Ulcers on a child’s tongue can cause severe pain and dramatically disrupt the baby’s general condition. Therefore, parents should be aware of other symptoms accompanying ulcers for earlier identification of the causative disease. This will make it possible, without wasting time, to immediately contact a dentist for help and achieve a speedy recovery.
Causes of ulcers on the tongue
Ulcers on a child’s tongue are manifestations of glossitis (inflammatory lesions of the tongue). The reasons leading to it are very diverse. They include:
- Direct mechanical injury from a tooth fragment or other object
- Effect of chemicals (abuse of sour foods, including lemon)
- Burn from boiling water
- Infectious lesions caused by herpes simplex viruses, candida, staphylococci and other microorganisms
- Pathology of the digestive system, incl. and with a violation of the absorption process, predisposing to various vitamin deficiencies
- Diseases of the hematopoietic system
- Hypovitaminosis (glossitis is especially often a manifestation of vitamin B12 and A deficiency)
- Specific infections of childhood (measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria)
- Allergies
- Aphthous stomatitis
- Tongue damage as a manifestation of lichen planus.
The spread of the pathological process to the deep layers of the tongue leads to the formation of first eroded surfaces, and then ulcerative ones. This may predispose to the development of a tongue abscess or more diffuse purulent inflammation - oral phlegmon. Therefore, if ulcers appear, you should not delay your visit to the dentist!
Ulcers on the tongue can be acute or chronic. A number of factors contribute to the chronicity of the process:
- Long-term exposure to the causative factor
- Disturbance of the microflora of the oral cavity
- Reduced function of the immune system, incl. and against the background of leukemia.
Sores appear on the child’s tongue – what to do and why does this happen?
Mouth ulcers are always painful and unpleasant.
Unfortunately, they often occur in young children due to the characteristics of their body and a number of other reasons.
Many parents are not aware that some diseases also cause ulcers on the child’s tongue. Every adult must know what to treat, how to prevent and what not to do in order to help their child.
What are ulcers and what causes them?
Ulcers, or aphthae in other words, are a reaction of the oral mucosa to changes in the body, mechanical stress or the appearance of viruses and bacteria.
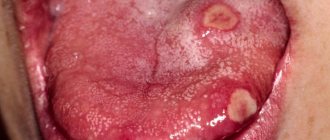
Photo of an ulcer on a child's tongue
All the reasons for their appearance can be divided into several large groups. Reaction due to illness: The immune system of children (especially young ones) is often weak and is susceptible to attack by many microorganisms.
In addition, babies have a tendency to put everything in their mouth, which causes a large number of bacteria to settle on the mucous membrane.
The most common causes of ulcers include the following:
- candidiasis (oral thrush). Formed when the body’s defenses decrease, as well as after taking antibiotics;
- stomatitis of various types;
- systemic diseases (scarlet fever, chickenpox, measles);
- herpes virus. Herpes is very contagious; it can enter a child’s body during childbirth from the mother or through contact with a carrier of the virus. If the baby becomes infected, he will become a carrier of herpes for life.
Mechanical damage:
- injury to the tongue when falling or eating food with sharp edges;
- with improper oral hygiene using a hard brush;
- with improperly growing teeth that constantly touch the mucous membrane of the tongue.
Chemical and thermal burns of the tongue occur when consuming hot food, drinks, products containing concentrated acid (vinegar, citric acid) or other dangerous ingredients.
Often ulcers appear for no apparent reason due to decreased immunity or lack of vitamins and microelements. In fact, this is how vitamin deficiency in the body is expressed.
Symptoms
Usually, parents immediately find out that the child has ulcers on the tongue, since they cause discomfort, react to any food and friction against the palate and teeth.
Refusal to eat and crying are characteristic symptoms of oral sores in babies.
Very young children find it difficult to suck breast milk or formula from a bottle, since the tongue is directly involved in this.
They communicate their discomfort by crying loudly. Older children are able to tell adults that something is bothering them in their mouth.
Since the nature of the origin of ulcers on the tongue can be different, their appearance also differs:
- It is not for nothing that candidiasis is called thrush, since it is characterized by a white, curd-like discharge covering the mucous membrane. A whitish or yellowish coating forms on the tongue, the tongue swells a little and after some time becomes covered with small ulcers, which in some cases may bleed. At the same time, a burning and itching sensation is felt on the tongue;
- Mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue is characterized by shallow, bleeding wounds, round or oblong, possibly somewhat deep;
- chemical damage is a burn of varying sizes, while the top layer in some area of the mucous membrane may come off, and a small ulceration will remain in the center;
- Herpes manifests itself in a characteristic way. Initially, small blisters form on the mucous membrane, which burst after a certain period of time, leaving small ulcers that exude;
- stomatitis can manifest itself in completely different ways, but more often it appears as characteristic whitish spots-ulcers, surrounded by an inflamed area of the mucous membrane that has a rich red color;
- with systemic diseases, corresponding inflammatory elements can form on the tongue and throughout the rest of the oral mucosa. A symptom of many childhood diseases are small blisters that burst, turning into wounds and ulcers.
General symptoms can help parents understand what is happening to their child and take immediate action, but it is best to consult a doctor. In some cases, the child may have an increased body temperature in addition to ulcers.
If self-treatment does not bring results or at least relief within several days, this is a reason to urgently consult a doctor.
Treatment
If a child has ulcers on his tongue, what should he do?
Usually, ulcers due to mechanical damage do not require any specific treatment and go away on their own in the shortest possible time.
The mucous membrane is unique in that it can quickly regenerate, especially in a young organism.
If ulcers are detected in older children who are no longer fed breast milk or formula, the menu should be reviewed.
Exclude from it traumatic foods, hot, sour, salty dishes. You need to monitor how the child brushes his teeth, cut his nails very short so that he does not injure his tongue again (this applies to children from one to 2 years old).
If the cause of the ulcers was damage from improperly growing teeth, the help of a dentist is required, because there will definitely be relapses.
If injury occurs due to improper oral hygiene, you should change the baby’s toothbrush, explain to him how to properly brush his teeth and control this process.
In any case, if ulcers are found on a child’s tongue, they must be disinfected.
A solution of hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine, Miramistin, is suitable for treating the tongue.
Infants and small children need to gently blot the ulcers with a cotton swab soaked in peroxide or chlorhexidine.
In this case, the preparations must be pre-diluted with boiled water in a 1:1 ratio. Older children who no longer accidentally swallow liquid can rinse their mouths with the same solutions, in the same proportions.
Pharmacy herbs have proven themselves well: chamomile, St. John's wort, sage, oak bark.
They can also be used to moisten wounds on the tongue or rinse your mouth.
If the ulcers bring severe discomfort or the temperature rises against their background, then it is necessary to give the child an anesthetic and antipyretic in a dose appropriate for his age. This could be Panadol, Nurofen or any other proven children's remedy.
After disinfecting the sores, you can lubricate them with local anesthetics. For children, special products are produced that relieve pain during teething, for example, Kalgel. This will help relieve itching, burning and pain in the tongue area.
In cases where the ulcers are caused by a fungus of the genus Candida and there is a cheesy coating, it is necessary to treat the baby’s oral cavity with a weak soda solution.
To do this, wrap a sterile bandage around your finger, moisten it lightly in a soda solution (1 teaspoon per glass of boiled water) and thoroughly wipe the child’s mouth. Baking soda is an alkali that effectively combats acidic environments, so the results will be noticeable.
Of the medications, children are most often prescribed Nystatin or Candide. You cannot use them on your own; you should definitely consult a doctor who will prescribe the correct dosage.
In addition, the child needs to take immunostimulating drugs and strengthen the body to avoid the recurrence of thrush and ulcers.
If the ulcers are caused by the herpes simplex virus, the pediatrician may prescribe antiviral drugs such as Acyclovir or Zovirax and immunomodulatory drugs such as Viferon, Anaferon, Interferon.
There are particularly severe cases of diseases that cause ulcers. Then the doctor can prescribe antibiotics and other necessary medications.
For an ailment such as an ulcer on a child’s tongue, treatment should in no case include treatment with iodine, brilliant green, potassium permanganate or alcohol-containing drugs. Firstly, this will only worsen the situation, the ulcers will be irritated even more, and this will bring severe pain to the child. Secondly, it is dangerous, since a child can swallow such substances.
Diagnostic search
What to do if your child has red or white sores? Do not self-medicate under any circumstances! It is necessary to seek help from a dentist, who will conduct a series of examinations to determine the nature of this condition. The diagnostic search includes the following tests:
- Cytological - examines the cellular composition of the mucous membrane and plaque on it. Using this test, the mycelium of Candida fungi is clearly detected, which indicates candidal glossitis
- Bacteriological – studies the bacterial composition of the oral cavity, identifying dysbiosis and inflammation of a bacterial nature
- Biochemical – makes it possible to determine the level of glucose in the blood and important vitamins on which the condition of the epithelial cover depends
- Immunological – for diagnosing disorders of the child’s immune status that predispose to the chronic course of ulcerative glossitis.
Treatment
How to treat ulcers on the tongue and under the tongue? Treatment must be aimed at creating rest for the mucous membrane and eliminating the possible causative factor. Therefore, it is recommended to change your eating habits:
- Avoid eating sour and salty foods
- Food should be at room temperature (neither hot nor cold)
- You should only eat food that is mechanically gentle (chopped).
In parallel, rinsing with antiseptic solutions is indicated. The most effective are potassium permanganate, chlorhexidine and furatsilin. These drugs help to subside the inflammatory process and prevent the reproduction and growth of pathogenic factors. However, in the presence of erosions, rinsing on your own is not enough. Daily qualified dental care is required. It consists of removing fibrin plaque from the eroded surface (mechanically and with the help of proteolytic enzymes) and subsequent application of an antiseptic to it.
But there are also erosions associated with vitamin deficiency. How to treat? In this case, both local and general therapy are required. The missing vitamins are selected based on the results of a biochemical blood test. At the same time, such children also need the help of a gastrologist, since very often there are concomitant diseases of the digestive system that impair the absorption of essential nutrients.
How to treat ulcers at home - traditional methods
As an additional treatment for ulcers on the tongue, you can use traditional medicine recipes:
- It is effective to use mouth rinses with home-prepared decoctions of plants that have antiseptic properties (calendula, sage, St. John's wort, viburnum berries, rose hips, chamomile, linden flowers). The brewing technology is simple - a tablespoon of dry plant is poured with 250 ml of boiling water. The container with the lid closed is left for 30-40 minutes. After filtering, you can carry out procedures. The oral cavity should be treated at least 5 times throughout the day. Keep the liquid in your mouth for about a minute each time you rinse.
- Ulcers will heal faster if they are treated with wound healing agents. These are mainly essential oils: sea buckthorn, calendula, rose hips, as well as aloe and Kalanchoe juices. They need to be applied pointwise, capturing only the affected tissue.
- Among the effective recipes, a solution based on soda , salt, iodine stands out (3 drops of iodine and a teaspoon of bulk ingredients per 200 ml of water). Applications and rinsing should be carried out at least 3-4 times a day for a week.
It is difficult to carry out medical procedures for babies less than a year old, and not all traditional methods can be used.
Therefore, the following treatment options for tongue ulcers have long been used for them:
- treatment of lesions with hydrogen peroxide;
- wiping the oral cavity, including the tongue, with a mixture of milk (100 ml), one yolk and honey (1 tsp);
- taking yarrow juice with honey (1 spoon 3 times a day for 3 weeks);
- processing with a mixture of egg white and water.
In what cases is it necessary to consult a doctor?
If you use folk recipes when identifying ulcers, you can get rid of them without the help of a doctor. But at the same time, the child’s condition must be stable.
If after a week’s treatment the lesions do not dry out or, in addition to them, other alarming symptoms appear (temperature, fever), then you should not hesitate to visit the clinic.