In the life of every woman, sooner or later there comes such an amazing period as pregnancy. At this moment, the expectant mother needs to take care not only of her own health, but also of the baby. The female body activates all mechanisms designed to preserve the life born in the womb, so any pathological process can lead to irreversible consequences. Standard tests, which are routinely prescribed by the attending physician, help to avoid unwanted failures and deviations in the body’s functioning. One of these important examinations is a blood sugar test during pregnancy.
Why do expectant mothers need to monitor their glucose levels?
Pregnant women often begin to experience various chronic diseases that may simply not have made themselves felt before conception. The period during which a woman is pregnant is a contributing factor to the development of diabetes in some cases. That is why frequent blood tests make it possible to identify unwanted abnormalities in the female body and promptly respond to elevated blood sugar during pregnancy.
The risk of developing diabetes is higher in pregnant women who:
- We were able to conceive a child for the first time after 30 years;
- Are overweight;
- Suffer from various pathologies in the body;
- They have a hereditary predisposition;
- In a previous pregnancy, gestational diabetes mellitus was missed. A clear sign of this phenomenon is children born large.
Diabetes symptoms
If a pregnant woman has high blood sugar, this may not be noticed; the disease often occurs in a mild form. This is why it is important to systematically test for sugar during pregnancy. And if a specialist discovers that sugar is elevated, he will prescribe an additional test in the form of a test for susceptibility (tolerance) to glucose. But in most cases, obstetricians-gynecologists who monitor pregnant women do not wait for any deviations and prescribe a detailed analysis at a certain period.
With normal levels, blood sugar will be at the level of 3.3-5.5 mmol/l, but even if such a level is 5.4 during pregnancy, this will be a reason for a repeat test. With impaired sensitivity to glucose, the levels sometimes reach a level of 7.1 mmol/l, but we can talk about pathological problems when the sugar level is 7.1 or higher.
A blood sugar test during pregnancy is also performed in another way. To do this, a test for glycated hemoglobin is performed. This test shows glucose for 7-10 days, and if the sugar level was exceeded during this period, then the test will definitely show this.
Symptoms of diabetes that should alert a pregnant woman may include:
- hunger, constantly present;
- frequent and even uncontrollable urination;
- regularly tormenting thirst;
- vision problems.
But such symptoms do not always indicate that there is an increase in blood sugar during pregnancy. Usually, during an interesting situation, all these symptoms accompany, and they are quite natural.
The first symptoms of diabetes in pregnant women
The expectant mother needs to donate blood to determine sugar and not wait for a scheduled test if the following symptoms appear:
- The number of urinations per day has increased.
- Appetite increases and weight gain occurs quickly.
- There was a feeling of dryness in the mouth.
- I am tormented by a constant feeling of thirst.
- An increase in blood pressure is observed.
- The woman feels weak.
The signs of diabetes listed above may indicate the onset of the disease. They are not contraindications for childbirth, but require a complete change in the pregnant woman’s lifestyle and constant monitoring by an endocrinologist.
Causes of increased glucose in pregnant women
Carrying a baby puts additional stress on an organ such as the pancreas, so high sugar levels are not a rare occurrence in expectant mothers. If insufficient insulin is produced, blood glucose levels increase.
Hormones that are activated during pregnancy act as insulin antagonists. They promote the entry of glucose into the blood, which there is not enough insulin to neutralize. This condition is called “gestational diabetes” in medicine. The disease most often recedes almost immediately after the birth of the baby, and the sugar level returns to normal values. Despite this, women are advised to monitor their blood glucose levels after pregnancy.
Why are glucose levels rising?
Under normal conditions, sugar levels are regulated by the hormone insulin, which is continuously produced by the pancreas. Under its influence, glucose that came with food gradually passes into the cells of the body, performing its function there. This reduces blood sugar levels. What happens during pregnancy and why does this established mechanism fail?
Hormones that allow you to bear a child are insulin antagonists. High blood sugar during pregnancy is due to the fact that the pancreas simply cannot cope with its work under such conditions. Pregnancy hormones activate the release of glucose into the blood, and there is not enough insulin, which can bind excess sugar. As a result, the so-called diabetes of pregnant women develops, which is dangerous due to its unpredictable consequences.
When is pregnant women's blood sugar checked?
When a pregnant woman registers at the antenatal clinic, she is given directions for basic tests, which make it possible to assess the condition of the expectant mother’s body. The list of tests always includes a blood and urine test for glucose levels.
After completion of the formation of the fetus in the womb, the study must be repeated. Typically, if the glucose level is normal at the beginning of pregnancy, the next sugar control is carried out between 24 and 28 weeks. Detection of an increased indicator at this time requires repeated testing to confirm or refute the presence of diabetes. This is explained by the fact that the detected glucose level is higher than normal may simply be a consequence of the abuse of high-calorie and sweet foods.
Elevated glucose levels are not a harmless signal from the body. It indicates an advanced complex of pathological mechanisms that can significantly worsen the condition of the pregnant woman. Hyperglycemia negatively affects the development of the fetus and increases the likelihood of a baby being born with manifestations of diabetic disorders.
Causes of high blood sugar during pregnancy
In order to understand the reasons for the increase in blood sugar during pregnancy, it is necessary to turn to our physiology. The level of sugar in our blood (both men and women) is maintained thanks to the hormone insulin. The hormone insulin in our body is produced by the pancreas.
Glucose is produced from food that enters our gastrointestinal tract and is naturally digested there. Insulin suppresses excess blood glucose levels, as a result of which our health remains stable and does not deteriorate due to excess blood sugar.
During pregnancy, a woman’s body’s functioning is completely restructured. In particular, the placenta, which provides life support to the fetus, produces a number of hormones that, on the contrary, increase the level of glucose in the blood. This leads to increased stress on the pancreas. And sometimes this organ can malfunction. Only one thing follows - the level of glucose in the blood begins to significantly exceed the norm.
So, the reason for the increase in blood sugar levels in a pregnant woman is the production of hormones by the placenta, which lead to an increase in sugar and a malfunction of the pancreas.
The effect of excess glucose on the body of a pregnant woman and the fetus
Isolated cases of increased sugar levels indicate low sensitivity of the cells of the expectant mother’s body to insulin. If this condition is observed constantly, then we are talking about developed diabetes mellitus. The nature of pregnancy in diabetes is complicated by the fact that the placenta is not fully supplied with nutrients and can age earlier than expected. Glucose damages the walls of blood vessels, the ovaries and the placenta. As a result, there may be a lack of estrogen.
The danger of excess glucose for the expectant mother:
- There is a high risk of miscarriage.
- Development of pyelonephritis.
- The risk of premature birth increases.
- Preeclampsia may appear. In this condition, a woman experiences swelling of the extremities, polyhydramnios, and high blood pressure.
- Rapid weight gain is noticeable.
- The likelihood of replacing a natural birth with a caesarean section.
- Complications in the postpartum period from the urinary system and kidneys.
The danger of excess glucose for the fetus:
- The birth of a large baby.
- The baby is lagging behind in physical development.
- The occurrence of respiratory disorders, which are a lack of the necessary substance for the full opening of the lungs.
- Newborn jaundice is observed.
- The child may be born with neurological disorders and impairments.
- The baby experiences low sugar levels in the very first days.
The listed complications can be avoided if you keep blood glucose within normal limits.
The effect of high blood sugar on pregnancy
This phenomenon occurs when carrying a baby, because poor tissue sensitivity to insulin occurs. But diabetes mellitus can also precede pregnancy. Be that as it may, high sugar levels pose a danger to the expectant mother and her child, because excessive glucose concentration increases the risk of miscarriage, gestosis, pyelonephritis, and complications during childbirth (there may be a need to carry them out by cesarean section). All these risks depend on the adequacy of diabetes treatment.
Pregnant women have their own standards for carbohydrate metabolism. Thus, fasting blood sugar should not exceed 5.1 mmol/l. If it is above 7.0 mmol/l, then a diagnosis of “manifest diabetes” is made. It means that after the birth of the baby, the woman’s disease will remain, and treatment will need to be continued.
When the fasting blood sugar level of the expectant mother is in the range from 5.1 mmol/l to 7.0 mmol/l, a diagnosis of “gestational diabetes mellitus” is made. In such a situation, one can hope for normalization of carbohydrate metabolism after childbirth.
If we rely on medical statistics, then in diabetes mellitus spontaneous abortions occur in every third pregnancy. And the reason for this is premature aging of the placenta. After all, its blood vessels are damaged due to excess glucose in the blood. As a result of this negative phenomenon, the full supply of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus ceases.
More on the topic
What should be the normal blood sugar level for pregnant women?
Blood sugar during pregnancy: high and low levels
Sugar in urine during pregnancy
Gestational diabetes mellitus during pregnancy
Diabetes and pregnancy
The negative tendency of the influence of diabetes mellitus is also manifested in the risk of developing late toxicosis. This occurs after 20-22 weeks of pregnancy in half of pregnant women. Late toxicosis is usually associated with low estrogen levels. Since sugar also damages the ovaries, they cannot provide the female body with estrogen.
Toxicosis in such cases is manifested by obvious or hidden edema, weight gain, the appearance of protein in the urine, and increased blood pressure. Also, women with high glucose levels may develop polyhydramnios. This pathology develops in 60% of pregnancies.
Twisting of the umbilical cord, fetal hypoxia, and breech presentation are also possible.
For an expectant mother, an increase in sugar levels can threaten vision impairment, retinal detachment, and the development of heart failure. Against the background of elevated sugar, infectious diseases sometimes develop, for example, pyelonephritis.
Therapy for gestational diabetes
Treatment of diabetes diagnosed during pregnancy includes the following recommendations:
- Changing your diet and following a diet.
- If it is not possible to correct sugar levels with diet, insulin therapy may be prescribed. The dosage of drugs is prescribed by an endocrinologist while in the hospital.
- Continuous glucose monitoring. To do this, you need to purchase a glucometer.
- Performing physical exercises if there are no contraindications
.
Diet for pregnant women with diabetes
Any diet has several goals:
- Consume foods allowed for illness;
- Balance your diet so that weight gain stops or decreases.
Achieving such goals by women during pregnancy is complicated by the fact that expectant mothers cannot limit themselves in food to quickly lose weight. Their main task is to provide the child with all the necessary nutrients without harming their own body. The way out of this situation is to reduce the calorie content of food without losing nutritional value.
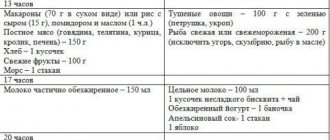
Diet rules if blood sugar is high during pregnancy:
- You need to eat in small portions, avoiding overeating. During the day there should be three main meals and two snacks (second breakfast and afternoon snack). After dinner, you are allowed to drink half a glass of kefir, milk, or eat half an apple 2 hours later.
- Avoid fatty foods, carbohydrate-rich foods and fried foods. Confectionery products and some fruits have the ability to be quickly absorbed and contribute to a rapid rise in blood glucose levels. To cover excess sugar, a pregnant woman needs to increase her insulin dose. This action is an unaffordable luxury for expectant mothers.
- You can eliminate morning nausea by eating 1 small cookie before getting out of bed. If a pregnant woman is recommended to take insulin to combat gestational diabetes, it is best to find out how to get rid of discomfort in the morning from a doctor. Cookies without an injection of the drug can only increase sugar.
- Eliminate all fast food products from your diet. These products are sold after pre-industrial processing, and therefore lead to an increase in glycemia.
- Consume foods that contain fiber. It is important for a pregnant woman to include 25 grams of this complex carbohydrate in her daily diet. Fiber promotes slow absorption of glucose and fat into the blood.
- The amount of unsaturated fats should not exceed 10% in the daily diet of a pregnant woman. It is recommended to avoid sausages, frankfurters, smoked meats, and fatty meats.
- Steam cooking or predominance of boiled and stewed dishes in the daily menu is preferred.
- You need to drink about 1.5 liters of liquid per day, including plain water.
- Add more vegetables and fruits to your diet.
Physical exercise
If pregnancy does not require bed rest, doctors often recommend moderate physical activity to women. They help maintain tone, prevent the addition of extra pounds and maintain good health. In this condition, the chances of achieving optimal blood glucose levels increase.
Physical exercise basics:
- Frequent walks in the fresh air.
- Swimming and doing exercises in the water.
- Avoiding stress on the stomach.
- Avoid horseback riding, skating, cycling and other sports where you can get injured.
- Perform exercises for pregnant women according to your doctor's recommendations.
Any exercise should be performed when the pregnant woman is in good health. Pain in the back or abdomen is a signal to stop exercising and a reason to consult a specialist about the possibility of continuing it.
It is important for pregnant women taking insulin to remember that any exercise can lower the amount of sugar in the blood. To avoid hypoglycemia, be sure to check your glucose levels before and after exercise. If 2 hours have passed since eating, then it is recommended to have a snack before performing any physical work.
Prevention
Diabetes most often occurs in pregnant women at risk. Sometimes the disease overtakes women who do not have the prerequisites for this, so it is impossible to completely exclude its occurrence.
Simple recommendations can help reduce the likelihood of diabetes while carrying a child:
- Maintain normal weight during pregnancy.
- Do not overeat and follow a diet that excludes sweets in large quantities.
- If a woman’s sugar has returned to normal after childbirth and diabetes has not been detected, it is not recommended to take drugs that increase insulin resistance.
Following the recommendations of an endocrinologist for pregnant women with elevated blood glucose levels allows them to avoid dangerous consequences and also makes it possible for the baby to be born healthy.