Causes
The main reasons for the development of diarrhea while taking antibiotics:
- allergic reaction to active substances;
- imbalance of beneficial and harmful microorganisms;
- accelerating the process of contraction of the muscular system of the intestines and stomach;
- poor absorption of fluid by the intestinal walls.
How do antibiotics cause diarrhea?
Antibacterial agents are aimed at destroying any bacteria that are in the body. Active substances destroy them, suppress growth and development.
Our friendly bacteria, which are necessary for the normal functionality of the digestive system, also lend themselves to this. To put it simply, there is an imbalance between beneficial and harmful microorganisms.
How does diarrhea occur:
- With dysbacteriosis, the quality and quantity of the composition of bacteria in the microflora is disrupted. The intestines contain many microorganisms that break down fats, synthesize carbohydrates, form immunity, promote the absorption of nutrients from food, dissolve lumps of the foods we consume and improve local motility. When antibiotics destroy them, their ratio with pathogens changes, which causes the formation of loose stools.
- If motor functions in the digestive organs are disrupted, then the digestion process also changes, and stagnation develops. And when lumps of food accumulate, they begin to rot and ferment. This is manifested by diarrhea, which is often replaced by constipation.
- When the absorption of water into the walls of the gastrointestinal tract is impaired, fluid accumulates inside, diluting the food excessively, so the stool becomes watery.
What antibiotics can cause diarrhea?
Almost all antibacterial drugs cause diarrhea, as indicated in the instructions for use (section with side effects). However, there are groups that are especially dangerous:
- Tetracycline group: Tetracycline, Doxycycline, Metacycline.
- For children, fluoroquinolones pose a particular risk - Fluoroquinolone.
- Penicillin antibacterial drugs: Amoxiclav, Flemoxin, Flemoclav, Amoxicillin.
- The macrolide group least likely to cause trouble: Clarithromycin, Sumamed, Erythromycin, Azithromycin.
Main causes of diarrhea
Loose stools, which parents can observe in their child during antibacterial therapy, are a symptom of one of the diseases. All of them have different clinical manifestations. And in order to understand the new diagnosis, it is necessary to study all the nuances. Only after this is a decision made on how to treat the child for diarrhea.
Gastrointestinal irritation and malabsorption
This is the most common reason that provokes the appearance of loose stools in a child after taking antibiotics. Most drugs have an irritating effect on the intestinal mucosa, provoking active muscle contraction. This interferes with the absorption of nutrients, and incoming food is quickly eliminated from the body.

A characteristic sign of such a deviation is diarrhea that occurs immediately after taking the drug. At the same time, the frequency of stool does not exceed 3-4 times per day, and the general condition of the baby remains within normal limits. The stool is light yellow in color; no mucus or blood is found in it.
Treatment of such diarrhea is exclusively symptomatic. And all unpleasant symptoms disappear on their own after stopping the antibiotic.
Dysbacteriosis
In medical practice, it is most often customary to use broad-spectrum antibiotics. The main danger of these drugs is that they do not act selectively only on pathogenic microflora, but destroy all types of bacteria in their path, including beneficial microorganisms. This imbalance is usually called dysbiosis.
We recommend: Reasons for the development of diarrhea in a child and pain in the abdominal area and the basics of therapy
Even severe dysbiosis when taking antibiotics usually does not cause much concern for children. Loose stools are present, but there is no abdominal pain, the temperature remains within normal limits. The color of stool may take on a green tint.
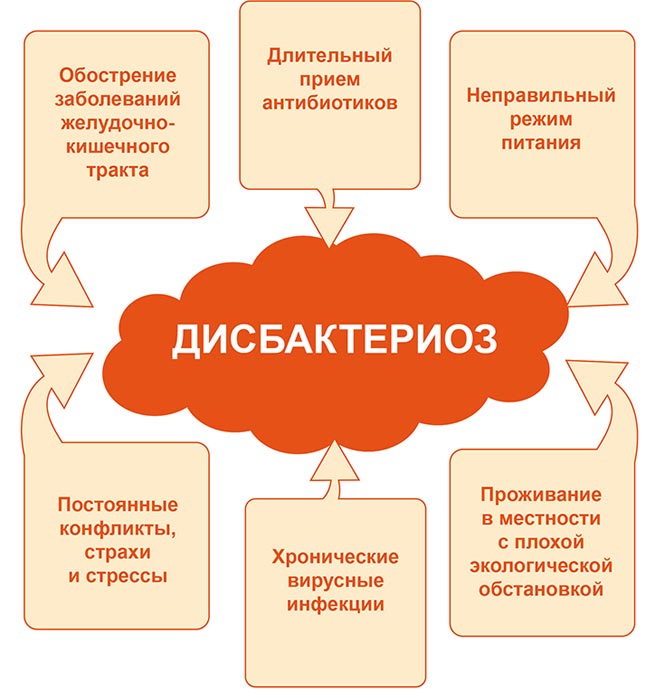
It is necessary to treat diarrhea due to dysbacteriosis with the help of beneficial bacteria, repopulating the intestines with them. For breastfed babies, it is sometimes possible to do without taking additional medications.
Pseudomembranous colitis
This type of disease is rare, but occurs with serious complications. Pseudomembranous colitis occurs against the background of uncontrolled proliferation of pathogenic microflora, in particular the bacteria C. difficile, which are present in small quantities in any healthy body. During their life, these bacteria release toxins that are dangerous to humans and cause digestive disorders. Only a specialist can tell you how to treat the disease. Standard measures and folk remedies are ineffective in this case. The highest risk group is children under 6 years of age.
Forms of diarrhea
Diarrhea while taking antibacterial drugs in a child occurs in the following forms:
- Mild - characterized by loose stools that are released up to 5 times a day. Symptoms are mild - slight discomfort and abdominal pain. After defecation, the signs disappear.
- Average - bowel movements occur from 5 to 15 times a day. There is an increase in body temperature and an increase in the pain threshold upon palpation of the abdomen. The feces may contain mucous or bloody clots.
- Severe – diarrhea occurs more than 15 times a day, body temperature becomes too high, and severe dehydration occurs.
- Fulminant – characterized by the immediate development of the above symptoms and severe pain.
Green stool after antibiotics
Green diarrhea in an adult or child
Green diarrhea - time to worry
Green feces - what could it be?
Probably everyone has at least once encountered a situation in their life when either themselves or their child had to detect green stool with a rather unpleasant odor.
This type of diarrhea can last for a long time. In an adult, green diarrhea can also occur during the course of an illness associated with an intestinal infection. In such cases, copious mucus and blood residues are often found. Other symptoms of acute intestinal disease are also observed: the temperature is significantly increased, acute pain in the abdomen, vomiting and nausea, and general weakness. In this case, leukocytes enter the stool in large quantities, which are the cause of green diarrhea.
Naturally, trivial situations cannot be ruled out when a person eats foods or drinks whose contents are full of artificial dyes in high concentrations. After this, green diarrhea may occur in an adult. But this only happens with serious disorders in the digestive system, therefore consultation with a specialist is highly advisable.
What to do if your child has green diarrhea?
Causes of green diarrhea in children
Green diarrhea in a child often appears when switching to artificial feeding, which contains a fairly large amount of iron-containing elements. The same thing happens when complementary foods are introduced - the concentration of iron in feces increases.
Intestinal dysbiosis is another common cause of green diarrhea. A lack of beneficial bacteria and an imbalance of intestinal microflora occur against the background of poor nutrition, allergic reactions, antibiotic use and decreased immunity. This disease is accompanied not only by loose green stools, but also by bloating, stomach pain, and nausea. Dysbacteriosis is determined by examining stool. If pathogenic bacteria are detected, treatment with antibiotics is necessary, and sorbents and probiotics are prescribed to restore normal microflora.
A common occurrence in infants is the transfer to a new type of feeding or to animal milk, which may cause problems with the intestines, and as a result, green stools. Also in such cases, bloating and flatulence are often observed. A simple solution to this problem may be to return to the previous feeding. But if this does not bring any visible results, then the specialist prescribes a course of taking probiotic medications, but only after carefully conducted research.
Treatment of green diarrhea - highlights
The first step in treating green diarrhea is changing your diet. Avoid foods and dishes that can cause diarrhea - fatty foods, dairy products, exotic fruits, foods containing dyes and other additives.
If, in addition to green feces, vomiting or nausea appears, the temperature rises, weakness or abdominal pain occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor.
You might also be interested in:
Every mother will be scared by changes in her baby's stool, be it a change in consistency, color or smell.
Deviations from the norm are constipation in infants. when stool appears less than once a day. In this case, the baby may experience painful bowel movements, crying, and gas. Diarrhea, the presence of mucus in the child’s stool, a foul odor, and greasy stool consistency are also considered abnormal. Of course, green stool in a child is also a deviation from the norm. What are the reasons for its appearance? Most often this is dysbacteriosis, which can be an explanation for many problems with stool in a child. In the child’s intestines there is a certain set of microorganisms that determine the normal microflora and vital activity of the intestines. Dysbacteriosis refers to various abnormalities in the intestinal microflora. If the ratio of bacteria in a child’s intestines is disrupted, this can cause a decrease in immunity and an increased risk of various intestinal infections. With dysbacteriosis, green stools with mucus, foam, and clots are possible. The best medicine for restoring the baby’s intestinal flora is mother’s breast milk. after all, it is what guarantees and stimulates the growth of its own microflora; it contains important substances that promote the growth of bifidobacteria.
If your baby is bottle-fed, then it is important to know that many infant formulas are fortified with iron, and they can also cause green stools in the child.
Undoubtedly, the nutrition of the nursing mother directly affects the child’s stool. Do not forget that during breastfeeding it is very important for the mother to follow a special diet.
Diarrhea after antibiotics
The main reasons for the development of such an unpleasant pathological condition, popularly called diarrhea, are specific infectious diseases of the stomach and intestines, viral, parasitic, bacterial and nonspecific inflammatory diseases, such as ulcerative colitis.
Antibiotic therapy and antibacterial therapy are often necessary in the treatment of many diseases, but, unfortunately, the use of antibiotics and other antibacterial agents often leads to a number of different side complications. Among all the negative symptoms that occur after taking antibiotics, the appearance of diarrhea is far from the least important. Other disorders of the digestive system are possible, such as nausea, constipation and vomiting.
As noted above, diarrhea can be a consequence of drug therapy and therapy with herbal preparations, for example, ergot alkaloids, digitalis preparations, laxatives.
Diarrhea is also caused by antibacterial agents, for example, sulfonamides, fluoroquinolones, nitrofuran drugs, as well as drugs with a cytostatic effect.
Diarrhea can also occur during long-term therapy with antifungal drugs, for example, ketoconazole, terbinafine and fluconazole.
It is after taking antibiotics that dysbacteriosis is considered the most common. Dysbacteriosis is a violation of the natural microflora in the intestines. Due to the action of antibiotics, the balance between harmful and beneficial microorganisms is significantly disrupted. This can manifest itself in the form of bloating and constant diarrhea.
This disorder, called dysbiosis, develops gradually, and some time passes for its development.
That is why these drugs are intended to reduce the risk of diarrhea and other undesirable consequences of antibiotic therapy. But still, before using them, you need to consult a specialist and study the instructions in detail.
Associated symptoms
Additional signs that are present in the first 2 stages of the severity of the disease:
- weakness of the body;
- nausea and vomiting;
- moderate pain, minor spasms;
- slight increase in body temperature (up to 38-39 degrees);
- bloating;
- moodiness and lethargy;
- alternating loose stools with normal ones;
- the presence of mucus and blood in the stool.
Associated symptoms in severe form:
- body temperature reaches 40-41 degrees;
- severe pain;
- There is a lot of mucus and blood clots in the feces, and white lumps are observed.
In the latter case, urgent hospitalization of the baby is required, otherwise there is a risk of severe dehydration and death.
First aid
The first thing to do is call an ambulance or go to the pediatrician. Before the doctor arrives, the child can be given Smecta and Regidron. The prescribed antibiotic should not be taken yet.
Particular attention is paid to the diet - certain foods are excluded, while others are introduced. The baby must drink enough clean water after each bowel movement. You can introduce unsweetened tea and compote based on dried fruits.
What can't you do?
- any fermented milk products;
- solid food;
- fresh fruits that irritate mucous membranes;
- raw vegetables;
- juices
When should you call a doctor?
A child's body tolerates diarrhea much more difficultly than an adult, so if loose stools occur, you must contact the clinic. You need to call a doctor in the following cases:
- frequent urge to defecate and defecate more than 10 times a day;
- severe pain syndrome;
- lethargy, physical inactivity;
- nausea and vomiting;
- lack of effect after stopping the consumption of antibacterial agents;
- the presence of mucus and especially blood in feces;
- increased body temperature;
- weakened response to stimuli.
It is especially important to call an ambulance if the baby is under 2 years of age.
Is it possible to feed a child?
You need to start feeding your baby after 24 hours. The exact diet is prescribed by the attending physician.
Causes of diarrhea
Due to their effectiveness, antibiotics are often used to treat various diseases. More and more people began to self-medicate using the drug. If you use a medicine too often, its effectiveness decreases, the human body gets used to it and stops responding to the active substance. When using the drug independently, it is often used incorrectly, which provokes the appearance of side effects after antibiotics.
A common side effect when using antibiotics is antibiotic-associated diarrhea, the occurrence of which is caused by the regular use of penicillins, cephalosporins, or a number of drugs at the same time. There are other reasons for the occurrence of loose stools after taking this drug.
Intestinal dysbiosis
The first reason why diarrhea may begin is intestinal dysbiosis (disorder). The occurrence is due to the use of antibiotics of the aminoglycoside and tetracycline groups.
The human body contains bacteria that arise when taking antibiotics when the microflora changes. The antimicrobial drug destroys the necessary bacteria responsible for the functioning of the stomach (bifidobacteria, lactobacilli) along with harmful bacteria (pathogenic flora). Due to the imbalance of harmful microorganisms, there are predominantly more beneficial ones. The urge to defecate occurs due to stimulation of the smooth muscles of the intestines.
Laxative effect of the drug
If the diarrhea started due to antibiotics, a drug that has a laxative effect may have been used. This minor effect lasts a couple of days. This side effect is typical for drugs that enhance intestinal motility, for example, the group of macrolides.
Pseudomembranous ulcerative colitis
One of the causes of diarrhea from taking antibiotics is considered to be pseudomembranous ulcerative colitis. The appearance is due to prolonged use of the drug or taking one type of antibiotic. The pathogenic microorganism Clostridium difficile causes harm to the body; it is difficult for the human body to get rid of the microbe. The microorganism Clostridium difficile is resistant to antimicrobial drugs.
Pseudomembranous ulcerative colitis is usually considered a separate disease; it is characterized by the following symptoms:
- copious, loose stools;
- bowel movements up to 30 times a day (discharge greenish in color, putrid odor);
- increased body temperature;
- weakness of the body, dizziness;
- I have a stomachache;
- migraine;
- vomit.
If the described symptoms occur, you should immediately contact a medical facility. Ignoring the disease will lead to the development of complications and dehydration of the body.
Diagnostics
Initially, the child is taken to a pediatrician, after which the doctor may refer him to an infectious disease specialist or gastroenterologist.

Diagnostic measures are carried out by a pediatrician:
- Interviews parents about the duration and frequency of diarrhea, accompanying symptoms, the structure of stool and other important indicators.
- Conducts an examination by palpation of the abdomen.
- Orders a collection of stool samples to detect helminths.
- Collects feces for biochemical research. Bile is also taken for the same purposes.
- Culture of intestinal microflora.
- Blood chemistry.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity.
- CT scan.
- Endoscopy of the intestines and stomach.
- If the diarrhea is functional, radiography, manometry or peripheral electrogastroenterography are additionally prescribed (motility is examined).
What antibiotics can infants take?
Breastfed babies receive a certain amount of antibodies every day along with their mother's milk to fight various diseases. But even with such support, it is still difficult for the newborn’s immature immunity to resist pathogenic microorganisms, so for severe infections, pediatricians often prescribe antibiotics. And, of course, the most important thing in such a situation is to choose the right drug that will give the desired result without side effects.
Of the existing antibiotics, infants are most often prescribed:
- Aminopenicillins (“Ampicillin”, “Amoxicillin”). These are broad-spectrum drugs - they are able to resist various types of bacteria. If necessary, they are prescribed even to newborns in the form of a suspension.
- Macrolides (“Erythromycin”, “Azithromycin”, “Sumamed”). They are among the latest generation drugs with the least toxicity. Most often they do not cause side effects, but, like any other antibiotics, they are not prescribed for prophylactic purposes.
- Fluoroquinolones (“Levofloxacin”, “Moxifloxacin”). Used only if other drugs have not brought the desired result. They are capable of destroying even the most resistant types of bacteria, but have a significant effect on the intestinal microflora.
Antibiotics are prescribed to newborn babies mainly in the form of suspensions - tablets are not suitable for treating infants, and injections are used much less frequently. If the child’s condition is of serious concern, he is prescribed one of the broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs - they successfully fight various types of pathogenic microorganisms, but often cause dysbacteriosis. When there is no threat to the baby’s life, with the help of additional tests it is possible to more accurately determine the type of bacteria attacking the body and select a remedy suitable for this particular case.
Treatment depending on the child's age
Therapy is aimed at the following goals:
- normalize water-salt balance;
- remove toxins and thicken stool;
- restore microflora and eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
But it is especially important to prevent dehydration, the signs of which are the following:
- dryness of the tongue, lips, mucous membranes;
- rare and scanty urination;
- formation of bruises under the eyes.
Recommendations for infants:
- You should not stop breastfeeding, as it contains sugar, which promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria, and lactulose, which forms a breeding ground for lactobacilli.
- Between feedings, be sure to give enough boiled water.
- Taking probiotics and absorbents.
- Drinking saline solutions (Hydrolit, Oralit).
Recommendations for older children:
- Strictly follow all doctor's instructions.
- Drink plenty of fluids - water, rice water, tea drinks, medicinal herbs.
- Take sorbents, hydration preparations and other products in accordance with the age category.
- Stick to bed rest.
The prescription of a specific drug and its dosage is determined by the attending physician. This depends on the severity of the disease, the cause of diarrhea after taking antibiotics, and the characteristics of the body.
Normalization of microflora
To restore the microflora, beneficial bacteria will have to be artificially populated. The following drugs will help with this:
- Bifidumbacterin is a probiotic that contains active and live bifidobacteria. The drug is available in the form of suppositories, tablets and dry mixture. Babies are usually given a dry powder that is added to formula or diluted with water. The dosage is prescribed individually.
- Hilak Forte is prescribed upon reaching 2 years of age. Available in the form of oral drops. Contains substrates of metabolic products.
- Bifiform also refers to a probiotic, which contains not only bifidobacteria, but also lactobacilli, B vitamins. The product is produced in the form of an oil solution, tablets, capsules, chewable tablets and dry powder.
- Rotabiotic is produced only in capsules; it additionally accelerates the process of digestion and absorption of nutrients. Can be taken from one year of age.

How to restore water-salt balance?
Restoring the water-salt balance is very important, since the baby loses nutrients and water during diarrhea and vomiting. For this purpose, there are medications - rehydration solutions:
- Rehydron is available in powder form, which dissolves in water. The drug is aimed at restoring the balance of water and salts and removing toxic residues. On sale you can buy powder packaged in disposable bags. One packet is enough for 1 liter of liquid.
- Humana Electrolyte is produced in the form of a mixture packaged in sachets. Mandatory condition: up to 3 years of age you need to buy a mixture with fennel, older ones - with banana. One packet is diluted in a large glass of water.
Thickening of stool
Antidiarrheals are needed to thicken the feces. The following medications are most often recommended for children:
- Smecta in powder form based on vanilla and orange flavors. It can be given from birth, after diluting it in milk or water. Up to one year of age, 1 sachet per day is recommended, older ones - 4 pieces.
- Enterosgel additionally removes toxic deposits, improves digestion, and strengthens local immunity. Available in the form of a thick paste and a transparent white gel.
Diet
The main rule for getting rid of diarrhea is adjusting your diet. It is necessary to review the menu and remove unnecessary dishes and products. In addition, it should be cooked exclusively by steam or in water. If your baby experiences frequent diarrhea after taking antibiotics, follow these guidelines:
- Introduce more buckwheat and rice cereals into your diet. They have an enveloping effect. Subsequent medications will not cause an aggressive reaction.
- Prepare fruit and berry jelly. They help restore the gastrointestinal tract and normalize stool.
Allowed dishes and products:
- lean broth;
- stale bread;
- River fish;
- steamed omelettes;
- cottage cheese with a minimum percentage of fat content;
- carrots, broccoli, zucchini;
- baked apples;
- lean meat;
- dry cookies without fillers.
Prohibited products:
- pasta;
- fast foods;
- milk;
- eggs;
- legumes;
- confectionery and baked goods;
- fruits (grapes, plums, peaches, apricots);
- smoked meats;
- fatty and fried foods;
- soda.

Folk remedies
To cope with diarrhea, you can use several child-safe alternative treatment recipes:
- Boil the rice. You should not add salt. Separate the porridge from the liquid mass and cool to room temperature. Use 3-4 times a day. Children under one year old - 1 tablespoon, older - 1/4 cup. Diarrhea stops after 2 days.
- Regidron will help restore the water-salt balance. But if it is not in your medicine cabinet, you can prepare the medicine yourself. You will need: sugar - 1 tbsp. l., salt – 1 tsp., warm water – 200 ml. Mix everything and give a few sips every 15 minutes.
- Oak bark. Method of preparation: brew a tablespoon in a thermos. Leave for about an hour. Strain through cheesecloth folded in several layers. You can add a few drops of valerian tincture. Use the resulting product to make enemas. For children under 3 years of age, oak bark is prescribed only by a doctor.
- Chicory. Children under 2 years of age should take this product with caution. It is advisable to consult a pediatrician. Pour 0.5 liters of water into a container and add a teaspoon of flowers. Place on the fire and cook for 10-15 minutes. Then strain through cheesecloth and give a teaspoon 3 times a day before meals.
- Banana diet. This fruit contains a large amount of potassium. Give your child one ripe banana every 2 hours. If your baby cannot bite on his own, mash the banana. The diarrhea will go away within a day.
- Apples. This fruit should not be consumed fresh if you have diarrhea. It needs to be baked. Give your baby one every hour.
- Pomegranate skins. Grind the peel and add water. Place in a steam bath and cook for 7 minutes. Cool the broth and give a tablespoon 3 times a day.
- Bird cherry fruits. They have an astringent effect. Place 10 berries in a glass of boiling water. Leave for about 40 minutes. Serve warm before meals.
- Dried blueberries. Prepare a decoction (30 grams of fruit per 250 ml of water). Take 1/4 cup 4-5 times a day.
- Alder. Pour 5 grams of raw materials into an enamel container. Pour in 200 grams of water. Boil for 10 minutes. Use 2 tbsp. l. 4 times a day.
- Salt. For newborns, the solution is prepared as follows: 200 ml of warm water and a teaspoon of salt. For older children, the amount increases to 2 tsp. Give 50 ml every 2 hours.
- Walnut leaves. You will need: one fresh leaf and 250 grams of “steep” boiling water. Leave for 15 minutes. Take for acute abdominal pain.
- Starch. Take a tablespoon of water and add a teaspoon of dietary supplement to it. Wait for it to thicken. Give to your child when diarrhea occurs.
- Coil. Grate the root on a fine grater. Pour water and put on low heat. As soon as it starts to boil, remove from heat and cool. Then strain and give your baby a teaspoon before eating.
- Burnet. Grind the root. Add water. Cook for 20 minutes. 30 minutes before meals you should drink a tablespoon.
- Chamomile flowers. Every home with small children will find medicinal chamomile. This is the most common remedy. It helps not only to treat various diseases, but also to cope with diarrhea. Pour 2 tbsp into a glass jar. l. flowers and pour boiling water over them. Let it brew, then give the baby the decoction to drink.
- Potassium permanganate. Dilute the solution (the water should be slightly pink). Give yourself an enema. This chemical element helps destroy microbes. But remember, the concentrated solution damages the mucous membranes.
- Sagebrush. Brew 1 tablespoon in 500 ml of water. Take 3 times a day, 10 grams 30 minutes before meals.
Diet as a method of treating diarrhea
To successfully cure diarrhea after taking antibiotics, it is necessary to approach the problem comprehensively. An important role in this scheme is assigned to diet correction. Without this point, the body’s recovery process can be significantly delayed. We wrote on this page what you can feed a child with diarrhea.
For children under one year of age who are breastfed, the ideal dietary option is only breast milk. But for this, the nursing mother will have to go on a diet with her baby. It is recommended to exclude from the diet all foods that, to one degree or another, can cause stool thinning. At the same time, it is advisable to add bananas, baked apples and rice to the menu.
We recommend: Causes and principles of treatment of diarrhea with mucus in an infant

For artificial ones, it is recommended to prepare the mixture by diluting milk with water in a ratio of 1:2. After a day, you can switch to 1:1 proportions, provided there is a noticeable improvement in the child’s condition. You can return to your normal diet after two to three days.
For children over one year old who are already familiar with adult food, it is suggested to prepare dishes from potatoes, rice, buckwheat porridge and heat-treated vegetables. For treats, you can offer your child homemade crackers, dried apples and baked green apples.
If a child has diarrhea, it is forbidden to give any fermented milk products until the stool normalizes. Kefir and natural yoghurts are allowed only with confirmed dysbiosis, when the frequency of trips to the toilet is reduced.
Among folk remedies, we can recommend an infusion of dill seeds, a decoction of chamomile or black peppercorns without chewing. But first, consult a pediatrician so as not to harm the baby’s condition.
Prevention
To prevent diarrhea after taking antibiotics, you need to know the following rules:
- do not give medicine on an empty stomach;
- Before taking the pills, the child should eat foods that have an enveloping effect;
- Additionally, give medications that support the microflora of the intestines and stomach.
If your baby takes antibacterial drugs and develops diarrhea, do not ignore this symptom - immediately tell your doctor about it. This will prevent complications and relieve the child from pain and other uncomfortable sensations.
source
Rules for taking antibiotics
Antibiotics should be taken only after a doctor's prescription, in accordance with the chosen dosage and other recommendations. Be sure to read the instructions for the drug. Need to know:
- what time to take the medicine: before meals, after, or it doesn’t matter;
- how many times a day should you give it to your child?
Depending on the severity of the disease, the prescribed courses of treatment differ in duration. They cannot be interrupted, even if the child feels better and the symptoms have gone away. Also, you should not reduce the dosage, citing a reduction in the negative impact of the disease on the baby’s body. It is much safer to give more medicine than intended, which is important in cases where the baby spits out some of what was offered. When the dosage is reduced, the risk that dangerous bacteria will survive increases significantly.
Principles of treatment
Parents should know how to help their child stop diarrhea. Fortunately, when the antibiotics wear off, the diarrhea stops. However, sometimes drug therapy is required.
First aid for intestinal upset due to the use of antibiotics should include three stages. Necessary:
- restore water-salt balance in the body;
- thicken stool;
- restore normal microflora in the intestines.
It is important to ensure the child’s water-salt balance is restored throughout the entire illness. In the process of frequent bowel movements, the body loses a lot of fluid and salts. To prevent dehydration, the child should be given fluids frequently. Clean water, homemade compotes and teas are suitable for these purposes. You should not give your child cocoa, coffee or sweet soda. This method can only make diarrhea worse.

You can also restore the water-salt balance with the help of special products sold in pharmacies. It could be:
- "Regidron";
- "Oralit."
Such drugs are inexpensive, but they perfectly restore salt balance.
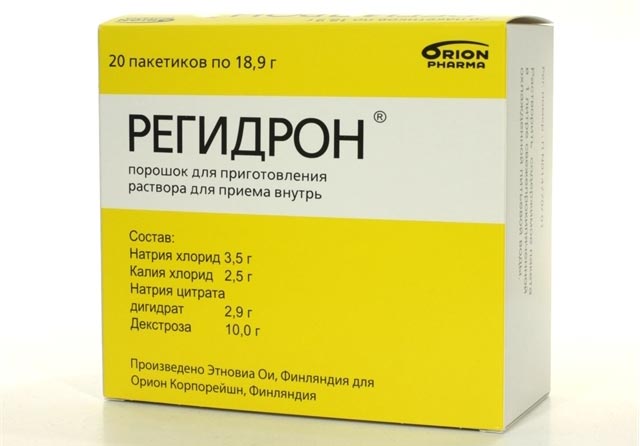
When taking rehydration solutions, it is important to strictly follow the instructions in the instructions when preparing them. The effectiveness of the treatment used will depend on this.
Stool thickening medications should only be taken if diarrhea occurs more than 4 times a day. Such drugs are sorbents:
- "Atoxil";
- "Enterosgel";
- "Smecta".
We recommend: What to do if a child has green diarrhea?
The use of medications such as Levomycetin or Loperamide is permitted only after a doctor’s prescription. It is prohibited to give such drugs to children on their own.

When using anti-diarrhea medications, it is important to consider that they can cause constipation. Therefore, after you feel better, such medications should be discontinued.
It is not advisable to use folk remedies to treat young children without the consent of a doctor. All organisms are different and what helped one may be contraindicated for another.
Use of probiotics
You can normalize the intestinal microflora by using bacteria and probiotics. A doctor can recommend a suitable drug.
Using probiotics is very important. These drugs help the body independently produce beneficial microflora. The most commonly used are the following:
- milk sugar;
- lactulose;
- fructo-saccharides;
- alimentary fiber.
Lactic sugar is a component found in breast milk. It stimulates the growth of lactobacilli inside the intestines.
Lactulose is a high-quality nutrient medium for beneficial microflora. The introduction of an enzyme into the diet is an excellent prevention of dysbiosis.
Fructo-saccharides are found in fresh fruits. This remedy is suitable for older children. You can give such products to a child only if they are already familiar to the little organism and there has been no negative reaction.
Dietary fiber helps the stomach digest food, which promotes more intensive production of beneficial microorganisms.
Causes of diarrhea after antibiotics
Diarrhea while taking antibiotics is the result of an effect on the intestinal microflora. Beneficial microorganisms may die, while the number of opportunistic microorganisms will increase. The number of harmful representatives of microflora is constantly growing, without seeing any obstacles to this. They have a toxic effect and can damage the intestinal wall, which then causes diarrhea. It also appears when microbes that are sensitive to the antibiotic become colonized.
How to treat diarrhea after antibiotics in a child:
- Take probiotic supplements as recommended by your doctor. Their effectiveness has not been proven, since it is impossible to detect a bacterium that can cope with any consequences of the actions of microorganisms. There is no such universal component that helps in any case. Symbiotics are also used, where, in addition to various beneficial microorganisms, there is a prebiotic - this is an environment where they actively reproduce;
- Offer water constantly. If the child does not drink, you need to pour in at least a sip from a spoon or syringe every 15 minutes;
- Do not force feed your baby. The main thing to remember is the liquid.
Nutrition for dysbiosis in infants
To figure out how to treat intestinal dysbiosis in a baby after antibiotics, it is not enough to simply purchase beneficial bacteria or anti-diarrhea medications at the pharmacy - it is important to organize a special gentle diet for the baby, which will help gradually restore the digestion process. During illness, children often lose their appetite and lose weight, so after recovery, many mothers begin to feed them well, making a serious mistake. After antibacterial treatment, the food should be light, mainly vegetable and dairy, even if this does not allow the baby to regain the lost grams in a couple of weeks.
For newborns who are exclusively breastfed, the mother's diet is important - it should not contain foods that cause bloating, constipation or diarrhea. At this time, it is better to give up potatoes, legumes, raw vegetables and fruits, especially cucumbers, beets and grapes, black bread, raisins, prunes, kvass and fresh kefir. The optimal diet for a nursing mother for several weeks after illness should consist of cereals, primarily oatmeal, boiled fruits and baked vegetables. And at this time, formula-fed babies will benefit from fermented milk mixtures.
Obviously, taking antibiotics is always a serious test for a child’s body, and first of all, for his intestines. Therefore, during treatment, it is extremely important to follow the doctor’s recommendations and monitor the condition of the infant’s digestive system, minimizing the risk of complications and side effects from taking medications.
The child's body is very susceptible to various viruses and infections. Therapy may include drugs of various effects, but when penetration of pathogenic microbes is observed, antibacterial agents are used. Diarrhea after antibiotics in infants is explained by disruption of digestive processes due to the death of beneficial intestinal microflora. To avoid this, parents should follow the rules of administration, dosage and not exceed the duration of therapy. In addition, probiotics, prebiotics and dietary nutrition may be prescribed.
Diagnosis of diarrhea in infants
Diarrhea in infants is a condition when the baby goes to the toilet more than 6 times a day. At the same time, the appearance of the stool changes: it becomes watery and is almost completely absorbed into the diaper. Newborns can go to the toilet after every meal. Their feces are not yet formed and are quite liquid. An unpleasant odor, the appearance of foam, mucus or streaks of blood should alert you.
Diarrhea can lead to dehydration, so you need to provide your child with plenty of fluids.
Note! If the baby does not stop diarrhea, call an ambulance. Dehydration in infants, especially in children under one month old, occurs extremely quickly. The condition is especially dangerous when diarrhea is accompanied by vomiting.
Komarovsky about recovery after antibiotics
Komarovsky, a famous children's doctor, believes that there is no need to take probiotics during and after antibiotic therapy. He is convinced that proper nutrition and strengthening the immune system will help the baby recover:
- Do not overfeed the child;
- you need to give up sweets, foods containing dyes and nitrates;
- Spend more time with your baby in the fresh air, dressing him according to the weather;
- Be sure to ventilate the room in which the baby lives, do wet cleaning daily, which will create comfortable conditions not only for him, but also for everyone at home.

How to help a child after antibiotics
When the baby shows anxiety after antibacterial therapy, parents need to take care of normalizing the condition of his body, starting with restoring the intestinal microflora in the baby and ending with diet and drinking regimen. You can cope with dysbiosis with the help of probiotics, for example, “Bifidumbacterin”, which contains beneficial microorganisms - bifidobacteria, as well as substances that support their viability. If after 2-3 weeks of treatment the child’s condition does not improve, he may be prescribed bacteriophages - viruses that work against pathogenic microorganisms, but are harmless to beneficial flora.
Prevention of diarrhea after antibiotics
To avoid diarrhea after taking antibiotics, you need to follow the following rules:
- Give the baby only the medicine prescribed by the doctor, do not replace it with analogues;
- Adhere to the prescribed dosage, based on the doctor’s prescription and the instructions for the drug;
- Give your baby probiotics to restore beneficial microflora in the intestines;
- Stick to a healthy diet. Do not introduce new foods during illness, do not overfeed the child. Remember that the basis of a baby’s diet is mother’s milk or formula. The first can be given during illness according to the child’s every request. It will strengthen the immune system and speed up recovery.
In what cases can I cause diarrhea?

Most of the broad spectrum species cause diarrhea. And also the occurrence of complications may be associated with non-compliance with the rules of administration. The main reasons for the onset of diarrhea after taking antibacterial agents are:
- The negative effect of medications on the walls of the digestive tract, when irritation and inflammation occurs.
- Manifestation of pseudomembranous colitis.
- Increase in pathogenic and decrease in beneficial intestinal flora.
Irritation of the mucous membranes of the digestive system occurs due to the effect of drugs on smooth muscles in the tissues of the gastrointestinal tract. This often occurs during treatment with Erythromycin. At the same time, the intestines begin to work actively and a laxative effect appears.
In case of intestinal irritation, diarrhea occurs immediately after taking an antibiotic, bowel movements occur no more than 4-5 times a day, feces do not contain abnormal inclusions or impurities, and have a familiar smell. The baby’s health is satisfactory, the temperature is normal, there is no pain, but the stomach is swollen. All symptoms go away on their own after completion of therapy and do not require other intervention. You can speed up recovery by following a drinking regime and diet.
Diet for infants
Proper nutrition is the basis for strong immunity and quick recovery.
Note! When a child is sick, you cannot force feed him. You definitely need to offer him food, but if he refuses, don’t insist.
The main thing during illness is to give the baby something to drink. It would be better to focus your energy on fighting the infection rather than on digesting food.
For artificially-bred children, the mixture must be diluted correctly:
- Do not pour more powder than indicated in the instructions. Be sure to stir thoroughly so that no lumps remain;
- Do not give more often than recommended by age;
- Be sure to add water.
Complementary foods for infants should be introduced in a timely manner, starting with vegetables and cereals. If the baby has already tried meat, then give only dietary meat, preferably turkey or rabbit. Porridges are welcome on water; it is advisable to avoid powdered milk. Vegetables are not prohibited; broccoli, cauliflower, and zucchini are considered the healthiest for babies. You can offer your baby apples and pears. Juices and other sugar-containing products should be avoided for up to a year. During illness and recovery, it is worth limiting flour as much as possible. Dairy products, if they are already in the child’s diet, can be given with caution. It is better to use curds and kefirs created specifically for children.

A baby may experience diarrhea after taking antibiotics. At this moment, the main thing is to prevent dehydration; you cannot stop giving the child water. Be sure to call the doctor who prescribed the treatment if your child has diarrhea from antibiotics; he will tell you what to do and how to proceed next. It is always better to contact a specialist who has already examined the patient to assess the progress of therapy.
Treatment of diarrhea
Diarrhea from antibiotics in a child is most often treated symptomatically, and the condition normalizes after discontinuation of antibacterial therapy. But the symptom cannot be completely neglected, since frequent loose stools can cause dehydration.
Standard measures to stop diarrhea caused by medications include:
- rehydration therapy to restore water-salt balance;
- treatment aimed at thickening stool and normalizing stool;
- restoration of the balance of microflora in the intestines.
Rehydration
Diarrhea is a pathological condition that causes accelerated removal of fluid and mineral salts from the body. And the first thing parents should do when their child has diarrhea is to replenish lost supplies. Many old-school experts recommend drinking more water, juices and teas. But, as recent studies have shown, these drinks will not give the desired effect, and in some cases they may even worsen the condition.
We recommend: Causes of diarrhea in a 3-year-old child and treatment methods

The best option for rehydration therapy is to take ready-made saline solutions that have the correct concentration of salt and glucose. In pediatrics, Regidron and Humana Electrolyte have proven themselves well. But be sure to follow the instructions, observing the dosage in accordance with the age of the child.
In infants, rehydration is carried out using frequent breastfeeding. Additionally, take one teaspoon of Regidron every 10–15 minutes.
Symptomatic treatment
If a child has diarrhea more than four times a day, it makes sense to prescribe antidiarrheal drugs. Classic medications that stop diarrhea are rarely used in pediatrics, as they can cause constipation. What to do in this situation?
Symptoms of diarrhea in a child after antibiotics can be eliminated with the help of the latest generation sorbents, for example, Atoxil, Smecta or Enterosgel. These drugs not only destroy toxins, but also have a slight bonding effect.
Probiotics
This category includes preparations of beneficial bacteria that populate the intestines. Today, pharmacies offer a huge selection of medicines to eliminate dysbiosis, but what exactly you will treat diarrhea with should be prescribed by your pediatrician. After all, even these remedies, if the instructions are not followed, can cause harm by increasing diarrhea.
Such drugs as Bifiform, Lactiale and Rotabiotic have proven themselves well in pediatrics.