Causes of sun allergies
The sun's rays themselves do not contain allergens. Why do some people, including young children, exhibit all the signs of an allergic reaction when exposed to ultraviolet radiation? The sun “launches” it, acting as a catalyst. The onset of a phototoxic process in the body can be caused by the following reasons:
- pellagra is a rare disease associated with nicotinic acid deficiency;
- Gunther's disease is a rare form of photodermatosis, a recessive mutation (according to some scientists, people suffering from Gunther's syndrome were mistaken for vampires in the Middle Ages);
- photosensitizers entering the body from drugs, household chemicals, food additives, hygiene or cosmetic products;
- tattooing - cadmium sulfate, used when applying a pattern to the skin, can provoke a phototoxic reaction;
- food products, especially those foods that contain a large amount of dyes, preservatives and flavors.
The risk group for developing sun allergies includes people suffering from individual intolerance to chocolate, nuts and coffee. Also, more often than others, an allergy to ultraviolet radiation manifests itself in patients with the first (Celtic) skin phototype - they can experience burns after a few minutes of exposure to the sun.
Types of pathology
The sun's rays act differently at different times. In the first minutes, there is a slight warming effect, the production of vitamin D and a positive effect on the nervous system. And after staying in the sun for more than 2 hours, sunburn, pigmentation, decreased immunity, and an allergic reaction may occur.
Depending on the manifestations on the skin, there are:
- Phototraumatic reactions are when sun exposure causes burns on the body. They can occur either as a result of prolonged exposure to the sun or short-term exposure to UV radiation. Therefore, the baby’s skin should be protected with special photoprotective creams or by wearing closed clothing and always a hat.
- Phototoxic reactions are when severe redness, blisters, and blisters appear as a result of the action of photosensitizers, which may be present in foods, medications, and cosmetics.
- Photoallergic reactions are a non-standard reaction of the body to ultraviolet radiation. As a result, severe swelling and inflammation can occur, which can lead to death if assistance is not provided in a timely manner. In young children, this reaction develops in the first minutes of exposure to the sun.
Photos of various manifestations on the skin:
Types of allergies to ultraviolet light
Depending on what causes an allergy to ultraviolet radiation, the pathological condition is divided into two main types. This is a photodermatosis of endogenous origin, that is, caused by congenital pathologies, and photodermatitis of an exogenous nature, provoked by the action of photosensitizers.
Exogenous photodermatitis (exposure to photosensitizers)
Exogenous photodermatitis develops under the influence of provoking substances that enter the body or onto the human skin. This type of allergy often affects people who have recently undergone an aggressive peeling procedure, so beauty salons specifically stipulate the need to refrain from prolonged exposure to the sun for a while. Taking a number of medications can also cause a phototoxic reaction:
READ ALSO: 15 face masks for blackheads at home
- antihistamines;
- barbiturates;
- neuroleptics;
- NSAIDs (Aspirin, Ibuprofen);
- drugs for the treatment of cardiovascular pathologies;
- hormonal medications;
- medicines against diabetes;
- antibacterial agents (including antibiotics of the tetracycline group);
- preparations for the treatment of skin diseases.
Exogenous photodermatitis
Also, an allergic reaction of an exogenous type can result from exposure to various substances that can come into contact with the skin in everyday life. These include oils (bergamot, sandalwood, sea buckthorn, St. John's wort, rose), pollen, parsley and dill juice, eosin, retinols, phenol, musk and so on.
Endogenous photodermatosis (congenital pathologies)
Only an experienced, qualified specialist can diagnose and treat endogenous photodermatosis. Such pathologies are extremely rare and represent congenital mutations and diseases, sometimes they are of hereditary origin. Such diseases include:
- Bazin's light pox;
- sun prurigo;
- solar eczema;
- porphyria;
- xeroderma pigmentosa.
Causes of allergic reactions to the sun in children
Sun allergies in children are diagnosed in the summer after prolonged exposure to direct sunlight. Even artificial sunlight used to treat certain pathologies can harm the skin of young patients. Photodermatitis makes itself felt after 20-30 minutes of exposure to the sun.
It is not the ultraviolet rays themselves that cause a skin reaction, but allergens that accumulate in large quantities on the skin. It is the interaction of the sun with foreign components of the skin that causes hives. Allergens are:
- a history of another type of allergy (to food, pollen);
- taking antibacterial agents (primarily the tetracycline group);
- avitaminosis;
- hereditary hypersensitivity to the sun;
- helminthiases;
- metabolic disorders;
- eating food with food additives (sweeteners).
Reduced immunity in a baby increases the risk of allergies to sunlight. The body of such a child is not able to withstand aggressive environmental factors, which include the sun's rays.
Children with the following diseases are predisposed to photodermatitis:
Characteristic allergy symptoms
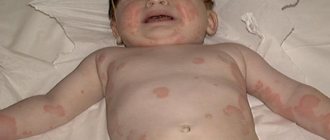
The symptoms of photodermatitis are very similar to the manifestations of any other allergic reactions, including to food. However, if almost immediately after exposure to ultraviolet light a small rash appears on the skin, and the lesions turn red, an allergy to the sun can be suspected.
In some cases, we will be talking about delayed manifestation of symptoms - then the first signs are noticeable some time after exposure to the sun (“delay” can be up to 12 hours). Characteristic signs of allergies are:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- heat;
- general malaise;
- peeling of the skin, burning sensation, itching (of varying intensity) in the affected areas;
- redness of areas of the skin directly exposed to ultraviolet radiation, the appearance of swelling in the affected areas.
Symptoms of hives almost always appear on exposed areas of the body that have been directly exposed to sunlight. In children, the area of the chest, shoulders, and arms is usually affected, and signs of allergies often appear on the face. On the legs, symptoms are detected much less frequently, since in this part there is a more pronounced subcutaneous fat layer. What the characteristic symptoms of sun allergy look like can be seen in the photo accompanying the article.
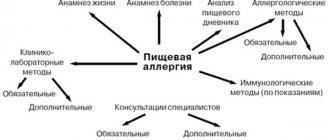
Diagnostic methods
It is impossible to establish an allergy to the sun in a laboratory way. Hypersensitivity of a child's skin to sunlight can only be determined by observation. In this case, parents need to find a relationship between the last contact with a light irritant and the appearance of an allergic reaction. The first symptoms are noticeable within a few hours after exposure to the sun.
In some clinical situations, a light test is used - a small area of the body is exposed to an ultraviolet ray. After the procedure, the condition of the skin is assessed for several days. The test takes place in several stages, in each of which the time of contact of ultraviolet light with the skin gradually increases.
Does the baby's age play a role in the occurrence of an allergic reaction?
Human skin contains special substances designed to counteract the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation. They are called chromophores. The concentration of chromophores depends on age - the younger the child, the fewer such compounds in his skin, which means the higher the likelihood of an allergic reaction to the sun.
READ ALSO: How to remove blackheads on the face at home in 1 day
Most often, urticaria appears in children under 3 years of age. Many children outgrow their ultraviolet allergy as the chromophores accumulate in the skin.
Causes of the disease.
Allergies often occur in infants and older children, since children's immunity is still quite weak.
The reasons for the skin's reaction to the sun's rays are a combination of internal and external factors.
External causes include cosmetic and local medicinal products that increase the body's sensitivity to the rays of the sun.
Antimicrobial and diuretic drugs also increase sensitivity to the sun.
Note: To avoid an allergic reaction, you must read the instructions before using various medications. If the side effect is a reaction to white ultraviolet light, then first of all, during a walk, it is necessary to hide the entire skin of the child from the sun's rays.
Pollen can also cause an allergic reaction. A mixture of a swimming pool and sunbathing can give such a picture.
When exposed to the sun, redness of the areas of the skin that were exposed to irradiation is detected (first degree), against the background of which tangible blisters with serous substance may form (second degree). The bubbles cause the child very severe pain. This chemical reaction usually occurs in the arms, legs and back. When exposed to huge concentrations, necrosis of the epidermis and dermis develops (third degree).
Allergy to the sun on the legs, due to the pronounced subcutaneous fat layer in children, often manifests itself as redness and itching.
Internal causes of sun allergies can be catalysts for digestive disorders, liver disease, and malfunctions of the immune system. Decreased immunity, hidden diseases, metabolic disorders in the body, lack of vitamins are allergy provocateurs. Therefore, comprehensive treatment of the whole organism is necessary.
In such situations, doctors prescribe a diet and liver cleansing to reduce reactions or completely eliminate them.
Principles of treatment in infants and children over 1 year of age
If you have urticaria, you will not only need to provide first aid - you will definitely need to consult with specialists who will not only help you get rid of the symptoms, but also identify and eliminate the cause of the allergy.
First aid
First aid should be provided when the child shows the first signs of an allergic reaction. If a rash appears on the baby’s body, redness occurs, he complains of general malaise and headache, or feels sick, then parents should take action immediately. Basic rules for providing first aid for ultraviolet allergies for children of any age:
- eliminate contact with the allergen (in this case, urgently move the child to a shaded place where direct sunlight does not penetrate);
- wet a cotton napkin in clean water (if possible, it is recommended to replace water with a decoction of calendula, chamomile or green tea), apply to the affected areas;
- Allergy to ultraviolet radiation is often accompanied by dehydration, which is especially dangerous for the youngest patients, so the child should drink a lot - it is recommended that older children be offered mineral water acidified with lemon juice;
- If an allergic reaction occurs in an infant, you should immediately seek medical help.
Antihistamines
Antihistamine medications can only be prescribed by a doctor. You cannot select a medicine yourself, based on advertising or recommendations from relatives and friends, especially when it comes to an infant. Before using antihistamines, you should consult not only your pediatrician, but also an allergist.
| A drug | Release form | Age restrictions |
| Suprastinex | Pills | From 6 years old |
| Drops | From 2 years | |
| Fenkarol for children | Pills | |
| Powder for preparing a drinking solution | ||
| Desloratadine | Pills | From 12 years old |
| Loratadine | Pills | From 2 years (children aged 2 years and older weighing less than 30 kg are recommended to take in syrup form) |
| Syrup | ||
| Astemizole | Pills | From 2 years |
| Suprastin | Pills | From 3 years |
| Water solution | Contraindicated in newborns |
Antihistamine drug Suprastin
Local preparations
Local medications help relieve swelling, relieve the child from itching, burning and other painful sensations. These are gels, creams or ointments that are applied directly to the damaged area of the skin and have an anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antipruritic and regenerating effect. The most popular topical agents include:
- Desitin – cream and ointment. It has a complex effect - antiseptic, adsorbent, anti-inflammatory, drying agent. Can be used in the treatment of children of any age.
- Wundehil ointment. The product, consisting of natural ingredients, has a tonic and regenerating effect. Has no age restrictions.
- Cream Gistan. A drug based on a synthetic glucocorticosteroid. Contraindicated for children under two years of age.
READ ALSO: How to get rid of blackheads, the best proven remedies
ethnoscience
An allergy to ultraviolet light is accompanied by very unpleasant and painful symptoms. After preliminary consultation with a specialist, it is permissible to supplement the prescribed course of therapy (including medication) with traditional medicine.
If you are allergic to the sun, traditional medicine advises drinking immunostimulating teas
The list of effective home recipes includes the following:
- Mix nettle, cocklebur herb, calamus root, dried or fresh. Pour 2 tbsp. mixture of herbs with a liter of boiling water, boil over medium heat for five minutes. Take a third of a glass twice a day before meals. The product relieves inflammation, cleanses the blood, and helps strengthen natural immunity.
- Grind the celery root in a blender or finely chop it with a ceramic knife. Squeeze out the juice. Use the resulting liquid to lubricate the affected areas of the skin.
- Grate fresh potatoes or cucumber. Apply the resulting paste to the affected areas for half an hour.
- Mix valerian root, St. John's wort, string, chamomile, sage and celandine. You need to take two tablespoons of each of the medicinal herbs. Pour 1.5 liters of boiling water, boil for 5 minutes. Leave for an hour. Add to bath before bathing.
Preventive measures
- Limit your baby's exposure to the heat, especially if the child is under 1 year old. You can go for a walk in the summer at any time, except during the daytime (from 11 to 16). During this period of time, ultraviolet rays are considered the most harmful.
- Use creams that protect against ultraviolet radiation. They should not contain dyes.
- Develop a child’s addiction to ultraviolet radiation, gradually increasing his contacts with it.
- Strengthen the child's immunity. To do this, you need to do daily exercises and introduce fermented milk products into your diet.
- In hot weather, cover the child’s torso with fabrics made from light natural materials.
An adequate attitude towards sun allergies in children is an important aspect of therapy. The duration of treatment and its outcome, as well as the likelihood of complications, depend on the tactics of the parents. It is important to detect the symptoms of the disease in time and seek help from a qualified specialist.
Summer is a hot time, during which the sun's rays irradiate our skin with ultraviolet radiation. During this period, sun allergies are common in children.
Prevention of allergies in children
Your child's summer vacation should be joyful, happy and carefree. Treating allergies is not easy and is also quite expensive.
These include the following tips:
- strengthen the immune system, do not neglect preventive examinations;
- eat a balanced diet, drink plenty of fluids in the heat;
- do not be in the sun without a hat;
- in summer use sunscreens (for example, sunscreen) (we recommend reading: which sunscreen is best for children?);
- after swimming, the skin on the body, arms and legs should be thoroughly dried and the sunscreen should be reapplied;
- limit walks with your baby at “dangerous” times (in the heat) - it’s better to go out for a walk in the morning and evening.
News MirTesen