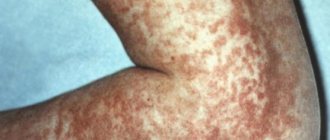
What is urticaria?
Urticaria or urticaria appears unexpectedly. Blistering rashes usually have an irregular shape. Urticaria is often accompanied by excruciating itching.
Sometimes the rash covers the child’s entire body, turning into a single spot. The duration of the symptom in question varies from several minutes to several days, and sometimes the blisters suddenly disappear, leaving no marks on the skin.
In children under 2 years of age, urticaria usually occurs in an acute form, and in older children - in a chronic form.
Basic information about pathology
More than 20% of the world's population have experienced symptoms of urticaria at least once in their lives. In this case, itchy blisters most often appear in childhood. An interesting fact is that girls and women are more susceptible to pathology. If contact with the allergen is not limited, urticaria can become chronic.
Urticaria is one of the most common forms of allergic reactions that appear in childhood. Parents themselves can easily diagnose the pathology. The problem is that childhood hives are not taken seriously. And refusal of full treatment can lead to the disease becoming chronic and the child remaining allergic for life.
There are several types of allergic rashes. Initially, the disease always develops in an acute form. Unpleasant symptoms appear within an hour after contact with the allergen. Hives in a child can be noticed after the baby has eaten an orange, chocolate, drunk a glass of milk, or eaten a nut. These products are strong allergens and should be offered to your baby with caution. Acute urticaria is easy to treat. You can remove itchy blisters with the help of a high-quality antihistamine that is appropriate for your age. Usually 24 hours is enough for the pathology to completely recede.
If contact with the allergen continues, the risk of developing chronic urticaria increases. In this case, more persistent symptoms may develop, and treatment may require quite a long period of time. Signs of the disease may remain for several weeks. At the same time, the number of allergens that cause blisters on the body increases. It is necessary to treat urticaria in children immediately when the first signs of the pathological process appear. This will give you a better chance of getting rid of the problem completely. If therapy is carried out correctly, stable remission can be achieved by the age of 7-8 years.
Cold urticaria is a rare form of allergy
The following types of urticaria are distinguished:
We also recommend reading:Urticarial skin rash
- Solar urticaria. The pathology appears only when the child’s skin is exposed to direct ultraviolet rays. The pathology is more difficult to treat than food allergies.
- Cold urticaria. A rare form of pathological process that manifests itself when certain areas of the body are overcooled. Most often, symptoms of urticaria in children can be seen on the cheeks or arms.
- Aquagenic allergy. Pathology can manifest itself with prolonged contact with water. The disease is very rare in children.
- Dermographic urticaria. Blisters on a child’s skin can appear due to mechanical damage to the skin (abrasions, scratches). The trouble can be noticed after sleep, when the baby injures himself. As a rule, unpleasant symptoms quickly pass without any therapy.
- Nervous (psychogenic) allergy. Pathology develops in children against a background of stress.
If it is not possible to identify the factor that provokes the appearance of signs of the disease, they speak of an idiopathic form of the pathology.
Causes
Urticaria in children appears for the following reasons:
- physical factors - ultraviolet radiation, cold water or wind, pressure;
- food products that contain preservatives, dyes, food additives;
- allergic reaction to food:
- confectionery products based on cocoa butter;
- strawberry;
- cheese;
- smoked sausages;
- sauerkraut;
- honey;
- milk;
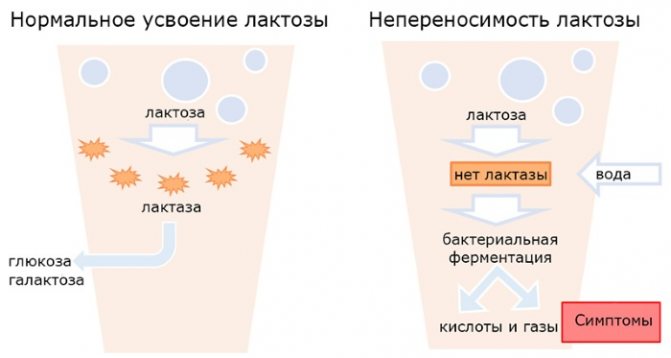
Milk can cause hives in a child. Other skin symptoms include vomiting and nausea. This pathology is called lactose intolerance. It cannot be treated! - eggs;
- nuts;
- citrus;
- viral, parasitic and bacterial infections;
- taking medications;
- reaction to vaccination, blood transfusion;
- insect bites;
- airborne allergens - plant pollen, animal hair, dust;
- allergies to cosmetics, household chemicals;
- the presence of chronic infectious diseases – adnexitis, tonsillitis;
- pathologies of the immune system;
- liver diseases;
- pathology of the thyroid gland.
Application of creams and ointments
Treatment of urticaria in children occurs using topical agents. They quickly relieve swelling, itching and prevent the spread of the pathological process to neighboring areas of the body. The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
- Fenistil. Antihistamine gel that can be used to treat children over 1 month of age. It directly combats allergy symptoms and relieves severe itching.
- Gistan. Contains natural ingredients. Due to the presence of dexpanthenol, it has an anti-inflammatory effect and relieves irritation.
- Elidel. An external remedy for the treatment of various manifestations of allergies in children from 3 months.
- Skin Cap. The drug contains zinc compounds and is effective in the treatment of dermatological diseases of an allergic nature.
Symptoms
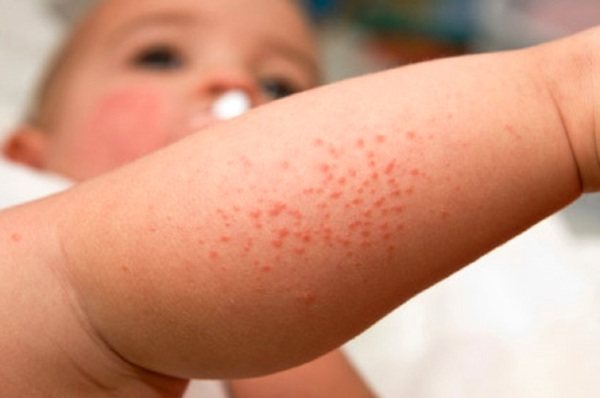
Urticaria in a child (symptoms and treatment will be determined by the attending physician) is characterized by the following symptoms:
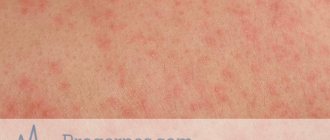
- a pale pink or bright red rash that resembles a nettle sting or insect bite;
- the rash may have a small depression in the center, and sometimes a red border forms around it;
- the affected areas of the skin itch;
- rashes appear on any part of the body;
- pain to the touch if blisters form on the skin;
- blisters turn pale when pulled;
- muscle and joint pain;
- local redness usually appears on the cheeks and abdomen, and then on the back and limbs;
- formation of solid red seals;
- headache;
- elevated temperature accompanied by chills;
- nausea and diarrhea;
- difficulty breathing;
- paroxysmal cough;
- suffocation;
- decreased blood pressure;
- In infants, seizures and loss of consciousness
- worsening sleep;
- mental disorders;
- Quincke's edema of various localizations.
Causes and symptoms
A nettle rash on the skin of an infant is a consequence of thinning of the capillaries under the influence of the release of histamine into the blood. Upon contact with an allergen, the concentration of histamine increases, the walls of blood vessels become fragile, and intracellular fluid begins to pour into the epidermis. This is how characteristic rashes form.
In infancy, the most common cause of urticaria is food allergies - this is how a child can react to complementary foods or new foods in the diet. Sometimes urticaria develops as a form of contact allergy - the skin of infants is very thin and delicate, and even the wrong powder for washing baby clothes can cause a rash.
A baby’s skin may develop urticaria to a vaccination, or more precisely, to vaccine components, to insect bites, or to the friction of a diaper or the seams of clothing.
Parents should be prepared for the fact that in about a third of cases the true cause cannot be identified.
It is difficult to confuse hives with something else, because unlike other allergies, diaper rash, prickly heat, it appears quickly, literally in a matter of minutes. The blisters are pink and numerous. They are practically never isolated . If the baby has single individual blisters, then an infection should be suspected, not urticaria.

Not only does hives appear quickly and look like a burn from the plant of the same name, but it also goes away quickly. As soon as the concentration of histamine in the blood begins to decrease, the rash also disappears . Neither diaper rash nor infection goes away so quickly. This is the main symptom of the pathology.
The rash with nettle fever (this is the second name for urticarial dermatosis) is itchy and itchy. There is slight swelling around the blisters. If the rash appears exclusively on the face or hands, then the general condition does not suffer. If the rash is extensive, a rise in body temperature is possible.
An infant with widespread, extensive urticaria experiences difficulty falling asleep, is capricious, and has disturbances in appetite and stool. Hives in infants is often called strophulus. With it, the blisters are small, not exceeding 3 millimeters , with a small bubble at the top.
With the development of giant urticaria, laryngeal edema (Quincke's edema) and other forms of edema are formed. In this case, the child has difficulty breathing and needs urgent medical attention. Before the ambulance arrives, parents must provide the child with a supply of fresh air.
Classification
| Form of the disease | Description |
| 1. Spicy | It develops almost immediately after exposure to an allergen (from 1 hour to a day) with pronounced symptoms. The provoking factor is easy to determine, since the body quickly reacts to the penetration of the allergen. Elimination of exposure is sufficient and treatment may not be required. This form of the disease usually lasts no more than 1.5 months. |
| 2. Chronic | The chronic form of urticaria is characterized by daily appearance of rashes, which lasts more than 6 weeks. Chronic urticaria usually occurs in people between 20 and 40 years of age. |
There are 3 forms of urticaria depending on the severity of the disease:
- mild when the child feels normal. There are no signs of intoxication and no painful itching;
- moderate, when nausea, diarrhea and fever appear. Swelling occurs in certain areas, which quickly spreads - Quincke's edema;
- heavy, when there is a threat to life. To the above symptoms are added intoxication, severe angioedema and damage to the gastrointestinal tract of an allergic nature.

Types of urticaria:
- grocery – appears after eating any type of food. It is characterized by fever, nausea, diarrhea and itchy rashes. They are localized on any part of the body: stomach, feet, cheeks, arms. The rash resembles a burn after contact with nettles in the form of pink or red bubbles. Food urticaria lasts up to 3 hours, and sometimes several days;
- demographic - swelling appears at sites of mechanical impact: scratching, hitting or rubbing. The resulting scars are white or red in color and disappear quickly;
- slow – the main factor causing the rash is compression. For example, clothes that are too tight or a heavy bag on your shoulder;
- cold - rashes form under the influence of cold wind or water;
- thermal – the provocateur is hot water (bathing), intense exercise or severe stress;
- solar – the appearance of urticaria is associated with exposure to the sun; the skin is sensitive to ultraviolet radiation. Factors influencing this process may be cosmetics, as well as kidney or thyroid diseases;
- vibration – rashes are formed under the influence of vibrations (working with impact mechanical tools);
- adrenergic – a type of urticaria in which rashes appear as a result of the production of huge amounts of adrenaline, which is usually associated with stressful situations;
- contact – when the skin comes into contact with an allergen. Usually they are plant pollen, animal hair, dust or jewelry made of various metals. The rash may be itchy;
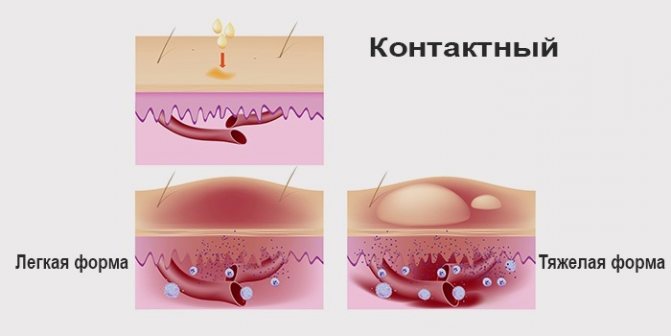
- water (water intolerance) - occurs as a result of water coming into contact with the skin, but the liquid does not act as an allergen. Water is a conductor, dissolving salts and other chemical elements;
- acute allergic pruritic dermatosis (cholinergic) – this type of urticaria appears after severe stress and physical overexertion. The disease occurs due to the intense production of acetylcholine in the body, which is more often typical for men at a young age;
- pigmentary urticaria, in which benign tumors consisting of mast cells form on the skin. Mastocytosis appears as brown-yellow, brown-red spots or papules. The diameter can reach 5 cm. In areas of rashes, the skin resembles an orange peel. If the disease develops, cosmetic surgery is performed;
- angiitis is a disease in which spots resembling hives appear on the skin. The disease is based on an inflammatory process affecting small vessels and capillaries, resulting in the formation of a rash;
- infectious - urticaria, which develops due to the entry of pathogenic foreign microorganisms into the body.
When a rash appears after taking medications, we are talking about drug urticaria (allergy to the drug). Urticaria is usually called idiopathic if, after a series of studies, the cause of the disease has not been identified.
Learning to recognize
The rash that looks so similar to nettle burns is called urticarial. The main difference between urticaria and all other types of rash is its rapid development. It, in the literal sense of the word, is formed suddenly. If many other types of rash appear gradually, from several elements on the body and gradually grow and spread, a nettle rash is usually always numerous and extensive at once. Its color is rich pink. In the cold form it is light.
READ ALSO: How to remove acne on a teenager’s face: do’s and don’ts
The initial stage is characterized by a large number of formations on the skin. After an hour, their number, if at all, increases, then only slightly. This “behavior” of a nettle rash can be explained by the concentration of histamine in the blood. While there is a lot of it, there is a rash, but after an hour it decreases and new elements do not form.
Therefore, look carefully at your child and understand one important detail: if several blisters appear, and then a few more, then we are probably not talking about hives at all, but about an infection. This is how chickenpox and many other viral illnesses begin.
It is important to evaluate other symptoms as well. With urticaria, the temperature rises only if the rash is very extensive, covering more than half of the body, the increase is insignificant - up to a little over 37.0 degrees. In infectious diseases, the temperature is usually high, there are signs of respiratory lesions and other complaints.
A nettle rash not only forms suddenly, but also disappears suddenly. As soon as there is less histamine in the child’s blood, the rashes begin to disappear, leaving no traces on the skin . Usually the rash becomes pale within a few hours and then disappears. The urticarial rash returns only if the child’s urticaria is chronic, and its symptoms recur with enviable frequency over several months.
Does the rash hurt? Not much, but quite noticeable itching and itching. And you need to pay attention to this too. It looks like small elements raised above the skin, prone to merging into wider ones, and there is swelling around each one. If the rash affects a small area of the body, then this usually does not affect the general condition of the child. But extensive rashes, especially edematous ones, certainly affect the general well-being - the child becomes lethargic, capricious, always tries to scratch the rash, and difficulty breathing may develop (with swelling of the respiratory tract).
READ ALSO: I squeezed out the wen, the liquid stinks
Perhaps, as already mentioned, the temperature may rise slightly and your appetite may suffer. Children with food allergies may experience abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea.
Since there are several types of urticaria, its symptoms may have their own characteristics. By the nature of the rash, attentive parents can try to determine not only whether it is nettle or not, but also the possible causes of its appearance.
Chronic form
Chronic urticaria is often accompanied by indigestion. In addition to the fact that urticarial rash appears frequently, exacerbation is also marked by the occurrence of diarrhea or constipation. Often the site of chronic infection is inflamed tonsils, or there are problems with the bile ducts, frequent stomatitis, caries - also accompany chronic urticaria. Remission is the period between episodes of the formation of a characteristic rash.
During the period of exacerbation, the child becomes nervous and complains of headache, nausea, and abdominal pain. Treatment should be aimed at preventing repeated attacks and reducing the likelihood of their aggravated course, for example, the development of edema of the meninges.
In infants
Urticarial rash in children of the first year of life is called strophulus. Most often at this age it is caused by food. The likelihood of developing urticaria is higher in children who are bottle-fed. The most dangerous moments are the periods of introducing new complementary foods for the baby.
Most often, characteristic rashes appear in the folds of the skin, on the face, and neck. Almost always, strophulus is accompanied by loose stools or constipation, and loss of appetite.
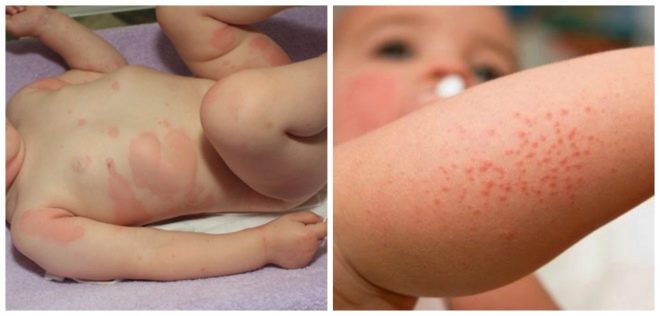
Edema form
Giant or edematous urticaria is easy to recognize. It is accompanied by suddenly developing edema. They can be on the arms, legs, neck, face. The higher you go to the head, the more dangerous, because Quincke's edema, for example, affects the larynx.
READ ALSO: Rash in the form of mosquito bites - SHOCK 11 types with photos
Swelling goes in the direction of the muscles. Swelling may persist for quite a long time. With Quincke's edema, it is difficult for a child to breathe, difficulty inhaling, and cyanosis (blue discoloration) of the lips appears.
Everything depends on the actions of the parents: you need to call an ambulance, give a dose of an antihistamine (age-appropriate), take the child out into the fresh air to ease breathing until the doctors arrive.
Temperature
Temperature or cold urticaria is usually the body's reaction to cold or sun. The rash appears in places that have been exposed to temperature - on the face, hands. If you are allergic to UV rays, the urticarial rash can be quite extensive. Typically, sun intolerance develops in children with a certain genotype: fair skin, blond hair and eyes.
With such urticaria, rashes can also develop in response to temperature changes , for example, if a child is brought from the cold to a hot bathhouse or vice versa.
It is noteworthy that the rash itself does not appear immediately, but several hours after exposure to UV rays or low temperature.
First signs
Urticaria in a child (symptoms and treatment are important elements in the course of any disease) usually begins suddenly. The disease in question is characterized by the sudden appearance of papules, spots or blisters in different parts of the body. Usually they are very itchy and itchy, sometimes merging into a single canvas. In some cases, weakness appears, headache and fever.
At the initial stage, the rash disappears as quickly as it appears. Usually a few hours are enough.
First aid
Rashes formed during acute form of urticaria disappear quickly (from several hours to 2-3 days).
The child may be very bothered by itching, so there are the following recommendations:
1. First you need to eliminate the allergen - pet, product or medication.
To eliminate burning and itching, special antiallergic creams are used, approved for children (age taken into account):

If these remedies are not available, cool compresses are made (250 ml of water and a tablespoon of vinegar) or sunburn cream is applied;
2. To reduce irritation and itching, it is advisable to dress the child in cotton clothes. To prevent the possibility of scratching the rash, you should trim your child’s nails;
3. in case of fever, nausea, diarrhea or Quincke's edema, call an ambulance immediately;
4. Before the ambulance arrives, the child must be given plenty of fluids. An alkaline solution (1 g of baking soda per 1 liter of water) or slightly alkaline mineral water is suitable for this.
To remove the allergen from the digestive tract, an enterosorbent is given:
5. When angioedema occurs as a result of an insect bite or injection, the area above the bite or injection is tightly pulled.
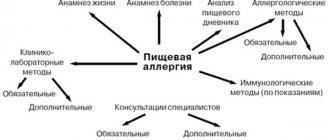
Diagnosis of urticaria in children
Urticaria in a child (symptoms and treatment are determined in accordance with the established procedure) requires diagnostic measures. To identify the disease and prescribe the correct treatment, you must first visit your local pediatrician.
This doctor can refer you to specialists:
- dermatologist;
- immunologist;
- allergist;
- neurologist;
- endocrinologist
To make a diagnosis, the following tests are performed:
- general blood and urine analysis;
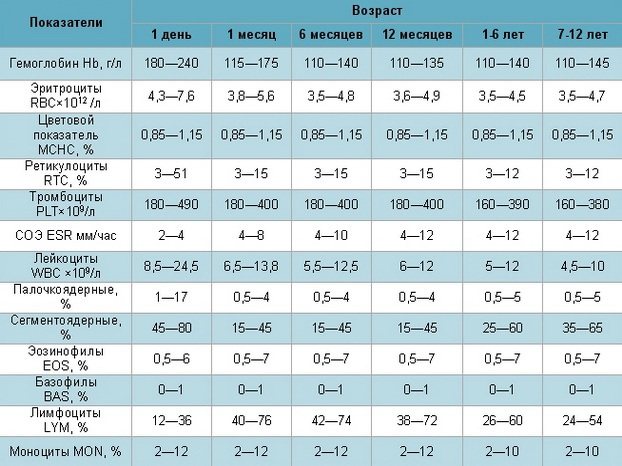
- blood chemistry;
- blood sampling for HIV, RW;
- coprogram.
When a more detailed examination is required to clarify what disease we are talking about, the following list of studies is prescribed:
- checking feces and oral mucosal materials for the presence of bacteria;
- rheumatic tests - a whole complex of biochemical studies aimed at diagnosing autoimmune conditions of the body;
- differential diagnosis for the presence of parasites: trichinella, echinococcus, opisthorchis and others;
- coprogram - a detailed study of feces.
Allergy testing includes the following procedures:
- identification of hereditary diseases and allergic reactions (collection of an allergic history);
- test tube tests (in vitro);
- tests to determine the body's response to cold, heat and pressure;
- allergy prick test;
- intradermal tests with infectious allergens.
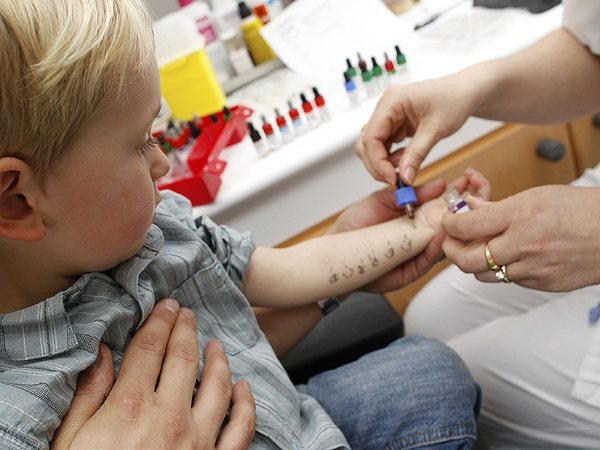
List of instrumental studies:
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- electrocardiogram;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a probing method that allows you to examine the stomach, duodenum and esophagus using a microcamera;
- X-ray of the paranasal sinuses;
- chest X-ray;
- Diagnosis of the state of the cardiovascular system using bicycle ergometry.
A set of examinations is prescribed individually after consultation with the attending physician.
Symptoms of urticaria
The main manifestation of this pathology is a nettle rash; papules with transparent contents may also appear. In this case, most of the elements are located on the scalp, face, neck and upper body.
But a rash can form not only in the above places, but also on the skin of the palms, soles and mucous membranes. The onset of the disease is usually sudden. The primary manifestation of urticaria is significant skin itching, redness and swelling. Bubbles then form against the changed background.
In severe cases, the rash may be accompanied by severe pain, disruption of the child’s general condition, and fever. Swelling can also be localized around joints, eyelids and lips.
Quincke's edema, or angioedema, is a serious complication of urticaria. It is characterized by deep swelling of the dermis and subcutaneous fibers in the trachea and larynx. The subglottic space of the larynx may swell, and this leads to difficulty passing air.
This complication can be recognized by the following symptoms: cyanosis of the fingertips or the area under the eyes, nasolabial triangle, difficulty and whistling when breathing, paroxysmal severe cough. This complication requires emergency medical care, since in the absence of pathogenetic therapy, death is possible.
The appearance in a child of symptoms such as nausea, repeated vomiting, and diarrhea may indicate damage to the mucous membranes of the digestive tract (esophagus, stomach). Damage to the hearing organs and membranes of the brain is manifested by weakness, dizziness, nausea, and headache.
The examination begins with collecting an anamnesis of the disease, namely data about the onset of the disease and its possible cause. The doctor also asks about family history and whether close relatives have allergic diseases. Anamnestic search can be quite complicated; sometimes it is necessary to retrospectively analyze episodes of the disease.
To diagnose and determine the etiological causes of urticaria in children, it is necessary to perform a number of laboratory and instrumental tests. To make a diagnosis, general clinical examinations are first performed, and if abnormalities are detected, specific tests are performed. Mandatory tests include a general blood and urine test, blood glucose, determination of helminths and stool culture for the microbial spectrum.
All children with a rash should have a physical examination. A dermatologist determines the localization of urticaria elements, their size and shape, the presence of pigmentation or peeling.
Disease activity is assessed using a special Urticaria Activity Scale. To determine the specific antigen that provokes the rash, it is necessary to conduct a series of diagnostic tests:
- Determination of the total and specific fraction of immunoglobulin E,
- Qualitative and quantitative detection of antibodies to immunoglobulins G and E.
- Skin test using specific antigens (household, food, biochemical, as well as plant and animal).
- With the development of chronic urticaria, complement fractions C3 and C4 are additionally determined.
To make a diagnosis of cholinergic or adrenergic urticaria, a number of provocative tests are performed:
- the occurrence of urticaria after mechanical irritation of the skin indicates a dermatographic variant of the disease;
- cold urticaria can be diagnosed after the Duncan test (placing an ice cube on the skin of the forearm);
- aquatic testing (application of a compress with cool water) diagnoses aquagenic urticaria;
As additional methods, biochemical analysis of venous blood, determination of the amount of liver enzymes, urea and creatinine are used. Instrumental tests include chest radiography, abdominal ultrasound, and ECG. An advanced diagnosis of infections may also be needed to determine the exact cause of the urticaria. When, after a full examination, the cause is not found, the urticaria is regarded as idiopathic.
Therapeutic measures
First, the cause of urticaria is determined and appropriate treatment is prescribed.
If an allergen is detected, part of effective therapy will be its elimination.
Treatment tactics for children from 1 to 3 years old are as follows:
- give the child an antihistamine;
- in the first hours of treatment it is customary to prescribe an enema;
- apply a special cream or lotion (prescribed by a pediatrician) to the damaged areas to relieve itching and inflammation;
- to avoid irritation, moisturizing soap and hypoallergenic washing powder are used;
- apply cold compresses to areas with rashes;
- include a sorbent in treatment to remove the allergen from the body;
- if urticaria is the result of an infection that has entered the body, antiviral therapy is prescribed;
- give the child warm water;
- It is recommended to adhere to a certain diet for several weeks;
- minimize walks in the sun and do not take hot baths;
- treatment of the underlying disease that caused the urticaria (if any).
Similar activities are provided for preschoolers, and detailed treatment is discussed with the pediatrician. In schoolchildren and teenagers, you should pay attention to the state of the nervous system , the amount of physical activity, and also minimize the pressure from a backpack or bag on your shoulders.
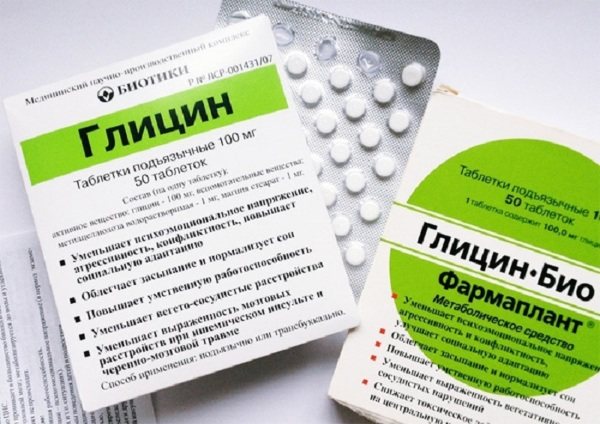
As a preventative measure, sedatives are prescribed: Glycine, Motherwort, Valerian.
Why does urticaria develop?
Anything can provoke the appearance of unpleasant blisters on a child’s skin: cold, ultraviolet rays, certain foods, stress, etc. However, the exact causes of hives in children should be looked deeper. After all, not every baby can develop such an allergic reaction.
Any negative reaction of the body indicates a malfunction of the immune system. Studies show that in 15% of cases, physical urticaria develops in children after an infection in childhood. Foci of chronic inflammation, in particular tonsillitis, caries, and otitis, are also of great importance. Failure to treat any disease in childhood can lead to the development of persistent allergies over time.

Your doctor will help determine the exact cause of the pathology.
The causes of the rash may also be due to autoimmune processes. In 20% of cases, the appearance of blisters is due to the fact that the body perceives its own cells as foreign. Antibodies are produced, causing swelling and itching. As a rule, the development of idiopathic urticaria is associated with this.
The state of the child’s immune system directly depends on how the mother’s pregnancy went and in what environment the child spends time. If a woman, while pregnant, did not eat well, smoked, or indulged in alcoholic beverages, the likelihood of developing urticaria in the newborn increases significantly. It is important to lead a healthy lifestyle until the baby is one year old. In the first 12 months, the baby’s immunity is weakened. If the child is in a smoky room or the mother neglects the simple rules of caring for the baby, hives will be difficult to avoid.
Infants who suffer from congenital diseases also often experience symptoms of urticaria. Thus, an itchy rash often appears in children suffering from diabetes. As the level of glucose in the blood increases, tissue nutrition is disrupted. This inevitably leads to a decrease in the child’s body’s defenses.
The trigger for the development of pathological urticaria can also be helminthic infestations.
What can you do at home?
Urticaria in a child is often treated at home, but only a specialist can prescribe correct and effective treatment based on the symptoms.
Urticaria is dangerous because it can develop into extensive Quincke's edema. If treatment is not started in time, there is a risk of suffocation.
At home you can use:
- hydrogen peroxide – 1 tsp. mixed with 1 tsp. water. A cotton pad is moistened and applied to the rash areas. This recipe will not relieve inflammation, but will temporarily relieve painful itching and burning;
- Cool compresses or baths help slow down the release of histamine. For better effect, it is recommended to add 2 tsp. finely ground oatmeal;
- baking soda – combine baking soda and water to create a paste. It is applied to the rash sites. This remedy stops irritation and reduces the discomfort of itching;
- Vinegar is a great remedy for itching. Vinegar is mixed with warm water (1 tsp + 1 tbsp). A cotton pad is moistened and applied to the areas where hives form.
To prevent inflammatory processes, you can start giving your child fish oil.
What is urticaria in newborns
Urticaria in infants is a type of dermatitis. In most cases, it is of an allergic nature. Almost immediately after contact with a dangerous object, the first symptoms appear, including:
- acute itching;
- skin redness;
- small blisters;
- swelling.
The swelling resembles the marks of a nettle “bite” – hence the name of the pathology.
Symptoms of general malaise and a slight rise in temperature occur less frequently. In an acute attack, Quincke's edema may develop, which affects the baby's lungs and can be fatal.

In this case, parents need to contact their pediatrician as soon as possible to identify the provoking factor and eliminate it.
Causes
The main reason for the appearance of rashes and blisters is an inadequate immune response to potentially dangerous irritants. In young children, it appears due to the fact that the immune system is not fully formed and the body reacts sharply to any influence.
- food allergies;
- pollen and plant sap;
- synthetics and wool;
- heat or cold;
- stress;
- infections;
- animals;
- medications.
Children from one to two years old are in the greatest risk zone. Usually complementary foods are introduced at this time, and the reaction to new foods is unpredictable. After three years, the immune system becomes stronger, and irritants do not affect the baby as much.
Newborns who are breastfed rarely develop urticaria.
The fault usually becomes the mother, who violated the diet. Strawberries, chocolate, citrus fruits or natural honey can trigger allergies. It is worth considering that urticaria is not always allergic in nature.
Why hives may appear in a baby, watch this video:
In rare cases, symptoms appear due to more serious disorders - tumors, diabetes or parasite infection. To be sure to find out the cause of the rash, you need to conduct a full examination of the baby.
First aid for urticaria in infants
To quickly get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of urticaria, you need to immediately exclude the child from contact with a potential irritant. If the baby has a food allergy, an enema is given or a natural sorbent is given.
If the reaction is caused by pollen or cosmetics, the child should be bathed in warm water without using soap or shampoo. The hives rash is accompanied by severe itching, but the spots should not be scratched.
To reduce discomfort, mild baby creams or ointments with a cooling effect are used. Folk remedies that include only natural herbal ingredients are also used.
You need to choose the most neutral composition so as not to aggravate the baby’s condition.
Drug treatment
The attending physician may prescribe treatment, including the following groups of drugs:
- antihistamines – 1st generation drugs that eliminate allergy symptoms. The most effective: Suprastin, Xizal, Clarisens;

- non-hormonal ointments and creams that relieve itching and have an antiallergic effect: Gistan, Bepanten, La-Cri;
- hormonal ointments (prescribed in severe cases): Soderm, Advantan, Hydrocortisone;
- 2nd generation antihistamines: Zyrtec , Claritin, Erius;
- enterosorbents: White coal, Polysorb, Activated carbon;
- to normalize sleep: Valerian, Motherwort.
Folk remedies
Effective folk remedies:
- Turmeric is a natural antioxidant and antihistamine spice. Turmeric is used topically and taken orally. For this, 1 tsp. spices are mixed with warm water. The child must be given 2 times a day;
- ginger – relieves swelling, removes allergens from the body and relieves inflammatory processes. Ginger root is brewed in boiling water, and the resulting tea can be mixed with honey;
- green tea is an effective antihistamine that enhances immune functions. A child can be given a maximum of 3 cups of tea per day, excluding taking it before bed;
- nettle – removes the allergen from the body and relieves swelling. Brew 2 tsp in 200 ml of boiling water. nettle leaves. Give the resulting infusion 2 times a day;

- Echinacea – relieves inflammation, has antibacterial and antiviral effects. 1 tsp. 200 ml of plant leaves are brewed. boiling water It is given to the child once a day before bedtime.
Diet
| Authorized products | Prohibited Products |
| First courses cooked in water or low-fat broth. It is allowed to add cereals and vegetables. | Bee products, confectionery products based on cocoa butter |
| Smoked meats, canned food and sausages. | |
| Porridge cooked in water: |
- oatmeal;
- rice;
- buckwheat;
- pearl barley;
- corn. Do not give preference to semolina porridge.
| Citrus. | |
| Lean dietary meat: rabbit or chicken. |
|
Vegetables you should pay attention to:
| Sauces, mayonnaise, seasonings |
| Crispbread, bread without yeast | Nuts |
| Bananas | Mushrooms |
| Green apples | All products containing dyes, preservatives, thickeners, emulsifiers. |
| Apricots | Chips, crackers, products containing palm oil. |
| Pears | Caviar and seafood |