What are the benefits of sea fish and seafood for pregnant women?
Sea fish and seafood are a source of high-quality protein, which the body needs in the same way as animal protein. Moreover, seafood contains a large amount of vitamins and minerals. They support the health of the expectant mother and also contribute to the harmonious development of the baby. Among them:
- Omega-3 and Omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids: have a beneficial effect on the mother’s heart muscle, reduce the risk of premature birth, and help the normal development of the child’s nervous system and vision.
- Vitamin D: helps the absorption of calcium and prevents its excessive loss from the mother’s bones, and also ensures the prevention of rickets in the unborn baby.
- B vitamins, in particular niacin (B6), folic acid (B9) and cobalamin (B12): stimulate the proper development of the neural tube and protect the mother from stress and mood swings.
- Calcium: is necessary for the formation of the baby’s musculoskeletal system, especially in late pregnancy, when the mother’s own reserves of this chemical element are already depleted.
- Iodine: very important for the thyroid gland and the baby’s brain.
- Phosphorus: activates cell growth and division, protects the thyroid gland, protects against immunodeficiencies.
- In small quantities - iron, fluorine, magnesium and zinc: also important for the development of internal organs and systems of the fetus and are consumed in large quantities.
The healthiest types of fish for expectant mothers:
Can I eat:
- smoked fish during pregnancy
Smoked, dried and dried fish are prohibited for pregnant women, since the processing of such products may not be sufficient to destroy all bacteria and helminths. Fish that has only been cold smoked is especially dangerous. In it, as in raw fish, listeria is often found - a rod-shaped bacterium that causes severe intoxication of the mother's body, delayed fetal development and miscarriage. Hot smoked fish is considered more acceptable as it undergoes heat treatment. However, another problem awaits here. Increasingly, unscrupulous manufacturers are using special chemical compounds to give the product a pronounced “smoked” taste, smoky aroma and golden color. Such substances are definitely harmful, so it’s not worth the risk.
- salted fish during pregnancy
Heavily salted fish is also contraindicated for expectant mothers. Excess sodium chloride only creates additional stress on a woman’s kidneys, increases blood pressure and increases swelling of the extremities. It is preferable to buy unsalted or lightly salted fish products.
- red fish during pregnancy
Salmon, trout and other types of red fish are very healthy for pregnant women. But due to the high fat content, such fish should be consumed no more than once a week. It is also important to remember the danger of allergic reactions. Red fish, like crustacean meat, contains large amounts of the amino acid histidine. It is this that can provoke a powerful release of histamine in the human body, up to anaphylactic shock.
- seafood during pregnancy
Seafood is a source of pure protein and valuable microelements. But they have practically no fat, and they are very easily absorbed by the body. Seafood also has a positive effect on intestinal function, stimulates appetite, reduces cholesterol levels in the blood and improves the condition of skin and hair, which often suffer during pregnancy. Therefore, it is highly advisable for expectant mothers to include seafood in their diet.
Squid, shrimp, scallops and crabs are rich in potassium, iodine and iron. They also contain vitamins B, E and C, which are so necessary for the harmonious development of the baby.
What fish should you not eat during pregnancy?
You should avoid smoked fish during pregnancy – both hung fish and hot and cold smoked fish.
Substances that penetrate into such fish along with liquid smoke are dangerous to everyone and over time cause damage to most organs.
However, young children and pregnant women are the most vulnerable - their bodies cannot withstand the onslaught of phenols, formaldehydes and carcinogens.
In addition, manufacturers often try to hide stale goods behind the smell of smoke: it is the expired fish that goes into the smokehouse. This applies to a lesser extent to home-smoked fish caught with your own hands.
Surprisingly, red caviar, considered one of the healthiest and vitamin-rich delicacies, is also prohibited (albeit not strictly) for pregnant women. If you want and have a reason, you can only afford a couple of sandwiches on New Year’s Eve.
Why is that? Precisely because of the vitamin diversity. More specifically, vitamin A is to blame, which, when concentrated in the body, becomes a threat to motherhood.
Tuna, shark, mackerel and swordfish are also prohibited. They contain mercury substances that cause irreparable harm to the fetus. Therefore, put off gourmet explorations for later.
Under no circumstances should you visit sushi bars and eat raw fish in the form of rolls and sashimi. In principle, it is better to pass by such establishments.
There are known cases of poisoning in women who ate only vegetarian rolls: they cut them with the same knife as raw fish.
Fish: what are its benefits?
All nutritionists unanimously speak about the advantages of fish over beef, pork and other types of meat. The tender flesh of sea creatures is rich in protein (from 6 to 1 g per 100 g of product), which is 97% digestible. Fish contains a variety of vitamins A and B, amino acids, and fats necessary for proper digestion. The product contains increased amounts of selenium, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium. These microelements are involved in the process of hematopoiesis, stimulate the development of brain cells, and strengthen the nervous system. Marine species are rich in iodine, fluorine, potassium, and vitamin D. Obtaining these components from other products is problematic, and vitamins in capsules are absorbed much worse.
Fish dishes have a positive effect on the well-being of a pregnant woman and are necessary for the proper formation of fetal organs. You need to eat at least 2 servings of the product per week, it is advisable to alternate varieties and cooking methods to make the table as varied as possible. Another advantage of fish is its ease of digestion. Tender, lean meat does not irritate the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines, which makes it suitable even for women with gastrointestinal problems. An individual allergic reaction may be a contraindication to eating fish.
Nutritionists and obstetricians warn that too much fish in the diet can be harmful to the health of a pregnant woman. Even the healthiest varieties accumulate small amounts of heavy metals. In small quantities they are not dangerous, but exceeding the dosage can provoke problems with the nervous system, cause nausea, diarrhea, headache and other unpleasant symptoms. That is why daily consumption of fish dishes is excluded; they must be alternated with poultry, vegetables, and cereals.
Seafood that pregnant women can eat
Sea fish is very healthy, especially if it is fresh. You also need to be confident in the seller. You can eat frozen seafood. This storage method allows you to kill all parasites. Boiled, stewed and baked fish retains all useful microelements and vitamins and has a beneficial effect on the body of a pregnant woman and child.
Salmon and red fish in general normalize appetite and stabilize blood pressure, and also help get rid of headaches. Fish broth has a positive effect on the functioning of the stomach and intestines. But doctors recommend eating canned tuna and red caviar in limited quantities.
It is worth carefully introducing shrimp, squid, scallops and hake into the diet. First you need to try a small piece. If an allergic reaction does not occur after 15–20 minutes, then you can safely include these products in the menu.
Which varieties are suitable for pregnant women
The question of which fish is the most useful during pregnancy occupies not only doctors, but also the women themselves who are expecting a child. This is not difficult to find out; it is enough to clarify the content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, which can vary significantly depending on the type. The champions in this category are marine species. Many nutritionists believe that the most beneficial fish are those from the cold northern seas: salmon, sockeye salmon, chum salmon, mackerel. These species feed on small marine organisms and algae that actively synthesize fatty acids. They are indispensable for pregnant women, as they have an active influence on the development of the child. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (docosahexaenoic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid) are considered especially valuable. These compounds contribute to the formation of the child’s nervous system and the maturation of brain cells). Sea fish dishes are especially needed in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. However, they are also useful at the beginning of fetal development, as they have a positive effect on the vision of the unborn child and strengthening his immunity.
Fish is necessary not only for the baby, but also for the expectant mother. It increases the elasticity and density of tissues, preventing ruptures during childbirth. Light and nutritious meals do not provoke constipation and diarrhea, and improve resistance to various infections, which are especially dangerous for pregnant women. Fish promotes the active production of serotonin, which improves mood and prevents depression.
The champion in the content of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids is the common herring. Mackerel and salmon take honorable second and third places. To obtain the daily norm of valuable acids, it is enough to eat 150 g of fish per day. The menu will be complemented by less fatty, but very healthy species: flounder, pollock, cod, catfish, whitefish. It is preferable to use fresh or chilled fish, but if this is not available, frozen fish can be used. It is worth considering that repeated freezing deprives the product not only of its taste and juiciness, but also of most of its beneficial qualities. Buy fish carefully from trusted retail outlets that guarantee the quality and unconditional freshness of the product.
Nutritionists are confident that young individuals who have not had time to accumulate harmful heavy metals in their tissues are especially beneficial. When purchasing fish, you should choose the smallest carcasses available for sale. Large specimens with caviar or yellowish fat are best left on the store shelf.
Note: what fish can pregnant women eat?
Of course, preference should be given to sea fish. All expectant mothers who are not allergic to this product are recommended to fish with an enviable content of polyunsaturated fatty acids. And this list has its own leaders.
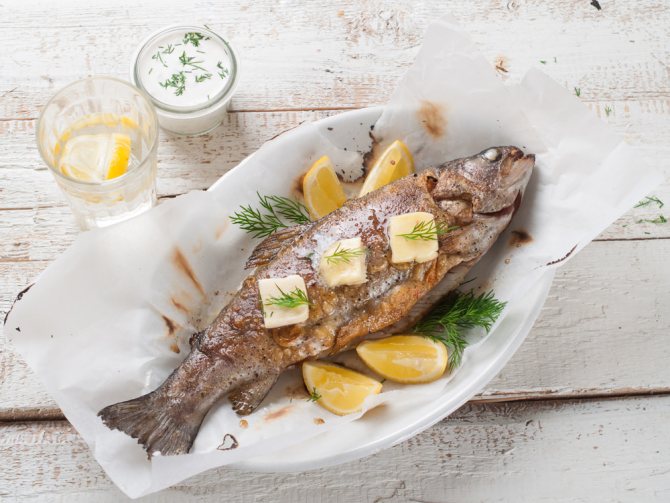

So, during pregnancy the following are especially useful:
- Salmon;
- Trout;
- Sardine;
- Cod;
- Whitefish;
- Catfish;
- Flounder;
- Chum salmon.
However, the type of fish is also important, meaning the method of preparation. In smoked and salted form, in addition to the beneficial properties that are reduced, there is also a lot of salt and other components that are not the most useful. Fish can be boiled, baked, stewed. The fish can be used in a salad or made into a delicious soup.
Not all fish is equally healthy: what should you avoid?
Despite the obvious benefits, some foods must be excluded from the diet during pregnancy. These include all dishes based on raw fish: tartare, sashimi, sushi, ceviche. They can cause severe food poisoning, provoke infection with helminths or deadly listerella.
Pregnant women should not eat salted and smoked delicacies, canned fish, or caviar. These products contain too much salt, preservatives and carcinogens, they contribute to fluid retention in the body and increase swelling.
Is it possible to eat red fish during pregnancy?
The short answer to this question is yes, you can.
But in what quantity? WHO recommends eating at least 2-3 servings of fish per week (about 300-350 grams of fish fillets). A larger quantity of red fish is also allowed if it is properly selected and prepared. You should not eat long-lived predatory and bottom-dwelling fish, because... they can accumulate mercury and other heavy metals. The largest amount of mercury is found in fish caught in the Baltic Sea, off the coast of Canada and the USA. Salmon has mercury accumulation properties. In addition, store-bought salmon often contains dyes, which help reveal the bright red color of the fillet. More about salmon during pregnancy.
The largest number of chemical compounds are stored in fat, so you should give preference to low-fat varieties of fish.
The best time to buy fish is from February to August.
Red fish is an extremely healthy product. It contains:
- B vitamins - participate in metabolism, prevent the formation of blood clots, improve the condition of the nervous system, normalize heart rate, stimulate adrenal function.
- Vitamin A - strengthens the immune system, stimulates collagen production, neutralizes free radicals, prevents stretch marks on the skin, is important for the formation and growth of the embryo.
- Vitamin D – regulates the synthesis of hCG, prevents gestosis, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes mellitus.
- Phosphorus – ensures normal kidney function and participates in the contraction of the heart muscle.
- Calcium - lowers cholesterol, improves liver function, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, participates in the contractile function of the heart muscle, and reduces blood pressure.
- Magnesium – activates metabolism, helps the body cope with stress.
- Fluoride – prevents atherosclerosis, reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases, affects the formation of teeth.
- Zinc – participates in protein synthesis and insulin formation, maintains acid-base balance in the body.
- Selenium is an antioxidant and protects against malignant tumors.
- Iodine – regulates the function of the thyroid gland.
- Omega-3 – has an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect, participates in the formation of the endocrine and nervous systems of the fetus, and prevents gestosis.
Fish is a product with easily digestible protein, which is quickly digested and perfectly absorbed by the body. It gives a feeling of heaviness, is low in calories, but at the same time filling, which is why fish is included in most healthy nutrition programs.
Important: if a woman rarely ate this product before pregnancy, a pregnant woman should start consuming it with a very small amount.
Fresh red fish in the early stages of pregnancy is a healthy product that should be included in your menu. There are very few restrictions here - the presence of an allergic reaction to the product and disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
An important condition is that the fish must be of good quality and undergo heat treatment. Although river fish (such as river trout) contain parasites to a greater extent, redfish are not immune to them and must be cooked carefully. You can become infected with parasites not only through undercooked fish, but also by tasting Japanese cuisine - sushi, rolls, or by trying salted or smoked fish.
The healthiest red fish is the one that is steamed or baked in foil. Fried fish increases the load on the digestive organs and can provoke attacks of gastritis or pancreatitis. The duration of cooking fish is calculated based on the formula - for every 2.5 cm of fillet in thickness, 10 minutes are allotted.
Red fish can be harmful during pregnancy under the following circumstances:
- Having an allergy to fish
- Chronic liver or stomach diseases
- Poor product quality
- Improper preparation of fish, use of salted and smoked versions
Canned fish is not a very healthy product. Firstly, it contains a lot of salt, secondly, fatty oil, and thirdly, the quality of canned fish is difficult to determine. In addition, the vast majority of canned food is stuffed with preservatives and flavorings, which are extremely undesirable while expecting a baby.
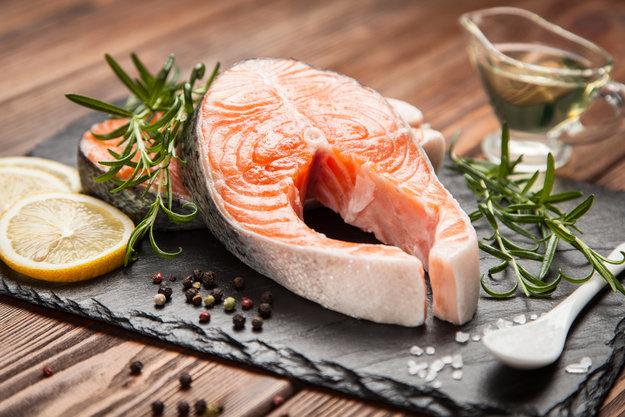

Red fish is best consumed baked or steamed. Consumption of salted red fish during pregnancy can occur if the quantity is small, the fish is of good quality and the pregnant woman does not suffer from edema, excess weight and other conditions in which salt is limited.
Important! It is difficult to determine the freshness and quality of salted fish at a glance, so be vigilant.
You should not eat lightly salted fish if:
- It was purchased on the market;
- It is poorly salted;
- Causes even minor allergies;
- It is difficult to determine its shelf life.
Even if there is no doubt about the quality of the fish, you can eat it carefully, in measured quantities (1-2 pieces). The reason is a large amount of salt, which can cause fluid retention in the body, swelling and excess weight gain. This is especially true for expectant mothers after the beginning of the second half of pregnancy.
Fish table: nutrition rules
You can prepare many nutritious and healthy dishes from fish. Fried foods are not suitable for pregnant women; it is better to steam or microwave fish, bake in the oven, wrapped in foil or covered with a layer of vegetables. These methods reduce calorie content and maintain the juiciness of the product.
The fish is suitable for preparing low-fat soups with the addition of cereals and vegetables, a variety of soufflés, steam cutlets, rolls, meatballs in a light sauce. To enhance the taste, add a small amount of sea salt, freshly squeezed lemon juice, spices, fresh or dried herbs to dishes: dill, parsley, rosemary, thyme, basil, celery. Food for pregnant women is prepared immediately before consumption; it cannot be stored for a long time.
If a woman cannot stand the taste of fish, you can replace it with fish oil pills. They have no taste and provide the body with valuable polyunsaturated acids, microelements, vitamins A and D. The dosage should be prescribed by the attending physician, who can also recommend the brand of the drug.
Fish is one of the healthiest foods for expectant mothers. To prevent it from causing harm, it is important to choose the right types and methods of preparation. To provide the body with valuable vitamins and microelements, it is enough to eat 2 servings per week. An excess of fish on the menu is just as harmful as its lack.
Fish during pregnancy: benefits and harms
Is fish allowed during pregnancy? This question causes a lot of discussion, both among home-grown experts and among professionals. Even when studying official information, it is difficult to come to a clear conclusion.
Some sources claim that a diet for pregnant women without fish will not be complete and will not provide the expectant mother and baby with a complex of nutrients. Others say that this product is strictly prohibited. We can immediately say that smoked fish is prohibited during pregnancy, but let’s figure out the rest.
Fish is a protein, a complex of vitamins and minerals. It is absorbed by the body much better than meat. After a fish dinner, you are unlikely to feel heaviness in your stomach. But not all types of fish are good for a pregnant woman: follow the recommendations given in this article and be safe.
What kind of fish can you eat?
But all this does not mean that now you can eat all fish products in a row. You need to know which fish will be beneficial for pregnant women, and which ones should be completely avoided. You need to eat the types of fish that contain the most nutrients and Omega-3 :
- salmon;
- mackerel;
- herring;
- sardine;
- catfish;
- flounder;
- horse mackerel;
- navaga;
- chum salmon
Important! You can separately consume fish oil, which contains more than 9 g of Omega-3 fatty acids per 100 g. But you need to be extremely careful when choosing, since these acids must be obtained from the body of the fish, and not from the liver.
Red fish is considered the most useful during pregnancy; it is enough to consume it in the amount of
150 - 170 g twice a week to get a sufficient amount of microelements for the body. But don’t forget about eating seafood such as squid, mussels, shrimp and kelp, which are also enriched with a whole complex of vitamins.

The benefits of fish
During the period of bearing a child, the body needs an increased complex of vitamins and minerals. Fish contains phosphorus, magnesium, vitamin A, and calcium. And sea fish is also supplemented with fluoride, vitamin D and iodine. All these substances play a significant role in the development of the child.
The main difference between marine fish and freshwater fish is the large amount of omega-3. This is a polyunsaturated fatty acid, the consumption of which has a positive effect not only on the health of skin, hair and nails. Omega-3s must be present in the menu of a pregnant woman, as they have a beneficial effect on the development of the brain of the unborn child.
Marine fish, which are bred in artificial conditions, contain more omega-6, but the inhabitants of natural reservoirs are rich in omega-3.
This is due to the fact that under natural conditions, fish feed on small marine organisms, which, in turn, feed on algae. The fatty acid combines with algae and in this way more omega-3 is formed. Our body cannot produce omega elements on its own, so we need to get it from food.
Scientists have proven that polyunsaturated fat compounds are important for the proper development of the fetal central nervous system. Most of the omega-3 is made up of two acids EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid).
DHA begins to accumulate in the baby’s brain cells from week 26 and affects the proper functioning of neurons. A deficiency of this acid in the embryo leads to delayed brain development.
A study by scientists from the USA showed that in babies whose mothers ate about 400 grams of fish per week during pregnancy, the development of the psychomotor system occurred in a timely manner.
The benefits of fish for the body
The benefits of fish dishes for the body of a pregnant woman can hardly be overestimated. Every year, scientists are finding more and more benefits of its use and beneficial properties, and doctors are increasingly recommending regularly adding fish to the menu. In addition to its nutritional value and high taste, it is endowed with a number of vitamins and microelements, such as:
- vitamins A and D;
- Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids;
- amino acids;
- calcium;
- phosphorus;
- selenium;
- magnesium;
- iron;
- fluorine;
- potassium;
- iodine.

During this period, the need for Omega-3 acids, which are most abundant in this product, increases. Namely two types:
- eicosapentaenoic acid or EPA;
- docosahexaenoic acid or DHA.
Sufficient joint consumption of these substances affects a number of processes occurring in the body of the mother and her unborn child;
- promotes the proper formation of cell membranes;
- improves metabolism;
- prevents blood clotting;
- reduces the risk of a woman’s hypertension;
- influences the increase in the level of intellectual development of the child;
- improves the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- accelerates the maturation of brain cells and has a positive effect on the baby’s psychomotor development;
- strengthens the immune system;
- helps a young mother avoid postpartum depression.
Scientists have also proven that eating fish helps maintain the good mood of a woman who gives birth to more active, intellectually developed and smart children.

Did you know? The shark is one of the most adapted fish for survival. It can increase its body temperature if caught in a cold current and live in low water temperatures.
What kind of fish can pregnant women eat?
The top list of the healthiest fish for pregnant women looks like this:
Fish dishes are best steamed or baked in the oven. This way you will preserve everything useful and will not gain extra calories and carcinogenic substances released during frying.
You can make soup from high-quality canned food.
The fish that should be in your diet during pregnancy are fatty fish, except for perch and tuna.

Or at least limit their use. Tuna is a delicious fatty fish, but it accumulates mercury, so a maximum of two tuna steaks per week weighing 150 grams.
Canned tuna is not considered fatty, due to the canning process.
Restrictions on fatty fish were introduced due to the polluted environment (dioxins, pesticides and other harmful substances may be contained in fish). But two servings a week will not cause harm and will be able to provide both mother and baby with useful minerals and vitamins without harm.
Fish for iodine deficiency and thyroid diseases
You should not get carried away with fish dishes if you have problems with the thyroid gland. Decreased thyroid function is a common problem in pregnant women; in this case, the body needs an additional portion of iodine.
Where can you get it, other than in fish? The source of iodine is seaweed, shellfish (scallops, squid, mussels). But eating shellfish during pregnancy also requires caution: no dried or canned shellfish - only thermally processed seafood is safe for expectant mothers.
And if the thyroid gland begins to secrete excess hormones, additional iodine is contraindicated. If you suspect a malfunction of the thyroid gland, it is important to be examined by a doctor and take a hormone test.
River fish for pregnant women
Freshwater fish from rivers and lakes is less fatty than sea fish. And this is a minus, because the absence of healthy fats will not make any contribution to the health of the expectant mother and her child.
In addition, river fish are often infested with parasites that are difficult to destroy even with the help of heat treatment.

Helminthiasis during pregnancy can not only cause vomiting, but also miscarriage. Raw fish during pregnancy also puts a person’s health and sometimes life at risk.
Fish recipes for pregnant women
The main requirement for pregnant women to consume fish is sufficient heat treatment and selection of the “right” varieties of product. Choosing good, healthy fish is your task, and the Its Kids team can provide you, dear readers, with simple but original recipes for fish dishes.
Sardine soup
Ingredients:
- canned sardine - 1 can;
- potatoes - 4 pieces;
- carrots – 1 piece;
- onion;
- salt - to taste.
Preparation:
- We clean the vegetables, cut the potatoes into convenient medium-sized pieces, and carrots into cubes.
- We put a pan of water on the fire and throw the vegetables into cold water; when the water boils, salt it.
- After cooking the vegetables for 15 minutes, add the whole onion to the pan. Pour the contents of the can into the pan and cook for another 10 minutes.
- Serve the finished soup hot with white bread.