Pharmacological properties of common pear
The common pear is a fruit tree reaching a height of 30 m of the Rosaceae family.
Much less often, the pear can be found in the form of a bush. The root system is very powerful, well developed, with a taproot.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpolicyandsafetyru
The pear trunk, up to 80 cm in diameter, is covered with wrinkled brown bark. The wood is very durable, hard and heavy. The trunk is usually curved, often twisted.
The crown can be either narrow or wide, cone-shaped or convex. The branches are gray, covered with shortened, reduced shoots in the form of thorns or thorns.
The leaves are long-petiolate, round or oval with a pointed apex, entire, finely serrate along the edge, bright green, shiny above, matte below. Young leaves are covered with a felt coating - densely pubescent. In autumn, the leaves are always very bright, and their color ranges from yellow to red.
The flowers are large (2–3 cm), white or pale pink, regular (actinomorphic), solitary or form from 6 to 12 thyroid inflorescences. Flowers appear before the leaves appear and are located on pedicels up to 5 cm long. The corolla is white or pink, up to 3 cm in diameter. Each flower has from 20 to 50 red stamens. Pistil with 5 columns. Pear blossoms from April to May, even before the leaves bloom. One mature tree continues to bloom for 10–14 days.
Pear fruits can be of different sizes and shapes. One of them gave the term “pear-shaped”. In some varieties, the fruits differ not only in size, but also in color and taste. Pear fruits are distinguished by the abundance of mechanical tissues in the pulp - the so-called stony cells. The seeds are covered with a dense brown skin. The fruits ripen from August to September. The pear tree begins to bear fruit at the age of 3–8 years.
A pear lives up to 25–50 years. According to some reports, it can live up to 150 or even 300 years. Varietal trees usually die off before 30 years. Every year, up to 80 million tons of pear fruits are harvested worldwide.
Pear spreads mainly by seeds. Fruit-eating animals play an important role in seed dispersal in the wild. Young shoots can renew themselves as shoots and occasionally produce root shoots.
Pear is cultivated in the Central Black Earth Region, Volga region, Rostov region, and the North Caucasus. But even in the Non-Black Earth zone, this crop is not uncommon, however, in the harshest winters, the pear in Central Russia freezes slightly, and some trees simply freeze out.
In the wild, pears in Russia and Ukraine grow in deciduous and mixed forests, shelter belts, ravines, ravines, and forest edges.
Medicinal raw materials are fruits, dry and fresh. Pears are harvested ripe when they are well removed from the tree or begin to fall off on their own. The collection takes place from mid-August to the end of September.
The collected raw materials are dried in dryers and ovens at a temperature of 85 ° C, as well as in the sun. Store in boxes in a well-ventilated area. Shelf life 1 year.
A good harvest is repeated after 1–2 years.
The fruits contain 6–10% easily digestible carbohydrates (glucose, fructose, sucrose), about 3.5% pectin, 0.3% tannins, almost 2.5% fiber, about 0.3% protein, up to 1% apple, citric and other acids, phytoncides, flavonoids, carotenoids, vitamins C (up to 22 mg%), P, trace elements.
Anthocyanins have been found in the bark, stems and roots of pears.
The buds and leaves of young pear branches are rich in glycosides, vitamin C, and contain hydroquinone and flavonoids.
The juice of the fruit contains sorbitol (a sugar substitute), flavonoids, catechins, anthocyanins, carotenoids, and up to 21% fatty oil accumulates in the seeds.
Research has established that the pear itself and its leaves have the same chemical components as lingonberry leaf and bearberry - they contain the glycoside arbutin.
Boiled pear has diuretic, antipyretic, analgesic, strengthening, and antiseptic effects.
All varieties of pear have an astringent effect.
Juice from unripe fruits and leaves of wild pear has the ability to inhibit the growth of common pathogens such as staphylococcus, E. coli and dysentery coli.
Ancient physicians used pear juice and a decoction of pears to quench thirst in patients with elevated body temperature. In the Middle Ages, pears, pear juice and decoctions were used to treat gastrointestinal disorders, including dysentery. The pear, its juice and a decoction of the leaves were used as a good and absolutely harmless diuretic for severe swelling of the body associated with heart and kidney diseases.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytaboutru
In the East, it was believed that the sweet pear helped with hemoptysis and malignant lung ulcers, strengthened the heart, and its seeds helped with pulmonary diseases and strengthened the stomach.
In Russian folk medicine, boiled, baked pears, as well as a decoction of dried pears, are recommended to reduce cough in case of tuberculosis and diseases of the upper respiratory tract, fever, and diarrhea.
The fixing properties are most pronounced in wild pears, since their tannin content reaches 20%. Pear decoction is also used for the same purpose; it is recommended for kidney stones. Due to the high potassium content, taking pear fruits helps reduce the acidity of urine. Therefore, the solubility of uric acid salts increases and the formation of kidney stones is prevented.
A decoction of dried pears is also recommended for feverish conditions, colds and coughs, as it acts as an antipyretic and antifever agent.
Pears heal wounds, tan the walls of the stomach, quench thirst and soothe bile. The juice and decoction of the fruits are used as a diuretic and are prescribed for gallstone disease.
Thickly boiled pear juice is useful for bilious diarrhea. Children with dyspepsia are given a decoction of dried pears with oatmeal.

Pear juice is a source of vitamins P, C, carotenoids, and is recommended in dietary nutrition as a medicine for strengthening capillaries and for urolithiasis.
The ashes of highly astringent and slowly ripening pears are used to treat mushroom poisoning.
Pears are useful for palpitations, burning in the bladder, and promote digestion of food. Fresh pears are also included in the diet for diabetes and hypovitaminosis.
Pear seeds have antihelminthic properties.
For cosmetic purposes, ripe fruits are used, preferably wild, stale pears, which contain large amounts of vitamins and biologically active substances.
Pear decoction. Boil 100 g of dried pears, 75 g of oatmeal in 500 ml of water for 30 minutes, leave for 1 hour and strain. Drink 50–100 ml 3–4 times a day before meals for diarrhea, gastritis, colitis, urolithiasis, cough, colds, tuberculosis.
Thick decoction of pears. Prescribed as a lotion for headaches.
Pear jelly. Boil 100 g of chopped dried pears in 200 ml of water, strain, add sugar to taste, pour in starch diluted in cold water and boil, stirring. Use for diarrhea.
Use 100 g of fresh pears 2-3 times a day for diabetes and hypovitaminosis.
Pear mask. Place peeled and seeded pears in a bowl (glass or porcelain), rub thoroughly and apply a layer of up to 0.5 mm to the skin of the face, neck, arms, and chest for 15–20 minutes. Then rinse off the mask with warm water, apply a soft towel to the skin and lubricate with cream.
Pears should not be overused. They should be eaten in moderation and not on an empty stomach, but 0.5–1 hour after eating. After taking the pear, you should not drink raw water, or eat dense, heavy food or meat.
Constipation is a contraindication to the use of pears.
Due to the presence of stony cells that give the fruits graininess, eating pear fruit pulp in any form is undesirable for certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular pancreatitis.
The fruits of cultivated and wild pears are used in fresh, dried and canned forms, as well as for making jam, marmalade, marshmallows and various drinks (kvass, compote, cider, essences).
Dried and young pear seeds are used as a coffee substitute.
Due to their significant sugar content, pear fruits are suitable for distilling wine and vinegar; kvass is made from them.
The harmfulness of mushrooms is significantly reduced if they are cooked with pears.
In the gardens, rows of pears of different varieties are alternated with each other, since to obtain a good harvest of high-quality fruits, cross-pollination with pollen from a foreign variety is necessary.
The common (wild) pear is widely used in horticulture as a source material for obtaining rootstocks of various cultivated varieties.
The pear tree reaches a height of 15-20 m, sometimes up to 30 meters, belongs to the Rosaceae family. The crown is pyramidal, with shoots elongated upward, narrower at a young age, and becomes spreading over time. The bark of young trees is smooth, but with age it becomes uneven, cracks and separates from the trunk in entire sections.
The leaves are varied in shape and size, most are round, broadly ovate or elongated, the edges are finely toothed or serrated with pointed teeth (may be irregularly serrated), the upper side of the leaf blade is bare, shiny, dark green, the lower side is light green, sometimes pubescent , the top of the leaf can be with varying degrees of pointedness (elongated or short, tapering gradually or suddenly).
The flowers are five-petaled, white, sometimes with a pink tint, sitting on pedicels singly or in groups in the form of a shield or umbrella. According to the timing of flowering, pears are divided into early-, mid- and late-flowering, the flowering time depends on the place of growth and weather conditions, the duration of flowering, like the apple tree, is from 3-4 to 8-12 days.
The fruits are pear-shaped (tapering towards the top), spherical (resembling an apple), oval, elongated or cubic, color green, yellow, yellowish with a pink blush, sometimes with a touch of rust of different shades, different sizes, sweet and sour, inside the pulp in in the immature state, there are stony cells around the seed nest, which disappear as they mature;
It blooms in April-May, the fruits ripen in late September-October.
Food use
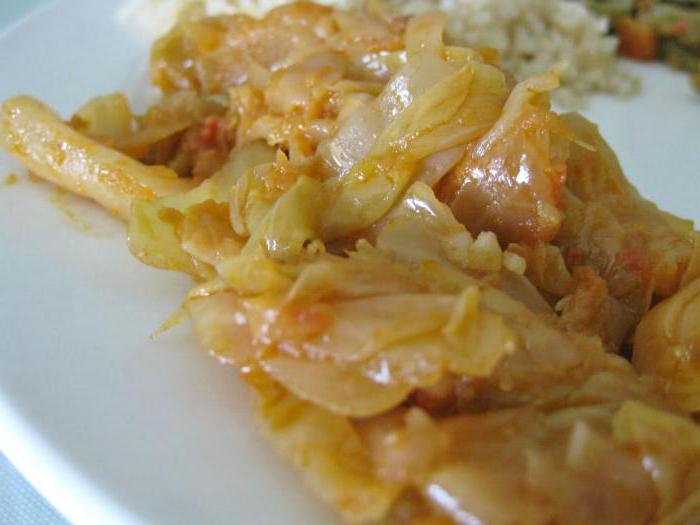
Let's start cooking cabbage
Stewed cabbage for breakfast in kindergarten is prepared as follows:
- Rinse the rice under running water. Then it is recommended to soak it in warm water for a quarter of an hour.
- Peel and finely chop the onion, saute it in oil until transparent.
- Finely chop the cabbage and add to the sauteed onion, simmer the vegetables for 10 minutes, while covering the frying pan with a lid (over low heat so that the onion does not burn). Stir the vegetables periodically.
- Add rice to the cabbage, pour broth over everything. It should cover the cereal. Add a little salt and simmer for 15 minutes.
- Grind the meat using a meat grinder or blender and add to the pan with vegetables. After adding the meat, the cabbage should be simmered for no more than 5 minutes.
That’s it, the cabbage stewed like in kindergarten (the photo in the article, it’s a pity, can’t convey its aroma) is ready. Bon appetit! Divide into portions and serve hot. Such stewed cabbage will delight not only the child, but also all family members.

How to plant a pear
Autumn planting and care differ from spring.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
In the south, autumn is warm and winter is very mild. When planted here in spring, the seedlings will not have time to grow stronger and will burn out during the dry, hot summer. A tree planted in the fall will have time to adapt and put down new roots before winter. In Siberia, autumn planting takes place in September. If seedlings are purchased in late autumn, they are dug into the ground at an angle and covered with peat, leaves and non-woven fabric to prevent them from freezing until spring.
In the fall, planting holes are prepared for trees that will be planted in the spring. A top layer of turf, about 20 cm, with grass down, is placed in a 70 by 70 cm hole. A support stake for a seedling 1.5-2 meters high is stuck into the center, the hole is filled in three stages with 2 buckets of 3-year-old manure, 2 buckets of peat or humus, 200 g of ash and fertile soil from the hole.
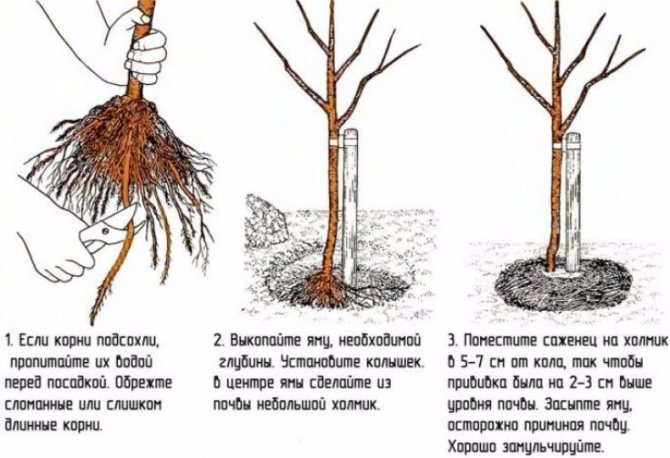
The procedure for planting pears.
Let's start cooking stewed cabbage in a slow cooker
Stewed cabbage like in kindergarten in a slow cooker is prepared as follows:
- Let's start with carrots. Wash and peel the vegetable, chop it into strips.
- Peel the onion and cut into half rings.
- Use young white cabbage, it is not only tasty, but ideal for stewing. You need to peel the top leaves from the vegetable and chop it. To do this, it is better to use a vegetable cutter. Thanks to it, the cabbage turns out to be thinly sliced.
- Pour a little vegetable oil into the multicooker bowl and add the carrots. Select the “Frying” mode. Cook the carrots in this mode for about three minutes, do not forget to stir.
- Then add the onions to the carrots and fry them as well.
- Next, add the shredded cabbage and continue cooking with the lid closed, stirring occasionally.
- After about 10 minutes, you will notice how the cabbage has decreased in volume. Remember to stir regularly, otherwise it may burn.
- Add salt and ketchup.
- Mix all the ingredients, set the multicooker to “Stew” mode - and that’s it, no need to look under the lid anymore. The cabbage will cook for 40 minutes. Thanks to this mode, the vegetables will simmer gently and release their juice, so there can’t even be any talk about water.
- As soon as the beep sounds, notifying you that the dish is ready, you can open the lid and try the stewed cabbage. It will turn out incredibly tender and juicy. It is worth noting that a young vegetable can be stewed faster. Serve the dish hot, garnished with some herbs. Bon appetit!

Pear care
A pear is shaped in the same way as an apple tree. It should be borne in mind that most of its varieties have a pyramidal crown type and sharp branch angles. Therefore, when growing skeletal branches, you need to give them an angle of 45-50° from a young age, and pruning should be carried out on the outer branches, expanding the crown for better illumination. In varieties with drooping crowns (Bere Giffard), pruning after the first years of fruiting should be carried out on rising branches.
Varieties with a pronounced ringed type of fruiting (Williams, Kieffer), with good annual growth, require shortening of the branches even after completion of formation.
After rejuvenating pruning of mature trees, much attention is paid to fatty shoots. Wen that grew at the base of the skeletal branches and on the conductor are removed to the ring, others are transferred to overgrown branches by tilting or pruning. They must first be thinned out so that they are placed at a distance of 15-20 cm from each other. A pear on a quince is formed in the same way as an apple tree on weak-growing rootstocks.
For the winter, young plants are wrapped in straw with herbs that repel mice: mint, wormwood, tansy and burlap treated with an anti-mouse drug - birch tar, dust, diesel fuel. The watering circle is cleared of weeds. The first year after planting, pears are watered at the root once a week with 1-2 buckets per seedling.
In the first 2-4 years, trees are fed with nitrogen during the leaf blooming period. Then - as necessary, if the tree is growing slowly and the foliage becomes atypically light. Organic matter is applied once every 3-5 years, mineral fertilizer - every autumn.
Stewed cabbage. Another great recipe
As you know, children are very picky eaters, so dishes that are not only healthy, but also tasty and beautiful should be prepared for them. Properly cooked cabbage will retain all its beneficial substances. Therefore, we will make stewed cabbage in a cauldron.
For preparation you will need:
- butter – 50 grams;
- cabbage – 500 grams;
- carrots – 1 pc.;
- onions – 1 pc.;
- salt to taste;
- tomato paste or one ripe tomato.
Pear propagation
There are several options:
- The seeds are planted in a pot with fertile soil. Over several years, the tree is transplanted two or three times into larger containers, then planted in the ground. This rather lengthy process does not guarantee high yields.
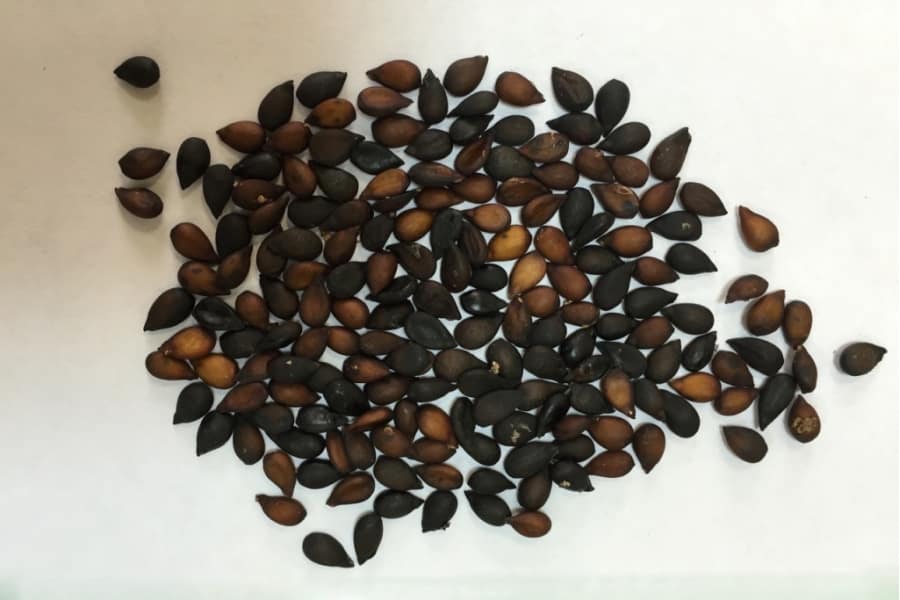

Pear seeds.
- Vegetative propagation is the best way to speed up the onset of fruiting: a cutting or part of a cutting with a bud of the variety you like is grafted onto a well-rooted fruit crop - rootstock. Quince, pear, and apple trees are suitable as rootstocks for pears; a good rootstock is the basis of the future harvest.
- The basal shoots that appear near the fruit tree are carefully dug up and separated from the mother plant in order to be transplanted from it. Such shoots have a developed root system, grow well and, with proper care, produce an excellent harvest in the future.
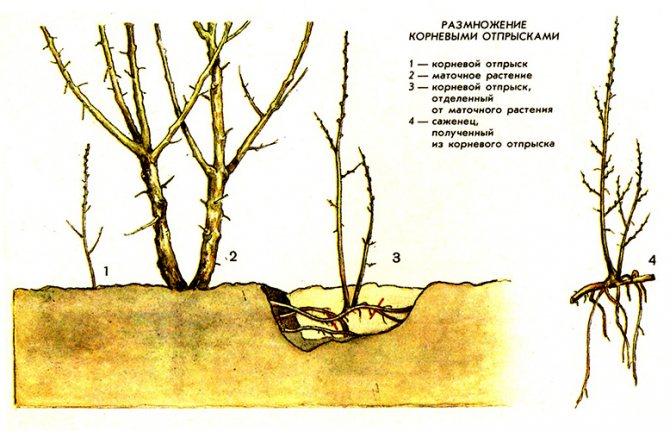
Basal shoots.
- When propagating by layering, carefully tilt one of the branches towards a box of soil and attach it to it so that part of the branch is in the ground. When roots appear on the branch, this part is separated from the tree and rooted in a new place. Such cuttings take root well.
- To propagate by cuttings, young side shoots are pruned in the morning, treated with growth activators and planted in fertile soil. The seedlings are intensively watered, fed with mineral fertilizers for 3-4 months, and after six months they are transplanted into open ground.
Preparing stewed cabbage
We will stew the cabbage without frying, because food prepared in this way is of no use to children. Finely chop the onion, grate the carrots using a medium grater. We take a cauldron and put butter on the bottom. Once it has melted, add the onions and carrots and simmer a little over low heat. Next add tomato paste and cabbage. Mix everything, add salt to taste. Simmer over low heat for an hour. The cabbage turns out boiled and stewed, juicy, with a delicate taste.

Pests, diseases and treatment of pear
- Green aphids infect young branches and leaves, and another dangerous parasite develops in the pest’s secretions – sooty mold. Before the buds begin to bloom, the pests are eliminated with Kinmiks, the flower buds are sprayed a second time with Agravertine, and the third time with Iskra when fruit ovaries appear. Solutions of dandelion, chamomile or garlic infusion are effective.
- The gall mite attacks young leaves. Colloidal sulfur is effective against it.
- The larvae of the pear moth devour ripe fruits. “Agravertine” solutions are used against the pest before and after the flowering period, “Kinmiks” is used 3 weeks after flowering, and another week later – the “Iskra” solution.
- From the influence of the pear psyllid (psyllid), the buds and fruits are deformed, the leaves fall off, the parasites are destroyed by the drug “Karbofos”, the plant is sprayed a second time after the flowering period with “Spark” or “Agravertine”. Decoctions of yarrow, chamomile, and dandelion also help.
- The leaf roller larvae twist the leaves into tubes and devour them. To combat them, the tree is sprayed with the preparation “Tsimbush” before the buds open.
In case of disease, you need to get rid of the infected parts of the tree as quickly as possible and begin treatment.
- Cytosporosis or stem rot from sun or cold burns is removed with a garden knife, and the wound is treated with copper sulfate and water or garden pitch.
- Moniliosis manifests itself as small brown spots on the fruits, from which the fungus is spread by the wind throughout the tree; the tree is sprayed with Bordeaux mixture or copper chloride in the spring and autumn.
- Rust (bright orange spots) on foliage is caused by a pathogenic fungus that can be transferred from juniper. The tree is treated with colloidal sulfur and Bordeaux mixture, in the spring - when buds appear, in the fall - after the leaves fall.
- A milky sheen appears from sunburn or from exposure to a wood-destroying fungus; when infected, the leaves become brittle and acquire a metallic tint. For prevention, all necessary agrotechnical measures are carried out: tillage, timely and sufficient watering, application of fertilizers.
- Black cancer appears as red spots on the leaves, wounds on the bark, black spots on the fruits; the bark is cut off with a garden knife along with a two-centimeter layer of healthy wood to prevent the spread of the fungus. Wounds are disinfected with copper sulfate, and for quick healing, mullein is used mixed with clay.
- Scab on foliage and fruits completely affects the tree with spots up to 3 cm in size if it is not treated immediately. The reason may be that the pears are planted close to each other; in the spring, the tree with near-trunk soil is treated with a 7% urea solution and Bordeaux mixture.
- Powdery mildew deforms young shoots with leaves, the plant is sprayed with colloidal sulfur in autumn and spring, and all measures for caring for fruit crops are strictly observed.
Other information about pear
Pear flowers produce a lot of nectar. Beekeepers believe that one hectare of pear orchard produces from 9 to 23 kg of honey and a lot of pollen.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyrightru
Pear wood is highly valued by craftsmen. It is strong and has a beautiful pattern, and lends itself well to processing and polishing. It is used by sculptors and craftsmen. It is used to make furniture, musical instruments, drawing boards, rulers, toys, etc. When coated with black varnish it looks like ebony.
Once upon a time, pear bark was used to dye handicraft carpets and fabrics brown.
Over 5,000 cultivated varieties of pears have been registered in the world, differing in the time of fruit ripening, their taste, color, shape, and size. Most of them are dessert. But there are others. For example, in England and France, varieties are specially bred from which peri is produced - a pear-like cider.
Now the pear ranks first in the world among pome fruit species in terms of area and harvest.
There are up to 18 species of wild pear growing in our forests, and they are also quite edible.
Common pear is widely used in steppe afforestation, field protection and roadside plantings.
A leafy pear tree is easy to recognize even when it bears no fruit. Orange-red spots often appear on the upper side of its leaves in autumn and spring, and pustules appear on the underside. These leaves are affected by rust fungus.