Causes and ways to solve the problem of childhood aggression in children of different ages. When your child fights to take a shovel from a peer in the sandbox, or hits a neighbor's girl for some unknown reason, it is already difficult to recognize him as that cute and clumsy kid. What to do if a child shows aggression?
Many parents panic, and, of course, want to teach him appropriate behavior and help their child get rid of aggression.
The manifestation of children's aggression is expressed, as a rule, in hysterics, screaming, fighting, biting, spitting, throwing and damaging toys and other objects.
First of all, in order to help a child cope with attacks of aggression and teach him to communicate with others, it is necessary to understand the causes of aggressive behavior.
Causes of aggression
Severely aggressive behavior has many causes. Here are some of them:
- This is often a reflection of the feelings that the child experiences:
jealousy, fear, despair, disappointment, uncertainty and sadness;
- brain diseases, somatic disorders;
- low self-esteem of the child;
- indifference to the interests and successes of the child on the part of the parents;
- lack of authority from parents;
- inconsistent parenting;
- scenes of violence in programs that the child watches.
This includes computer games.
- physical violence from parents;
The problem of aggressive behavior also has age-related characteristics.
For a young child (under 3 years old), the reason may be a reluctance to share toys, defending their territory, or lack of attention from adults. Often such aggression becomes the only opportunity for a child to attract attention.
The habit of throwing tantrums and offending other children becomes permanent. At this age, the child is just beginning to learn ways to communicate with others, find a common language and engage in play.
An attempt by parents to use force may lead to the child’s desire to strike again, and will only worsen the situation. It is better to calmly switch the baby’s activities in a different direction and help him calm down.
Children from 3 to 5 years old can express their thoughts and communicate with other children through words. But at this stage it is still difficult for the child to accept someone else’s point of view; they are very self-centered. A child can distinguish between good and bad; there is no other way for him.
At this age, a child has difficulty distinguishing between fiction and reality; it is difficult for him to separate a communication situation in real life from a television program or cartoon. The desire of another child to play with him can be regarded as an intrusion, hostile intentions.
Defense can be any form of aggression. To avoid this, parents need to talk with the child more often and teach the norms of behavior in society. A child’s wild imagination can also be channeled into a peaceful direction.

At the age of 6-10 years, children can already control themselves. And aggression can occur in the case of defending one’s interests or point of view.
A showdown can lead to a fight. Both boys and girls often choose a verbal form of aggression: calling them names, calling them names, or ignoring them. As a rule, such children have severely low self-esteem.
During adolescence, aggressive behavior is determined by the social environment in which the child finds himself. Peers can encourage aggression and provoke it.
Development of aggression
When faced with child aggression, parents often ask the question: “Why is my child behaving this way?” Often, adults tend to believe that a child is aggressive only to annoy them. However, the development of aggression in a child occurs for very good reasons: family dysfunction, lack of parental participation in his life. And only in rare cases is children’s aggression a test of their behavior on adults.
Children under 4 years of age most often resort to physical activities. For example, by biting a peer or an adult, they are trying not only to show strength or assert their rights (for example, to a toy), but also to express emotional experiences, disappointments, fear, and stress.
The reasons for this are often the harsh attitude of the mother or father towards him, which can lead to neuroses in the baby. It is important to understand that a child’s behavior is a mirror reflection of what is happening in the family in general. As soon as you realize what became the basis for such behavior of the child, you can correct the situation, teach him to control himself, and not resort to such actions, since a child of this age learns everything from his parents.
By the age of 5, the development of aggression takes on clearer forms, and children learn to express their desires in words. Already at this age, aggressive behavior in boys manifests itself more in physical actions, and in girls - in verbal ones (nicknames, ignoring, silence).
At 6-7 years old, a child develops emotional stress. He is able to hold back, accumulate resentment, and becomes prone to revenge. At this age, aggressiveness gradually becomes a permanent character trait.
go to top
What to do?
It should be remembered that children do not have as much self-control as adults. In some cases, they simply need to be listened to, supported and helped. With young children, it is recommended to use fairy tale therapy methods, where the character learns to resolve various conflict situations without losses and fights, through peaceful negotiations, and the search for compromises.
You can also use role-playing games with your child, create a play situation where there is confrontation, and toys resolve the existing dispute or conflict without hysterics.
It is difficult for a child to understand that he is behaving aggressively if the family does not give him the concepts of good and bad behavior. Personal example is another important point in solving a problem. In a family where parents use swear words and use physical aggression, children receive clear patterns of aggressive behavior.
Emotional security is very important for a child. Actions and feelings are inseparable for a child under 6 years old, and an aggressive method of influencing others is one of the ways to feel safe. If parents do not take control of this, it is often difficult for the child to understand where to stop and what consequences this may lead to. It is important to talk with your child about possible consequences.
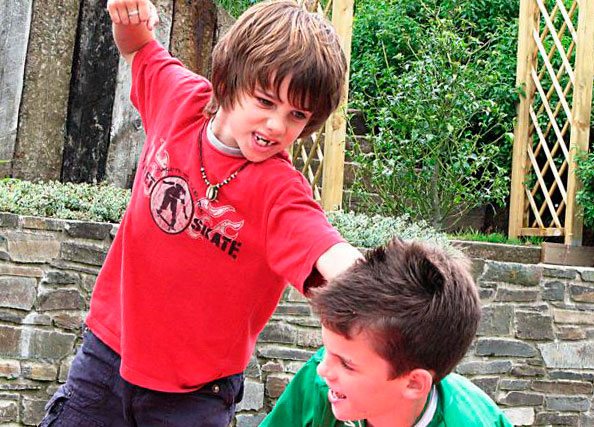

If a child is nervous and disobedient, this may be a symptom of a mental disorder. Read more in the material at the link.
Also, a child’s bad behavior may be a sign of hyperactivity syndrome; read more about it in our material “Hyperactive child - what parents should do.”
How to deal with aggression in a child? consultation on the topic
How to deal with aggression in a child?
One of the pressing problems today is the problem of childhood aggressiveness, namely the aggressiveness of preschoolers. This is due to the fact that research and numerous observations show that aggression developed in childhood remains a stable trait and persists throughout a person’s later life. It is during the preschool period that the foundations of ethics are laid, and individual options for relating to oneself and others are formalized and strengthened. Already in preschool age, certain internal prerequisites are formed that help overcome it.
Reasons causing aggressive behavior in preschool children:
- Fear. Parents may not even realize that the child is afraid of something or consider the cause of fear to be a mere trifle. Ignoring the problem on the part of adults can lead to hysterics.
- Prohibitions. With authoritarian parents, the child is “crushed” by constant “no”, “cannot” and “must”. They shout at the child, accuse or reproach them of something.
- The child defends his territory or the border of his personality.
- Quarrels between parents or family members cause fear, protest and, as a result, aggressive outbursts.
- The child expects an attack and fears hostility.
- Tries to prove his independence and independence.
- Excessive emotional stress.
- The child feels that he is not loved or even hated.
- Copies the behavior of surrounding adults or children.
If drastic measures are not taken, aggression in preschool children can become a character trait and bring a lot of trouble to a person in adulthood.
Children gain knowledge about aggressive behavior patterns from three main sources. The family may both model and reinforce aggressive behavior. Children's likelihood of aggressive behavior depends on whether they encounter aggression in their home. They also learn aggression through interactions with peers, often learning the benefits of aggressive behavior during play. And finally, children learn aggressive reactions not only from real examples (the behavior of peers and family members), but also from symbolic ones offered by the media.
How to deal with an aggressive child: 8 tips
- To teach a child under 4 years of age to cope with strong emotions, classical psychology instructs parents to show, using the example of dolls, animals, characters from fairy tales, cartoons, and other people, how unpleasant someone who gets angry and fights looks. In fairy tales, evil and aggression are personified by the Wolf, Karabas-Barabas, Koschey...
- To teach a child to recognize and manage emotions, we must name his states out loud and accept them: “I see you’re angry!”, “Are you sad? I understand”, “I feel bad too.” The law here is simple: a positive emotion shared with others increases, and a negative one decreases.
- If you yourself fell into a rage, scolded a child or someone else in front of him, show how annoyed you are and apologize. The sooner you announce your mistake, the better. Children quickly learn from their parents the rules of behavior in the family and society.
- Children with an increased level of latent aggression are discharged through active physical games, exercises, and actions. As soon as a child begins to engage in strength sports, or go to the pool, or play football, he will become reserved and attentive to others. The main rule of truly strong people: do not offend the weak, on the contrary, protect those who cannot stand up for themselves.
- Several ways will help to switch the attention of a child in a state of aggression:
- a strong signal that will puzzle the baby - it could be the ringing of an alarm clock, the sound of a radio turned on at full volume, a short cry; at the table you can tap a spoon on a cup or plate;
- unexpected action - turn off the light; lift the baby high up for a short time, and then lower him down; leave the room by closing the door;
- an offer to call some famous person, to whose name the child reacts unambiguously - with interest. Before your child realizes it's a joke, he will calm down and then laugh with you. Laughter will serve as a positive release of tension that the child could not cope with on his own.
Knowledge of the physiology of arousal helps in education: in order to extinguish one source of excitation, you need to create another.
- Children with strong-willed behavior skills (after 7 years) can learn special techniques for managing emotions - just like adults. In a state of excitement, an adult may pinch his hand, clench his fists or expander, grab a chair, raise his arms and take a deep breath, and clap his hands loudly several times. Remember what helps you cope with yourself and share this important secret with your child. Parents who admit to small weaknesses become even closer to their children.
- If, in a state of aggression, a child offends someone or breaks a toy, then the consequences will have to be eliminated - an apology, repair. When the child calms down, it is worth returning to what happened. Why did he do this? What have you achieved? How do those who were nearby feel? Do other children want to be friends with an angry child? How can I improve the situation? How can you prevent a recurrence? The social and psychological consequences of bad deeds are always worse than the physical ones. People are more important and stronger than things. “Fixing” relationships is more difficult than broken toys.
- How to punish outbursts of aggression? Isolation and a ban on active outdoor games will further anger children with strong temperaments. They do not like to obey and may harbor resentment or anger. A more effective way is to do extra housework.
Children, like adults, do not really like to clean, wash dishes, take out the garbage, or do laundry, but they understand the need to do such work. Punishment with routine but rewarding work will be perceived as fair and reasonable.
Games for aggressive children:
Activities in which the child can understand that there are other ways to attract attention and show strength can help reduce a child’s unmotivated aggressiveness. Psychologists recommend the following ways for children to splash out negative emotions:
- Tear a piece of paper into pieces;
- Shout loudly into the “scream bag”;
- Run and jump at the stadium, playground, sports section;
- Periodically beat out rugs and pillows;
- Hit a punching bag;
- Voice your feelings (“I’m upset,” “I’m angry”).
Water games
Contemplation of bodies of water and observation of the life of the inhabitants of aquariums will calm even the most desperate rebel. Recommended educational and active games with water:
- After the rain, run through puddles;
- Transferring liquid from one container to another. The activity will allow you to concentrate and cool down your angry ardor;
- Throw stones into any body of water;
- Children's fishing, which can be arranged in a basin or in a bath;
- Swimming, visiting a pool or water park;
- Create waves in the bathroom while bathing. To prevent water from spilling out, use curtains and fill half the bath.
- Installation of a mini-pool in the yard in the summer.
Games with bulk materials.
Playing with sand and cereals builds perseverance and helps fight internal tension.
- Sifting through a sieve or mill with a sieve;
- Burying figures in the sand;
- Castle construction work;
- Laying out pictures from colored sand.
Creative games
After an angry outburst, you should wait until the child calms down. You need to ask him to write down or draw his anger and the feelings of the “victim” whom he hit or insulted. It is important not to be shy about emotions, and to describe everything as it was (“I wanted to hit him,” “everything was seething inside me”).
After analyzing these recordings and putting yourself in the shoes of another person, the child will gradually learn to control behavior and begin to listen to people’s feelings
It is possible to extinguish and defeat aggression in a child, but this path will be quite long. And it is the parents who can do this. In this situation, the role of family education is more important than ever. Talk to the kindergarten teacher, ask for support during this difficult age period, because preschool age allows you to successfully correct the child’s behavior, and it is very important not to miss this moment.
Sources:
- https://www.7ya.ru/article/Rebenok-stal-agressivnym-6-prichin-agressivnogo-povedeniya-u-detej/
- https://vseprorebenka.ru/vospitanie/psihologija/agressivnyj-rebenok.html
- https://www.rastut-goda.ru/preschool-child/8491-agressivnost-u-detej-doshkolnogo-vozrasta.html
How to cope with manifestations of aggression?
Depending on age, aggressive behavior can be corrected in different ways. For a 2-3 year old child, switching to another game or activity will be enough. At an older age, a child can already remember the rules and norms of behavior.
It is better to take the child aside, help him calm down if necessary, and offer to remember how to and should not behave with others. The child must be made to understand that it is possible to be angry, but not to offend or beat. There is no need to try to change everything at once, it is better to be consistent.
If a child is nervous and it is necessary to prevent an attack of aggression, it is better to take him to another room, or just to the side, sit down to his eye level and say that you understand him, you are nearby and are ready to help. Tactile sensations will help the child feel safe, so it would be a good idea to hold hands, hug, and stroke. There is no need to accuse and lecture; in a state of overexcitation, the child is not ready to accept criticism and notations. To summarize, it should be recalled: an aggressive child is always frightened by something and experiences internal discomfort. Aggression is a way to attract attention and overcome your failures and fears. Finding the cause and dealing with it together is the task of parents, educators and teachers.
Remember that none of the listed tips will bring results if the action is one-time. Only by establishing a relationship with your child, showing attention and patience, can real changes be achieved.
Our next material is devoted to answering the question of how to get rid of an unwanted pregnancy.
How to treat aggression?
Raising a child should consist of unity and consistency in the requirements of both mother and father, as well as personal positive example
Only with this approach can we talk about correct and harmonious education. The actions and actions of parents must first of all meet all the requirements that they themselves present to their child. In a family where there are constant attacks of aggression, he will perceive it as the norm.
Treatment of aggression in children may include various methods and means:
- Offer your child an associative game. Let him draw something that makes him angry and irritated, and then tear up the drawing.
- He can learn to distract himself, for example, by counting to himself to ten, or to take out aggression by hitting a pillow and a punching bag.
- Switching the child's attention to a game or any other exciting activity.
- During the onset of aggressive reactions, parents should try to use as few words and criticism as possible so as not to aggravate the situation.
- Try to become a personal example of calm and self-control for your child.
- Enroll your child in a sports section. Regular training and exercise will help transform energy and aggression.
- Special breathing exercises and relaxation exercises aimed at relieving tension.
- The child can take additional courses of mineral and vitamin complexes.
It is possible and even necessary to treat aggression. Otherwise, this mental disorder can easily develop into a more serious illness, which will make a full life for the child impossible.