The central nervous system continues its development until the end of puberty. The ventricles also gradually increase in size, that is, their size is proportional to the growth of the skull. Asymmetry of the cerebral hemispheres is considered normal, since this concept characterizes the asymmetrical performance of higher mental functions of the two parts of the central nervous system. But for the ventricular system, significant asymmetry is a sign of pathology.
Ventriculomegaly: Ventricular size matters
In the brain of a person who has not yet been born or has already been born, small or adult, there are four cavities that communicate with each other, which are filled with cerebrospinal fluid. They are called cerebral ventricles.
Each of them should ideally correspond to certain dimensions at which the influx or outflow of fluid (CSF) can occur without problems. If there is an increase in the ventricles of the brain, then the circulation process is disrupted. This can lead to various pathologies of the peripheral and central nervous system.
Important! The most common diagnoses for similar symptoms are hydrocephalus and, although these are extreme degrees of complications with ventriculomegaly.
Cases where enlargement of the ventricles of the brain, with timely diagnosis and proper treatment, does not affect the quality of health of a small patient, are quite common.
Normal size of the ventricles of the brain in newborns
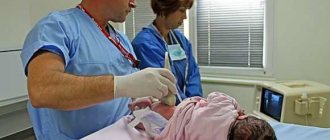
In the first days of a newborn’s life, various tests are taken, vaccinations are given, and examinations are also carried out in order to obtain complete information about the general condition of the child. One of the main procedures is ultrasound of the brain.
It allows you to find out not only about any abnormalities and the degree of development of the brain, but also to check the overall dimensions of the ventricles of the brain in a newborn, the norm of which is a certain value.
Examination of a baby is an important stage in his life, since disorders and pathologies that are not immediately identified can negatively affect the future life and development of the baby.
What to do if suddenly an ultrasound showed an enlargement of the ventricles of the brain in a newborn? If newborns with enlarged ventricles of the brain are in normal condition and do not have any serious neuropathological abnormalities, then a specialist can schedule regular visits to a neurologist to monitor and monitor the condition. But if the deviations from the norm are quite serious, and the neuropathological symptoms are pronounced, then the child needs special treatment, which is prescribed by a neurologist.
Causes of deviations in the development of the ventricles of the brain
At the moment, many factors are known that influence the appearance of pathologies of the ventricles of the brain in children. All of them can be divided into two categories: acquired and congenital. Acquired causes include those reasons that could arise during the pregnancy of the child’s mother:
- Infectious diseases that a woman suffers from during pregnancy.
- Infections and sepsis inside the womb.
- Penetration of foreign bodies into the brain.
- Chronic diseases of the mother that affect the normal course of pregnancy.
- Delivery ahead of schedule.
- Hypoxia of the fetus inside the womb (insufficient or, conversely, increased blood supply to the placenta).
- Abnormal duration of the dry period.
- Injury to the baby during childbirth (suffocation by the umbilical cord or deformation of the skull).
- Stormy birth.
Congenital causes include a genetic predisposition to enlarged ventricles; abnormalities occurring in chromosomes, as well as various neoplasms (cysts, malignant or benign tumors, hematomas). Along with the listed reasons, characteristic changes in the size of the ventricles of the brain can be provoked by traumatic brain injury, cerebral hemorrhage, or stroke.
Anatomy of the ventricles of the brain
The human brain is a very complex structure, in which each substructure and each component part is responsible for fulfilling certain goals.
In humans, there is a special structure in the brain that contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The purpose of this structure is the circulation and production of cerebrospinal fluid. Every child and adult has 3 types of brain ventricles, and their total number is 4.
They are connected to each other through channels and holes, valves. So, the ventricles are distinguished:
- Lateral.
- Third.
- Fourth.
The lateral ventricles are located symmetrically relative to each other. The left is designated first, the right is designated second, they are connected to the third. The third ventricle is the anterior one and houses the centers of the autonomic nervous system.
The fourth is the posterior one, it is shaped like a pyramid and is connected to the spinal cord.
Changes in the size of the ventricles entail a disorder in the production and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, which can lead to an increase in the volume of fluid in the spinal cord and disruption of the working condition of a vital organ.
Enlarged ventricles: manifestation
As is known, one of the functions of the ventricles is the secretion of cerebrospinal fluid into the cavity between the meninges and spinal membranes (subarachnoid space). Therefore, disturbances in the secretion and outflow of fluid lead to an increase in the volume of the ventricles.
But not every increase and change in size is considered a pathology. If both lateral ventricles become symmetrically larger, then there is no need to worry. If the increase occurs asymmetrically, that is, the horn of one of the lateral ventricles increases, but the horn of the other does not, then pathological development is detected.
Enlargement of the head ventricles is called ventriculomegaly. It exists in 3 types:
- Lateral (dilatation of the right or left ventricles, enlargement of the posterior ventricle).
- Cerebellar (the size of the cerebellum and medulla oblongata changes).
- Pathological release of cerebrospinal fluid in the frontal region.
There are 3 degrees of the disease:
Sometimes the disease is accompanied by disruption of the central nervous system. Enlargement of the ventricles in large children with a non-standard skull shape is considered normal.
Interpretation of the appearance of dilated ventricles
Deviation from the normal size of the ventricles does not always indicate the occurrence of pathological processes. Most often, these changes are a consequence of the anthropological characteristics of the baby. Almost all newborns up to one year of age have ventriculomegaly. It appears as a result of impaired fluid outflow or excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
According to statistics, enlargement of the lateral ventricles is more common in children born prematurely. In them, unlike babies born at the right time, the sizes of the first and second cavities are more enlarged. If there is a suspicion of asymmetry, measurements, diagnostics and qualitative characteristics should be determined.
Symptoms of venticulomegaly
With venticulomegaly, due to a large amount of cerebrospinal fluid, the pressure inside the baby’s skull rises; swelling of the cortex, gray matter, and tissues appears. The pressure disrupts the blood supply to the brain, and deterioration and disruption of the central nervous system are also observed.
The following symptoms are observed with enlarged ventricles:
- Increased muscle activity.
- Deterioration of vision (defocus, squint, downcast gaze).
- Trembling of limbs.
- Strange gait (movement on tiptoes).
- Inactive reflexive manifestations.
- Lethargic, apathetic behavior.
- Increased moodiness and irritability.
- Insomnia, sleepwalking.
- Lack of appetite.
An obvious symptom of venticulomegaly is regurgitation and vomiting, the amount of which exceeds the norm. This occurs due to irritation of the vomiting center in the fourth ventricle, which is located at the bottom of the diamond-shaped fossa.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnostics are carried out to clarify the diagnosis. A doctor can notice a chronic form of venticulomegaly as early as three months of age using an ultrasound. The examination includes the following procedures:
- Examination by an ophthalmologist (this will reveal swelling of the eyes and hydrocephalus).
- Magnetic resonance imaging (the MRI procedure helps monitor the growth of the ventricles after the fusion of the cranial bone. To carry out the examination, which takes from 20 to 40 minutes, the baby is put to sleep with the help of drugs).
- CT scan. In this case, medicated sleep is not required because the procedure does not take much time. So CT is the best option for children who cannot tolerate anesthesia.
Ultrasound is prescribed for children born after a pregnancy during which there were complications. It is done in the first year of life, and if there are no neurological abnormalities, then it is repeated after three months.
Indicators of normal sizes
Each ventricle has certain sizes that are considered normal. Deviation from them is a pathology. So, the normal depth of the third ventricle is no more than 5 mm, the fourth ventricle is no more than 4 mm. When taking side measurements, the following values are taken into account:
- Side cavities - depth should not exceed 4 mm.
- Horns in the occipital part – 10 – 15 mm.
- The horns in the front part are 2–4 mm.
The depth of a large tank is no more than 3–6 mm. All cavities and structures of the brain must have a gradual development, consistent and linearly dependent on the size of the skull.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment can only be prescribed by a neurosurgeon or neurologist. Drug therapy is usually used. Not all episodes require treatment, but it is used in cases of pronounced neuropathological abnormalities. The main medications are:
- Diuretics are used to reduce cerebral edema, normalize and accelerate fluid excretion.
- Potassium-containing preparations compensate for the deficiency of the required amount of potassium while accelerating the process of urination.
- Vitamin complexes are used to replenish lost vitamins, as well as to restore the patient’s body.
- Nootropics improve blood supply to the brain, circulation in microtissues and vascular elasticity.
- Sedatives have a calming effect and reduce neurological signs such as tearfulness, moodiness, and irritability.
If the cause of deviations in the size of the brain cavities is mechanical damage to the head, then surgical intervention is required.
Source: https://glmozg.ru/stroenie/razmery-zheludochkov-mozga-u-novorozhdennyh.html
Why do the cerebral ventricles enlarge?
The reasons for the enlargement of the ventricles of the brain can be either hidden, when the diagnosis of ventriculomegaly is made to the fetus without obvious deviations from the norm during the pregnancy of a healthy mother, or obvious. The latter include:
- genetic abnormalities during complicated pregnancies, which are most often observed in expectant mothers aged 35 years and older;
- heredity;
- infections that were transmitted from mother to unborn child during its intrauterine development (including toxoplasma and cytomegaloviruses);
- injuries that the expectant mother and her child could receive during pregnancy;
- internal bleeding in the fetus caused by thinning of the vascular walls;
- in an unborn child;
- improper formation of brain convolutions and other anomalies in the development of the central nervous system.
Enlargement of the cerebral ventricles can be either an independent, isolated disease or one of the symptoms of a third-party pathology.
How to detect enlarged cerebral ventricles?
Enlargement of the ventricles of the brain in newborns is detected during the second planned ultrasound, which is performed approximately in the fifth or sixth month of pregnancy. By this time, the child’s nervous system is already practically formed. But one ultrasound report is not enough, so for an accurate diagnosis, the expectant mother, after consultation with a geneticist, needs to undergo several more procedures:
- repeat ultrasound a few weeks after the previous one to assess the dynamics of possible pathology in the fetus;
- take a blood test for spectral karyotyping, which will allow you to assess the degree of possible damage to the chromosomes of future parents;
- transverse scan of the fetal head.
Only after a comprehensive diagnosis can we talk about any type of ventriculomegaly. Recently, in difficult cases, it has been suggested to do an MRI of the fetus.
Main types of ventriculomegaly
Normally, the size of the cerebral ventricles should not be more than 10 mm. This indicator is considered borderline. Its excess is a cause for concern for the health of the unborn baby. However, not all cases of ventriculomegaly lead to irreversible consequences in the development of the nervous system. It is no coincidence that this disease is divided into three types:
- mild, in which the enlargement of the cerebral ventricles varies between 10-12 mm;
- medium, if the size of the pathology is up to 15 mm;
- severe if the enlargement of the lateral ventricles of the brain in the fetus exceeds 15 mm.
Depending on the type of disease, a treatment strategy is developed.
Treatment of ventriculomegaly
With ventriculomegaly, treatment performs two tasks: firstly, it is necessary to eliminate not the symptom itself in the form of enlarged ventricles of the brain, but the cause that caused such a pathology, and secondly, it is necessary to neutralize as much as possible the consequences of the disease for human development.
If the doctor is dealing with a mild type of disease in the fetus, if an increase in the ventricles of the brain in newborns is recorded in an isolated form, which is not associated with underlying chromosomal abnormalities, then he prescribes drug therapy designed to stimulate the development of the nervous system. It is possible to use diuretic drugs against, drugs that prevent oxygen deficiency in the body, and vitamins. Massage and therapeutic exercises can also help.
In severe cases of ventriculomegaly with changes in the brain and genetic pathologies, termination of pregnancy is not excluded. That is why it is so important to detect enlargement of the ventricles of the brain in a child or fetus as early as possible in order to prevent the pathology from progressing.
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain in children and adults
Quite often, parents of infants are faced with a diagnosis of asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain (lateroventriculoasymmetry). This causes them to panic, but in most cases everything is not as scary as it seems. In adults, this phenomenon is also sometimes diagnosed - but much less frequently.
Ventricles of the brain: types, structure, functions
Ventricles are containers in the brain that synthesize and also accumulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). There are four of them in total.
The lateral ones are located to the left (first) and to the right (second) of the midline. They have special holes through which communication occurs with the third and fourth. Characterized by larger sizes than the other two, they resemble the letter S. They are symmetrical in relation to each other.
The cerebrospinal fluid accumulated in the ventricles is transported to the subarachnoid space (the area between the brain and the spinal cord). Next, new fluid is produced. This is a normal physiological process.
Characteristics of the anomaly
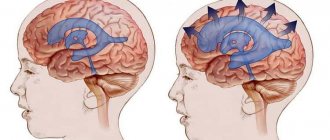
Sometimes the system crashes. The removal of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles that produce it becomes difficult; excess fluid accumulates in them. The lateral ventricles of the brain begin to enlarge. This phenomenon is commonly called hydrocephalus.
The increase itself is precisely the asymmetry. Sometimes the volumes change for only one of them, and sometimes for both. But their symmetry in relation to each other is always violated.
This condition is not considered a pathology. But it can be caused by various diseases. Often this discrepancy in size is an individual feature. If it is small and does not manifest itself in any way, there is nothing to worry about. In most cases, abnormal development of the ventricles of the brain, diagnosed in newborns, goes away on its own over time.
Reasons for asymmetry
Most often, the deviation is detected in infants. Moreover, the overwhelming majority of cases occur in premature babies. And the more pronounced the asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain in newborns is, the earlier the child is born. This is due to the baby’s head circumference being too small and is not considered a pathology.
Other reasons for enlarged cerebral ventricles in newborns include:
- Hypoxia during intrauterine development.
- Infections that penetrate the placenta.
- Injuries during childbirth.
As for adults, similar brain problems can be caused by:
- New growths in the head.
- Infectious diseases (encephalitis, meningitis, etc.).
- Strokes.
- Thrombosis of cerebral vessels.
- Head injuries.
If an anomaly diagnosed in childhood is often a temporary physiological deviation, then in adults everything is different. Deviation from the norm is usually the result of some serious pathology associated with the brain.
Symptoms and features of asymmetry in children and adults
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain in adults does not manifest itself if it is insignificant. In severe forms, people complain of:
- dizziness,
- Headache.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Increased fatigue.
- Feeling of fullness in the head.
- Nausea.
In children, a slight increase in the ventricles of the brain also often does not make itself felt. In cases where the violation is significant, the child may:
- Cry a lot.
- Refuse food.
- Throw back your head.
- Burp frequently.
- It's bad to gain weight.
If, as a result of the obstructed outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, a lot of the latter has accumulated, the baby’s head becomes enlarged. And this can already be seen with the naked eye. In such cases, cerebrospinal fluid retention leads to hydrocephalus and requires immediate medical intervention.
Diagnostic measures
It is quite difficult to understand whether there is asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain when it is not particularly pronounced. A visual examination by a therapist will not give results here. Therefore, if you suspect a problem, do:
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
- Neurosonogram.
- Lumbar puncture (in rare cases).
Another common diagnostic method is fundus examination. If hemorrhages, swelling, spasms, etc. are observed, problems with the lateral ventricles are possible. Infant head growth should be assessed monthly.
Treatment of asymmetry
If there are no clinical manifestations of enlarged cerebral ventricles, treatment is usually not carried out. Doctors practice watchful waiting while monitoring the patient’s condition. In those cases where symptoms are present, asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain requires active medical intervention.
Conservative therapy involves taking sedatives and diuretics. Nootropics are also used that activate the cells of the ventricles of the brain.
The development of hydrocephalus often becomes a reason for surgical intervention. A large accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles is very dangerous.
Asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain in adults requires treatment depending on the causes of its occurrence. If growth is caused by a tumor, it is removed. In cases where the cause is infection, a course of antibiotics and antiviral drugs is prescribed.
The process of combating asymmetry is long and difficult. But if there are indications, treatment is necessary. Otherwise, complications cannot be avoided.
Possible consequences
The consequences of a slight enlargement of the ventricles of the brain in infants can be a slight developmental delay. Usually, over time, the baby catches up with everything. In more complex situations, asymmetry threatens cerebral palsy, severe mental disorders, growth of the skull to enormous sizes, etc.
In adults, the lack of treatment for diseases that provoke changes in the volume of the ventricles means the progression of these pathologies. They often pose a threat to life.
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain is sometimes completely harmless and goes away on its own, but the opposite situations are also common. Most often, asymmetry is diagnosed in newborns (especially premature babies). In adults, it usually results from other pathologies. In any case, the anomaly requires the help of specialists. You can’t let everything take its course.
bolitgolova.info
Why is ventriculomegaly dangerous?
Down and Edwards syndromes, cerebral palsy, pathologies in the development of the brain and heart, and fetal death are the most severe consequences of the disease. But they are possible only when the cerebral ventricles are enlarged by more than 15 mm in combination with other pathologies and chromosomal abnormalities. But in most cases, if the problem in its isolated form is detected early and treated correctly, it does not affect the child’s development.
Enlargement of the ventricles of the brain in adults is also diagnosed quite often. But it is not considered dangerous and does not affect the normal life of an already formed person. Timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment. Therefore, pregnant women need to carefully undergo all examinations in order to identify the problem at its initial stage and ensure a healthy future for their baby.
Dilatation of the lateral ventricles of the brain - is asymmetry dangerous?
There are a number of anatomical features of the human brain. In some cases, some nuances of its structure that differ from the norm are considered physiological and do not require treatment.
However, certain deviations from the norm can cause the development of neurological pathologies. One such condition is asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain. This disease may not cause clinical symptoms, but in some cases it indicates the presence of a number of diseases.
What are the ventricles of the brain, their role
The ventricles of the brain are strips of tissue necessary for the deposition of cerebrospinal fluid. External and internal factors can lead to their increase in volume. The lateral ventricles are the largest. These formations are involved in the formation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Asymmetry is a condition in which one or both cavities are enlarged to varying degrees.
Types of ventricles:
- Lateral. The ventricles are the most voluminous, and they contain cerebrospinal fluid. They connect to the third ventricle via the interventricular foramina.
- Third. Located between the visual tuberosities. Its walls are filled with gray matter.
- Fourth. Located between the cerebellum and medulla oblongata.
Causes of dilatation
Enlargement or dilatation of the lateral ventricles of the brain occurs due to increased production of cerebrospinal fluid. This leads to the fact that it cannot be excreted normally.
This, in turn, leads to disruption of the flow of cerebrospinal fluid. This disease most often occurs in premature babies, but is observed in people of any age.
What causes the disorder in newborns?
This is how dilatation of the lateral ventricles looks schematically
Dilatation of the lateral ventricles of the brain in infants is often a sign of hydrocephalus, and can also be caused by a number of other reasons.
In newborns, asymmetry is caused by trauma or space-occupying lesions in the brain. Regardless of the possible cause, urgent consultation with a neurosurgeon is required.
Mild asymmetry may be a congenital disorder that does not cause symptoms. In this case, only constant monitoring is required so that the difference between the ventricles does not change.
The main causes of dilatation include:
- viral and other diseases of a woman during pregnancy;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- premature birth;
- birth injuries;
- malformations of the central nervous system.
Ventricular asymmetry can also result from hemorrhage. This pathology occurs due to compression of one of the ventricles by an additional volume of blood. Due to hemorrhage, the ventricles of the brain in an infant may be enlarged for the following reasons:
- various maternal diseases, for example, type I diabetes or heart defects;
- intrauterine infections;
- a long time between the water breaking and the baby being born.
The most common cause of dilatation is hypoxia. Other causes account for less than 1% of cases. It is hypoxia that leads to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid, which, in turn, increases intracranial pressure. This leads to expansion of the cavity of the lateral ventricles.
Risk zone for adult patients
A change in the size of the lateral ventricles leads to disruption of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain in adults occurs for the following reasons:
Provoking diseases
The main disease causing this pathology is hydrocephalus. It can interfere with the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. This leads to its accumulation in the lateral ventricles.
Excessive formation of cerebrospinal fluid is also observed with serious lesions of the central nervous system. Poor circulation is also associated with the formation of cysts, tumors and other neoplasms.
A common cause of hydrocephalus is a defect of the Sylvian aqueduct. If this defect was discovered during the prenatal period, termination of pregnancy is recommended. At the birth of a child, complex systematic treatment will be required.
Another cause is aneurysm of the vein of Galev and Arnold-Chiari syndrome. However, in children, the disease can be caused by rickets or due to the specific structure of the skull, so observation by a specialist is important if there is a predisposition to the disease.
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disorder
In adults, ventricular asymmetry rarely causes symptoms. However, in some cases, this anomaly can cause the following symptoms:
In addition to these symptoms, the picture of the disease can be supplemented by symptoms of diseases that caused ventricular asymmetry.
Such symptoms include cerebellar disorders, paresis, cognitive impairment or sensory disorders.
In infants, symptoms depend on the severity of the pathology. In addition to general discomfort, symptoms such as throwing back the head, regurgitation, increased head size and others may occur.
Symptoms of the pathology also include strabismus, refusal to breastfeed, frequent crying, anxiety, tremors, and decreased muscle tone.
However, quite often the pathology does not cause characteristic symptoms and can only be detected after an ultrasound scan.
Health care
Dilatation of the lateral ventricles of the brain itself does not require treatment. It is prescribed only in the presence of symptoms characteristic of the pathology. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the disease that is causing the dilatation.
The following drugs are used to treat ventricular asymmetry:
- diuretics;
- nootropic substances;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- vasoactive drugs;
- neuroprotectors
- sedatives;
- if the disease is caused by infections, antibacterial agents are prescribed.
If the pathology is caused by a cyst or tumor, their removal is required. If the patient's condition quickly deteriorates, an operation is performed to form a new connection of the ventricular system, which will bypass the anomaly.
Most often, ventricular dilatation occurs in infants. In the absence of timely and competent therapy, dilatation may persist and even worsen. With mild dilatation and the absence of obvious symptoms, the condition does not require special treatment. All that is needed is constant monitoring of the size of the asymmetry, as well as the general condition of the child.
If the disease is caused by injury, intrauterine development disorder, infection or tumor, constant monitoring of the patient, treatment of symptoms, and, if possible, elimination of the causes of the pathology are required.
The child is treated by a neurologist together with a neurosurgeon. To minimize the risk of complications, a child with this diagnosis should be constantly monitored by doctors. Most often, diuretics are prescribed for treatment, which promote the production of cerebrospinal fluid, which puts pressure on the lateral ventricles.
Additionally, it requires taking medications to improve blood supply to the brain, and sedatives are prescribed.
Massage, therapeutic exercises and other methods of physiotherapy are required. Infants with this diagnosis are observed on an outpatient basis. Treatment of the pathology may take several months.
Older children are treated depending on the cause of the pathology. Antimicrobial drugs are prescribed if the cause of the asymmetry is a brain infection. In case of tumors, cysts and other formations, surgery is prescribed.
Mild pathology most often does not cause any symptoms. In rare cases, a slight delay in the motor sphere may occur, but this also goes away completely over time. A severe form of the pathology can lead to cerebral palsy as a result of high intracranial pressure.
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain is not the most dangerous, but it requires attention pathology that occurs in people of any age.
If this problem is detected, you should visit an experienced specialist who will prescribe the appropriate tests to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment consists of eliminating the cause of dilatation, as well as reducing intracranial pressure.