Probably every mother has encountered the problem of constipation in a child at least once in her life. How to treat, or even better, prevent such a condition? In order to answer this question, you must first understand why it occurs and why it bothers the baby so much. Let's start with this.
- What is considered constipation and how does it affect the child’s body?
- What happens: forms of constipation in children
- Causes
- Clinical manifestations
- Examination and diagnosis
- First aid
- What to do, how to help your child Correction of nutrition
- Medications
- Physiotherapy, massage and therapeutic exercises
What is considered constipation and how does it affect the child’s body?
From a physiological point of view, constipation is considered to be a situation when the intestines empty:
- irregularly;
- incomplete;
- untimely;
- with difficulty.
Any of the above problems, alone or in combination with others, can be considered constipation. Improper bowel movements are a problem that cannot be ignored. When digestive waste is not removed from the body, but remains in it, the processes of fermentation and decay begin. The toxins released during this process are absorbed into the blood and poison the entire body of the baby. The intestinal microflora is disrupted, iron deficiency develops, and inflammatory processes begin. As a result, such children:
- suffer from headaches;
- get tired quickly;
- sleep poorly;
- become capricious, irritable and even aggressive.
In advanced cases, the following symptoms are added:
- severe pain in the abdomen;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- elevated body temperature.
Did you know? Accidentally swallowing chewing gum cannot cause constipation - that's a myth! In order to block the intestines in this way, you need to eat a lot of chewing gum. In a single version, it will simply be digested, and the remaining part will be passed out without problems along with the feces.
From the solid feces accumulated in the intestines, it begins to increase in volume, very painful cracks form in the anus, which cause the baby special suffering precisely when trying to go to the toilet, as a result, the upcoming bowel movement begins to cause horror in the child, he begins to restrain the urge to do so emptying, and the problem grows like a snowball. One of the possible options for the development of this situation is the spontaneous leakage of feces from the anus, which can cause a child (especially those attending preschool institutions or school) psychological trauma, the consequences of which will haunt him throughout his life.

Thus, it is very important to relieve a child of constipation as quickly as possible, before this condition leads to the development of other somatic and psychological problems.
The main causes of bowel dysfunction
- In some cases, stool retention may be associated with serious diseases of the rectum or abnormalities in the development of the gastrointestinal tract. If you do not take this fact into account and give your baby medications against constipation, you can significantly worsen the course of the disease.
- In situations where stool retention in 3-year-old children is caused by functional digestive disorders, poor diet, lack or excess of nutrients, it is much easier to cope with it.
- Parents should know that the disorder can also be of a psychological nature: if one day the child went to the toilet very painfully, he may have a strong fear of the next bowel movement, which is why the baby himself will restrain the urge to defecate and resist visiting the restroom. Such behavior of the baby provokes even greater disturbances in the digestive system, and remedies for constipation alone cannot be used here, since it is necessary to take into account the psychological side of the problem.
Thus, it is necessary to select a method of treating constipation in children 3 years old only after the causes of the disorder have been clarified. In this case, it is best to use an integrated approach, involving nutritional correction and the use of safe laxatives.
What happens: forms of constipation in children
Depending on why constipation occurs, it is customary to distinguish three main forms:
- Functional. It is associated with impaired intestinal motility, while no systemic diseases of the internal organs are observed. This type accounts for more than 90% of all childhood constipation.
- Organic. Unlike the previous form, in this case we are talking about a specific anomaly of the large intestine. As a rule, such pathologies are congenital, manifest themselves quite quickly and require exclusively surgical treatment. Fortunately, they occur quite rarely.
- False. This form, in fact, is not constipation; the mother simply believes that her baby soils the diaper too rarely. Treatment boils down to providing psychological assistance to the mother.
Did you know? It has been noticed that starving, homeless, and poor people experience constipation much less frequently than prosperous and well-fed people.
Depending on the frequency of manifestation, constipation is divided into:
- Episodic - occur from time to time, usually during an acute illness, accompanied by an increase in body temperature (due to dehydration of the body and hardening of the stool for this reason), or as a result of taking certain medications;
- Chronic - occurs constantly: the child cannot empty his bowels for a long time, is afraid of this, and experiences serious general discomfort.

Types of constipation

Constipation in children, as in adults, can have different forms:
- acute form (stool retention is observed for 1-3 days);
- chronic form (problems with stool can be observed for several months or a year, while the amount of feces excreted decreases and its complete absence during the day).
In children 7 years old, the following types of stool retention are distinguished:
- Nutritional. Constipation is caused by improper and irregular diet. Large amounts of fatty, fried, protein foods with insufficient fluid intake.
- Dyskinetic. Associated with asynchronous work of intestinal motility in its different parts.
- Organic. Stool retention is caused by compression of the intestine or narrowing of its lumen by tumors or polyps.
- Conditioned reflex appearance or habitual constipation. Systematic suppression of the child's urge to defecate.
- Intoxicating. Slow peristalsis due to acute or chronic poisoning with toxic substances.
Treatment of constipation is carried out by a pediatrician depending on its type and type of course.
Causes
Constipation, as we have already understood, can occur for various reasons. The worst thing, of course, is if it is associated with a serious internal disorder, for example, abnormal intestinal structure, metabolic problems, etc. One of such diseases is the so-called Hirschsprung's disease. Its essence is that in a certain area of the intestine the nerve cells “do not work”. As a result, it constantly contracts, and the feces seem to be “blocked” above this area and simply cannot move further. In this case, the child needs urgent surgery.
A common problem in infants is colic. Dill water, Infacol, Babynos, Baby Calm, Bobotik, Plantex, Bifidumbacterin, Espumisan Baby are used against them.
Other dangerous pathologies accompanied by constipation include elongation of the sigmoid (dolichosigma) or one of the sections of the colon (dolichocolon), enlargement of the large intestine (megacolon), congenital narrowing of the intestine, etc.
The good news is that the likelihood that a child's constipation has such a fatal cause is extremely low. In children over three years of age, in the vast majority of cases, problems with bowel movements are functional.
Important! Constipation is never the only symptom of a dangerous disease! In 99% of cases in children and in 100% of cases in adults, bowel movement does not pose a threat to human life.
Functional constipation is very often caused by simple dehydration. Due to the lack of fluid, the child’s stool becomes hard, which makes it difficult for it to come out. Therefore, before you panic and consult a doctor, try to help your baby with the usual correction of living conditions: humidifying the air in the nursery, frequently ventilating the room and increasing the amount of liquid (fruit drinks, juices, compotes) in the baby’s diet.
Symptoms in a child such as abdominal pain and nausea may indicate: intestinal infection, adenovirus infection, appendicitis and staphylococcus.
The cause of constipation can also be poor nutrition, in particular, a lack of plant fiber (it is this that best stimulates the contractile function of the intestines) and an excess of high-calorie foods, as well as foods that have undergone excessive heat treatment.

The third possible cause of functional constipation is an unhealthy lifestyle. If a child sits a lot and spends little time outdoors in active games, his muscles do not receive full load. Weak abs and atrophied muscles of the anterior abdominal wall also have a depressing effect on intestinal motility.
Unfortunately, psychological factors are far from the least important among the causes of childhood constipation. The cleanliness of the toilet, its accessibility, comfortable temperature and pleasant smell in it - all this at the subconscious level helps us empty our intestines without hindrance. If a child is unexpectedly deprived of at least one of the external conditions under which he is accustomed to solving his delicate problems, he may well begin to experience first psychological, and then completely objective, physiological difficulties with bowel movements.
Did you know? Surprisingly, the problem of constipation is usually unknown to residents of communal apartments with one toilet “for thirty-eight rooms”: they simply cannot afford such a “luxury”. This is further confirmation that constipation very often occurs in the brain, and not in the intestines.
Psychological causes of constipation include other negative factors - stress, emotional (or physical) overload, problems in the family or school. In other words, any problems associated with the nervous system very often negatively affect the normal functioning of the intestines.

Finally, constipation can be caused by the presence of intestinal parasites in the baby’s body, such as pork or bovine tapeworms, whipworms, and roundworms. But the presence of Giardia in the intestines, as a rule, does not cause difficulties with bowel movements.
What is considered constipation in a child?
From the age of one and a half years and older, the child poops 1-2 times a day, and his stool is no longer mushy, but formed. If you are prone to constipation, the intervals between bowel movements become longer, and the act of bowel movement itself can be difficult. Constipation is also considered to be bowel movement with normal frequency if it is accompanied by pain and hardened stool.
Parents should pay attention to the following “bells” signaling a violation of intestinal function in a child:
- a child under 3 years old goes to the toilet less than 6 times a week;
- over the age of 3 years, the child has less than 3 bowel movements per week;
- the child complains of abdominal pain, in children it manifests itself as crying and anxiety;
- the process of defecation is accompanied by pain, straining, and occurs with difficulty;
- the stool is abnormal in nature: it separates into small “dry” fragments (sheep feces) or forms a very dense mass in the form of a thick cylinder;
- incomplete emptying is observed.
The systematic appearance of such symptoms should be a reason to contact a pediatrician. The duration of signs of constipation for more than 3 months already indicates a chronic course of the disease.
Why do children get constipated?
If the causes of bowel retention are not identified and eliminated, constipation can become chronic, and then it will not be easy to get rid of them. Many adults suffer from constipation for years, which begins in childhood. It is pointless to achieve regular bowel movements with the help of enemas and laxatives if you do not get rid of the factors that provoke the disease.
Organic constipation
Among the causes leading to constipation in children, organic ones are considered unlikely. In this case, defecation disorders are a consequence of intestinal abnormalities, congenital or acquired. Congenital pathologies, such as elongation of the sigmoid colon and lack of innervation of the large intestine, are usually detected and treated by the age of 2-3 years, since they manifest themselves acutely and almost from the first days of a child’s life.
Organic constipation in a preschooler should be ruled out if the lack of independent bowel movements occurs in the context of a normal diet and lifestyle and is accompanied by symptoms of indigestion. Bloating, gurgling, and abdominal pain can be caused by the accumulation of feces and gases in the intestines due to an obstruction formed in it. These can be tumors, polyps, adhesions, leading to acute or chronic obstruction. Treatment in this situation is usually surgical.
In most cases, intestinal problems in children are functional and psychological in nature.
Functional constipation

Functional constipation can be a consequence of:
- poor nutrition of a child for a long time, with a predominance of protein and fatty foods in his diet and a lack of plant fiber;
- chronic fluid deficiency in violation of the drinking regime, when the child drinks little or gets moisture exclusively from the “wrong” drinks (not water, but juices, tea, lemonades, etc.);
- imbalance of intestinal microflora, which develops against the background of antibacterial therapy and nutritional disorders and leads to putrefactive processes and weak peristalsis;
- food allergies, as a result of which the released histamines damage the intestinal walls;
- enzyme deficiency, when due to congenital pathologies and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, this or that food is poorly processed in the intestines;
- helminthiases, in which helminthic infestations disrupt intestinal function;
- rickets, which is accompanied by decreased tone of muscle tissue, including those located in the intestinal walls;
- iron deficiency in the body, due to which oxygen starvation of the intestinal muscles develops;
- hypofunction of the thyroid gland, the clinical manifestation of which is constipation;
- violations of the emptying reflex due to damage to the nervous system;
- abuse of drugs that affect the digestive tract (enzymes, probiotics, fixatives, antacids);
- frequent use of laxatives and enemas, which leads to the disappearance of the urge and the intestines getting used to external stimulation, losing their ability to independently get rid of feces.
These factors lead to disruption of intestinal motor function: they reduce peristalsis, wall tone, and damage the mucous membrane. As a result, the movement of digestive waste slows down and a “congestion” forms.
Psychological constipation in children
Constipation due to psychological reasons is also functional in nature, but is classified as a separate group due to the difference in approaches to treatment.
The urge to “big” occurs after feces, thanks to intestinal motility, reach its lower sections and irritate the nerve receptors located there. Unlike babies under one year old, in older children the process of defecation occurs consciously and is under the control of the central nervous system. But if a child is in uncomfortable conditions, he can hold back the urge for a long time, preferring to be patient than to go to the toilet in an unusual place. Suppression of the reflex to defecate leads to the accumulation of feces, its compaction, which at the time of defecation results in pain and injury to the anus.
Such problems often arise in children during the period of getting used to kindergarten, when they find themselves in an unfamiliar place (in a hospital, at a party) and in other situations. Constipation may accompany potty training in 2-3 year olds. Conscious restraint of defecation and prolonged ignoring of the urge sooner or later leads to the “losing” of the bowel movement mechanism itself, and constipation becomes chronic. A child may be afraid to poop even under normal conditions, since he reflexively expects pain.
Transient constipation
Each child can experience a “one-time” constipation when he ate something constipating, fell ill with a fever and signs of dehydration, or overheated outside in the heat. In this case, stool compaction is associated with errors in nutrition and temporary fluid deficiency in the body, the correction of which in itself leads to the restoration of normal consistency and frequency of stool. In such a situation, there is no need to take radical measures to eliminate constipation; it is enough to establish the “correct” diet and drinking regimen.

Clinical manifestations
Constipation in our minds is always associated with rare visits to the toilet. But is the absence of bowel movements for, say, a day always a problem worth worrying about? It turns out that if we are talking about very young children, then no.
Important! For a breastfed baby, bowel movements every other day or even once every three to five days, provided there are no signs of poor health, is the absolute norm. Moreover, this means that mother’s milk is of high quality, it is ideal for the baby and is almost completely absorbed by his body!
You should be concerned if, in the absence of bowel movements for several days, the child shows signs of anxiety, cries, is capricious, and does not gain weight well.
Symptoms of constipation include:
- a feeling of pain, heaviness, “bloating” in the abdomen, cramping pain without clear localization (after defecation the condition immediately stabilizes);
- severe gas formation, rumbling in the stomach;
- leakage of feces in small quantities (encopresis) - it can manifest itself in the fact that a child who has not visited the toilet has panties stained with feces;
- painful sensations during bowel movements;
- mood changes - fatigue, loss of appetite, weakness, irritability;
- hard and tense stomach;
- blood in stool;
- very hard stool, often in the form of lumps or balls.

And, of course, the main symptom of constipation is infrequent bowel movements.
The normal frequency of bowel movements is a very relative concept. In infancy, it can be several days, but as the child grows up, the stool usually becomes systematized. Thus, for children over two years old, the norm is to visit the toilet from twice a day to once every two days. However, if the child feels well, you should not specifically count how many times he empties his bowels. Excessive attention to this issue, especially if we are talking about an older child, can cause just those psychological problems that we talked about above.
Features of the problem depending on age
The causes of constipation in children depend on the age of the little patient. There are indicators of normal stool frequency in children:
- From birth to 9 months, the frequency of bowel movements is from 6 to 10 times a day. If the baby is breastfed, stool occurs more often. With the frequency of stools, the amount is small - about a teaspoon of mushy consistency. The cause of constipation in infants is the lack of water consumption by the nursing mother, and in artificially fed children - frequent changes in diet and lack of drinking. Constipation is considered if there is no stool for a day and its consistency is hard.
- Children from 1 year to 2.5 years go to the toilet at least 6 times a week, the stool is already formed. If a child has a tendency to constipation, then the intervals of going to the potty increase, and the bowel movement itself is painful.
- In children over 3 years old, the frequency of stool should be once a day or every 2-3 days. Depends on the composition of the food consumed and the amount of liquid drunk.
If bowel movements are difficult and the child strains a lot, there are frequent complaints of abdominal pain, the stool has become small and dry, then the child is constipated. This is a reason to consult a specialist, otherwise constipation will become chronic and will be difficult to treat.
Examination and diagnosis
If a child has the symptoms of constipation described above, and reasonable first aid measures have not led to relief of his condition, the baby may need to be examined. At least to make sure that there are no serious pathologies that caused constipation.
Such an examination begins with a preventive conversation. The age of the child is clarified, specific complaints are clarified (in addition to the violation of the frequency of stool), living conditions (temperature and humidity in the room, daily routine, etc.), diet, amount of fluid drunk, the child’s visit to a child care facility and the connection between the first signs of constipation and the onset of constipation. such a visit, etc. Very often, already at this stage, parents receive from the doctor the necessary recommendations that help solve the problem without special treatment.
If the doctor detects certain alarming symptoms, additional examination may include:
- rectal examination of the rectum (this makes it possible to detect existing cracks, scars, narrowing of the lumen, as well as neoplasms);
- Ultrasound of the pelvis, kidneys, abdominal cavity;
- X-ray or MRI of the spine (to exclude pinched nerve);
- stool analysis (for dysbacteriosis, for the presence of intestinal parasites, as well as a comprehensive study of the composition of stool);
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy.

Specific diagnostic methods that are used in such situations are anorectal manometry, endosonography, scintikolodefectography, electromyography, sphincterometry, colodynamic examination of the rectum and others, however, in most cases, the diagnosis and treatment of constipation does not require such complex examinations.
At the same time, to establish the cause of constipation and eliminate it, the therapist may need to consult with specialized specialists, in particular, a neurologist, gastroenterologist or psychotherapist.
Symptoms of the disorder
Constipation in children occurs:
- Organic (5%) occur in a child from birth and are a consequence of an anatomical defect in intestinal segments. Underdevelopment of the nerve endings of the intestinal walls leads to the fact that its lower sections narrow and the upper sections expand. This slows down the movement of stool. This pathology is rare. More often, there is an elongation of one of the sections of the colon, which begins to move uncontrollably and violently, disrupting the movement of feces to the exit. This disease occurs in children 3-4 years of age. Symptoms of organic constipation in infants are a decrease in the number of bowel movements and their short duration. The child experiences turbulence, bloating and pain in the abdomen due to the accumulation of feces in the intestines, when the obstacle described above prevents its exit.
- Functional constipation (95%) in children is very common and depends on many factors. During breastfeeding, the quality of stool depends on the mother's nutrition and the composition of the baby's complementary foods; a lack of water intake plays an important role. On artificial feeding - from frequent changes in formula, diet, lack of fluid. Excess protein and fat in a baby’s diet disrupts bowel regularity. Constipation occurs if the child has the following diseases: iron deficiency anemia, rickets, central nervous system damage during childbirth, intestinal dysbiosis, food allergies. Frequent use of drugs that stimulate digestion leads to intestinal dysfunction and constipation. Symptoms of functional constipation are: hard stool that looks like beans, straining during bowel movements, which takes up a quarter of the time of bowel movements, in one case out of four there is a feeling of not emptying the intestines, a feeling of obstruction of stool during bowel movements and stool less than 2-3 times a week.
Children aged 2 to 6 years are often embarrassed to go to the toilet and deliberately hold back their bowel movements.
Moving, getting used to kindergarten or parents' divorce, as well as potty training are psychological obstacles to bowel movement. Parental support is important here: it is necessary to talk to the child in time and explain how to go to the toilet correctly.
Dr. Komarovsky’s opinion on the causes and treatment of constipation in children:
First aid
If constipation in a child is not caused by any intestinal abnormalities, first aid to a small patient can be provided by the parents themselves. Of course, in the future it is important to try to adjust your child’s lifestyle and diet, but right now you need to help him have a bowel movement.
The most famous and radical remedy for constipation is an enema. Let’s immediately make a reservation that, strictly speaking, children should be given it only as prescribed by a doctor. If you decide to carry out this procedure at home, do it correctly. The water for the enema must be boiled, but cooled to room temperature (warm water will provoke the absorption of toxins released as a result of stagnant feces into the blood, and cold water will only intensify intestinal spasms).
Important! The volume of the enema should correspond to the age of the child: five-year-old children need to be given 0.5 liters of liquid, children from two to five years old - no more than 300 ml, babies over one year old - up to 250 ml, from six months to a year - up to 200 ml, three-month-old children - 60 ml , from birth to three months - 25-40 ml, depending on the exact age.
The enema fluid should be administered very carefully and slowly.

The next first aid method is to insert gas tubes into the anus to mechanically stimulate intestinal motility.
Rectal suppositories and special microenemas are also used.
Treatment of constipation in infants
Constipation in a 7-month-old child requires immediate evacuation of intestinal contents. Therapy for the condition is aimed at regulating bowel movements and eliminating the cause of the delay in defecation.
The most important thing in the treatment of infants is nutritional correction, which includes the following principles:
- sufficient amount of liquid;
- adherence to diet;
- optimal amount of fiber;
- use of probiotics;
- exclusion of foods that contribute to flatulence.
Food should be mechanically and chemically gentle, enhance intestinal motility and peristalsis and not cause putrefaction.

Recommended products for constipation:
- carrot;
- pumpkin;
- plum;
- beet;
- zucchini;
- dill.
It is recommended to exclude products:
- bananas;
- apples;
- rice porridge.
Children who are breastfed need to normalize their drinking regime. The child should be given purified, boiled water with the addition of fennel, compotes based on prunes and dried apricots.
Formula-fed children should be given only adapted milk formulas, since they contain the optimal amount of microelements and vitamins that help prevent the development of stool disorders.
What to do, how to help a child
When first aid has been provided, it’s time to think about how to make sure that you no longer have to resort to such unpleasant and even humiliating events.
For the treatment and prevention of constipation in children, such drugs as Acipol, Lactobacterin, Duphalac are suitable.
Nutrition correction
For this purpose, first of all, you should adjust the child’s diet. Since the main problem with constipation is hard stool and/or weak intestinal motility, we act in this direction.
The diet should consist of:
- Products containing coarse plant fiber. These are vegetables and fruits, the best being carrots, zucchini, pumpkin, cauliflower and Brussels sprouts, plums, melons, and watermelons. Cucumbers and tomatoes are less rich in fiber. If you have a choice between juice and whole fruit, choose the latter. In addition, preference should be given to raw vegetables, and if you heat-treat them, stick to al dente (undercook a little or leave them half-raw).
- Bran. This is also an excellent stimulator of intestinal motility, in addition, they remove bad cholesterol and other harmful substances from the body.
- Gray cereals, especially buckwheat.
- Foods containing potassium - apricots, peaches, plums (raw or dried), asparagus, walnuts.
- Fermented milk products (best in the morning on an empty stomach).

An important condition is that the child should eat a large amount of food (if it is vegetables, such a lunch will not be too high in calories). We need to fill the intestines and get them working.
Important! Food should be as coarsely processed as possible (not ground, twisted or overcooked).
Another important condition is to give your child as much water as possible. In the morning on an empty stomach, the baby should drink at least 200 ml of a cool drink, then during the day receive at least another liter in the form of compotes, soups, juices and clean, unboiled water.
Medications
It is known that laxatives are very often used for constipation. This method of treatment is also applicable for children, but you need to know that such drugs act differently. In particular, they can be aimed at:
- fluid retention in the intestines;
- strengthening its peristalsis;
- increasing the volume of its contents.
For this reason, it is very important to understand what exactly you are giving to your baby.
For example, if a child has accumulated hard stool in his body and is given a drug that increases intestinal contractions as a cure for constipation, serious trouble can occur. In order not to harm their children, parents should therefore consult a doctor, not a pharmacist. Nevertheless, self-medication (or rather, treating your child without consulting a doctor) in this case is quite acceptable. But only on the condition that the baby has no other symptoms besides constipation. Otherwise, the therapy is determined by the doctor, and, most likely, it will not be limited only to laxatives.

So, without a doctor’s prescription, a child can be given a mild laxative containing senna (Regulax, Senadexin, Glaxena and others) or liquid oils (castor, vaseline, almond, olive) for constipation. At the same time, parents should understand that the goal of treatment is not just a one-time bowel movement, but the development in the body of a reflex to regular bowel movements with a certain frequency. Therefore, having selected the appropriate dose of the drug, you need to continue taking it for at least 10 days (preferably up to two weeks). If the medicine does not help, contact your doctor immediately.
Safe medications for the treatment of childhood constipation are also:
- lactulose syrup (under any trade names, and you don’t have to buy expensive ones, you can use domestic ones). This drug has virtually no age-related contraindications. It stimulates the proliferation of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, which is why it is sometimes even added to dairy products;
- suppositories with glycerin (it is not absorbed by the body and does not harm it);
- candles with sea buckthorn oil.
Physiotherapy, massage and therapeutic exercises
Increasing physical activity and special procedures will also help develop and consolidate the habit of emptying the intestines at the same time.
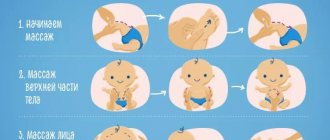
For example, regular morning exercises are extremely beneficial. After the child wakes up, drinks a glass of cool kefir or juice and performs several active exercises, feed him a “proper” breakfast and ask him to squat down, pressing his legs tightly to his stomach. If the urge to defecate is not apparent, massage the baby's tummy, while the child should rhythmically contract the muscles of the anus (for younger children, the mother massages the point between the tailbone and the anus).
For constipation, children are advised to take long walks, fresh air, active games, swimming, and skating. There are also special exercises aimed at stimulating bowel function, but a much greater effect can be achieved by simply playing football with your child until you drop. Offer the little ones a fun game: collect small objects scattered on the floor without getting down on all fours or squatting.
What not to do
For constipation, it is strictly contraindicated:
- poking in the anus with a thermometer and other objects;
- sticking laundry soap into a baby’s butt (this is an original Soviet know-how, which causes real horror in civilized countries);
- endure and restrain the urge to defecate;
- eat high-calorie, chopped or overly processed and refined foods;
- drink carbonated drinks and boiled water;
- sit at the computer for days on end;
- use laxatives and other drugs without a doctor’s prescription (except for the drugs mentioned above).
Prevention measures
To prevent your child from experiencing constipation, you need to follow simple rules:
- the room where the child is located should be cool and humid;
- The baby’s nutrition must be correct;
- he should receive plenty of fluid;
- going to the toilet should not be associated with psychological discomfort; you need to work on this especially seriously.

Constipation, even in childhood, is a delicate problem, but this does not mean that it is not necessary to talk about it. In the vast majority of cases, difficulties with bowel movements are not associated with any serious diseases, but they can cause serious inconvenience to the child, both physical and psychological. The sooner parents notice the disorder, the more tact and wisdom they show, the more painless the recovery process will be.
Constipation Diseases of children