Symptoms of thrush in newborns in the mouth
Determining the presence of a fungal infection in a child is not difficult due to the obvious manifestations of the disease in the form of a white coating on the palate and tongue. Detection of the first symptoms requires contacting a pediatrician to identify the cause of cheesy plaque in the mouth and prescribe appropriate treatment.
- the mucous membrane is covered with a white coating, which looks like milky films on the palate, tongue and cheeks;
- white spots are observed on the mucous membrane of the mouth, gums and lips (may look like milk residues after feeding);
- with mechanical action, curdled crumbs are difficult to remove, ulcers and wounds form in the mouth, which begin to bleed;
- the child refuses to eat, begins to cry often during feeding, and becomes capricious (the fungus causes discomfort to the baby);
- temperature increase;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
Causes and mechanisms
The body of a newborn has many structural and functional features and differences, and some persist into older age. Therefore, when you see white formations on the oral mucosa, you should not immediately think about pathology. There are a number of conditions that do not cause concern:
Three of the described phenomena (except the last one) make up, perhaps, the majority of cases when parents complain to pediatricians about whitish spots or dots in the mouth of a newborn. However, children may also be susceptible to pathological changes:
- Thrush (candidiasis).
- Aphthous stomatitis.
- Measles.
Based on the variety of possible factors, you will have to exclude them all. And in differential diagnosis you can’t do without a specialist. Most likely, there is no danger in white spots, but parents need to be completely sure that there is no pathology.
The causes of whitish spots or spots on the mucous membrane can be both physiological and pathological changes. Therefore, they cannot be ignored.
The origin of a particular sign can be established based on a complete picture of what is happening. And it can be compiled during a comprehensive examination, the first stage of which will be a survey, examination and other physical methods (for example, palpation). This will provide an opportunity to make a preliminary conclusion and reassure worried parents.
Bohn's nodules are small (up to 3 mm in diameter) cysts formed from the rudiments of the salivary glands. They have a spherical shape and are located on the soft palate. One or more similar formations are detected in the baby, but over time they will disappear on their own. The nodules do not cause any discomfort.
The so-called Epstein pearls are similar to the phenomenon described above. These are epithelial cysts located in the midline of the palate, where two plates merge with each other during the prenatal period. Such tubercles are somewhat elongated and filled with keratin masses. After the latter are removed, the white dots on the palate of the newborn dissolve.
Gum cysts are another condition that can cause whitish bumps to form in the mouth. They are localized along the anterior surface of the alveolar process of the jaw and are formed from the ectodermal ligament, which gives rise to teeth. Gingival cysts are still mistaken for congenital teeth, but, unlike the latter, they have an elastic consistency and are capable of spontaneous rupture (without any consequences).
The teeth that a child has at birth, without the presence of additional anomalies, are a feature inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. They mainly appear on the lower jaw in the incisor area. Congenital teeth have a smooth surface or differ from normal teeth in roughness and discoloration. They have a shorter root, which gives much greater mobility.
Almost all neonatal teeth are further included in the series of primary teeth. But in some cases they become additional (supernumerary), and therefore require removal. In addition, the appearance of congenital teeth is sometimes a sign of quite serious genetic abnormalities.
A white coating on the palate and tongue of a baby most likely indicates thrush. This is the more common name for candidiasis, a disease of fungal origin. It costs nothing for a young child to become infected with it, because his oral microflora is just beginning to form.
And if at first small white lesions (spots) may appear with thrush, they will soon increase in size and merge with each other, forming a continuous plaque. It comes off well, but reveals a reddened and somewhat swollen surface underneath. In severe cases, painful erosions even form, which leads to disruption of the general condition:
- Moodiness.
- Refusal to eat.
- Temperature increase.
Despite the fact that thrush is considered by many to be a mild condition, it cannot be neglected. You should always consult a doctor on time for diagnosis and treatment.
Many parents have probably encountered oral thrush in their children. But it can also cause white spots.
Aphthous stomatitis can appear in both infants and adults. Its substrate becomes an inflammatory process or an allergic reaction. A characteristic sign of stomatitis will be the formation of erosion (aphtha), which is covered with a white fibrinous coating. Such spots appear mainly on the reddened mucous membrane of the cheeks or lips, less often they cover the palate - with single or multiple elements. This brings significant discomfort:
- Burning and pain.
- Change in taste.
- Difficulty chewing.
- General malaise.
Aphthae heal through epithelization, which takes from one to several weeks. Sometimes the process becomes chronic with periodic exacerbations.
White spots in a child’s mouth may turn out to be Belsky-Filatov spots, which are a characteristic symptom of measles. They occur during the catarrhal period of infection, when rashes have not yet appeared on the body. The spots are localized on the inner surface of the cheeks, gums and lips, surrounded by a red halo. Other symptoms will be present at this time:
Belsky-Filatov spots are a pathognomonic (very characteristic and reliable) sign that makes it possible to diagnose measles at the initial stage of the disease.
Whitish spots on the oral mucosa may indicate infectious diseases, in particular measles.
Signs of thrush
The main symptom of oral candidiasis in a newborn is white cheesy deposits on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and gums. On the palate they are initially located pointwise, in the form of small grains, then merge into large spots, which are easily removed by scraping.
When an infection occurs in the mucous membrane of the tongue, swelling and hyperemia occurs. The baby has difficulty eating, and it becomes difficult and painful for him to suck. Older children complain of dry mouth and a burning sensation; eating food, especially hot food, is accompanied by severe pain.
Oral candidiasis can progress to a chronic stage, which requires long-term treatment, and in severe cases, hospitalization of the patient in a hospital.
When not to sound the alarm
It is important to know that a white tongue and other mucous membranes are not always a sign of illness.
It is worth examining the baby's mouth before and after feeding. If a slight coating appears after feeding and only on the tongue, do not worry. It disappears on its own or after drinking water. These are traces of feeding with breast milk or formula. A small amount of cheesy plaque may also appear from regurgitation during or after feeding. This is milk that has begun to be digested in the stomach.
However, there are no changes in the child’s behavior. He eats and sleeps well and his bowel movements are normal. Remaining white marks can be carefully removed with a sterile cloth or bandage soaked in boiled water.
Hands must first be thoroughly washed with soap; the procedure is performed very carefully so as not to injure the tongue and mucous membranes of the mouth.
Such manifestations in the first year of life are considered normal. Attentive parents notice them in most infants.
But much more often, everything is not so rosy, and a white coating in the mouth of a newborn child is a symptom of candidiasis. The disease is also called candidal stomatitis, oral candidiasis, thrush. In this case, the plaque is not removed, and other signs of the disease appear.
Clarifying the diagnosis
A change in the color of plaque in the mouth can signal symptoms of diseases of the internal organs and the development of inflammatory processes.
To diagnose this disease, the attending physician prescribes a number of laboratory measures:
- a visual examination of the oral cavity is performed to assess its condition;
- a clinical detailed blood test is prescribed to determine the inflammatory process based on the results of the leukogram;
- To make an accurate diagnosis, a microflora culture from the oral cavity is performed to determine the type of fungal strain;
- antibiogram – establishes the sensitivity of pathogens to therapeutic drugs and bacteriophages;
- The coprogram allows you to detect a yeast-like fungus in a child’s stool.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe additional blood tests to detect the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and cytology of the contents of plaque on the mucous membranes of the mouth.
Read,
We suggest you read: Treatment of pulpitis of primary teeth in children
How do suction cup dentures work?
.
How much do suction cup dentures cost? More details here.
Candidiasis

The most common disease that manifests itself as a white coating in the mouth (on the cheeks and tongue) in infants and older children is candidiasis, better known as thrush. Its cause is reduced immunity, which cannot cope with the excessive proliferation of a fungus called “candida”. This fungus is present in the body of absolutely every person, but in small quantities and does not pose any health hazard. But, since in newborns the immunity is at the stage of formation, contact with another carrier of this infection (most often children borrow it from their mother) or a slight stress on the body is enough for the fungus to begin to multiply quickly. This is expressed in the form of the formation of whitish plaques on the oral mucosa. After trying to remove this plaque, red spots form underneath. If treatment is not started, it will become denser and spread further - over the entire inner surface of the oral cavity and to the lips. The presence of these symptoms causes discomfort to the child - he begins to be capricious, refuses to breastfeed, and sleeps poorly.
Candidiasis is treated quite easily and quickly, sometimes a few days are enough for recovery. But still, if its symptoms appear, it is better to contact a specialist who will do a full examination of the child. After all, candida can spread not only in the mouth, but also on the genitals - for girls this can have very unpleasant consequences.
If the cause of the appearance of a white coating on the tongue is indeed candidiasis, then the following measures are usually taken.
- The mucous membrane is treated with a soda solution (1 teaspoon of soda per 250 ml of water) using a sterile bandage wrapped around the finger. It is necessary to gently wipe the infected areas without trying to remove the plaque. This procedure is done several times throughout the day.
- In the same way, you can treat your baby’s mouth with a solution of 1 tsp honey and 1 tsp. turmeric per 100 ml of water - this composition will have a disinfecting effect, and the taste will not cause unpleasant sensations.
- Medicines usually recommended in such cases are Candide (in the form of a 1% solution), 1% hydrogen peroxide, nystatin (in the form of an ointment or tablet dissolved in water), and maramistin. The dosage of these drugs, as well as the frequency of their use, should be determined by the doctor, based on the condition in which the child is.
- In some cases, when the disease is advanced or cannot be treated externally, it is necessary to use antibiotics that act directly on the fungus. Such treatment is carried out only under the supervision of a specialist.
A good environment for the proliferation of fungi of the genus Candida is the dry mucous membrane. The fact is that saliva contains substances that prevent their excessive reproduction. And since salivation in infants is reduced, favorable conditions are created for the development of candidiasis. The situation can be aggravated by dry hot air in the room, as well as frequent crying and screaming of the child. Therefore, sometimes thrush does not need special treatment: it is enough to humidify the air in the house (the norm is 40–50%) and create conditions under which the baby will breathe through his nose (calm down while crying, relieve nasal congestion, etc.), so that the fungus stops spreading.
In addition, it has been noted that children born prematurely, as well as those who do not have the opportunity to feed on mother's milk, are most susceptible to thrush. This is due to the fact that such babies have lowered immunity, which means the body has less strength to cope with the disease.
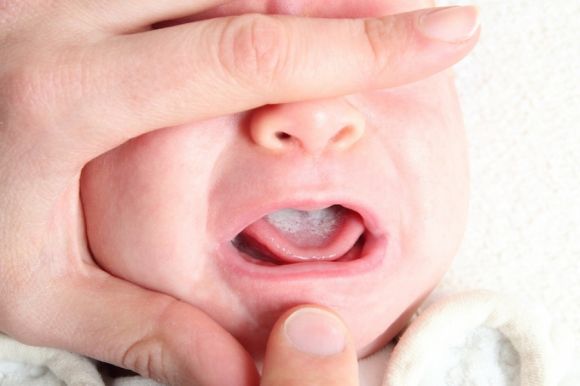
To prevent candidiasis, the following measures must be taken.
- If the mother has candidiasis, it should be treated as soon as possible to avoid infecting the baby. When breastfeeding, it is necessary to treat the breasts and nipples with a soda solution or a decoction of oak, chamomile, and calendula before and after each feeding.
- Children's dishes, toys and pacifiers must be sterilized regularly.
- Maintain oral hygiene.
- Humidify the air if necessary (but do not forget that with a humidity of 80% or more, another fungus can develop in the room - mold).
- Strengthen the child’s immunity, if possible, feed him with mother’s milk.
Features of treatment and symptom relief
After all diagnostic examinations have been carried out and the etiology of the disease has been determined, the attending physician prescribes a course of medication. Correctly prescribed therapeutic drugs improve the baby’s condition already on the first day of their use.
Popular drugs in the fight against oral thrush in children are listed in the table.
| A drug | pharmachologic effect |
| Candide | Broad-spectrum antifungal agent, imidazole derivative. The solution is completely safe for newborns; the glycerin in its composition gives it a sweet taste. It is used according to the following scheme: 10 drops are applied to a cotton swab and distributed evenly throughout the mucous membrane of the mouth. The course of treatment is 10 days. |
| Diflucan | There are no age restrictions for use, but give this medicine to newborns under the strict supervision of a pediatrician. The convenient form of release in the form of a suspension is suitable for any age. The dose for a single dose is calculated from the ratio of 3 mg of active substance per 1 kg of child’s body weight. The frequency of administration is 1 time per day, the course of treatment is 3 days. |
| Retinol | Widely used as a means of accelerating the healing of wounds and ulcers of the mucous membranes in various diseases. Eliminates dryness and irritation. After eating, treat the oral cavity with a cotton swab soaked in a solution of vitamin A. |
| Nystatin | Available in the form of ointments, tablets, a very convenient form in the form of drops for treating children under one year of age. Nystatin is a very good remedy in the fight against thrush and stomatitis in children, but is rarely prescribed, as it has a large list of contraindications and side effects. |
| 1% sodium bicarbonate solution | The solution is prepared in the following ratio: 1 glass of boiled water at room temperature and 1 teaspoon of baking soda, mix well. Using a sterile cloth soaked in solution, the inside of the cheeks, gums, and tongue are treated. |
Drug treatment of thrush in babies under one year of age
If you notice thrush in your child, contact your doctor. Trying to cure the disease on your own is dangerous due to the development of bacterial stomatitis under the influence of strong antiseptics. If candidiasis in newborns is treated incorrectly, it can develop into a chronic form and make itself felt even during teething.
First of all, you will need to get rid of the reasons that cause thrush in children. Wash your hands thoroughly before touching your child. Boil toys that your baby touches. Soak the nipples in the soda solution. Protect your baby from communicating with other people during treatment. Wash your nipples with plain water without additional products before breastfeeding.
Treatment of thrush in children is often complicated by the fact that many antifungal medications cannot be given to newborns and infants. List of approved drugs that must be applied topically to affected areas:
- Candide solution is an effective remedy for newborns. Apply up to 20 drops of the solution to the affected areas with a cotton swab or swab. Treatment with the product is required 3 times a day.
- Diflucan. The maximum dose is 3 mg/day. Newly born babies are given the drug at intervals of three days, two weeks and older - at intervals of two days.
- Fluconazole is an analogue of Diflucan.
- Nystatin ointment is rarely prescribed by doctors today. The reason for this is the frequent occurrence of swelling and itching in the affected areas.
- Levorin ointment is a good remedy, which, however, is contraindicated in children under 2 years of age.
- 1% soda solution. Dip a cotton swab in a soda solution and treat the mucous membrane three times a day. Baking soda is an excellent home remedy.
- Means for healing the mucous membrane. These include oil solutions of vitamin A and sea buckthorn, as well as Shostakovsky balm (Vinilin). These drugs require treatment of the mucous membrane at least three times a day.
- Zelenka. There are 2 ways to treat green spots. The first of them is to dip the pacifier in brilliant green and let it suck. Another is to lubricate the affected areas of infants with such a solution after each meal.
How to treat?
| Disease | Medicine | Features of application |
| Thrush (candidiasis) | Soda solution (1 tsp per glass of water) | Cleaning the baby's mouth and toys he touches, wiping the mother's breast before and after feeding. Used for mild forms of the disease. |
| Candide solution | Wiping and treating the oral mucosa. | |
| Vitamin B12 solution | ||
| Acidophilus powder | ||
| Nystatin ointment | ||
| Cream, spray, Canesten solution | Used in advanced cases of candidiasis. The treatment period is 5 – 10 days. It is important to continue using the drug as prescribed, even if the symptoms of thrush have disappeared. | |
| Diflucan suspension | ||
| Clotrimazole | ||
| Mikomax | ||
| Ketoconazole | ||
| Herpetic stomatitis | Acyclovir | Necessary to fight viruses. |
| Bonafton | ||
| Zyrtec | Antihistamines. | |
| Tsetrin | ||
| Furacilin solution | Antiseptic for wiping affected areas. | |
| Infectious diseases | Candles Genferon | Injected into the rectum, they help increase the synthesis of interferon by the body and are necessary to stimulate the immune system. |
| Suppositories Viferon | ||
| Paracetamol | Relieves pain and reduces temperature. | |
| Panadol | ||
| Miramistin solution | Used for mechanical removal of plaque. | |
| Augmentin | Antibiotics to fight infection. The course of treatment is from 7 to 10 days. | |
| Suspension Ecoclave | ||
| Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (therapy is prescribed depending on the disease) | No-spa drops | Reducing discomfort. |
| Almagel | Reduces the frequency of regurgitation after feeding. | |
| Smecta | Helps improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and removes toxins. | |
| Activated carbon | ||
| Omeprazole | Prescribed for acid reflux. | |
| Regidron | Used for dyspepsia (impaired digestion of food). At the same time, a water-tea diet and adjustment of portions of milk or formula must be prescribed. | |
| Glucosolan | ||
| Bronchopulmonary diseases | Amoxicillin suspension | Used to destroy pathogenic flora. |
| Amoxiclav | ||
| Ceftriaxone | The antibiotic is administered intravenously in a hospital setting. | |
| Dysbacteriosis | Powder and suspension Nifuroxazide | Antibacterial drug to improve digestive function. |
| Linex | Preparations that include beneficial bacteria that populate the intestines and normalize the balance of microflora. | |
| Bifidumbacterin | ||
| Lactulose | A prebiotic that triggers the mechanism of increasing the colonies of its own beneficial microorganisms in the intestines. | |
| Bobotik | Reduce gas formation. | |
| Espumisan |
Often the mother also undergoes treatment along with the baby. During therapy, she is required to carefully adhere to diet and personal hygiene. The course of treatment prescribed by the doctor must be completed in full - this will avoid relapse of the disease.
If there is a white coating in the child’s mouth, but there are no serious illnesses, and the doctor approves of traditional methods of treatment, it can be removed with honey or sea buckthorn oil. You need to moisten a cotton swab in one of these products and remove the deposits. It is better to use the oil before feeding. You must first make sure that the baby is not allergic to these folk “medicines”.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Designation of teeth in the dental formula
Causes
This phenomenon occurs in almost all babies and is not considered something serious. Plaque can form on the inner surface of the cheeks, palate and lips. There are three main reasons why plaque may form in a baby:
- normal whitish contents appear on the tongue as a result of the infant’s feeding habits. Due to the fact that his main food is mixtures, the tongue is often covered with a whitish coating, which does not require treatment;
- candidiasis is a pathology that affects the oral cavity.
Such contents are more dense and are quite difficult to remove.If you manage to get rid of it with a gauze swab, you will see a bright scarlet tongue, sometimes even bleeding.
Every reasonable person knows that the human body is inhabited by many microorganisms. Candida fungus lives on the skin and mucous membranes, which is recognized as part of the natural human microflora. This microorganism is one of the opportunistic pathogens, which is capable of causing candidiasis under certain conditions.
If the body's defenses are weakened by antibiotics or excessive room humidity, the fungi begin to activate and become externally noticeable, turning into a white coating. Moreover, this plaque can cover not only the entire tongue, but also the entire mucous membranes of the mouth.
If you ignore candidiasis in your child, it will certainly spread to the throat further and to all internal organs. It is worth noting that this should not be allowed, because in this case the treatment becomes much more complicated and prolonged.
With stomatitis, a white coating does not always appear in the mouth of a newborn child, but it is worth talking about.
The disease looks like whitish sores with clear edges, which can be in any part of the mouth.
These wounds can be accompanied by severe pain and cause particular discomfort. In this case, the baby even stops eating due to severe pain. Stomatitis is often accompanied by high fever.
The main factors for the occurrence of the disease are:
- damage to the oral mucosa;
- lack of vitamins;
- nervous shock and stress;
- allergic reactions;
- decreased immune strength;
- the presence of candidiasis in the mother;
- A woman’s failure to comply with hygienic principles creates a favorable environment for the development of the disease.
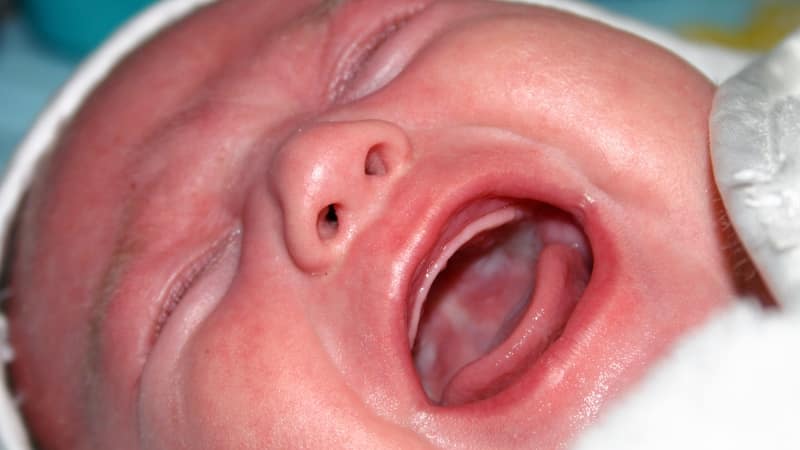
If a white coating appears in the mouth of an infant, you should consult a specialist
So, the trigger mechanism of the disease is a number of factors. The speed of recovery will depend on the speed of treatment started.
The formation of a whitish coating can be due to many other reasons. These are problems in the functioning of internal organs. Considering the severity of the pathological process, the shade of plaque can be gray, green, or yellow.
In this situation, it is impossible to do without going to the doctor. Only a specialist can recognize the enemy by sight and determine effective treatment tactics. Be sure to find the cause of the pathology so that the child does not get thrush again.
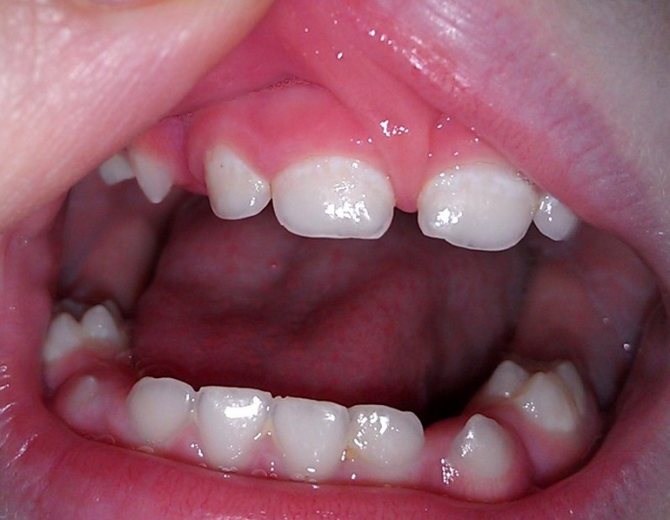
The causes of white plaque lie in diseases:
- gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, dysbacteriosis, enterocolitis);
- respiratory system (acute respiratory infections, flu, bronchitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, bronchial asthma);
- oral cavity (stomatitis, caries, thrush);
- infectious diseases (scarlet fever, diphtheria);
- other (allergies, psoriasis, dehydration).
Gastrointestinal tract
Problems of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) include:
- gastritis. A white or brownish thick coating with small grooves forms in the center of the tongue;
- enterocolitis. Inflammation of the small and large intestines, which manifests itself as discomfort in the abdomen, constipation or diarrhea, and a light coating on the root of the tongue. In severe cases of the disease, the temperature rises;
- dysbiosis.
If the plaque does not go away throughout the day, or, moreover, causes discomfort to the child, then one can suspect that the baby has some kind of disease.
- Inflammatory process in the oral cavity: inflammation of the oral mucosa, fungal infection or caries.
With stomatitis, plaque may be heterogeneous, with light inclusions. If you try to clean the plaque, the surface of the tongue may bleed.
In older children, a persistent white coating on the tongue may primarily be a sign of problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Almost immediately its appearance is accompanied by diarrhea or constipation, nausea and vomiting. Children complain of heaviness in the abdomen, frequent pain, and cramps. The child may develop gastritis and even an ulcer. If the area near the root of the tongue is covered with a white coating, enterocolitis may develop. You can’t do this without the help of a doctor.
Gastrointestinal diseases provoke inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tongue itself. It also causes whitening and is called glossitis.
The presence of white plaque may be the result of another unpleasant disease - dysbiosis, which was mentioned above.
Most often, the appearance of plaque in a child’s mouth or lips indicates the development of stomatitis (thrush). At the first signs, you should contact your pediatrician to prescribe adequate treatment. The disease progresses due to the proliferation of Candida fungi.
In general, thrush has a long incubation period: fungi can settle even after the baby is born, but manifest themselves under certain conditions, for example, hypothermia, decreased immunity. This disease has this name because the film covering the oral cavity is similar to curdled milk.
Typically, a white coating indicates the development of a fungal infection - thrush, which can be triggered by various phenomena. To prevent candida from spreading to the internal organs of the baby, timely treatment is necessary. In general, yeast-like microorganisms exist in everyone’s mouth, but under certain conditions they begin to multiply, which provokes disease. It is these particles that make up the healthy microflora of the body.
Microscopic fungi are present in the oral cavity of every healthy person, including newborns. This is a familiar local microflora. Among others, there are also yeast fungi.
When their quantity exceeds the permissible concentration, for example, due to weakening of the immune defense, thrush develops.
In an adult body, the immune system is clearly formed. In babies, it is still immature.
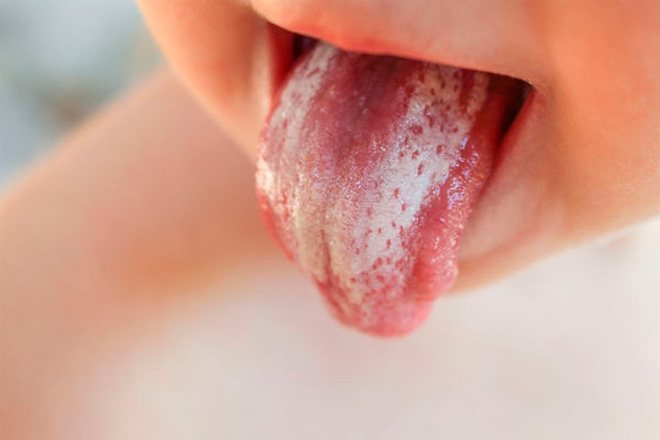

Therefore, they suffer much more often from various lesions, including fungal ones. The disease can develop in the presence of favorable circumstances for pathogenic organisms.
Factors contributing to the appearance of thrush
- Infectious or viral diseases. During, for example, a cold, the baby’s body is weakened and fungal stomatitis can join as a secondary infection. The same tendency appears in HIV-infected patients.
- Digestive problems. If a baby often burps or the baby experiences bouts of vomiting, then a favorable environment is created in the oral cavity for the development of fungal infections.
- Drying of the mucous membrane in the mouth due to insufficient saliva production or due to dehydration, which can be caused by fever, vomiting, blood loss, poor drinking habits, diarrhea, and the use of diuretics.
- Poor or insufficient dental and oral hygiene. Eating excess amounts of carbohydrates, including sweets, as well as sour juices and drinks with added acids (malic, citric, less often phosphoric) leads to an increase in the acidity of the environment in the mouth. And the higher this indicator, the better for microorganisms. Therefore, after eating, you should rinse your mouth, brush your teeth and tongue, or use chewing gum.
- Taking antibiotic drugs. Broad-spectrum antibiotics destroy pathogenic microorganisms, but also inhibit the functioning of beneficial microbes. This leads to digestive disorders and changes in the alkaline-acidic environment. Under such conditions, yeast fungi begin to actively multiply, and protective mechanisms do not have time to fight them. This is how candidiasis develops.
- Vitamin deficiency, iron deficiency, lack of folic acid.
- The presence of damage in the child’s mouth, including mechanical and thermal origin, excessive hygiene, gum disease, teething.
- Presence of tumors, including cancer.
A baby can become infected from another patient, for example, from the mother during birth, feeding, etc.
The disease may not develop immediately, but later, when circumstances are favorable for the development of the Candida fungus.
Adults need to be vigilant
It is quite difficult to recognize the development of thrush at the initial stage, since it manifests itself in the form of barely noticeable whitish dots. It can be localized both in individual areas of the mucous membrane and throughout the entire oral cavity.
If parents are not vigilant and miss the development of the disease at the very beginning, thrush can become severe.
Spread to the larynx and throat area. In infants, this stage very often manifests itself in the form of cracks in the corner of the mouth, candidiasis. They are accompanied by an increase in body temperature to 39 degrees, moodiness and refusal to eat.
The main difference between milk residues and pathological plaque is that milk disappears after a short period of time, but thrush remains.
What is the danger of the disease
Delayed initiation of treatment for candidiasis can progress to a chronic stage and provoke allergic reactions and decreased immunity.
White plaque in the mouth is not only a sign of thrush, but also a signal about the onset of the following inflammatory processes in the body:
- stomatitis;
- gastrointestinal diseases: gastritis, enterocolitis, duodenitis;
- acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza;
- diphtheria;
- whooping cough;
- scarlet fever;
- leptotrichosis.
There are often cases when candidiasis affects other organs. It poses the greatest danger to premature babies with low weight and an immature immune system, causing severe complications that can be fatal.