How premature? Degree of maturity of the newborn
Typically, the baby's body weight is very dependent on the stage of pregnancy. A premature baby is significantly different in appearance from a full-term baby. Premature babies, in addition to low weight and height, are characterized by disproportionality in their physique, their skin is more hyperemic (red), their bones are soft, and there may be non-fusion of cranial sutures. In girls, the labia majora are underdeveloped (they do not cover the labia minora), and in boys, the testicles are not descended into the scrotum.
If a child is born with a body weight of less than 1.5 kg, then he is considered very premature, and with a body weight of less than 1 kg, a child is considered a fetus. To determine the severity of prematurity, in addition to weight and gestational age, other signs are taken into account, such as the presence of pathological conditions, compliance with the degree of maturity, the presence of diseases in the mother, etc. Determining the degree of maturity is a very important sign.
Modern medicine is improving specialized care for such children, and even in the most severe cases there is every chance of even a very premature baby being born.
The degree of maturity is determined by the child’s reaction, the presence of reflexes, the state of muscle tone, motor activity, ability to retain heat, etc. Even premature babies weighing about 2 kg, if they are healthy, can be quite active, have good tone, reflexes, be able to suck, etc. Children born with a body weight of about 1.5 kg can suck from a bottle by the first week of life.
The situation in children is much more difficult if the woman’s pregnancy was fraught with complications and the child could suffer, for example, from intrauterine hypoxia. Such children are usually born in a more severe condition. The most difficult babies are considered to be those born with a body weight of 900 g or less. Despite the apparent severity of the health of these children, doctors have experience in caring for children even with such a body weight. Due to the immaturity of many internal organs and the risk of developing pathological conditions, a premature baby is immediately given a set of measures in order to create the most optimal conditions. After birth, the baby is immediately sucked out of mucus from the upper respiratory tract, and mucus from the stomach can also be sucked out. If the child does not breathe or breathes poorly on his own, he is given artificial ventilation. The baby is also given the necessary medications to maintain his health.
Depending on his condition, the child is placed in a specially designed incubator. The design of the incubator allows you to create a microclimate inside it that is suitable for a premature baby. The temperature is set depending on the degree of prematurity of the child, and air humidity must also be regulated. The incubator allows you to monitor the child’s condition and carry out many manipulations without removing him from it. The length of stay of the baby also depends on the child’s body weight, then the child is transferred to an open incubator, and then transferred to a specialized department.
Data on the physical condition of premature newborns, taking into account gestational age (G.M. Dementyeva, E.B. Korotkaya)1
| Gestational age (weeks) | Macca body (r) | Body length (cm) | Head circumference (cm) | Chest circumference (cm) | Weight-height coefficient |
| 28 | 1124 ± 183 | 35,9 ± 1,8 | 26,6 ± 1,9 | 23,9 ± 1,9 | 31,2 ± 3,9 |
| 29 | 1381 ± 172 | 37,9 ± 2,0 | 28,0 ± 1,5 | 25,7 ± 1,7 | 36,3 ± 3,3 |
| 30 | 1531 ± 177 | 38,9 ± 1,7 | 28,9 ± 1,2 | 26,4 ± 1,4 | 39,4 ± 3,7 |
| 31 | 1695 ± 221 | 40,4 ± 1,6 | 29,5 ± 1,5 | 26,7 ± 1,6 | 41,9 ± 4,3 |
| 32 | 1827 ± 267 | 41,3 ± 1,9 | 30,2 ± 1,6 | 27,9 ± 1,9 | 44,1 ± 5,3 |
| 33 | 2018 ± 241 | 42,7 ± 1,8 | 30,6 ± 1,2 | 28,1 ± 1,7 | 46,4 ± 4,6 |
| 34 | 2235 ± 263 | 43,6 ± 1,7 | 31,3 ± 1,3 | 28,9 ± 1,7 | 49,9 ± 4,9 |
| 35 | 2324 ± 206 | 44,4 ± 1,5 | 31,9 ± 1,3 | 29,6 ± 1,6 | 51,7 ± 4,6 |
| 36 | 2572 ± 235 | 45,3 ± 1,7 | 32,3 ± 1,4 | 30,1 ± 1,9 | 53,6 ± 4,9 |
| 37 | 2771 ± 418 | 47,6 ± 2,3 | 33,7 ± 1,5 | 31,7 ± 1,7 | 57,9 ± 6,6 |
| 38 | 3145 ± 441 | 49,6 ± 2,3 | 34,7 ± 1,2 | 33,1 ± 1,6 | 63,6 ± 6,9 |
| 39 | 3403 ± 415 | 50,8 ± 1,6 | 35,5 ± 0,9 | 34,3 ± 1,2 | 66,9 ± 6,6 |
| 40 | 3546 ± 457 | 51,5 ± 2,1 | 35,7 ± 1,3 | 35,0 ± 1,7 | 68,8 ± 7,5 |
What determines the body weight of the unborn baby?
"How much does he weigh?" - a question that every mother asks the midwife. A baby's weight at birth is of great importance for his future health. That is why this parameter must be kept under control throughout the pregnancy.
Normally, a full-term newborn should weigh 3200–3500 grams with a body length of 50–51 centimeters. Experts note that deviations from these generally accepted indicators, as a rule, indicate certain problems with the baby’s health: excessive weight may hide some endocrine disorders, for example, diabetes, and underweight may indicate weak immunity. However, hereditary predisposition also plays a significant role here. If large babies have always been born in your family, then you also have a great chance of giving birth to a “hero.” In some families, on the contrary, all children from generation to generation are born with low body weight and do not have any deviations in further development. It has been noticed that most often children with low body weight are born to thin parents of short stature.
How to measure the weight of an unborn baby A gynecologist determines the circumference of the abdomen and the height of the uterine fundus using a measuring tape. These parameters are key to determining the approximate weight of the fetus. Obstetric formulas are used to calculate weight. The simplest: the abdominal circumference (in cm) is multiplied by the height of the uterine fundus (in cm). This formula is very approximate, as it does not take into account the thickness of the subcutaneous fat of the expectant mother. It should be noted that a large belly during pregnancy does not mean that the baby will necessarily be born large. The abdomen may be voluminous due to polyhydramnios or excess weight of the woman.
Olga Sekirina, gynecologist-endocrinologist, doctor of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences: “The baby’s weight is genetically determined. The weight of the fetus decreases when the conditions of intrauterine existence worsen - with a lack of oxygen and nutrients, malnutrition occurs. The baby is born on time, but his weight is below normal. Under normal conditions, a child inherits weight from his parents. If mom and dad are overweight, a tendency to which they have inherited, this will affect the formation of the fetus. Birth weight is especially closely inherited. If the future father was born weighing 4600 g, then the child will have a similar weight, regardless of gender. Children of such parents are born with a gigantic weight of 5–6 kg, through cesarean section. To normalize the weight of the fetus, pregnancy without complications, vitamin therapy, a healthy diet, and most importantly, weight gain during pregnancy should not exceed 7–9 kg. An increase of 15–20 kg reduces the oxygen supply to the fetus. The body requires oxygen in the same way as the fetal tissue, but the baby's share decreases due to the increase in the body of the expectant mother. This is exactly how malnutrition (malnutrition) and hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the fetus occur.”
Low-weight baby Low- weight babies include babies whose birth weight is less than 2500 g. If we are not talking about a constitutionally low-weight fetus, when the small weight of a healthy baby is inherited from the parents, then a small fetus may indicate a pathology - intrauterine growth retardation syndrome (hypotrophy). Hypotrophy can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. With symmetrical, all organs are reduced evenly; with asymmetrical, the brain and skeleton develop normally, but the internal organs suffer. The first signs of malnutrition may appear at 24–26 weeks, and a symmetrical shape is noted. The onset of the syndrome after 32 weeks is characteristic of the asymmetric form, usually accompanied by fetal hypoxia.
Reasons for the development of malnutrition ✓ Smoking and drinking alcohol cause severe vasoconstriction and reduce uteroplacental blood flow. ✓ Chronic infections: tonsillitis, bronchitis, pyelonephritis, cardiovascular diseases, anemia, respiratory diseases. All diseases in which the expectant mother’s body suffers from intoxication and oxygen deficiency most often cause asymmetric malnutrition, especially in the last trimester of pregnancy. ✓ Age of the expectant mother. Less than 15 years old - the body of a girl who is too young is not yet ready for the stress of pregnancy. Over 35 years old - a woman often comes to this age already with a “baggage” of chronic diseases. ✓ Multiple pregnancy, when nutrients have to be divided between two (three) babies. All these factors interfere with the normal functioning of the placenta, which provides the baby with everything necessary. As a result, the transport of nutrients is disrupted, and subsequently the gas exchange of the fetus, which leads to a delay in its growth and the development of intrauterine hypoxia.
What threatens Low birth weight babies tolerate childbirth worse, they more often develop hypoxia and asphyxia, and neurological disorders. Children who suffer from oxygen deprivation often develop lung diseases. This is explained by the immaturity of the lung tissue - the bubbles in the lungs do not expand completely, which contributes to the penetration of infections into the respiratory alveoli. Such newborns have difficulty adapting, suffer from hyperexcitability, increased or decreased tone, do not gain weight well, and may lag behind in psychomotor development. The consequences of the condition can affect even at an older age. Recent studies have shown an association between low birth weight and the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, obesity, non-insulin-dependent diabetes and elevated blood lipids. These diseases are associated with congenital pathology of the endocrine system in low birth weight babies.
Treatment and childbirth Vasodilators are prescribed to improve blood supply, drugs that relax the muscles of the uterus - its contractions impair blood flow. Medicines are also used against fetal hypoxia, since it usually accompanies malnutrition. The timing and method of delivery depend on the condition of the baby. If therapy is going well, there is no point in rushing things. It’s another matter if, despite all efforts, the baby does not gain weight, then they resort to early birth. The operation is performed if the baby is too weak to be born naturally.
Large baby A child is considered large if at the time of birth he weighs 4000 grams or more. According to recent studies, the incidence of large fetus births is quite high and varies between 8–8.5%. Babies weighing more than 5000 g are rare - 1 in 3000–5000 births. Reasons ✓ Post-term pregnancy. Despite the missed due date, the baby continues to grow, which inevitably leads to him gaining excess weight. ✓ Diabetes mellitus. Causes an increase in glucose levels in the baby, which stimulates excessive secretion of insulin - growth hormone - in his body. In this case, special pregnancy management is required. Most likely, you will have to go to the maternity hospital no later than the 32nd week so that doctors can keep the sugar levels in the blood and urine of the expectant mother under control. Very large babies are also often born to mothers with hypothyroidism, in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. Such children, as a rule, suffer from metabolic disorders. ✓ An incorrectly prepared diet for the expectant mother is one of the most common reasons for the birth of an oversized baby.
What threatens Large newborns are more likely to have birth injuries, for example, a fractured collarbone or cephalohematoma (an accumulation of blood under the periosteum of the skull). They often suffer from metabolic disorders. If the baby suffered intrauterine hypoxia or asphyxia during childbirth, then disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system may be observed. Such babies must undergo neurosonography, and they are regularly observed by a neurologist. Fat people, as a rule, are big lazy people and do not like to move, so they have delays in motor development.
We give birth to a “hero” Such births, as a rule, take longer, since the passage of the baby’s large head through the birth canal takes more time. Difficulties may arise if the baby lingers in the mother's womb - his skull bones are denser and adapt less well to the birth canal. Due to overstretching of the uterus, labor may be weak. Be prepared to have an episiotomy. This will protect against rupture of the birth canal and injury to the rectum. The question of a caesarean section may arise: ● with an oblique or transverse position of the fetus and breech presentation; ● if there has already been an operation; ● with a clinically narrow pelvis; ● during complicated pregnancy; ● if the baby suffers during a post-term pregnancy.
Let's eat right! The weight of the baby largely depends on your diet. Can't give up cakes, fatty meats and fried potatoes? In 9 months you will get a well-fed cherub with thick cheeks. Following fad diets even during pregnancy is the other extreme. This can lead not only to the birth of a low birth weight baby, but also to miscarriage. Except in special cases, the expectant mother does not need a special diet. The main thing is that the diet is balanced and varied. At the same time, do not forget to monitor your weight gain, especially in the 2nd half of pregnancy. You should not gain more than 300–350 g per week. The total number of kilograms gained depends on your constitution. With a normal build - 10-12 kg, thin - up to 14 kg, overweight - no more than 7-9 kg.
First trimester Calorie needs are no different from the usual norm before conception. At the same time, remember that the baby’s organs are now being formed. Provide him with all the necessary elements. Folic acid. Deficiency leads to low baby weight and nervous system defects. Introduce liver, lentils, spinach, and wholemeal products into your diet. It is recommended to take folic acid in the form of a supplement. Vitamin B12. The deficiency leads to impaired lipid metabolism in the fetus, and subsequently to obesity. Sources of vitamin B12 are meat, liver, yolk, milk. Zinc. Deficiency can cause low weight and weak immunity. Do not give up beef, pork, dairy and seafood, and cereals.
II trimester The baby is rapidly gaining weight, which means the need for nutrients increases - by 200–400 kcal/day. The increase should come from protein, the main building material. It is also necessary to increase the intake of essential vitamins during this period. Calcium. Reduces the risk of having a low birth weight baby. Include fermented milk products, green vegetables, legumes, nuts, and figs in your diet. For complete absorption of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium are also needed. Milk, chicken, and fish are rich in phosphorus. Magnesium - nuts, soy, vegetables. Iron. Deficiency can lead to anemia, which can lead to premature birth and decreased birth weight of the newborn. Iron is best absorbed from meat. Also include fish and eggs in your diet.
Third trimester Your diet has the greatest impact on your baby's weight. Monitor the presence of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in your diet. Squirrels. Their presence in sufficient quantities is especially important - the baby is gaining weight more actively than ever. Sources of complete protein are meat, fish, milk, low-fat cottage cheese, low-fat cheeses. Fats. Even a temporary fat deficiency leads to a decrease in fetal body weight. Therefore, 25–30 g of vegetable oil per day is now the norm for you. Carbohydrates. Their deficiency leads to a decrease in blood glucose levels. Then proteins will be used as fuel, which will negatively affect the development of the baby. The best carbohydrates are wholemeal bread, unrefined cereals, fresh vegetables and fruits.
Related posts:
pregnancy in the big city
is new! educational children's keyboards
shape-mother No. 10 2010
Advice for parents of a premature baby
- Your child is still a little different from everyone else, but over time and with your help, he will be able to catch up with his peers in his development.
- Fight for breastfeeding, it is very important for such babies
- Particular attention is paid to nutrition; such children eat more slowly and usually in smaller portions, but somewhat more often than full-term children. The interval between feedings should not exceed 4 hours.
- Premature babies are easily susceptible to infections, so you should carefully monitor the cleanliness of the room and limit the number of people who want to visit the baby at first.
- At first, doctors do not recommend putting such weakened babies to sleep on their tummy; it is better to place the child on his back.
- When swimming, the water temperature should be at least 37°C
- In the room where the premature baby is located, the temperature should be about 23-25°C. — Sterilization of bottles and nipples is mandatory for such children; try to follow this rule, especially in the first months of the baby’s life.
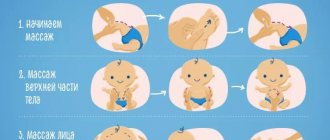
- Premature babies benefit greatly from a special massage that can be performed by an experienced specialist. After consultation, parents can perform simple massage techniques on their own.
- Complementary foods and vaccinations are prescribed strictly on the doctor’s recommendation, after assessing the baby’s condition.
- Be sure to follow all the doctor’s recommendations; if necessary, immediately call a doctor at home or an ambulance.
Features of the health of premature babies
A premature baby not only weighs less than a full-term baby, they differ in appearance and have fundamentally different needs.
In extremely premature babies (weight less than 1500 g), the subcutaneous fat layer is almost completely absent. Their skin is very thin, dark red in color, and covered with thick down. The size of the head compared to the body is much larger than that of full-term babies. All fontanelles and junctions of the skull bones are open, the ears are underdeveloped and very soft. The nail plates are very short and do not cover the phalanges of the fingers. The navel is not located in the center of the abdomen, but at its very bottom.
“However, prematurity is determined not only by external signs. A much more important indicator is the maturity (that is, readiness to function in the outside world) of vital organs and systems. The viability and tactics of nursing a premature baby depend on the degree of this maturity.
If a child is born much earlier than expected, then he is not yet ready for independent extrauterine life. For example, they cannot breathe on their own, and immediately after birth they are placed in special incubators (equipment designed to create optimal conditions for nursing a premature baby) with artificial lung ventilation devices.
If the child cannot suck and swallow on his own, then at first he is fed expressed breast milk or special formulas through a tube.
For premature babies in the first weeks of life, air temperature is critical; such babies very quickly overheat or become hypothermic. The incubator is maintained at a constant temperature and humidity. In some cases, water mattresses are installed in incubators, which create conditions similar to those in the womb.
Many parents are familiar with the problem of children who have a reduced body weight, who eat poorly and do not keep up with their weight gain. Usually, low weight, both at birth and in the future, is very worrying for parents, as this may indicate health problems and deviations from normal physical development. Why do children gain weight poorly, although all the conditions for a full gain have been created for them? Let's try to understand this problem in more detail.
Who are low birth weight babies?
Pediatricians call low-birth-weight children those babies who do not gain the required body weight by a certain period of gestation (weeks of pregnancy). Or those who gain weight poorly after birth for months, and it is difficult to feed them, you have to almost force feed them, or those children who seem to eat normally, but at the same time their weight is gaining at an extremely low rate. This often greatly worries the local pediatrician observing the child, and no less greatly worries the parents themselves, looking at the neighbor’s toddlers, growing by leaps and bounds. At the same time, children develop quite normally, but weigh very little. According to medical terminology, such low birth weight babies can be called differently; this group also includes premature babies who have low body weight due to being born prematurely. The general name for such a deviation in weight from the norm, which unites all possible variants of reduced weight in children in comparison with age norms, is the term malnutrition (low nutrition level) used by doctors. In world sources, another term is taken as a basis - this is a violation of nutritional status. In essence, this is the same thing, but in our country it is the term malnutrition that is adopted. Today we will talk about the problem of the development of prenatal malnutrition - this is a type of malnutrition that develops in utero, before the birth of a child. In this case, babies with malnutrition are born on time, but have a low birth weight. Sometimes, in connection with this phenomenon, another term appears - IUGR (intrauterine growth retardation), but this does not always correspond to the true state of affairs, although most often low birth weight and IUGR go hand in hand. Why might such a problem arise? Why would the child’s intrauterine development suddenly be delayed if the mother herself gained weight during pregnancy? Why are children born so small?
What are the reasons for having low birth weight babies?
There are quite a lot of reasons for a child to be born low birth weight, and in each specific case they will be different and special, sometimes it will be a combination of a number of factors. To understand this survey and understand the reasons for the birth of such small children, it is worth starting from the very beginning of pregnancy and, as it were, looking inside the pregnant uterus. So, from the moment of conception until about sixteen weeks of pregnancy, the unborn baby is a very small lump of cells, rapidly growing and dividing, turning into tiny organs and tissues. In just three to four months, one cell turns into a baby up to fifteen centimeters in length with arms and legs, nails, a beating heart and its own feelings and emotions. After sixteen weeks, the baby’s cells are no longer dividing at such a rapid pace, not so actively, but those cells that are already present begin to grow quickly and intensively and “get fat”, increase in size - up to thirty-two weeks the baby is growing rapidly and gaining weight . From this period until the moment of birth, the future baby practically does not form new tissues, while all existing organs mature, and the baby himself grows and actively gains weight. Depending on which of these three periods the problems of the mother’s body will arise, the form and severity of the development of IUGR will depend, and the baby’s weight at birth will depend on this.
The reasons for the birth of children with low weight at the time of birth are the very young age of the mother, when her body itself is still immature (this is up to eighteen to twenty years), or the birth of children by women after forty to forty-five years. In addition, the child’s weight is significantly influenced by the presence of diseases in the mother during pregnancy - a decrease or increase in blood pressure, kidney disease (pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis), the presence of diabetes mellitus, manifestations of chronic tonsillitis, the presence of anemia, carious processes. The development of low weight is also influenced by the presence of viral infections during pregnancy, existing gynecological diseases both before and during pregnancy, as well as previous miscarriages and abortions, cycle disorders and hormonal imbalances. The weight of children before birth is no less strongly influenced by gestosis of pregnancy, constant stress, eating disorders of the woman herself to please her figure, the presence of bad habits, unsatisfactory living conditions and occupational hazards.
Why are all these factors so influential? It's simple - these reasons lead to disruption of normal blood circulation and functioning of the placenta, and this, in turn, leads to disruptions in the supply to the fetal body of both nutrients necessary for normal growth and development, and oxygen, which the fetus needs in very large quantities. Fetal hypoxia is the most basic cause of suffering in all organs and systems of the baby; first of all, the endocrine, nervous and immune systems of the fetus suffer from it, that is, all those systems that are mainly responsible for the normal growth and development of the fetus. Since the functions of the placenta are disrupted, this disrupts the supply of nutrition to the fetus, which means it causes a slowdown in the growth and development of the fetus - this is what the doctor sees.
If adverse effects were exerted on the fetus in the earliest stages of its development, before sixteen weeks of pregnancy, when the most intense cellular processes in the baby’s body take place, then disturbances in the development of the fetus will be the most obvious and pronounced. Such a child at the time of birth will have not only low body weight, but also very short stature. Outwardly, these children will look quite normal, they will just be uniformly reduced in both height and weight. But, at the same time, in the body of such children there will be more developmental problems; their manifestations will not be visible immediately, but will gradually begin to manifest themselves. After this period, the influence of harmful factors will mostly be reflected in the weight of the fetus, while at birth the babies will look thin and have a long body. That is, the growth of such children may be quite normal for the duration of pregnancy, but body weight is usually less than three kilograms. After a low birth weight baby is born, the pace and mechanisms of development in such children will be their own, special. And all this will depend on at what stage of pregnancy, how long and how strongly the negative factors influenced the fetus, what exactly they were and how irreversible the disorders became.
Groups of low birth weight children
Among neonatologists and pediatricians, a special classification of low birth weight babies has been adopted, which divides them all into four main groups based on weight and height. These include:
The first group - children are born with completely normal height, but at the same time have low weight. Usually, from the first days of life, such children have a rather restless character, they scream a lot, sleep poorly and restlessly, can exhaust the whole family with their whims and feel calm only in the arms of their parents, they do not latch on well or suck a bottle well, they burp a lot, May confuse day and night. With such a restless nature, weight gain per month may be uneven and low, which will cause concern to doctors and parents. This can continue for quite a long time, but in the end the weight is usually corrected.
The second group - the baby’s body weight at birth is usually low, while growth is slightly behind the norm. In such babies, inhibitory reactions of the body are predominant, they can sleep for a long time and a lot, they need to be woken up every time for feeding, they sluggishly and reluctantly suckle at the breast or formula, refuse complementary foods, and feeding becomes a whole operation - since children eat little and with with great reluctance. Such children may simply turn away from any food or do not open their mouths to be fed. Such children may also lag somewhat behind in psychomotor development - they begin to hold their heads up, sit, walk and talk later than their peers; they begin teething later than usual and the large fontanel closes.
The third group is children with proportionally reduced weight and height, who look like a very reduced normal baby. Usually, after birth, such children do not cause any special trouble in terms of feeding and care, but the development of such children is slower than usual, their height and weight do not increase as actively as in ordinary children, as would be expected by age. Psychomotor development will also be slow; these children often get sick for a long time, since their immunity is sharply weakened.
The fourth group includes children with profound disorders of intrauterine development, with noticeable delays in weight, growth and mental development. Such children have significant deviations in both weight and height gains and skeletal development; these are usually children with disabilities and developmental problems. Such cases are rare. Usually children have the first three groups of problems.
Tomorrow we will continue this topic.
It is very important for every mother that her child grows up as a happy baby, is healthy, and develops properly. A very important indicator in this case is the child’s weight.
Parents are very upset by the fact that their child weighs or looks smaller than his peers. They are trying to “shove” into the child the amount of food that is completely unnecessary for him. They seek advice from specialists who are trying to convince parents that in fact everything is normal and they just need to carefully monitor the overall dynamics of the baby’s development.
That is why many women, while pregnant, monitor their weight and take vitamins. Although, as a rule, the expectant mother herself gains weight, not the child. After all, the main part of the weight gained is the fat layer and amniotic fluid.
Weight of the premature baby and degree of prematurity
Approximate body weight of the child at different stages of pregnancy:
| Gestational age in weeks | Average body weight of a child, in gr. |
| 27-28 | 850-1300 |
| 1150-1500 | |
| 1250-1700 | |
| 1300-1750 | |
| 1400-1950 | |
| 1550-2300 | |
| 1800-2500 | |
| 35-36 | 1950-2500 |
Depending on body weight, the child is assigned a certain degree of prematurity:
| Degree | Child's body weight | Gestational age |
| 1st degree | 2.5 - 2 kg | 37 - 35 weeks |
| 2nd degree | 2 - 1.5 kg | 35 – 33 weeks |
| 3rd degree | 1.5 - 1 kg | 33 - 31 weeks |
| 4th degree | less than 1 kg | 31 – 29 weeks |
1 Zaitseva M.L., Uzunova A.N. Features of changes in basic anthropometric data in children born prematurely. Pediatric Bulletin of the Southern Urals, Chelyabinsk, 2020.
The baby was born with low weight
If such a diagnosis was not made during pregnancy, and the child was born with low birth weight, then the newborn may be given this diagnosis. To do this, pediatricians analyze the height-weight indicator, height in cm divided by weight in grams. Normally, at birth it is at least 60, but if less than 55, then a diagnosis of intrauterine growth retardation is made.
Babies born with low birth weight need special care and attention, both from medical staff and from parents. After all, even the process of childbirth itself is a great stress for such children. They may also have poor nutritional absorption and therefore lose weight. The adaptation period in children with a weight lag of 2-3 weeks in relation to the gestational age usually passes faster. For children with a long delay, special treatment may be required in a neonatal unit.
Children born with low birth weight are characterized by neurological disorders and adapt less well to a new life. At a younger age, they can be very excitable, increased or decreased muscle tone may occur, and they often regurgitate. At the age of 7-8 years, hyperactivity appears and they can be clumsy. Only by the age of 9-10 are they no different from their peers, although they catch up with them in weight by the age of two.
The birth of small children is associated with pathology of the placenta, severe gestosis, some maternal diseases, unfavorable working conditions for women during pregnancy and bad habits.
But, as a rule, miniature women give birth to babies with low weight and this has nothing to do with fetal growth retardation syndrome.
In any case, the best way to prevent a problem is prevention. It is necessary to plan your pregnancy, undergo all tests, and visit a doctor on time during pregnancy. The expectant mother should eat well and get proper rest: sleep 8 hours at night and 1-2 hours during the day. Then the development of this disease can be avoided and even eliminated altogether.
Changes in a child's weight in the first year of life
What happens to the baby's weight after birth? A child of normal weight may lose weight or gain little weight. As a rule, in the first days of life, a child loses up to 10% of his weight. This is due to fluid loss and a small amount of breast milk consumed. This weight loss is considered normal, and the baby will soon begin to gain weight. Until the age of six months, the baby gains on average 800 g per month, in the second half of the year - 400 g. If the child is not gaining weight well, you should consult a doctor for advice.
Many parents are familiar with the problem of children who have a reduced body weight, who eat poorly and do not keep up with their weight gain. Usually, low weight, both at birth and in the future, is very worrying for parents, as this may indicate health problems and deviations from normal physical development. Why do children gain weight poorly, although all the conditions for a full gain have been created for them? Let's try to understand this problem in more detail.
Who are low birth weight babies?
Pediatricians call low-birth-weight children those babies who do not gain the required body weight by a certain period of gestation (weeks of pregnancy). Or those who gain weight poorly after birth for months, and it is difficult to feed them, you have to almost force feed them, or those children who seem to eat normally, but at the same time their weight is gaining at an extremely low rate. This often greatly worries the local pediatrician observing the child, and no less greatly worries the parents themselves, looking at the neighbor’s toddlers, growing by leaps and bounds. At the same time, children develop quite normally, but weigh very little. According to medical terminology, such low birth weight babies can be called differently; this group also includes premature babies who have low body weight due to being born prematurely. The general name for such a deviation in weight from the norm, which unites all possible variants of reduced weight in children in comparison with age norms, is the term malnutrition (low nutrition level) used by doctors. In world sources, another term is taken as a basis - this is a violation of nutritional status. In essence, this is the same thing, but in our country it is the term malnutrition that is adopted. Today we will talk about the problem of the development of prenatal malnutrition - this is a type of malnutrition that develops in utero, before the birth of a child. In this case, babies with malnutrition are born on time, but have a low birth weight. Sometimes, in connection with this phenomenon, another term appears - IUGR (intrauterine growth retardation), but this does not always correspond to the true state of affairs, although most often low birth weight and IUGR go hand in hand. Why might such a problem arise? Why would the child’s intrauterine development suddenly be delayed if the mother herself gained weight during pregnancy? Why are children born so small?
What are the reasons for having low birth weight babies?
There are quite a lot of reasons for a child to be born low birth weight, and in each specific case they will be different and special, sometimes it will be a combination of a number of factors. To understand this survey and understand the reasons for the birth of such small children, it is worth starting from the very beginning of pregnancy and, as it were, looking inside the pregnant uterus. So, from the moment of conception until about sixteen weeks of pregnancy, the unborn baby is a very small lump of cells, rapidly growing and dividing, turning into tiny organs and tissues. In just three to four months, one cell turns into a baby up to fifteen centimeters in length with arms and legs, nails, a beating heart and its own feelings and emotions. After sixteen weeks, the baby’s cells are no longer dividing at such a rapid pace, not so actively, but those cells that are already present begin to grow quickly and intensively and “get fat”, increase in size - up to thirty-two weeks the baby is growing rapidly and gaining weight . From this period until the moment of birth, the future baby practically does not form new tissues, while all existing organs mature, and the baby himself grows and actively gains weight. Depending on which of these three periods the problems of the mother’s body will arise, the form and severity of the development of IUGR will depend, and the baby’s weight at birth will depend on this.
The reasons for the birth of children with low weight at the time of birth are the very young age of the mother, when her body itself is still immature (this is up to eighteen to twenty years), or the birth of children by women after forty to forty-five years. In addition, the child’s weight is significantly influenced by the presence of diseases in the mother during pregnancy - a decrease or increase in blood pressure, kidney disease (pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis), the presence of diabetes mellitus, manifestations of chronic tonsillitis, the presence of anemia, carious processes. The development of low weight is also influenced by the presence of viral infections during pregnancy, existing gynecological diseases both before and during pregnancy, as well as previous miscarriages and abortions, cycle disorders and hormonal imbalances. The weight of children before birth is no less strongly influenced by gestosis of pregnancy, constant stress, eating disorders of the woman herself to please her figure, the presence of bad habits, unsatisfactory living conditions and occupational hazards.
Why are all these factors so influential? It's simple - these reasons lead to disruption of normal blood circulation and functioning of the placenta, and this, in turn, leads to disruptions in the supply to the fetal body of both nutrients necessary for normal growth and development, and oxygen, which the fetus needs in very large quantities. Fetal hypoxia is the most basic cause of suffering in all organs and systems of the baby; first of all, the endocrine, nervous and immune systems of the fetus suffer from it, that is, all those systems that are mainly responsible for the normal growth and development of the fetus. Since the functions of the placenta are disrupted, this disrupts the supply of nutrition to the fetus, which means it causes a slowdown in the growth and development of the fetus - this is what the doctor sees.
If adverse effects were exerted on the fetus in the earliest stages of its development, before sixteen weeks of pregnancy, when the most intense cellular processes in the baby’s body take place, then disturbances in the development of the fetus will be the most obvious and pronounced. Such a child at the time of birth will have not only low body weight, but also very short stature. Outwardly, these children will look quite normal, they will just be uniformly reduced in both height and weight. But, at the same time, in the body of such children there will be more developmental problems; their manifestations will not be visible immediately, but will gradually begin to manifest themselves. After this period, the influence of harmful factors will mostly be reflected in the weight of the fetus, while at birth the babies will look thin and have a long body. That is, the growth of such children may be quite normal for the duration of pregnancy, but body weight is usually less than three kilograms. After a low birth weight baby is born, the pace and mechanisms of development in such children will be their own, special. And all this will depend on at what stage of pregnancy, how long and how strongly the negative factors influenced the fetus, what exactly they were and how irreversible the disorders became.
Groups of low birth weight children
Among neonatologists and pediatricians, a special classification of low birth weight babies has been adopted, which divides them all into four main groups based on weight and height. These include:
The first group - children are born with completely normal height, but at the same time have low weight. Usually, from the first days of life, such children have a rather restless character, they scream a lot, sleep poorly and restlessly, can exhaust the whole family with their whims and feel calm only in the arms of their parents, they do not latch on well or suck a bottle well, they burp a lot, May confuse day and night. With such a restless nature, weight gain per month may be uneven and low, which will cause concern to doctors and parents. This can continue for quite a long time, but in the end the weight is usually corrected.
The second group - the baby’s body weight at birth is usually low, while growth is slightly behind the norm. In such babies, inhibitory reactions of the body are predominant, they can sleep for a long time and a lot, they need to be woken up every time for feeding, they sluggishly and reluctantly suckle at the breast or formula, refuse complementary foods, and feeding becomes a whole operation - since children eat little and with with great reluctance. Such children may simply turn away from any food or do not open their mouths to be fed. Such children may also lag somewhat behind in psychomotor development - they begin to hold their heads up, sit, walk and talk later than their peers; they begin teething later than usual and the large fontanel closes.
The third group is children with proportionally reduced weight and height, who look like a very reduced normal baby. Usually, after birth, such children do not cause any special trouble in terms of feeding and care, but the development of such children is slower than usual, their height and weight do not increase as actively as in ordinary children, as would be expected by age. Psychomotor development will also be slow; these children often get sick for a long time, since their immunity is sharply weakened.
The fourth group includes children with profound disorders of intrauterine development, with noticeable delays in weight, growth and mental development. Such children have significant deviations in both weight and height gains and skeletal development; these are usually children with disabilities and developmental problems. Such cases are rare. Usually children have the first three groups of problems.
Tomorrow we will continue this topic.
258 days is how long a baby needs to spend inside the mother’s womb to be born full-term. What if he was born earlier? Daria Kinsht, head of the neonatology department, neonatologist, anesthesiologist-resuscitator at the Medical Group, spoke about how often premature babies are born, what is the minimum due date and what developmental problems parents of such babies may encounter.
Weight gain in newborns up to one year old
Generalized norms of weight gain in children aged from birth to one year are presented in the table:
| Age, in months | Monthly increase (in grams) | Weight gain since birth (in grams) |
| 1 | 600 | 600 |
| 2 | 800 | 1400 |
| 3 | 800 | 2200 |
| 4 | 750 | 2950 |
| 5 | 700 | 3650 |
| 6 | 650 | 4300 |
| 7 | 600 | 4900 |
| 8 | 550 | 5450 |
| 9 | 500 | 5950 |
| 10 | 450 | 6400 |
| 11 | 400 | 6800 |
| 12 | 350 | 7150 |
A special form is also used to calculate weight:
- for a child aged 1-6 months: birth weight (in grams) + 800xN, where N is the number of months;
- for newborns over 6 months: birth weight (in grams) + 800x6 + 400x(N-6), where N is the number of months after 6.
Normal weight gain in newborns
The approximate average weight of a full-term baby ranges from 2600...4500 grams. Sometimes babies are born weighing more than 5 kilograms, but this is rare.
During the first week, babies lose some weight. The physiological norm is approximately 5%...10%. This is explained as follows:
- The child’s body is freed from original feces and moisture reserves.
- The baby's feeding schedule has not yet been established.
- The cut umbilical cord is healing.
- A child’s body spends a lot of energy during the first few days of its life adapting to a new world.
Body weight will be restored approximately by the tenth day after birth.
1-3 months. Maximum weight gain in children is observed precisely from the first to the third months of life. At this time, the child sleeps quite a lot and moves little. In addition, the only food the baby receives is breast milk or formula.
During the first month, babies gain up to 20 grams daily. For the second, this figure increases to 25...30 grams per day. This is why the child gains the most weight.
4-6 months. Starting from the fourth month, babies begin to move actively. By six months, as a rule, they are already trying to sit. And during this period, babies gain from 400 to 600 grams within a month.
6-9 months. After the baby turns six months old, the baby’s weight gain slows down even more. And on average, a child gains from 300 to 500 grams.
9-12 months. At this age, the child can already move independently, and therefore is almost always on the move. And almost all the calories that come to him from food go to replenish energy costs. The average weight gain during this period of time is 100...300 grams.
On average, a child's weight increases approximately three times over the course of a year.