Features of a baby's nose
While the baby is in the womb, he does not breathe through his nose. Only after birth does the baby begin to use the nasal passages for breathing. The nasal mucosa during this period is loose and abundantly supplied with blood vessels. Therefore, with any inflammation, it quickly becomes swollen.
The nasal passages are narrow compared to those of an adult, which causes breathing problems during a runny nose. In addition, they are short and located close to the ear canals. Therefore, children in the first year of life often suffer from otitis after a runny nose. The nasal passages are formed in a child only by the age of 4-5 years. Due to the short passages in the nose, mucus stagnates and crusts appear, which make breathing through the nose even more difficult.
Physiological runny nose in infants
As you know, a runny nose in adults occurs as a result of various diseases. But a child’s body is structured differently, and a runny nose is associated with the physiological characteristics of the child. A physiological runny nose lasts for an infant on average up to 2-3 months. And parents should know that such a runny nose does not always indicate pathology, but is only an adjustment of the nasal passages after a long stay in the womb.
Closer to 10 weeks, the nasal mucosa begins to adapt to the external environment; little mucus is produced, so dry crusts often form. After this, there is a trial version of large mucus production, during this period liquid snot is released from the nose. They do not affect the general condition of the baby, his sleep and sucking. You should not treat a physiological runny nose at this time, otherwise you can disrupt the natural process in the child’s nasal passages.
The only correct actions on the part of parents should be the following measures:
- Humidify the air in the room where the child is.
- Airing the room.
- Frequent walks in the fresh air.
A child’s runny nose does not go away for a long time
As a rule, standard nasal discharge stops already 7-8 days after the onset of the disease. Minor clear discharge may continue for a couple of days. A child’s runny nose does not go away for a long time if its active course is observed for more than two weeks. In most cases, additional symptoms are completely absent. A similar picture can be traced due to the further penetration of viruses into the nasal cavity and their active work. Additional reasons may include allergic reactions to various pathogens. Mechanical injuries often provoke a long, continuous flow of clear nasal discharge.
When a child’s runny nose does not go away for a long time, the problems may lie in the following:
- Complications after acute rhinitis due to the active action of bacteria. Viral pathogens in symbiosis with bacteria lead to the appearance of purulent brown discharge from the nasal cavity for several weeks.
- Teething. A runny nose is typical for children in the first two years of life. This process is caused by increased blood circulation in the gums. This leads to an increase in the amount of mucus produced that needs to be released.
- Prolonged runny nose with improper treatment. Incorrect use of vasoconstrictor drugs leads to a slower healing process and weakened immunity.
- Anatomical predisposition. A deviated nasal septum, either congenital or after injury, leads to a prolonged runny nose.
- Allergy. Contact with an irritant leads to the fact that a child’s runny nose does not go away for a long time. As soon as the interaction stops, normal functioning of the glands is restored.
For adequate treatment, it is advisable to understand why the child’s runny nose does not go away for a long time and take the necessary measures.
Runny nose during teething
During the period when the baby's upper teeth begin to erupt, snot may appear, which does not in any way affect the overall well-being of the baby. This is due to irritation of the nerve branches that pass into the jaw area, connecting the wings of the nose and the area of the teeth. The tissues located near the erupting tooth are irritated, and at the same time the nerve going to the nasal part is also irritated. On the same side, water may appear from 1 nostril. This condition is considered normal, doctors even have their own slang about this - dental snot. But if, during the period of teething, it became difficult for the child to suck because of a runny nose, his sleep worsened, the baby became whiny, and the body temperature rose above normal, then the cause of such a runny nose is some kind of disease.
A runny nose is a symptom of infection
At seven months, the appearance of rhinitis in a child may indicate an infection - viral or bacterial. How to cure a runny nose in this case? In this case, the pediatrician, after a diagnostic examination, prescribes antiviral drugs or antibiotics. Vasoconstrictor drops, saline solutions or preparations based on sea water are used locally.

An infectious runny nose in an infant can be of the following nature:
- The viral nature of the appearance of a runny nose. In this case, nasal discharge is abundant and clear. If body temperature rises, it does not exceed 38°.
- Microbial infection. The runny nose is long lasting. A week after infection, the discharge from the nose becomes green, the mucus becomes thick, and the body temperature sometimes exceeds 38°. The child has poor appetite and sleep suffers. All of these symptoms indicate a bacterial infection.
- Allergic cause. Snot resembles viral rhinitis. But allergic rhinitis is accompanied by sneezing and lacrimation. Children often suffer from diathesis and other skin rashes that are accompanied by itching.

Treatment options
If your child’s runny nose does not go away for a month or more, then treatment should be carried out taking into account the cause of the protracted illness.
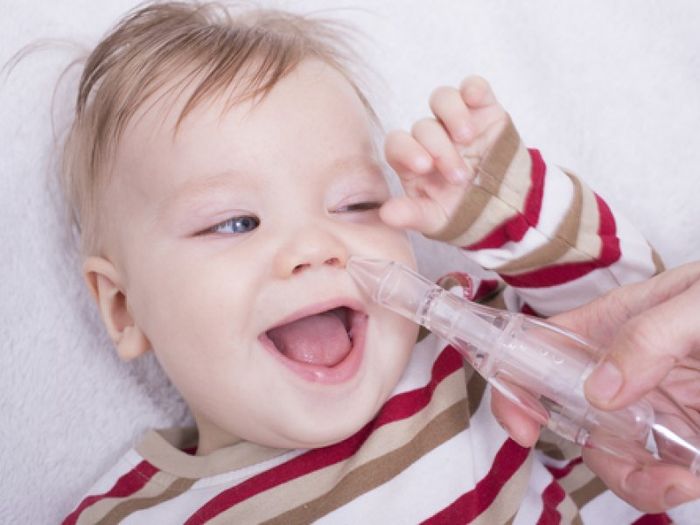

First of all, be sure to regularly rinse your baby’s nasal cavity. With this manipulation, you can wash out all bacteria, viruses, allergens and foreign bodies from the nasopharynx. Pathological mucous secretions are also removed. The most effective preparations used for rinsing the nose are those containing sea salt, as well as herbal decoctions.
Treatment of bacterial and viral rhinitis requires the use of herbal remedies that have a complex effect. They often contain oils with essential properties. In addition, these medications have antiseptic, mucolytic and deodorizing properties, which can significantly facilitate respiratory processes.
It is strictly forbidden to use vasoconstrictor drugs for more than a week, so as not to cause addiction in the child. If the patient is less than 24 months old, then this category of medications is not prescribed. Herbal inhalations and cold inhalations (with essential oils) are another mandatory element in the treatment of bacteriological and viral rhinitis.
An allergic runny nose can last a month or more. It requires immediate elimination of the allergen that caused it. Wet cleaning of the children's room should be done once a day, without using any chemicals. Sometimes you have to radically change a child’s entire diet. Specialists may prescribe antihistamines.
To prevent a runny nose, as well as many other diseases, it is worth remembering daily walks, as well as hardening your children. Health to you and your children!
General recommendations for the treatment of runny nose in infants
A runny nose in children 7 months and older is most often associated with illness. In this case, therapy for the underlying disease should be prescribed.
How to treat a runny nose in a 7 month old baby? In this case, the following treatment measures are taken:
- It is advisable not to increase the air temperature in the room where the baby is, the optimal value is +18°C. If the air is cool and humidified, the nasal mucosa will not dry out. In cases where it is not possible to purchase an air humidifier, you can use regular water containers or install an aquarium.
- If mucus accumulates in a child’s nose, it is removed using cotton wool. From 7 months, children can already use an aspirator, i.e. a device for sucking out mucus. As your baby gets closer to one year old, you can start teaching him to blow his nose on his own.
- In the first 6 months, the baby can put breast milk in his nose. It is believed to contain antibodies that fight viruses. But doctors advise not to take risks if there is a suspicion of a bacterial infection, since microbes will begin to multiply in a favorable environment.
- If you have a runny nose, you need to raise your child's head, placing a high pillow under it and his shoulders, so the mucus will not bother the baby.
- Vasoconstrictor drops for children over 7 months of age are allowed to be used, but only on the recommendation of a doctor, no more than 2 times a day and no longer than 3 days.
Treatment of a runny nose in a 7 month old child
Article last updated: 05/09/2019
The very first illness in a child’s life is usually a runny nose. Its appearance can be explained by both infection and allergies.
When faced with this problem for the first time, parents are at a loss when choosing medications offered by modern pharmaceutical companies.
First of all, you need to contact a specialist who will quickly determine the cause of the nasal runny nose and prescribe effective medications to combat the disease.
How and what to treat a runny nose in a 7 month old baby
Currently, you can find a huge number of nasal medications in pharmacies. The choice of medication depends on the cause of the disease.
Allergic rhinitis can be cured with special remedies presented in the form of drops or tablets. For a seven-month-old baby, the first option is more suitable. Firstly, the drops act locally, so the speed of action of the drug increases. Secondly, convenience - putting drops into a baby’s nose is much easier than giving a pill. Doctors recommend using Zyrtec or Fenistil.
Most often, a runny nose, which is of a bacterial nature, affects not only the nose, but the entire body as a whole. Therefore, immediate comprehensive treatment is required. If you have a high fever, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
They are available in the form of tablets and nasal drops. The former affect the entire body, the latter - exclusively on the nasal cavity. It is allowed to treat a child with such means for no more than five days.
For a seven-month-old baby, such drugs can only be prescribed in emergency situations. The most effective antibiotics in tablets are Flemoxin Solutab, Amoxicillin, Sumamed, and in drops - Isofra.
During such treatment, it is necessary to give the baby medications that maintain the intestinal microflora in a normal state. The most effective is Laktofiltrum.
Antiviral drops and syrups will help cure a viral infection in the nose. Drops include Derinat and IRS-19. Antiviral syrup "Cefekon" can be used as a supplement.
To reduce temperature during viral and bacterial infections, Nurofen and Paracetamol are used. These two syrups have a pleasant taste, and they come with a measuring spoon or syringe for the most convenient dosage of the drug. There is no need to lower the temperature to 37 degrees.
To ease breathing during feeding and day and night sleep, the use of vasoconstrictor drops is allowed. They cannot be used to treat rhinitis, since their frequent use can only aggravate the situation - the disease will drag on and become chronic.
A mandatory procedure for a child with a runny nose should be rinsing and cleansing the nose. At seven months, you can rinse the nose with saline solution, drops of sea water, or a homemade saline solution.
You should remove snot from a child’s nose using special devices: aspirators and small bulbs called snot ejectors. Before the procedure, drop a couple of drops of sea water or saline into each nasal passage to soften dried mucus and gently clean the nose. If you are afraid of damaging the mucous membrane, you can use cotton swabs.
Folk remedies
There is a category of people who do not trust modern medicines and prefer treatment with traditional recipes. For many years, there has been debate among experts about the safety of such a panacea. It is allowed to use both exclusively natural products and their combination with medications.
The most effective are drops prepared from vegetable oils and vegetable juices. They are usually prepared from carrot or beet juice, mixed with a few drops of onion and garlic juice and sea buckthorn or vegetable oil. Instilling aloe or Kalanchoe juice diluted half with water is considered very effective.
It is very easy to prepare a saline solution at home. It is enough to dilute one teaspoon per two hundred milliliters of water.
Tea made from cumin, anise and chamomile has general strengthening and healing properties. You can assemble such a bouquet yourself or purchase a ready-made one in the store.
Under no circumstances should you use breast milk as a nasal drop. Absolutely all doctors warn about the danger of developing fungus when using this method, and the benefits from this are no greater than from instilling tap water.
General recommendations and prevention
It has long been a known fact that it is easier to prevent a disease than to cure it. A few simple rules will help protect your child from rhinitis and other pathologies of the nasal mucosa that occur at the age of seven months.
Daily walks are not only educational, but also very useful. Being in the fresh air strengthens the baby's immunity. And since, starting from the age of six months, the immune-strengthening properties of mother's milk decrease significantly, it becomes simply necessary to walk every day.
It is imperative to observe the temperature regime in the apartment - no more than 18-22 degrees.
In a stuffy room, you are much more likely to catch rhinitis, because it is in such air that a favorable environment for the development of bacteria is formed. The room must be ventilated at least three to four times a day.
And in order to maintain air humidity, you can purchase a humidifier or simply place containers of water near the battery.
Any illness is a serious test for the baby and his parents. But with qualified and competent treatment, all fears recede. The child should be treated strictly according to the instructions prescribed by the doctor.
Source: https://rebenokrazvit.ru/rebenok-do-goda/bolezni/lechenie-nasmorka-rebyonku-v-7-mesyacev.html
How can you not treat a runny nose?
Everyone is interested in how to treat a runny nose in children from 7 months, but it is also worth remembering what not to do during this period:
- For small children, it is absolutely contraindicated to instill the juice of various plants, such as aloe or Kalanchoe, into the nose, as well as onion or garlic drops, carrot or beet juice. In this case, the baby's delicate mucous membrane can be significantly damaged. As a result, atrophic rhinitis will develop, and the child will lose his sense of smell.
- Instillation of essential oils into the nose. Their negative effect on the nasal mucosa in a 7-month-old child is as follows: the risk of developing allergies and getting a burn to the mucous membrane, gluing of nasal cilia, which opens a direct path for infections in the nasopharynx.
- In early childhood, mustard plasters, baths and dry mustard (for pouring it into socks) are prohibited.
During the cold season, you need to be especially attentive to your child. You should not take him out to crowded places. For prevention purposes, it is recommended to place plates of chopped onions indoors; they contain phytoncides that kill microbes.
If a runny nose does appear, its treatment is the task of the doctor; you should not experiment with a newborn child. The baby’s body is not yet strong, and any thoughtless intervention may threaten his health.