What it is?
Pseudotuberculosis refers to Far Eastern scarlet fever and yersiniosis. This is an acute infectious disease. With this disease, toxic, allergic and focal symptoms are observed. About 10 thousand cases of infection are diagnosed in Russia. Pseudotuberculosis affects all age groups, but most often occurs in children under 14 years of age.
Causes of disease in children
The carriers of the disease are animals. These can be rodents, large and small livestock, dogs, horses and poultry. A patient with pseudotuberculosis is not contagious.
The disease is transmitted by the fecal-oral route. For example, this may be contact with food that was in the habitat of the pathogen. You can get sick by consuming:
- unwashed vegetables and fruits;
- contaminated meat or dairy products:
- confectionery and bakery products that were stored in contaminated containers.
The disease occurs regardless of the time of year, but outbreaks are most often recorded between February and March. Pseudotuberculosis is often diagnosed in children who eat in canteens.
General information about pseudotuberculosis in children
origin of name
The concept of “pseudotuberculosis” was introduced by the German physician Ebert in 1885 .
He isolated the pathogen from various organs of rabbits. This disease began to be registered only in the middle of the 20th century, and before that it was believed that it was an animal pathology. Due to the similarity of manifestations with scarlet fever, the disease was initially called “Far Eastern scarlet-like fever.” It is interesting to note that Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (the causative agent of pseudotuberculosis) belongs to the same genus Yersinia, along with the causative agents of plague and intestinal yersiniosis.
Frequency of occurrence
Pseudotuberculosis is widespread throughout the world. Until the middle of the last century, this diagnosis was made only through pathological examination. Outbreaks of this disease are rare, mainly isolated isolated cases of pseudotuberculosis are observed.
The disease is registered throughout the year, but the risk of its development and spread is slightly higher when the temperature reaches +2-+4 degrees, which is due to the basic properties of Yersinia.
The most vulnerable age for this disease is 3-6 years. In younger children, pseudotuberculosis is practically not detected, which is due to the characteristics of their diet.
Characteristics of the pathogen
The causative agent of pseudotuberculosis is Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. It is a gram-negative bacterium that can adapt to various conditions. This is a very cunning microorganism. It is able to live in a warm-blooded host, in the external environment and actively reproduce at low temperatures.
Yersinia thrives on vegetables in the refrigerator or warehouse and even then actively reproduces. It grows well on both liquid and solid nutrient media. At the same time, the optimally comfortable temperature for this is room temperature, but at a temperature of +2-+4 degrees, the growth ability is preserved.
That is, Yersinia can live and reproduce both at room temperature and in the refrigerator. Moreover, low temperature can even enhance the activity of some of its enzymes.
Yersinia can withstand freezing, and dies in hot water only after 40 minutes-1 hour. She is only afraid of the effects of ultraviolet rays and chlorine-containing disinfectant solutions.
Thus, Yersinia is insidious, unpretentious and capable of living and reproducing in the external environment for a long time without a host.
Factors predisposing to the development of the disease
- The source of pseudotuberculosis in nature is wild and domestic animals. The carriers most often are rodents (mice, rats, voles), which live in vegetable stores, warehouses, and basements.
- Infection can also occur from domestic animals - rabbits, cats, guinea pigs, dogs.
- Infection and development of the disease is possible through direct contact with animals, during cutting of meat or its insufficient heat treatment.
- Unpasteurized milk can also be a source.
- A significant role in the occurrence of pseudotuberculosis is played by the consumption of vegetables and fruits contaminated with Yersinia in the soil or during storage.
- We should not forget that environmental factors can also be sources - water, soil, in which Yersinia not only live, but also actively reproduce.
Symptoms of pseudotuberculosis
In children, a localized form of the disease is most often diagnosed. The disease begins suddenly. The baby's body temperature jumps to 38-39 degrees. The child experiences the following symptoms:
- chills;
- vomit;
- loose and frequent stools;
- abdominal pain;
- headache;
- general weakness;
- intoxication of the body;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
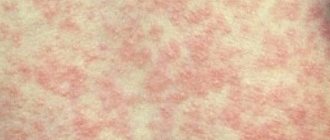
Fecal masses acquire a porous structure and a green tint. The presence of blood clots indicates damage to the colon. The baby has joint pain and may look swollen. On the third day after infection, a scarlet rash appears. With pseudotuberculosis, the child's tongue becomes covered with a white coating, and after 2 weeks it acquires a crimson tint.
Pseudotuberculosis: symptoms in children (photo)
Pseudotuberculosis in children provokes severe symptoms after the incubation period has expired, which lasts from 3 to 18 days. An acute manifestation of the disease is characteristic: a sharp increase in temperature above 38 degrees. Cases of gradual increase in symptoms are much less common.
At the initial stage, pseudotuberculosis in children has the following symptoms:
- weakness;
- headache;
- insomnia;
- decreased appetite;
- chills;
- soreness in muscles and joints;
- nasal congestion;
- cough;
- abdominal pain;
- nausea and vomiting.
When examining a child, the doctor notes typical symptoms of pseudotuberculosis , namely hyperemia (redness) of the neck and face, pallor of the nasolabial triangle, hyperemia of the conjunctiva, and a rash on the child’s wings of the nose and lips. The appearance of a gray-white coating on the tongue is also characteristic. Cleansing of the tongue occurs on the third day, the mucous membrane acquires a crimson hue.
The development of symptoms occurs gradually, the peak of the disease occurs 3-4 days after the onset of manifest signs of the pathological process. At the peak of the pathology, intoxication symptoms worsen, the temperature reaches maximum values, a rash on the body and damage to internal organs is possible.
In some cases, the following striking symptoms may appear:
- “glove” symptom - a rash on the hands in the form of a pinkish-bluish coloration of the hands;
- “sock” symptom - a rash on the legs in the form of a pinkish-bluish coloration of the feet;
- the “hood” symptom is a rash on the face and neck in the form of redness with a hint of cyanosis.
Routes of infection
The infection enters the body through the oral cavity along with contaminated food and drinks. The virus reaches the intestines and infects lymphoid formations. Next, the infection penetrates into the mesenteric nodes. Contact with an infected person does not pose a threat.
We recommend: Brain cyst in a newborn
In some cases, the connective tissue is immediately affected, where the virus begins to actively multiply. In this case, bacteremia occurs, which distorts the clinical picture of the disease. Through the circulatory system, the virus infects the spleen, kidneys and lungs.
Treatment of pseudotuberculosis in children
Levomycetin is prescribed for the treatment of pseudotuberculosis. The therapeutic course should last about 2 weeks. It eliminates fever, relieves symptoms of intoxication of the body, and also reduces the risk of exacerbation.
Depending on the child’s condition, it is recommended to take symptomatic and pathogenetic medications. To eliminate the severity of intoxication, Ringer-Locke solution is used.
In severe cases, corticosteroid drugs are prescribed. During treatment, the child must remain on bed rest and diet. Discharge is made only after complete clinical recovery. To confirm, 2 bacteriological examinations are carried out.
Treatment of pseudotuberculosis
The most effective treatment for patients with pseudotuberculosis is chloramphenicol (0.5 g 4 times a day) until the 5th day of normal body temperature, but not less than 10-14 days. The use of tetracycline, gentamicin, rifampicin, streptomycin, Bactria, Furazolin is also effective. Due to frequent relapses of the disease, drugs that enhance immunity are used: pentoxyl (0.2-0.4 g per day), methyluracil (1 g 4 times a day), sodium nucleinate (0.25 - 0.3 g 3 times a day). All patients are prescribed a complex of vitamins and desensitizing drugs. If necessary, detoxification therapy is carried out - rheopolyglucin, glucose solutions with vitamins, Ringer's solution. In severe cases, glycocorticosteroids are prescribed at a dose of 30-40 mg (0.5-2 mg per 1 kg of body weight) per day based on prednisolone. For arthralgic patients, NSAIDs are added. In the abdominal form with signs of mesadenitis and appendicitis, it is mandatory to examine a surgeon to decide on surgical intervention.
Complications
If treatment is incorrect or untimely, dangerous complications can occur. These include the following clinical conditions:
- hives;
- Quincke's edema;
- nephritis;
- arthritis;
- renal failure;
- erythema nodosum;
- pneumonia;
- myocarditis;
- Reiter's syndrome.
If complications occur, the doctor prescribes symptomatic therapy aimed at eliminating the disease and improving the general condition of the small patient.
Therapy methods
Treatment of pseudotuberculosis in children should be carried out in a hospital setting. If a particularly severe case is detected, then bed rest is necessary until the fever disappears. It is worth immediately noting that therapy should be comprehensive. After all, using all methods together gives excellent results.
Let's consider the main ways to cope with pathology:
- Taking antibacterial drugs. Among them are Netilmicin, Cefotaxime and Gentamicin.
- Use of detoxification agents (plasma replacement drugs, glucose-saline solutions). You can also add heart medications and vitamin complexes here. These drugs are aimed at eliminating symptoms, which is one of the most important parts of treatment.
- Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Naklofen, Diclofenac sodium). The most effective drugs in the fight against the icteric form are Karsil, Hepatosan, and Essentiale Forte N. Therefore, if a patient has a problem of this kind, the doctor will definitely prescribe these medications.
- Special diet. You need to adjust your diet and stick to proper nutrition for three or four months, even after the symptoms disappear. It is necessary to exclude spicy, fried and fatty foods; even concentrated broth is not allowed.
READ ALSO: New Line - a professional line from the Cora brand / Reviews of cosmetics and perfumes - Kosmetista
Prevention
There is no vaccine against pseudotuberculosis. To prevent the development of such a disease, it is necessary to adhere to the following preventive measures:
- All rats and mice should be exterminated in the house.
- Food products must be stored in accordance with all hygiene requirements and standards.
- A child should not be given raw water.
- Contact of the baby with street animals and birds should be excluded.
It is important to have explanatory conversations with your child and tell him about the dangers of dirty water and eating unwashed fruits and berries. It is recommended to completely avoid purchasing fast food from street outlets.
Pseudotuberculosis causes general intoxication of the body and affects the abdominal organs. Often the symptoms of the disease are disguised as other diseases, which complicates diagnosis. No specific prevention is required, just follow all hygiene standards and avoid contact with street animals.