheating can lead to very serious consequences;
- dehydration.
Normal temperature indicators
What temperature a child should and can have at 4 months depends on the baby’s living conditions, type of feeding and many other factors.
Usually, up to six months, a child rarely suffers from infections caused by viruses, since social contact is limited. It is still possible to catch the disease during a routine examination by a pediatrician or if one of the family members carries the disease. The temperature varies between 36-37.5 degrees.
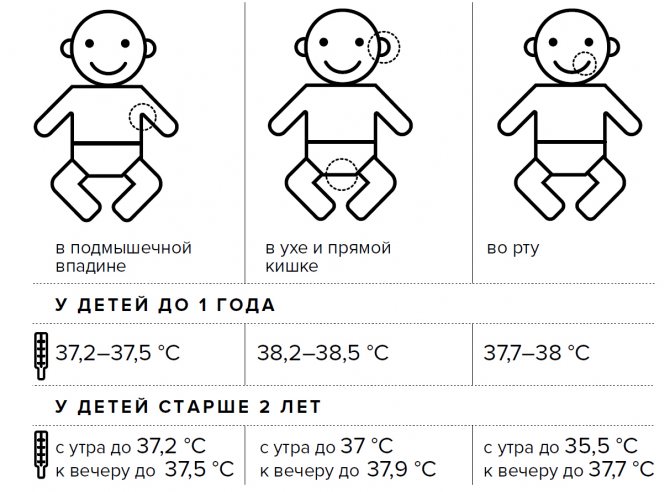
Indicators of normal temperature and methods of measuring it
Starting from six months, the risk of getting sick increases: complementary feeding is introduced, the baby is in active contact with other children and adults, and can catch chickenpox, rubella, and ARVI.
You should monitor the child’s condition and seek the help of a specialist if the following symptoms are detected:
- the baby is lethargic and weakened – this is a sign of the onset of an infectious disease;
- a runny nose appears, the color of the snot is yellowish-green - an allergic reaction or a cold;
- dry cough – the onset of bronchitis, pneumonia, colds or allergies;
- hoarse voice - this happens in the case of measles, tonsillitis, influenza, diphtheria, asthma, pneumonia;
- vomiting began - a consequence of food poisoning, gastrointestinal diseases, encephalitis, meningitis;
- diarrhea – the presence of an intestinal infection;
- headache – a consequence of ARVI, influenza, sinusitis, thermoneurosis, intoxication;
- abdominal pain - the onset of acute respiratory infections, poisoning, tonsillitis, whooping cough, measles, the presence of a foreign body in the stomach.
Additional Information. If a child's infectious disease is not treated, it can cause complications: pneumonia, bronchitis, tonsillitis and sinusitis. Therefore, it is important not to miss its onset, which usually manifests itself in an increase in body temperature.
Low-grade fever is normal
The normal temperature of a 4-month-old baby can be completely different at different times of the day. The most important thing is that the baby should be active, cheerful and cheerful, and have a good appetite.

If the baby is active and cheerful, there is no reason to worry
If the measurements are accurate, then if the readings are elevated, the fact of teething or vaccination that was done the day before should be excluded, since in these cases the temperature can be kept around 37.2-37.6. You should wait a while, a few days.
In addition, low-grade fever is a consequence of imperfect thermoregulation of the infant, which does not require any intervention. You should contact your pediatrician if your baby has chills, sneezing, lethargy and moodiness.
Note! Low-grade fever persists after taking antibiotics and suffering a serious illness. In this case, treatment is not necessary, but the situation should be kept under control. If a repeated runny nose or cough appears, then this may be a relapse, the appearance of a new infection.
Temperature readings for a three-month-old baby
The question of what normal temperature is considered in a 3-month-old child remains a conditional issue. The process of thermoregulation at this age is still not formed, so the reaction to temperature changes occurs extremely slowly. It will also be normal if the indicator fluctuates within one degree during the day. And this will depend on the activity of his behavior, what he did on the eve of thermometry (sleeping, eating, moving).
When a child is 3 months old, a temperature of 37, or more precisely 36.4-37.4 degrees Celsius, is considered normal and acceptable at this age. The main thing for the child is to be comfortable. Otherwise, he will be capricious, sweat, and show his dissatisfaction.
But a baby's body temperature is not a specific indicator of health or well-being at three months of age. So, the doctor pays attention to many other symptoms that can occur with a 3-month-old baby. So one 3-month-old child with a temperature above the specified indicator feels great, while for another it is a sign of the onset of some kind of inflammatory process in the body.
Why does the temperature rise
If the readings rise above 37.5 degrees, this indicates the onset of the disease. Most often it can be ARVI, overheating, teething or flu.
The most popular causes of fever among infants are:
- The onset of infectious childhood diseases: chickenpox, rubella, scarlet fever, whooping cough, measles. They can usually be found in children aged 2-5 years, when they begin to go to kindergarten and visit other institutions.
- Baby teeth will be coming through soon. From three months, the baby begins to put everything in his mouth, salivation increases, snot and runny nose appear, and the temperature may rise. The indicators do not rise above 38-39 degrees, and fall off for a short time.
- Presence of intestinal infection. In some cases, as early as four months, children are introduced to complementary foods that may contain pathogenic microorganisms. Once in the intestines, they contribute to the rapid development of poisoning or disorders. Symptoms of vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal pain appear.
- Inflammation of the upper respiratory organs: pharyngitis, laryngitis, otitis media, tonsillitis, pneumonia. In the treatment of these ailments, antibiotics are required.

Otitis in a baby
- The onset of a viral illness: ARVI, influenza and colds. Infection occurs through contact with a carrier of the disease. Treatment is carried out in combination with therapy and drug intervention.
Note! To prevent your baby from overheating, you should not wrap or swaddle him; it is advisable to dress him according to the weather. It is important to provide all the conditions for a comfortable microclimate in the room to prevent the development of various ailments.
Body temperature in newborns
In the first minutes of life, the body temperature of a newborn baby is approximately the same as that of the mother. After which, there is a decrease in temperature by 1-1.5 degrees (this is why prevention of hypothermia in the first hours of a baby’s life is so important). By about 5-6 hours of life, the temperature gradually rises and reaches average values - 36.5 -36.8 degrees. During the first week, the temperature may rise to 37.0 degrees.
A small percentage of newborns, on days 3-5 of life, may experience a sharp rise in body temperature to 38.0 -39.0 degrees. This condition is called transient hyperthermia of the newborn.
Transient hyperthermia can be manifested by the following symptoms: the child becomes restless, drinks or suckles greedily, and has dry mucous membranes. Predisposing factors for transient hyperthermia are: overheating of the child (high air temperature in the room, location of the crib next to the radiator or in direct sunlight, warm clothes), lack of food (during the hot season). Treatment of transient hyperthermia involves eliminating the factors that led to an increase in body temperature; physical cooling of the child (the child is left naked, while body temperature is regularly monitored); an additional amount of liquid is prescribed (add with 5% glucose solution in a volume of 50-100 ml).
Transient hyperthermia is not so common - only 0.3-0.5% of cases. To a greater extent, newborn children are prone not to an increase in body temperature, but to a decrease (hypothermia). This is due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of newborns and the fact that the child finds himself in new (not as comfortable as before) living conditions.
Due to imperfect thermoregulation processes, newborn babies (especially premature babies) easily overheat and cool under external conditions that are not comfortable for them.
To prevent hypothermia, immediately after birth the baby is wrapped in a sterile diaper (pre-heated under a source of radiant heat), carefully wiped (wet) with this diaper, removed and replaced with a dry one. The child is placed on a heated table under a radiant heat source. The air temperature in the delivery room should be at least 24-25 degrees. A cap is placed on the baby's head.
There is no daily rhythm of body temperature in newborns; it begins to form after 2 months of life and is less pronounced than in adults.
Due to imperfect heat production and heat transfer in a newborn, in the first weeks of the baby’s life, it is better to give preference to diapers rather than undershirts and rompers. The baby will feel more comfortable in diapers.
Many parents are afraid of overheating or overcooling their baby and therefore often wonder what the air temperature should be in the room where the newborn baby is. Different experts give different figures and the spread is quite large - from 18 to 25 degrees. I would recommend focusing on your own feelings, and observing the baby and his temperature, and then choosing the optimal air temperature. The recommended way to dress a child is that the child should have as many layers of clothing as an adult, plus one layer.
It should be remembered that a short-term increase in body temperature is not always associated with the presence of any infectious diseases in the baby.
The cause of an increase in body temperature can be prolonged crying, intense physical activity, too warm clothing, and even breastfeeding and digestion of food.
Normal body temperature in children from 1 month to 5-7 years
- In the armpit - 36.4-37.3 degrees;
- In the rectum (rectal) - 36.9 - 37.6 degrees;
- Oral (in the mouth) - 36.6-37.2 degrees.
How to relieve fever correctly
At four months the temperature does not drop below 38 degrees. If you give an antipyretic at this moment, it can provoke an even deeper exacerbation.
Initially, the reason that caused this situation is indicated. The best solution is to consult a doctor who will prescribe treatment or, in the case of teething, suggest options for relieving the symptom.
If the thermometer shows high values, first of all, the baby needs additional fluids and hydration. You should feed breast milk more often and lubricate the baby's body with a sponge.

Gv, drinking plenty of fluids - help in reducing fever
Having identified the cause, you can begin treatment after coordinating it with your pediatrician. In case of pneumonia, antibiotics and sputum thinners are prescribed. Simply taking an antipyretic drug is not enough and is unacceptable - this will worsen the situation.
In most cases, relieving a fever is not a cure; it can often simply hide the underlying problem for a period of time.
Note! Under no circumstances should you wipe your baby with vodka, vinegar or alcohol, as this can cause intoxication of the body. It is also prohibited to wrap very young children in cold diapers, as this will provoke vasospasm and further convulsions.
Up to a value of 38.2, the baby should be wiped with water and compresses should be applied: safe physical methods should be used. The well-known pediatrician and candidate of medical sciences, Evgeniy Komarovsky, believes that a temporary increase in temperature does not pose a threat to the baby, but it should definitely be shown to a competent specialist in order to exclude the presence of serious illnesses.
Choosing an antipyretic drug
Drugs that contain aspirin and analgin are contraindicated for newborns. In many countries around the world, even adults are prohibited from taking them. For infants, antipyretics are available in the form of a suspension, syrup or rectal suppositories.
What options can be purchased at the pharmacy:
- Children's paracetamol, analogues of which are Panadol, Efferalgan. They relieve pain. The syrup is consumed at intervals of 4 hours, 5-8.5 ml.
- Ibuprofen. Relieves inflammation and painful reaction. Can be used from six months, in the form of suppositories - from three months. It is advisable to use no more than 3 days in a row, 3 times a day, exclusively at high temperature readings. The suspension is used in 2.5 ml doses, suppositories - 1 suppository every 6-8 hours.
Important! The dosage and dosage regimen should be strictly adhered to, taking into account the weight and age of the patient. If the temperature cannot be brought down, you should call an ambulance and not exceed the recommended dose of the drug.
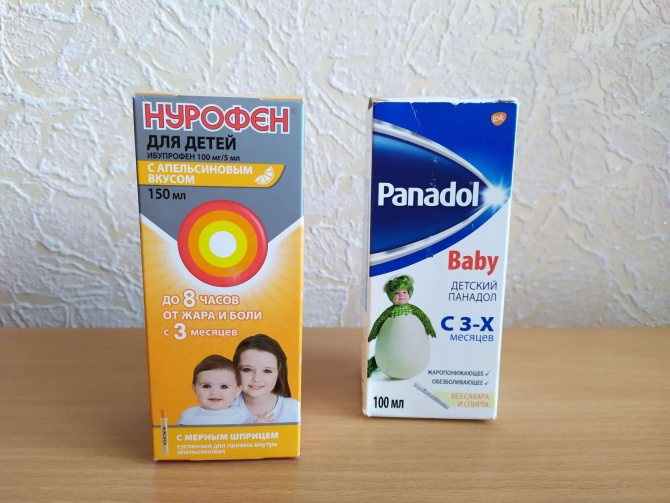
Antipyretics for children
When to lower the temperature
In heat up to 38.5°C, taking into account the child’s normal condition, it is not recommended to lower the temperature, since the baby’s body must form its “immune response” to the infectious disease.
However, if the child is registered with neurology or has so-called “white” fever, when at high temperatures the limbs remain cold and the skin becomes marbling, then it is necessary to reduce the temperature after reaching 38.0 ° C. This condition is dangerous due to the development of seizures. Also, for symptoms of “white” fever, pediatricians recommend giving medications that relieve vasospasm. Normally, children tolerate temperature well, remaining mobile and active. Of course, a little lethargy and refusal to eat are quite acceptable. In some cases, with individual intolerance to heat, if the child literally lies flat, refusing to eat and drink and experiencing various ailments in the form of headache, nausea, etc., it is allowed to bring down the temperature, even if it has not yet risen to the appropriate level.
37.4 lasts more than a week
If the readings change from time to time, this is either measurement errors or evidence of overheating. You should monitor the baby and record his changes in behavior and condition. If it is active, then no treatment is needed. When low-grade fever persists for more than a week, there is no need to rush into taking antipyretics.
Proceed as follows:
- Find out what is bothering the baby: runny nose, cough, pain.
- Be sure to follow a drinking regime. As the temperature rises, the water-salt balance is disrupted and dehydration occurs. Put your baby to your breast more often, give him some water to drink from a bottle - that’s all you need. Older children can be offered cranberry juice or dried fruit compote.
- If the condition worsens, wheezing, convulsions appear, vomiting occurs, breathing is difficult, and the temperature begins to rise even after taking medications, be sure to call an ambulance.
- A certain microclimate should be created in the children's room - 21-22 degrees Celsius, moderate humidity. If the air is dry, complications may occur: bronchitis, otitis media, pneumonia.
- If the baby is not cold or shivering, then dress him in light clothes made from natural fabrics: rompers, a cotton shirt or blouse are ideal. When the baby is sleeping, cover him with a fleece blanket or flannel diaper.