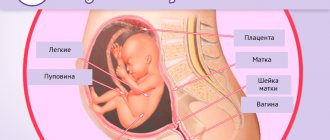
Immunoglobulin during pregnancy is prescribed if the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the baby's health. In the initial stages of pregnancy, the body's defenses are reduced, so it does not perceive the fetus as a foreign body. The active components of immunoglobulin (antibodies) increase immunity, which means they provide the prevention of pathologies during pregnancy. The drug is based on natural blood serum. It is administered to pregnant women so that the immune system maintains its properties and the body can resist illnesses.
How does immunoglobulin work during pregnancy?
The purpose of administering immunoglobulin is to stimulate the body's protective properties. A few days after vaccination, resistance to infectious diseases increases. If the body contains pathogens of any pathologies, it shows resistance to them, and accordingly, prevention is provided.
Administration during pregnancy is advisable if there is a threat of miscarriage. The drug is prescribed when there is a threat of developing an infectious disease. There are cases when, as the infectious process progresses, the body does not respond to antibiotics. Then the doctor decides to use immunoglobulin. Indication for use is Rh conflict between mother and fetus.
Is it necessary to administer anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin?
The introduction of immunoglobulin can really insure a woman against the development of subsequent Rh conflict with her unborn baby. But in order for prevention to be effective, the following conditions must be met:
- Administer the drug as indicated, including during pregnancy.
- The sooner after birth, the more effective. Most manufacturers indicate an acceptable time interval of 72 hours, but, for example, similar Russian drugs should be used up to 48.
- It is imperative to adjust the dose of administered immunoglobulin depending on the expected blood exchange between mother and child.
The standard dose is 200 - 300 mcg (this is about 1 - 1.5 ml), but after a cesarean section, manual separation of the placenta and many other manipulations, the amount must be increased by 1.5 - 2 times.
Otherwise, not all red blood cells in the mother’s blood will be bound, and an immune response will still develop to the remaining portion. As a result, the effectiveness of prevention is reduced to zero.
Read more about the indications
Immunoglobulin is administered in a hospital rather than an outpatient setting. The dosage depends on many factors. The doctor takes into account the patient’s health status, takes into account the characteristics of her body, and the timing of pregnancy. The doctor also takes into account how the pregnancy is progressing and analyzes the risk of developing infectious pathologies. The administration of immunoglobulin during pregnancy must be correct. Doses are individual in each case. The medicine does not lead to congenital defects and fetal developmental anomalies. Types of medicine:
- Human immunoglobulin;
- Anti-D.
Indications:
- Immunoglobulin injections during pregnancy are prescribed if there is a threat of miscarriage. In this case, the drug is administered regardless of the timing;
- The drug is prescribed when an ectopic pregnancy ends;
- The medicine is administered if there was an abortion;
- Indications for use are trauma to the abdominal cavity;
- Immunoglobulin is used for immunodeficiency diseases;
- If the mother's blood enters the embryo's bloodstream, the doctor decides to administer medication;
- When active substances enter the body, resistance to bacteria, the causative agents of infectious diseases, increases.
Immunoglobulin against rhesus conflict: consequences
Every pregnant woman, especially one who did not plan to have a child, immediately upon learning about her situation, tries in every possible way to strengthen her immunity, because now she will have to work under increased load.
However, in the first weeks after conception, the body deliberately lowers its immune defense. This is done so that the embryo, and subsequently the fetus, is not regarded by her as a foreign body. Otherwise, the fertilized egg may be rejected and a miscarriage may occur.
Many women were prescribed immunoglobulin during pregnancy. What it is? Immunoglobulin is a combination of certain antibodies that strengthen the immune defense. This drug is produced on the basis of blood serum of potentially healthy individuals. The main indication for its use is the need to build immunity in the presence of serious disorders.
Basically, during the period of bearing a child, it is prescribed only in exceptional cases as an effective and potent immunomodulatory drug. By injecting the drug, the risk of contracting various infections is reduced, but, in addition, the body’s resistance to pathogens already present in it increases.
If you carefully read the instructions, it becomes clear that its effect on pregnant women has not yet been fully studied, so doctors prescribe injections, taking full responsibility upon themselves.
In most cases, this drug is used if there is a serious threat of spontaneous abortion. But it is also used to fight a dangerous infection that progresses and does not respond to antibiotic therapy.
Another indication for use is Rh conflict - different Rh factors in the mother and fetus.
The substance is introduced into the human body by droplets in a hospital setting. It is never prescribed on an outpatient basis. The dosage is adjusted in each specific case based on the characteristics of the body, the duration of pregnancy and its course, and the purposes of use.
Despite its widespread use, no studies have been conducted on its effect on pregnancy. Medical practice shows that the administration of the drug generally does not lead to any pathologies in the development of the child in the womb.
It should be noted that there are two completely different immunoglobulins - human normal and anti-D. Each of them has its own testimony.
When normal human immunoglobulin and anti-D during pregnancy:
- Threat of miscarriage at any stage;
- In case of termination of an ectopic pregnancy;
- Induced abortion;
- After amniocentesis;
- In case of severe abdominal trauma;
- Maternal immunodeficiency detected before or during pregnancy;
- When the mother's blood enters the baby's bloodstream.
Immunoglobulin is highly valued for its ability to improve the deficiency of IgG antibodies, which allows the body to increase the body's resistance to bacteria and viral infections.
Consequences that occur after an immunoglobulin injection during pregnancy
Since the drug is created on the basis of natural human fluid, side effects may occur as a result of its administration:
- Shortness of breath;
- Joint pain;
- Drowsiness, increased fatigue, weakness;
- Increased blood pressure and temperature;
- Itching, skin rashes, irritation of mucous membranes;
- Nausea, vomiting, stool upset;
- Dry cough, bronchospasm;
- Tachycardia;
- Chest pain.
Immunoglobulin is administered during Rh negative pregnancy. Its use is due to the fact that the mother’s immune system recognizes the fetus as a foreign organism and begins to produce immunoglobulin antibodies to it.
When the body first encounters an antigen (foreign protein), M-immunoglobulin begins to be produced, which transmits information to the B lymphocyte. The latter, in turn, synthesizes immunoglobulin G class antibodies, which upon subsequent encounters with the antigen begin to interact with it.
When there are antibodies to an antigen in the blood, the phenomenon of sensitization of the body occurs. In gynecological practice, this phenomenon suggests sensitization of the mother to the child’s red blood cells.
Blood is divided into several systems. Some of the most common are AB0 and Rhesus. It is the latter, in case of incompatibility, that leads to serious problems during pregnancy. Proteins on the surface of red blood cells (Rh factor) are either present (Rh+) or not (Rh-). When a woman is Rh negative and the fetus is Rh positive, sensitization develops.
In this case, when the fetal blood enters the mother’s body, the latter begins to produce antibodies - anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins. These substances, passing through the placenta, destroy the baby's red blood cells. This phenomenon provokes the development of jaundice, anemia, and in especially severe cases, damage to the baby’s heart and brain. The consequences caused by Rh incompatibility are called hemolytic disease of newborns.
But anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin may not be synthesized during an uncomplicated first pregnancy. The risk increases with infections, gestosis, diabetes in pregnant women, invasive manipulations, during childbirth, abortion after 8 weeks, placental abruption, and ectopic pregnancy.
In some cases, normal human immunoglobulin is administered to enhance immunity, and anti-D immunoglobulin is administered within 72 hours after birth. This need is due to the fact that during the first pregnancy, antibodies may not be produced in sufficient quantities, therefore, they will not harm the child, but in subsequent pregnancies, the Rh conflict will definitely make itself felt if measures are not taken.
- A woman with negative Rh should avoid invasive interventions;
- Avoid abortion. It is worth choosing high-quality contraception;
- When transfusing blood, it is necessary to carefully check its individual and group compatibility.
In addition, in the field of gynecology, a study has long been practiced to determine the amount of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins in a woman’s blood. That is, there is a unique version of drug prevention of sensitization. During pregnancy, this study is carried out once a month until 32 weeks, every two weeks until 36, then weekly until the birth itself.
If there are no antibodies before the 28th week or their indicators are no more than 1:4, then an injection of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin is necessary during pregnancy. That is, ready-made antibodies to the baby’s red blood cells will be injected into the body, which will act for 12 weeks and then are eliminated. If the baby’s red blood cells somehow enter the woman’s bloodstream, the administered immunoglobulins will destroy them, so there will be no immune response and sensitization will not occur.
When the levels of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins are above 1:16, the study is carried out every two weeks, ultrasound, CTG and Doppler are periodically performed to monitor the condition of the fetus.
If signs of hemolysis appear, there may be a need for an intrauterine blood transfusion to the child, and the question of delivery also arises. The introduction of an artificial drug in this case is strictly prohibited.
Based on materials from mjusli.ru
Adverse symptoms during pregnancy
Anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin during pregnancy can have side effects, since it is based on a natural liquid.
- In some cases, apnea occurs (it becomes difficult to breathe).
- Side symptoms include headache, weakness, discomfort in joints and muscle tissue.
- After administration, the patient may feel weak.
- Possible increase in pressure.
- Sometimes there are disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
- A common side effect is diarrhea.
- Some women experience a cough accompanied by bronchospasm.
- A side symptom is chest discomfort.
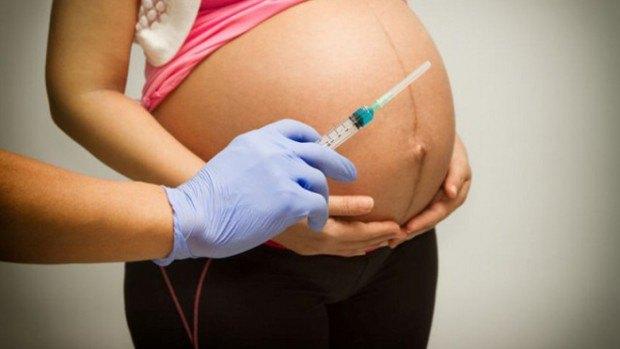
Use of medicine in case of Rhesus conflict
The drug is administered when the mother's immune system perceives the fetus as something foreign. When a woman's body encounters an antigen, it begins to produce M-immunoglobulin. If the baby's blood reaches the mother, antibody production begins. These components pass to the child and have a detrimental effect. The result is the development of diseases and the newborn. Rh conflict between the mother and child is called hemolytic pathology. The risk of the disease increases if the patient has diabetes.
To boost a pregnant woman's immunity, the doctor may prescribe human immunoglobulin at 28 weeks. 2-3 days after birth, anti-D immunoglobulin is prescribed. If a woman becomes pregnant for the first time, the body can produce antibodies in sufficient quantities and there will be no harm to the child’s health. If this is the second or third pregnancy, the likelihood of Rh conflict is higher, and therefore measures need to be taken, for example, administering Ginipral by drip.
How to avoid resource conflict? Preventive measures
If the patient is Rh negative, she should avoid invasive interventions. Prevention of Rh conflict is the avoidance of abortions, high-quality contraceptive measures. If blood transfusions are performed, compatibility must be checked. It is necessary to undergo routine examinations. Modern techniques make it possible to detect the level of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin in a woman’s body. If signs of hemolysis appear, it becomes necessary to transfuse blood to the child in utero. No artificial drug is administered.
Prevention of Rh conflict using immunoglobulin
As a rule, women with a negative Rh factor are vaccinated with immunoglobulin long before pregnancy in case she has to:
- have an abortion (or the pregnancy will fail arbitrarily);
- undergo an invasive intervention;
- do an urgent blood transfusion.
The most important task of this vaccine is to prevent the development of Rh conflict during pregnancy. But keep in mind that even if you have such a vaccination, your doctor will still direct you every month to take a blood test to detect antibodies. If they are determined, then you will be prescribed immunoglobulin, as well as many other studies that will monitor the child’s condition.
There are many women with a negative Rh factor who have successfully given birth to not just one child, but several. All this suggests that you should not worry too much about the fact that you will have to be under special medical supervision for 9 months. You have a very high chance of giving birth to healthy and strong babies if you follow all the doctors’ orders. We wish you an easy pregnancy and a safe birth! Be healthy and take care of your children!
General information about the medicinal composition
Immunoglobulin for pregnant women - protection against infectious diseases and Rh conflict. The active substance of Immunoglobulin is a fraction obtained from human plasma. This fraction was subjected to purification. The drug does not contain antibodies to hepatitis C and HIV. Immunoglobulin does not contain antibiotics.
The purpose of administering the drug is to correct immunity. The drug contains antibodies that resist bacteria and viruses. It is also prescribed for a lack of IgG antibodies, due to this, the risk of developing infectious diseases in people with immunodeficiency is reduced. Immunoglobulin compensates for the lack of natural antibodies in the blood serum. If the drug is administered intravenously, the active components penetrate into the blood plasma.
Opinions of doctors and patients
Some doctors argue that the administration of immunoglobulin is the only way to save the fetus in case of Rhesus conflict. Others do not advise using the drug during pregnancy, since it has not undergone enough testing that could confirm its effectiveness. Serum for injection can lead to the side effects described above and only worsen the condition of the expectant mother. In exceptional cases, the use of serum leads to dangerous side effects, such as tachycardia (Analgin with Diphenhydramine has worked well in the fight against it), fainting, and anaphylactic shock.
There were situations when the medicine increased the production of antibodies in the body of a pregnant woman and the Rh conflict remained. Self-therapy is strictly prohibited, as it can lead to serious complications. Before determining the dosage, the doctor conducts tests to understand the degree of Rh conflict.
Rh factors: “plus” and “minus”. How to understand them?
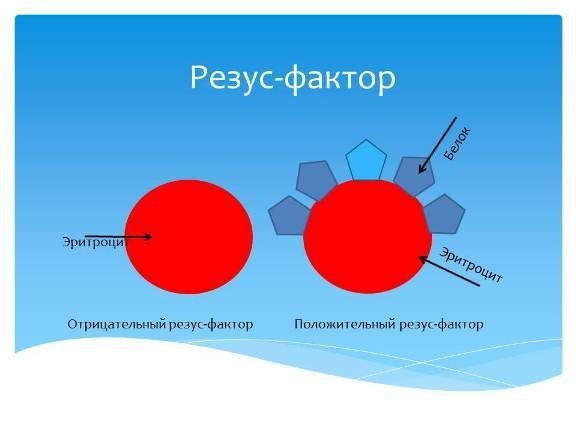
As a rule, the general concept of the “Rh factor” is known to everyone. Briefly, it can be described as follows: the Rh factor is a protein that is located on red blood cells. 85% of people have this protein in their body (these are people with a positive Rh factor), and 15% do not have it (these people have a negative Rh factor). People belonging to this 15% are no different from the rest of the majority, and the negative Rh factor is considered a small, harmless feature of genes.
But it is the negative Rh factor of the blood that can become quite a serious cause for concern, especially for the woman who decided to get pregnant and give birth to a baby.
Just as in mathematics, “minus times minus gives plus,” the rule applies to the reproductive system of the human body. For example, if potential parents have a negative Rh factor, then conception and pregnancy will not cause any problems. And the newborn will have either a negative or positive Rh factor.
If the father has a positive Rh factor and the mother has a negative Rh factor, then in most cases the ongoing pregnancy can have huge risks of fetal pathology and miscarriage. After all, from about 7-8 weeks of pregnancy, the embryo begins to secrete a tiny amount of red blood cells that enter the mother’s bloodstream. If the baby also has negative Rh, then there will be no problems. But most often it happens that the baby has a positive Rh factor.
Of course, no mother would wish harm on her long-awaited baby, but the human body is designed in a special way: as soon as it notices that something inside it is not going according to the planned pattern, or, to be more precise, that the patterns of mother and baby do not coincide— then the adult organism begins to methodically destroy what it considers wrong. But in this case, the baby’s blood seems wrong to him. Rhesus conflict is provoked. Still, you should not be afraid of giving birth to Rh-negative women. One of the main rules for a successful delivery is to follow all the recommendations of the attending doctor.