What can cause bronchitis in a baby ? The occurrence of bronchitis in infants should not be underestimated, because even slight swelling of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract and the appearance of some mucus can lead to a decrease in air access. The child has rapid breathing, he breathes with obvious effort. Since insufficient oxygen enters the bloodstream due to inflammation of the bronchi, the baby should be sent to the hospital, where he will be given antibiotics and, possibly, oxygen for breathing.
Causes of bronchitis in a baby
Bronchitis refers to diseases of the respiratory system. It often occurs in infants and young children. Most cases are recorded in late autumn, early spring and winter, since during these periods the body is usually weakened. The development of the disease is facilitated by factors such as cold air, staying in crowded places, and insufficient ventilation of rooms. Viruses that cause bronchitis damage the epithelium and infect the mucous membrane of the lower respiratory tract, facilitating the penetration of bacteria from the nasopharynx into the bronchi. Bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics.
Examining a smear from the mucous membrane of the throat and nose helps determine a child’s bronchitis is caused A positive test result for respiratory secretions indicates the presence of a bacterial infection. Sometimes bronchitis can also be caused by non-infectious factors - such as allergies, asthma, obstructive pulmonary disease, inflammation of the mucous membrane caused by toxins. Allergens and toxins destroy the mucous membrane of the throat and bronchi, contributing to the occurrence of chronic inflammation.
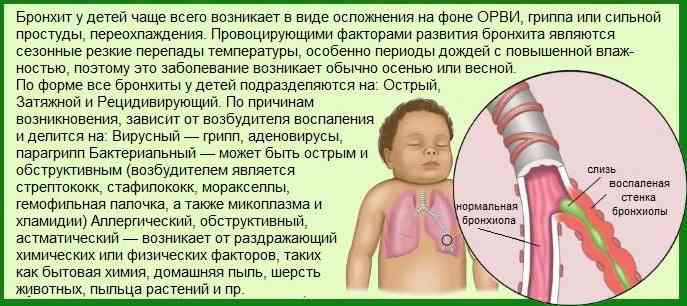
It happens that bronchitis is a complication after influenza, laryngitis or measles. In this case, the disease is accompanied by high fever and myalgia. Inflammation of the bronchi caused by viruses is often accompanied by inflammation of the conjunctiva and photophobia.
Recurrent bronchitis in infants
This form of the disease is characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tree, which occurs in young children three or more times a year and lasts at least 14 days.
The causes of recurrent bronchitis are:
- allergic reactions (for example, to animal hair, household dust);
- climatic conditions (high humidity, severe frost, etc.);
- tobacco smoke, air pollution;
- low immunity.
loading…
Most often acting as an independent disease, recurrent bronchitis can also be a complication after infections.
Typically, attacks of this form are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- spontaneous increase in temperature (often up to 38.5°C);
- Strong headache;
- nasal congestion, which can sometimes be accompanied by purulent discharge;
- sore throat;
- The cough appears after 3-5 days. At first it is dry, but then becomes wet with the discharge of light or purulent mucus;
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath.
After an exacerbation, which can last up to 14 days, children feel normal, there are practically no signs of inflammation.
Symptoms of bronchitis in infants
Three to four days before the appearance of obvious symptoms of bronchial inflammation, a runny nose occurs. Then a cough begins - first dry, then wet (this is due to the secretion of secretions in the respiratory tract, the presence of mucus). Babies cannot get rid of the mucus that forms, so they usually swallow it. Sometimes vomiting occurs. During breathing, characteristic wheezing , which indicates poor bronchial patency. The temperature rises, the child loses appetite, the baby wakes up at night and cries, behaves restlessly, and abdominal pain may occur. Breathing problems are noticeable when the child breathes. Chest retraction combined with shortness of breath are quite rare.
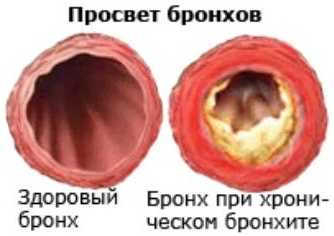
the symptoms of bronchitis appear slightly. As the infection gets worse, noises appear in the lungs, whistling or wheezing can be heard when breathing. Bronchitis can be acute or chronic. Acute bronchitis begins unexpectedly, suddenly, but it does not last long. About a week after the illness, the bronchial epithelium is restored, but the cough may persist for some time - attacks usually appear in the morning. Chronic bronchitis requires quite a long treatment.
Obstructive appearance in an infant
The obstructive form is one of the most serious in children in the first months of life. The main danger is a strong narrowing of the bronchial lumen, which threatens attacks of suffocation. The inflammatory process caused by infection causes obstructive syndrome. It is characterized by blockage of the lumen of the bronchi due to swelling of the mucous membrane and a large accumulation of secreted secretions.
An incompletely cured disease can cause bronchial asthma.
Symptoms of an obstructive type of disease in infants are:
- breathing accompanied by various pathological noises;
- dyspnea;
- difficulty breathing, both during inhalation and exhalation. In this case, a retraction of the chest is observed;
- paroxysmal dry cough with a small amount of sputum;
- fever that occurs on the second or third day after the onset of the disease.
The cause of obstructive bronchitis in infants can be viral infections (for example, tonsillitis or influenza) and bacteria such as Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella.
Treatment of bronchitis in infants
You should remember the need to constantly humidify the air in the room where the sick child lives. It is necessary to minimize the number of his contacts with sick people, it is necessary to isolate the baby from the toxic effects of tobacco smoke. Do not expose your child to sudden changes in temperature. During treatment, aerosol therapy is used, in particular. It is also recommended to use drugs to thin the mucus in the bronchi. Antitussive syrups should not be given because they will interfere with the removal of inflammatory secretions.
When treating infants antibiotics are mainly used , since the infection is predominantly of bacterial origin. The decision about the need for such therapy will be made by the doctor. Be sure to give your child the prescribed antibiotic in the doses prescribed by the specialist and for as long as the pediatrician indicates (even if you think the symptoms have already disappeared). If bronchitis occurs as a result of a viral infection, treatment with antibiotics is usually not carried out. The doctor must assess the general condition of the child. If there is a high temperature, the baby should take antipyretic drugs in the form of syrup. It is also necessary to remember that the child should drink a large amount of liquid - breast milk, water, diluted juices, compote. In small allergy sufferers, inflammation of the bronchi often leads to a narrowing of the airways, and the baby may have breathing problems. Obstructive bronchitis occurs. The child should receive medications that dilate the bronchi; inhalation is recommended.
In addition to taking medications, you can also use some proven ways to combat the symptoms of bronchitis in infants:
- place the baby in the crib so that his head is higher than the rest of the body (this should make breathing easier),
- use inhaled airway moisturizers; You can spray sea water indoors from time to time; when a debilitating cough begins, take the child into a steamy bathroom for about 5 minutes - you can add a few drops of eucalyptus oil or a pre-prepared decoction of chamomile or sage to hot water.
Children with chronic diseases or low immunity may experience complications from bronchial inflammation. The most common complications among newborns: pneumonia, pneumococcal infection. With chronic bronchitis, hypertrophy of the right ventricle of the heart, obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema, increased bronchial reactivity, and asthma may also occur.
Bronchitis in a baby - video
Bronchitis in infants: treatment and symptoms
5 (100%) voted 1
Symptoms

The symptoms of bronchitis in infants are quite similar to those in adults. The development of the inflammatory process can be determined by the characteristic symptoms even in children.
Symptoms of bronchitis in children under one year of age:
- There is a dry cough for the first few days. Then sputum discharge appears. There is quite a lot of it, but it is liquid and comes out well. If the cause of the disease is an infection, the mucus looks like pus. And when a virus provokes this, it will be transparent with a yellowish tint, and later it will acquire a greenish color.
- The infant will cough for at least 14 days. Even then, residual symptoms of cough can be observed for a month. If the cough does not go away after this, you need to tell your doctor about it. Only he will be able to determine how to treat obstructive bronchitis in children.
- The baby may wheeze and gurgle will be heard. This is due to the fact that a child at this age cannot yet cough well, and during the period of inflammation a lot of fluid and mucus accumulates.
- A small child will find it difficult to breathe, especially when exhaling. In this case, you can even hear a whistle. Shortness of breath will become quite noticeable.
- Nasal congestion and throat redness may occur. This manifests itself at the very beginning of the development of bronchitis in infants. But these are not the main symptoms of bronchitis. You cannot treat bronchitis in children and ignore it.
- An increase in body temperature may occur for several days (up to 10 days). When this symptom is absent, it can be assumed that the disease is due to an allergy or a weak immune system. Bronchitis in an infant can cause complications. Bronchitis in infants must be treated correctly.
- Against the background of all these signs, the baby will become lethargic, capricious, and will have difficulty sleeping and eating. Signs of intoxication may be observed. By their manifestations one can judge the extent of damage to the bronchi.
Therefore, if similar symptoms appear, you need to contact your doctor and not delay it any longer. You can even call an ambulance. The doctor must examine, listen, and, if necessary, conduct a blood test and take an x-ray. This examination will help recognize bronchitis in an infant. A pediatrician should treat bronchitis in children. All these recommendations will be useful if tracheobronchitis is detected at 7 months.
The risk of respiratory tract disease is at 4 months, but almost 2 of those cured may remain coughing for a long time. Bronchitis in an infant can be confused with cold symptoms only at the beginning of the disease.