The causes of flat feet in children are factors that influence the onset, development and aggravation of pathology in children. Parents should take a responsible approach to identifying factors in the development of the disease immediately after the first symptoms appear. The disease can be corrected at an early age, you can completely get rid of it, but it is almost impossible to do this in an adult. The disease is characterized by flattening of the arch of the foot, a gradual disruption of the mechanism of full movement. Many people mistakenly perceive the problem as a cosmetic defect. The disease is much more dangerous and entails pathology of the musculoskeletal system.
Diagnosis of flat feet in children of different ages
A baby’s feet seem flat – a physiological feature; as they grow older, the arches of the feet transform by the age of 3. Parents should pay attention to foot placement from early childhood. It becomes especially noticeable when the baby takes his first steps. Pathologies are detected during routine examinations in kindergarten. If the child does not attend kindergarten, he should be examined regularly by an orthopedist for preventive purposes.
The disease is often detected in schoolchildren. The orthopedist at the appointment evaluates:
- The height of the arch of the foot.
- The relationship between the feet (is there any expansion, lengthening).
- Turning the anterior section outward. Heel deviation.
- The presence of corns, hyperkeratosis.
- Hypertrophy, atrophy of leg muscles.
X-ray and plantography are additional diagnostic methods that allow you to confirm the diagnosis.
I want to study the sand you walked on...or is it possible to determine flat feet on your own?

All of us have long become omniscient in any field, and medicine is no exception, right? The great thing the Internet will find an answer to any question, and we, knowingly, having read the thoughts of those who have gone through “fire, water and copper pipes,” look for signs of diseases in ourselves and our children and begin to be treated, although often there is nothing to treat.
Do you need to ring the bells if you can’t shake the obsessive thought that your child may have flat feet? "Forewarned is forearmed!" - the golden rule for everything related to health. Nothing prevents us from looking for something that may hint at problems, but only a specialist is obliged to put an end to it. So, parents need to think about it if:
- the inside of the sole of children's shoes and the heels are worn unevenly, one shoe is stronger than the other;
- the child moves less and rests more due to tired legs;
- the baby complains of pain in the legs after long walks;
- the child's gait has changed; while walking, the feet move either to the outside or to the inside.
There are home tests that are simple, but quite informative, to identify signs of flat feet.
- By imprint. The simplest option, scientifically called “plantography”. To obtain a photocopy of the foot, you can smear the child’s foot with something bright and smearing. Of course, green paint or iodine should not cause spontaneous fear, albeit groundless, especially since erasing such art will be problematic.
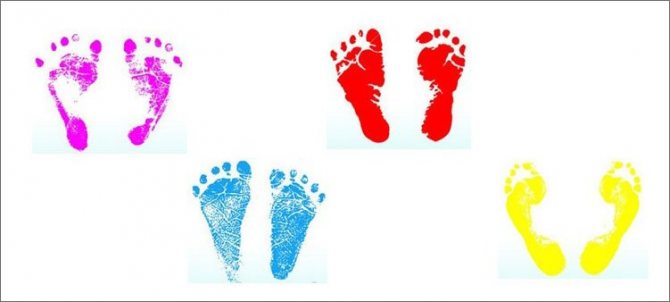
It is better if it is oil, cream or regular paints. If the “crescent” is not clearly visible in the print, and the narrow part is more than a third of the entire width of the foot, then there is nothing to think about - you need to go to the doctor. For other smaller deviations, plantography is only the starting point for a full examination. - By posture. Problems can be identified by seeing irregularities in posture. Place the child with his back to you without outer clothing. If you notice that the spine has clearly “floated” somewhere to the side, schedule a visit to an orthopedist in the near future.
- By appearance. Examine the child's foot and pay attention to its color. If the mark is a pale pink color, then there is nothing to worry about. A white foot indicates insufficient blood circulation, and a bluish tint indicates venous stagnation. Both external discrepancies should raise red flags.
Here are just a few symptoms that may suggest an existing problem or that it may soon arise and lead to an orthopedist, and he has other diagnostic methods in his stash to determine flat feet.
Causes of appearance in children
Pathology occurs in a child for a number of reasons. Studies have shown results according to which children who have the opportunity to regularly walk barefoot in the early years are much less likely to experience illness than their peers who constantly wear shoes.
Parents should know that allowing their child to walk barefoot on pebbles, fine gravel, and grass is a good habit that helps shape the correct position of the foot. It must be remembered that physical activity is the most important factor in leg health. The risk of pathology increases significantly if your lifestyle is sedentary.
Congenital
Among the congenital causes of the disease, doctors identify:
- hereditary weakness of the ligamentous apparatus;
- incorrect position of the talus bone in the ankle causes valgus foot;
- congenital, genetic disease leading to weakening of muscles;
- pathologies of the fetus during intrauterine development (infection suffered by the mother during pregnancy, complicated toxicosis, fetal hypoxia, difficult labor, injuries during delivery).
The congenital form of the disease appears quite rarely - it is detected in only 3% of the total cases of diagnosing the pathology. The problem is detected at an early age. If left untreated, the situation may worsen and the degree of foot deformity increases. Young men with such a disease are not accepted into the army or are considered limitedly fit for service.
Acquired
Flat feet can develop for the following reasons:
- The disease becomes a consequence of congenital diseases: Down syndrome, cerebral palsy.
- With a deficiency of vitamins, microelements, and nutrients, rickets can develop. The consequence will be improper bone development. The sole gradually deforms, unable to support the weight of the body. A common cause of flat feet in preschool children is both obesity and underweight.
- Excessive loads during sports - lifting weights by teenagers, long hours of training, dancing - can cause the development of pathology. This is especially true for teenagers who are actively growing. The load must be balanced. If you have complaints about pain in your legs, you should inform your doctor in order to adjust your training load or change your sport in time.
- Excess weight is the cause of an acquired type of deformity.
- Among the systemic diseases that lead to the development of pathology are rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes mellitus.
- Incorrectly selected shoes with high heels or completely flat soles. Children of preschool age, in the first years of study at an educational institution, should not wear flat shoes, as the foot develops. The optimal heel height is 1-1.5 cm. A preschooler cannot wear shoes with narrow toes - this provokes foot deformation. During the school period, the rule should also be observed.
- A sedentary lifestyle leads to weakening of muscles and ligaments. There is no necessary load for proper development.
- Pathology can appear after foot fractures.
Possible consequences
How dangerous is flat feet for a child? At first glance, the diagnosis does not pose a threat.
An outwardly not very noticeable deformity, if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed, can rapidly progress and manifest as undesirable consequences for the health of the entire body.
The omission of physiological shock absorbers contributes to improper distribution of load during physical activity. The foot becomes more deformed every day, creating additional discomfort not only for the feet, but also for the knees and ankles.
In adulthood, children's flat feet lead to the appearance of arthrosis and arthritis of the joints of the lower extremities.
Young children may experience fatigue and pain in their legs. If such complaints appear, it is necessary to pay close attention to the problem and make an appointment with a pediatric orthopedist for a detailed examination by a specialist.
A consequence of the intensive progression of untreated flatfoot is curvature of the spine. Violation of the spring functions of the foot leads to a constant “shake” of the spinal column. Scoliosis of varying severity is aggravated by pelvic deformation and significant impairment of gait and posture.
From the above it is clear why the consequences of flat feet in children are dangerous.
The consequences of flat feet are disruption of the normal functioning of the joints of the lower belt, limited range of motion, gait disturbance, and curvature of the spine await the baby in adulthood.
How to avoid developing foot deformities
Knowing the reasons why flat feet can develop in children, it is easier to prevent the process using preventive measures. It is more effective to correct the problem at the initial stage. As an adult, it is almost impossible to change anything.
- It is necessary to visit an orthopedist on time.
- Regular foot massage from birth is a good prevention of the problem.
- The child should walk barefoot on uneven surfaces: sand, grass, pebbles.
- It is important to choose the right shoes from birth. Give preference to natural material, high quality. The sole must be flexible, there must be a small heel and a hard heel. It should be comfortable to wear without squeezing your fingers.
- Sports should be done with the right load: basketball, swimming. At the first painful symptoms, you should consult a doctor and change the nature of your activities.
- Controlling body weight will ensure healthy joints, relieving them of excess weight.
- An active lifestyle - regular walks after school, rest on weekends will benefit the whole family.
How to treat flat feet in a child?
Physical therapy and massage are still the best ways to treat flat feet, but how to treat flat feet in a child? It will be easier for the baby if the treatment sessions take the form of a game. At the initial stage, it is necessary that, as directed by his mother, he learns to perform certain exercises, and then he can begin physical therapy. Walking on your heels, on your toes and on the outer arches of your feet is very useful - such exercises have a strengthening effect on the muscles of the feet. The main thing is to ensure that the child never walks on the inside of the foot.
A great exercise that a little one can enjoy and captivate is collecting games. You need to scatter balls, pencils or some other small objects on the floor, and then ask the baby to collect them only with the help of his toes. Also a good exercise, but less accessible, is drawing various shapes with your feet in the sand.
It is recommended to carry out such exercises for 5 minutes several times a day. Then the baby will not get bored, and you will see the result soon enough.
Among other things, walking barefoot on grass, rocks or pebbles is an excellent treatment. In the summer, such an activity will not only be beneficial, but also give the child great pleasure, and in an apartment, rough rugs can be used for these purposes. This kind of walking shapes and strengthens the arches of the feet, since the muscles of the foot are very tense during it.
In addition to exercises, you should also pay attention to the activity of the baby, which he shows every day. The more he moves, the better. Standing still without moving, in turn, only contributes to the development of flat feet. Even if you and your child are standing at a stop waiting for the bus or holding his hand while standing in line, ask him to run around or jump, this will only bring joy and benefit to the baby.
How do doctors determine the presence of a disease?
The specialist always begins the diagnosis by collecting information from the parents if the child cannot independently talk about the problem. If the child is over 7 years old, the orthopedist pays attention specifically to the complaints of the little patient. This allows you to more accurately determine what is bothering the child and at what stage the pathology is developing.
The following signs in the anamnesis during the initial interview will tell the doctor about the extent of the disease:
- If a child has minor pain, discomfort in the foot area, legs in the evening, after physical exercise, excessive long walking, the ligaments are weakened by palpation, we can talk about 1st degree flat feet. In this case, the height of the arch may be close to ideal,
- 2nd degree flatfoot has the following symptoms: visual manifestation of the disease (when the foot seems blurry), pain in the legs, knees, foot, gait changes, swelling is observed,
- Severe deformation of the feet, swelling, pain in the legs and lower back, and a significant change in gait indicate grade 3 flat feet.
Flat feet can be longitudinal or transverse. The type of disease can also be determined by an orthopedist during the initial examination. Diagnosis of flat feet in children necessarily includes the stage of determining the type of pathology; without this, it will be difficult to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
The first type is transverse flatfoot, which manifests itself in the drooping of the transverse arch of the foot. As a result, the anterior section rests on the heads of all metatarsal bones. It is recognized by the separation of the big toe, it begins to protrude outward, and the foot itself becomes reduced in length and increased in width.
The second type is longitudinal flatfoot. It manifests itself in the flattening of the longitudinal arch of the foot. Often the disease leads to clubfoot. Manifests itself in the form of elongation of the leg, the foot is in 100% contact with the floor, and the shoe wears excessively along the inner edge.
Attention!
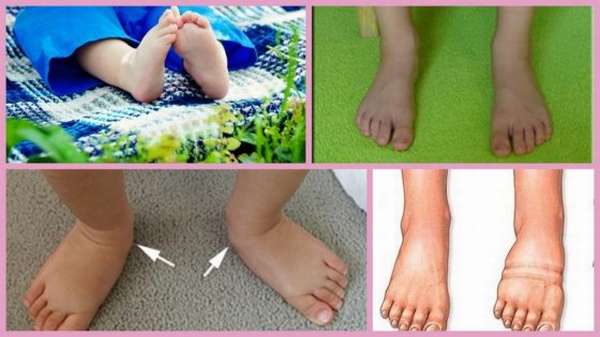
Separately, it is worth mentioning valgus flatfoot. It is often given to children from one to three years of age, when the child begins to learn to walk. If physiological flat feet in infants is the norm until a certain age, then the hallux valgus manifestation should be treated in a timely manner to avoid adverse consequences.
Valgus flatfoot or, as doctors say, curvature manifests itself in the form of longitudinal flatfoot when the middle part of the foot drops. During diagnosis, the specialist notes that the child’s toes and heel bone turn outward. When walking, this deviation is noticeably greater than when standing. Parents can independently monitor the placement of the leg. If a child has one or two legs that seem to be sticking out, you should seek the help of an orthopedist as soon as possible.
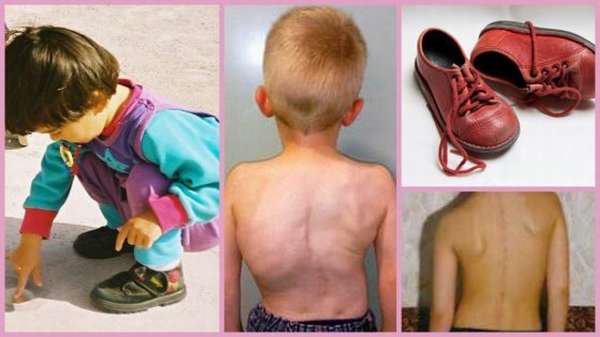
To recognize flat feet in a child, an orthopedist pays attention to the following signs of the disease:
- Wear of shoes (flat feet are indicated by wear on the inside),
- To understand that a child has flat feet is helped by the size of the foot (the foot is increased in width or length, which leads to the purchase of shoes a size larger),
- Overgrowth of a bone on the big toe,
- Quick fatigue after long walking, exercise,
- Unnatural posture, scoliosis,
- When squatting, it is difficult for a child to maintain balance,
- Wearing shoes with flat soles or heels causes discomfort and pain,
- Night cramps in the legs.
Doctors use the following technique in practice and recommend using it at home. Plantography is an imprint of a child’s foot or sole. The position of the drawing and the contours printed on paper help to understand whether children have flat feet. It is worth paying attention to:
- Angle of deviation of the big toe and heel,
- Arch height (the void between the heel and toe in the print).
Sometimes orthopedists, when making a diagnosis, may use additional research methods, such as radiography, electromyography, computed tomography, digital photography, and dynamometric multicomponent platforms. The last 3 methods are modern and most effective.









