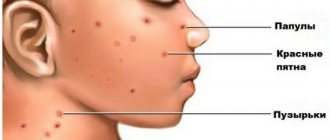
Causes of low temperature
A low temperature of less than 36.2℃, also known as hypothermia, is an indicator of either low heat production or increased heat transfer.
What could be their reasons:
- Thermal energy is produced in internal organs and muscles due to metabolic reactions and muscle function. A decrease in temperature indicates a slowdown in the functioning of some body systems. The causes may be normal adaptive reactions or pathologies. In any case, it is important to understand what the reasons are and do everything possible to eliminate them.
- The release of heat to the environment usually depends on external factors. Then it’s clear what to do - eliminate the source of hypothermia. It is dangerous not in itself, but as a factor that provokes the onset of an infection or inflammatory process.
When a child was in a cold room, outside in light or wet clothes that were not suitable for the weather, everyone understood why he had a low temperature. Need to:
- bring to a warm room
- change clothes
- give it a hot drink.
If after these procedures the temperature rises to 36.6℃ or even higher, everything is fine. Explain to an older child how to behave so as not to get sick. And keep an eye on the little one more closely in the future.
Another absolutely normal phenomenon is a child’s low temperature in the morning.
35.5-36.5℃ is a natural decrease. All body processes slow down during sleep, and less energy is produced. But if you constantly have hypothermia in the evening, this is no longer so good, you need to look for the cause.
If a child has a low temperature for several days, you need to carefully monitor him to see if there are any other alarming symptoms, and consult a doctor to help determine the cause and tell him what needs to be done.
After all, this indicator, if it is observed for a long time, can be a symptom of various deviations from the norm or diseases. Diseases or conditions with low temperature 34.9-35.9℃ in children
| Disease or condition | Signs | Causes | What to do |
| Congenital hypothermia (rare) |
| Genetic features. |
|
| After taking antipyretic drugs - up to several days |
| General weakness after suffering from acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, measles and other diseases for which it is necessary to reduce the temperature |
|
| Effect of vasoconstrictor drugs |
| A sharp decrease in blood pressure. |
|
| Viral disease |
|
|
|
Internal illnesses:
|
|
| Consultation with a pediatrician, referral to a specialist, ultrasound, urine and blood tests (general, hemoglobin, sugar and hormones) |
Low temperature in a child from 1 month to 1 year
In infants, thermoregulation is just beginning to develop, like all other functions of the body.
Children aged 1-12 months are still learning to keep their temperature at 36.6, so a decrease easily occurs with the slightest hypothermia.
Due to their even less development and inactivity, premature babies are characterized by constant hypothermia of about 35.5℃. But a low temperature can also appear due to a painful condition. This is typical for the following situations:
- One of the forms of a viral infection. It can occur without a previous increase in temperature. If a baby at 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 months stays at about 35℃ for 3-4 days and shows at least some signs of a cold or just a lethargic and drowsy state, fatigue, you need to consult a doctor.
- Reaction to the vaccine. This immune response is less common than fever. But recently, on parent forums, you can increasingly read about such cases after the 2nd and 3rd DTP (adsorbed tetanus-diphtheria-pertussis toxoid). Therefore, there is no need to take Paracetamol, Ibuprofen or other antipyretics in advance after vaccination, as some doctors advise. After all, if a child is 1-12 months old and still has hypothermia, the consequences can be catastrophic. After vaccination, it is necessary to measure the temperature every 2-3 hours, especially at night when sleeping, and act according to the situation.
- Loss of strength, which manifests itself as a low temperature in a child after illness, remains at 35.8-36.0℃ for 2-5 days. This is a reflection of the state of immunity weakened in the fight against infection. Or a prolonged reaction to antipyretic drugs taken at the end of treatment for influenza, acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections. To regain your strength, you need to spend more time in the fresh air and eat well.
- Consequences of using drops for a runny nose. They act as vasoconstrictors, and can affect the small body of a baby at 5 or 7 months not only on the vessels of the nasal mucosa, but also on other capillaries. Their narrowing can lead to hypothermia and even fainting. You need to be careful when using nasal drops, read about side effects and contraindications. The safest in this sense are preparations based on sea salt, such as Aqualor Baby, Aquamaris for children, Otrivin Baby.
In children aged 1 to 6 years, with the development of walking skills and other active movements, thermoregulation gradually normalizes. Therefore, as the child grows up, regular temperature reduction should be given even more importance. The causes of hypothermia may be the same as in infants, but the deviations should not be as noticeable and return to normal faster. By the beginning of primary school age, other reasons for the decline may appear.
Normal temperature in infants
In full-term healthy babies, the temperature is usually measured in the armpit or on the inside of the thigh. In premature babies with low birth weight, skin parameters are determined using special equipment. This is done in a hospital, since such children must be under the supervision of a neonatologist.
The normal temperature of a baby fluctuates throughout the day and depends on sleep, wakefulness and nutrition. After eating certain foods, the temperature may rise slightly - this is due to energy metabolism.
Scientists have found that the average normal body temperature is 36.6ºC. Fluctuations, depending on the time of day, can be from 36.2ºС to 37.0ºС. Temperature decreases and increases outside these limits are caused by various factors.
Important to remember! Despite the fact that measuring temperature rectally gives the most accurate results, this procedure is not recommended for young children . Since the thermometer must be inserted 2 cm deep into the rectum of premature babies, and 5 cm deep into the rectum of full-term babies, the intestines can be accidentally injured. With the rectal measurement method, normal values are 3ºC higher.
Reduced temperature at 7-17 years old - reasons and what to do?
Starting from 1st grade, the cause of a drop in temperature can be overwork. They lead to him:
- workload with studies, various clubs, sections, studios;
- unbearable mental and physical stress;
- lack of rest and fresh air;
- lack of sleep when the child sits at night in front of the TV or computer, drifts through social networks or plays virtual games;
- stressful situations, worries about grades, conflicts with teachers, parents or classmates.
A low temperature in a schoolchild is a signal from the body that something is wrong. If you do not respond in time, the consequences may be diseases that doctors call school diseases:
- neurosis - a violation of the normal reactions of the nervous system to stimuli;
- gastritis - inflammation of the gastric mucosa, caused by bacteria, but provoked by stress and overwork;
- myopia - myopia of varying degrees, aggravated by the influence of flashing screens of mobile phones, tablets and laptops;
- scoliosis is a curvature of the spine due to constant and uneven loads.
What should parents do?
- reduce the load, leave those additional activities that the child likes most;
- walk more often with your son or daughter in the fresh air;
- monitor your daily routine and exclude the possibility of computer entertainment at night.

If a decrease in temperature is first observed with the onset of puberty, then prolonged hypothermia may be a sign of the onset of the development of an endocrine disease:
- disruption of the thyroid gland with a decrease in hormone production - hypothyroidism;
- diabetes mellitus
What to do in such cases? First consult a therapist, do an ultrasound of the internal organs, take blood and urine tests. If no diseases of the heart, kidneys, liver, or lungs are detected, or no neoplasms are found, then you need to go to an endocrinologist and check your sugar and hormone levels.
Helping a child with a low temperature
If the baby has a low body temperature from birth and is not accompanied by any accompanying symptoms, the child does not need help: this is his usual (that is, normal) condition. If it is a consequence of some disease and is characterized by headache, drowsiness and lethargy, the child needs help before he is seen by a doctor. This will help him endure this painful phenomenon much easier. A child in this state needs warmth, even if he says that he is not cold. Warm him up by any means necessary.
- Don’t panic yourself, no matter how low the temperature the thermometer shows, and don’t show your worries to your baby.
- In such cases, it will always be useful to have a second thermometer in the house. It often happens that just one thermometer becomes unusable and shows incorrect results. Buy an electronic device that gives more accurate readings.
- Dress your baby warmly.
- In the room where it is located, you need to close the windows and make sure that the temperature in the room does not fall below 20°C.
- Bed, clothes, shoes - everything should be dry.
- Wrap your baby in a blanket. Apply a warm heating pad to your feet.
- Give him hot tea.
- As soon as the child's temperature returns to normal, unwrap him and let him lead a normal play life.
- Make sure your child gets 8–9 hours of sleep on such days.
- Increase his diet with fresh fruits, vegetables, and berries.
- Go for walks with him more often (after dressing him warmly).
- Limit the time he spends on the computer (tablet, laptop, phone).
- Free him from mental and physical stress as much as possible.
- Monitor your baby carefully: if a drop in temperature is accompanied by other symptoms of an unhealthy condition (dizziness, pain, nausea, cold sweat, lethargy, irritability, general malaise, weakness, etc.), you should urgently show him to a doctor.
Useful: Is elevated temperature in a newborn normal or a problem?
With low body temperatures in children of different ages, parents should be on alert and know when to sound the alarm and when to just wait it out. The future health of the baby may depend on timely measures taken, so not a single detail should be missed here.