0
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2017.08.22
404
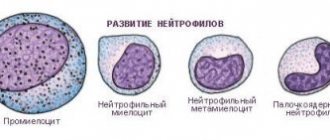
Leukocytes
Blood composition indicators in a child are of great importance, since the doctor can use them to judge the health or presence of diseases that need treatment. One of the main indicators is the level of leukocyte cells. It can increase or decrease under the influence of various factors.
What are leukocytes?
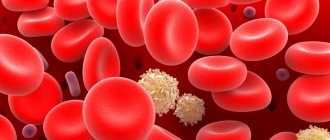
Leukocyte blood cells are white cells whose function is to destroy foreign bacteria, microbes or viruses. Active synthesis of these particles occurs when pathogenic microorganisms enter the body, causing a great risk to health. The number of leukocytes that are formed in the blood indicates the functioning of the immune defense. If there is a low level of leukocytes, then the child’s body’s vulnerability to disease increases. Reduced leukocytes in the blood of a child indicate the development of pathological processes that cause a decrease in the synthesis of protective cells.
Leukocytes
Normal level of leukocytes in the blood of a child
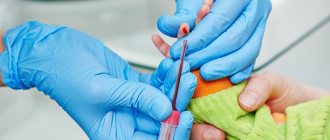
To find out the presence of the disease, the doctor sends the patient for a complete blood test (CBC). This is a convenient diagnostic method that allows you to identify the disease at the initial stage of development. The number of white cells in children is very different from the indicators that are normal for adults. Moreover, the number of leukocytes in an infant and a child of 5 or 15 years will be different.
In the first days after birth, the content of leukocytes in the blood of a newborn is increased due to the process of adaptation to life outside the womb, hormones that penetrate the placenta, and blood thickening. Next, the number of white cells decreases and the composition of the leukocyte formula changes. White blood cell norms by age are presented in the table:
| Child's age | Normal values (x109 units/l) |
| Newborns 1-5 days | 8-24,5 |
| 1 month | 6-19 |
| Six months | 5,5-17 |
| Year | 6-17,5 |
| 2 years | 6-17 |
| 4 years | 5,5-15,5 |
| 6 years | 5-14,5 |
| 8 years | 4,5-13,5 |
| 10 years | 4,5-13 |
| 16 years | 4 -13 |
OAC is performed if the patient has complaints, as well as during a preventive examination, before vaccination and surgery. For newborns, analysis is carried out monthly without fail. The data obtained during the study can be useful in prescribing therapy for diseases in an acute form and monitoring the dynamics of chronic diseases.
Normal indicators in children
The content of leukocyte cells is determined using a laboratory test of a blood sample from a finger. This process is planned, especially in children. For each childhood age period, its own norm of leukocytes is established. The difference in values is determined by changes associated with the child's development.
For example: immediately after birth in a newborn up to 2 years of age, the immune system is especially strong, since it needs to protect the helpless body from the penetration of infections and viruses. Therefore, the limits of leukocyte counts at this age in children are higher than in adults.
During a detailed blood test, the doctor takes into account the indicator of total leukocyte cells in the blood and their type as a percentage:
- The number of neutrophils is 60%.
- The number of lymphocytes is 45%.
- The number of monocytes is up to 8%.
- The number of eosinophils is up to 5%.
- The number of basophils is up to 0.99%.
If a child’s white blood cell count is low, this condition is called leukopenia.
Analysis in a child
Komarovsky’s opinion and advice on a general blood test
Dr. Komarovsky writes about how broad the concept of “blood test” is, because it is the main biological fluid of the body, and changes in it reflect the state of all organs and systems of the human body.
There are a large number of different blood tests that reflect different aspects of a person's health or illness.
A general blood test is the most common among them - this laboratory test allows you to see the most obvious pathological processes in the body.
Changes in the CBC will occur with any disease, which is why this analysis is carried out for all diseases, as well as in healthy children and adults during a regular medical examination.
A general blood test is completely safe for a baby at any age, starting from birth. The only unpleasant sensation is the puncture of a finger with a scarifier, but this action does not harm the little patient.
Even school-age children can be afraid of blood, so when taking a test they are allowed into the treatment room with their parents.
In order for the test result to be reliable, it is important for parents to know several rules for taking it and make sure that the child follows them. Often, even adults, and not just children, do not understand the meaning of these rules, so they commit violations in preparing for the analysis, so Dr. Komarovsky explains in detail what their meaning is.
- The test must be taken strictly on an empty stomach (12 hours after the last meal). That is why OAC laboratories work in the early morning hours, most often from 8 to 9 o'clock. You should not have breakfast before the test. This is due to the fact that food intake changes some blood characteristics, in particular ESR. As a result, the analysis data may give a false picture of the pathological process. In some laboratories, together with the OAC, they do a glucose test, and then eating food is strictly contraindicated.
- The day before the test, you need to limit physical activity - it can provoke hemolysis and the release of various biologically active substances into the blood, which increase its viscosity. For the same reason, immediately before the analysis you need to sit quietly for 10-15 minutes.
- If a child undergoes any procedures or takes medications, he needs to be tested before the manipulations - a side effect of many drugs is to change the laboratory characteristics of the blood.
- If a child needs to be tested several times, then this should be done at the same time - this will minimize the influence of extraneous factors. Another reason why the operating hours for treatment rooms look the way they do.
These rules apply to most laboratory tests, but sometimes other restrictions are added to them depending on what kind of analysis is to be taken.
Some experts, including Komarovsky, advise refraining from fatty foods 2-3 days before the analysis. Unfortunately, when the analysis is carried out at school or in kindergarten, parents are not always warned in advance, so it is not always possible to follow the last rule.
If a teenager is to be tested, parents should keep an eye on one more important parameter - they should not drink alcohol before the test. The same applies to adults who need to take a general blood test.
Causes of leukopenia
A low number of leukocyte cells in children's blood (less than 4 grams per liter) is a cause for greater concern than exceeding normal levels. Let's consider the reasons for the reduction of leukocytes.
The lack of white blood cells leads to the fact that the child’s body is left without protection from pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms.
Why do leukocytes need to be increased? The condition of leukopenia is dangerous, because it can lead to:
- The occurrence of sepsis.
- Too rapid spread of infection in the body.
- Inability to effectively cure the disease.
- Life-threatening.
Leukopenia can be moderate, uniform, and sometimes characterized by a decrease in specific forms of leukocytes (for example: only lymphocytes, only neutrophils or group 3 leukocytes decrease).
The main reason why leukocytes in the blood begins to decrease is a malfunction of the bone marrow, during which the required number of protective cells ceases to form. This condition occurs after:
- Radiation or chemical therapy.
- Intoxication of the body, especially derivatives of heavy metals.
- Excessive intake of antibiotic drugs and sulfonamides (if you stop using the drugs, the white blood cell count will normalize on its own after a while).
- Hereditary blood pathologies.
- Severe stress and shock.
- Experienced serious operations.
- The appearance of cancer cells.
There are other reasons for a decrease in white blood cell counts in children:
- Exhaustion of the child's body.
- Lack of building substances for cell growth and production.
- Wrong diet.
- Frequent fasting reduces the production of protective cells.
- Condition after a severe infectious disease (measles, influenza, herpes, etc.).
In such cases, it is necessary to take the necessary measures to restore the composition of the blood and protect the child’s body. To do this, provide a fortified diet rich in beneficial microelements.
Prevention
As such, there is no prevention of leukopenia in newborns. Measures to prevent the disease depend directly on its causes. Parents of a newborn should pay attention to the following points:
- exclude the possibility of using any medications in infants without a doctor’s prescription;
- regularly visit the local pediatrician with your child;
- do not neglect prescribed tests;
- a nursing mother should lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right;
- strengthen the baby's immunity;
- take a walk in the fresh air every day;
- prevent pathogenic bacteria and viruses from entering the child’s body;
- be attentive to the health of the baby.
the boy was born on July 6, 2014 by caesarean section at 38 weeks and 1 day. indications for cesarean: large fetus (3780), breech presentation and tilted head. I was admitted to the maternity hospital with contractions, my water broke, and after a couple of hours I had a Caesarean.
The child is clinically good, as doctors say, and is actively gaining weight! Today we went 5 days.
every day they take blood from our leg and every day they don’t like the white blood cells in the blood! they are demoted! They don’t tell me how much they have been reduced, they don’t say anything at all, except that “we’ll see the next analysis.” Today they were supposed to discharge me, but they came and said that my leukocytes were still low and they would count them manually. They are deciding whether to transfer to a hospital!
please tell me the reasons for low leukocytes in a newborn! Why haven’t they increased for 4 days already! I understand that without data it’s difficult to say anything, but at least general information, why could this be? I'll be exhausted until I wait for the next round! Why can we be admitted to the hospital?!
my blood is good, pregnancy without complications, all screenings are excellent!
Reasons for the downgrade
Let's look at the most popular reasons for a decrease in white blood cells.
Autoimmune diseases
This group includes diseases that “force” the immune system to perceive healthy cells in the body as hostile. Prominent representatives of the group:
- lupus;
- scleroderma;
- rheumatoid arthritis.
Lupus
Impaired functionality of the endocrine system
A reduced concentration of white cells is provoked by diabetes mellitus (congenital and acquired) and hypothyroidism. Also, leukopenia can be a consequence of improper functioning of the thymus gland (thymus).
Taking medications or toxic poisoning
Leukopenia may be a consequence of taking:
- antispasmodics (Analgina, Papaverine);
- sulfonamide drugs (Etazol and Sulfazin);
- antibiotics (Levomycetin);
- barbiturates;
- antiparkinsonian drugs;
- anti-tuberculosis drugs;
- NSAIDs.
Papaverine
Vitamin B deficiency
The development of vitamin deficiency in children is often accompanied by a decrease in immunity and a violation of the norm of leukocytes, erythrocytes and platelets. Ideally, children should get all their vitamins from food, but this is not always possible. To replenish vitamin B reserves, your baby should eat:
- nuts;
- green vegetables;
- greenery;
- beef;
- poultry meat.

Vitamin B
Other reasons
White blood cells may decrease due to:
- typhoid fever, malaria and influenza;
- oncological diseases;
- congenital diseases;
- HIV.
How does leukopenia manifest itself?
Leukopenia can be chronic, acute or recurrent. If the decrease in leukocyte particles occurs steadily, then the child’s lymph nodes become inflamed and increase in size. Children in this state become weak, lethargic, often restless, irritated, and feel pain in the head. However, there are no specific clinical symptoms by which leukopenia can be determined.

Symptoms
A reduced level of leukocytes manifests itself clinically when immunity declines against the background of an infectious disease. In this case, the symptoms of a low white blood cell count will be:
- Heat.
- Increased heart rate.
- Pain in the head.
- Hoarseness of voice.
- General weakness.
- The appearance of blood from the gums while brushing your teeth.
- Chills.
- Exhaustion.
If there are fewer leukocytes after a chemical therapy procedure, then the child:
- Hemorrhagic syndrome appears.
- He falls into a feverish state.
- The skin turns pale.
- The baby becomes weak and broken.
How to increase white blood cells?
Getting rid of leukopenia requires complex therapy, which consists of both drug treatments and folk remedies.
Treatment with medications
If there are few leukocytes in the blood, then drug therapy is aimed at increasing the production of these substances in the body. The doctor may prescribe medications such as: Leukogen, Pentoxyl or Methyluracil. These drugs help activate regenerative processes and restore immune function.
In addition, in the treatment of leukopenia, medications are used that are aimed at activating the bone marrow, due to which the process of production of leukocytes is enhanced. Among such drugs are Sargramostim, Filgrastim, Leograstim.
To enhance the body's immune function and improve health, biological supplements and other related medications are prescribed.
Attention! Special medications intended for enhanced production of leukocytes have no contraindications. They are used regardless of the form of leukopenia. But this does not mean that you can take any dose.
During drug treatment, patients need to undergo regular follow-up tests to understand whether the chosen methods are effective.
If a child's white blood cell count is below normal and symptoms of bacterial infectious diseases are observed, the doctor will prescribe antibacterial medications. Usually antibiotics are taken for no more than seven days. The doctor chooses a specific drug taking into account the child’s age and condition.
Leograstim
Lifestyle
In addition to the therapy prescribed by the doctor, parents should help the child overcome leukopenia. For this, a proper diet with a high content of fresh fruits and vegetables, natural protein, vitamins and healthy elements is recommended. It is advisable to exclude too fatty foods, and give sweets in doses. Milk-based products, nuts, and cereals are good for a child. It is not recommended to use a lot of salt, spices and herbs.

Proper nutrition
Traditional methods
Folk remedies will be an auxiliary way to raise the level of leukocytes, but not the main one. Therefore, any unconventional methods should be discussed with a doctor so as not to harm the child.
Effective recipes that increase white blood cells:
- Wormwood tea. To prepare, take dry wormwood - 30 grams, pour 0.5 cups of boiling water. Infuse the drink for three hours. Give children one small spoon before breakfast and after dinner. Yesterday's decoction should not be consumed; it is better to prepare fresh tea.
- Oat decoction. To prepare, take 40 grams of oats (unpeeled) and pour half a glass of boiling water. Boil the broth over low heat for three minutes. Then the drink should brew for a couple of hours. Children are given the healing liquid 1 teaspoon before meals three times a day.
- Rose hip tea. You will need one handful of berries and 200 ml of boiling water. Everything is mixed and sealed tightly. The drink must be infused for at least 12 hours. You can drink it instead of tea, adding honey.

Self-medication is strictly prohibited; remember that a child can seriously suffer from an incorrect diagnosis and improper treatment. Only a competent specialist has the right to prescribe drugs or other methods of therapy to increase white blood cells.
MariaOk
Hello! While you are waiting for the doctors' response, read the article
“Leukocytes are the formed elements of blood that represent the immune system”
“Leukopenia (syn. leukocytopenia) is a decrease in the level of leukocytes below normal. Leukocytosis occurs during acute infections, especially bacterial infections, during purulent inflammatory processes, during oxygen deficiency and dozens of other causes. Leukopenia is highly likely with viral infections, with severe infectious and toxic conditions that are accompanied by bone marrow suppression, with some bacterial infections, with radiation sickness, with... again, dozens of different reasons. It is clear that information about the number of leukocytes can draw attention to the severity situations, characterize the state of immunity, and bring some clarity to the diagnostic process. But to understand the essence of what is happening, to be confident in the diagnosis, this, in most cases, is not enough.”
Ask your doctor to explain the situation to you in more detail. I remember that in the maternity hospital, every morning the neonatologist told each mother about the condition of her child, what procedures and tests were being performed on him, and explained the results. I hope that everything will return to normal for you and that everything will be fine!