When a rounded lump appears on the child’s body, most often the neck, noticeable upon visual inspection, parents panic. Every adult knows that an enlarged lymph node is a sign of an incipient disease. However, children's doctors reassure parents, explaining: if a child's lymph nodes are inflamed, they need to look for the cause, and then draw final conclusions.
Enlarged lymph nodes in a child cause concern for parents
Cervical lymph nodes in the human body
Experts explain that the organs have lymph nodes: submandibular, axillary, cervical, occipital. They are part of the lymphatic system, part of the human circulatory system, and are located in the superficial zone of the body and can be easily examined and felt.
For your information. The role of the lymphatic system in the human body is invaluable, since it is responsible for anti-infective protection, that is, the immune function. Lymph nodes are a kind of filter where lymph is cleansed and saturated with protective antibodies.
Children's doctors explain to parents: the main support for the health of children is the cervical lymph nodes. In addition to the function of maturing immune cells, they perform a barrier function, preventing bacteria and viruses, allergens and toxins, and internal pathogens from entering the body.
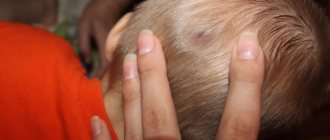
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck is quite common in children. The disease is called cervical lymphadenitis, which is dangerous because it occurs quite close to the brain. If the lymph nodes on the child’s neck are swollen, on the left or right, this may mean: the lymph system is fighting an infection. Its main task is to prevent infection from entering the brain tissue.
For your information! Lymph nodes do not become inflamed without a reason.
Up to a certain time, this well-functioning system protects the body, but sometimes it fails, which is why inflammation is a signal of the development of some pathology.
Why do the lymph nodes in a child’s neck become inflamed?
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck
About 150 groups of lymph nodes are located on the periphery of the body; they can be felt in case of inflammation or pathological location. That is, an enlarged organ is not necessarily a sign of disease.
Lymphocytes perform a protective function. If an infection enters the body, the nodes begin to actively produce immune system cells. In the case of a large number of pathogenic bacteria, an increase in lymph nodes is observed.
Often, a child under three years of age experiences a slight enlargement of the lymph nodes. This happens because children explore the world around them by putting dirty hands and bacteria-filled toys into their mouths. If the cervical lymph nodes are slightly larger than usual, then your child’s body is currently actively fighting an infection.
Lymphadenopathy is an enlargement of the lymph node, determined by the size of the area palpable through the skin. This way, the mother will be able to determine the severity of the disease at home.
- The size of the seal is up to 1 centimeter - there is no need to worry about the baby’s health.
- Size from 1 to 1.5 cm – there may be an infection in the body at the moment, so seek advice from a specialist.
- An enlarged lymph node from 2 centimeters means there is an inflammatory process. Most often, the lymph nodes in a child’s neck become enlarged due to a cold.
If the infection is serious or there are a large number of bacteria in the body, purulent inflammation of the lymph nodes may occur. Then, in addition to compaction of the organ, you can see redness, a local or general increase in temperature. Often inflammation is accompanied by painful sensations.
Causes of enlarged lymph nodes in a child’s neck
Lymph nodes that are localized in the neck become inflamed either on one side or on both. This localization depends on the type of infection. Unilateral inflammation indicates a direct infection in the area of the enlarged node, a disease of the throat or oral cavity. Bilateral inflammation may indicate a general infection in the body.
This pathology in a child is not a disease in itself; it is mainly a symptom of other diseases. Factors that lead to an increase in nodes:
- Infection. An increase in the upper nodes on the neck in a child’s body can indicate a variety of diseases: infection in the nose or throat, caries, inflammation of the oral cavity. If a lump is visible at the back of the neck, the child may have purulent inflammation on the scalp, otitis externa, or a tick bite in this area.
- Cold. In the case of a viral disease, the child experiences a stuffy nose, runny nose, and cough. Treatment should not be carried out independently, as it requires the use of medications.
- Cat scratch. Sometimes pathogenic bacteria enter the body with a scratch, causing inflammation of the lymph nodes. Therefore, it is recommended to treat scratches with antiseptics.
- Infectious mononucleosis. There is a high probability of contracting this disease in childhood, since the child’s immunity is not yet strong. The symptoms of mononucleosis are similar to those of a sore throat; sometimes the viral disease is called monocytic sore throat. You should not treat the child yourself, as immunomodulators and antibiotics are used in therapy.
Other causes of inflammation include:
- Oncology;
- Allergy;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Mechanical damage to lymph nodes.
If you notice the presence of lymphadenitis on a child’s neck, do not panic. You should consult a doctor. He will make the correct diagnosis of the disease that led to this pathology. The pediatrician will prescribe treatment and also monitor changes in the child’s condition. Therefore, in case of complications, timely assistance will be provided.
Manifestation of inflammation
Lymphadenitis in children
Developing lymphadenitis can cause both local and general reactions of the body. Local inflammation is manifested by an increased size of the node, redness of the skin, and pain when touched. The formation can be easily felt; its consistency can be either hard or soft. A soft lymph node indicates the presence of pus in it. If the disease that caused the inflammation is not treated, lymphadenitis breaks through and spreads internal pus to all nearby organs.
Common symptoms of the disease include:
- Weakness, moodiness, sleepiness;
- Refusal to eat;
- Headache;
- Pain when swallowing;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Increased body temperature;
- Sick appearance of the child, pale skin, bruises under the eyes.
During inflammation, children may complain of abdominal pain and their bowel movements are disrupted. As with any illness, the baby becomes lethargic, tearful, and loses weight.
When feeling the child at home, it is necessary to remember that lymphadenitis is located not only on the sides, but also in the back and in front. If the inflamed nodes at the back of the neck are not treated, the disease process can start, which subsequently threatens surgical intervention.
Possible complications of cervical lymphadenitis
A disease associated with enlarged lymph nodes cannot be treated at home. Cervical lymph nodes are located close to the brain; the pathological process can affect the brain and lead to meningitis. Also, advanced lymphadenitis threatens infection in the blood, which means sepsis can occur, the infection will spread throughout the body. In this case, the baby’s life will be at risk.
Advanced lymphadenitis can lead to serious complications
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is powerless against pathologies of the lymph nodes, since they cannot be cured without knowing the cause of the development of lymphadenopathy.
As a rule, traditional medicine suggests using various decoctions and infusions for rinsing the mouth if swollen lymph nodes are associated with infectious processes in the mouth. For this purpose, decoctions of calendula, sage, oak bark, and chamomile are used. You cannot rely on such remedies; you must show the child to a doctor and consult with him about the advisability of using traditional medicine recipes.
Dr. Komarovsky about enlarged lymph nodes in the neck
According to Dr. Komarovsky, the most common causes of cervical lymphadenitis are numerous lymphotropic viruses, which include the well-known herpes, chickenpox, and adenovirus infection.
According to Komarovsky, if the nodule is inflamed on the left or right side, there is no need to worry. This indicates that this particular node is activated in the functioning of the immune system, as it takes on an additional load. In most cases, urgent treatment is not required. Often an inflamed lymph node returns to normal on its own, without any effort from doctors.
When is it necessary to contact a specialist?
The size of the lymph nodes in the neck area is considered normal, not exceeding 1 cm. You should be concerned if they enlarge and become more than 1.5 cm in diameter.
Residual lymphadenopathy deserves special attention. This phenomenon occurs after the baby gets sick with the flu, ARVI or other infectious disease.
Enlarged and inflamed lymph nodes in a child’s neck may persist for a month after recovery. In this case, there is no need to treat the inflamed nodes. Within a month after recovery, the formations on the neck will disappear on their own without additional therapy.
Advice. However, if there is progressive growth of the lymph nodes, or there is no effect from the treatment, or the enlargement of the lymph nodes is in a rare location (for example, the supraclavicular fossa), then both the pediatrician and parents should be concerned.
An increase in temperature with lymphadenitis is a reason to urgently consult a doctor
There are situations in which you should not hesitate to seek medical help:
- Lymph nodes have been constantly enlarged for more than a month;
- Nodes enlarge in several areas of the body at once;
- A child under one year of age has a fever due to lymphadenopathy;
- The formation is red, hot to the touch, touching the node causes severe pain;
- Lymph nodes connect to each other and to surrounding tissues.
In case of such changes, regardless of the child’s well-being, you should consult a doctor who will help determine psychosomatics and prescribe the necessary tests: blood tests, ultrasound, x-rays.
If the inflamed lymph node turns red, this may indicate suppuration. In this case, the temperature rises, the baby’s condition worsens, fraught with a breakthrough of purulent contents into the internal tissues.
Recommendation. So, Dr. Komarovsky, at the first sign of redness, advises immediately contacting a pediatric specialist, because purulent lymphadenitis often has to be treated surgically.
Causes of enlarged submandibular lymph nodes in a child
Lymph nodes on the human body can be easily felt under the jaw, in the armpits and in the groin. The normal size of a lymph node is about the size of a small pea. It should be mobile, not connected to the skin and not soldered to other nodes.

It often happens that this size increases several times. In this case, the lymph node becomes painful on palpation. There is redness on the skin. Submandibular lymph nodes are filters for nasopharyngeal infections. During the inflammatory process, their increase is noted. But sometimes they can be slightly enlarged without any other signs (there is no pain when palpated, their mobility remains). An increase may be normal, but to make an accurate diagnosis, it is better to consult a specialist.
Lymphadenitis is a disease in which the lymph nodes become inflamed. With frequent inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes, we are talking about nonspecific lymphadenitis.
Causes of nonspecific lymphadenitis:
- Flu
- ARVI
- Mononucleosis
- Toxoplasmosis
- Tonsillitis
- Angina
- Otitis
- Rhinitis
The disease can be acute, but in chronic forms, the lymph nodes usually become enlarged. In order for the lymph nodes to shrink to a normal state, it is necessary to cure all chronic inflammation in the body.
Also, the cause of enlargement of the submandibular nodes can be caries. Bacteria constantly multiplying in the mouth affect the immune system, causing an increase in lymphatic indicators. You need to urgently visit the dentist and treat your child’s caries.

When vaccinated, a child's body may respond with enlarged lymph nodes. But there is nothing dangerous in this; after some time, when immunity is developed, the lymph nodes will return to normal.
The child must be regularly taken to see the pediatrician. This will allow existing diseases to be identified and treated in a timely manner.
Prevention of inflammation of the lymph nodes
In order not to encounter such a serious disease as lymphadenitis, it is necessary to carry out preventive procedures:
- Try to avoid injuries near the nodes;
- Avoid infection of injured skin areas;
- Treat chronic diseases in a timely manner;
- Identify and treat colds in a timely manner;
- Visit the dentist regularly with your child;
- Observe the rules of child hygiene;
- Avoid purulent processes on the skin and treat any damage with antiseptic drugs;
- To maintain immunity, it is recommended that children under one year old include more foods enriched with vitamin C in their diet and harden them.
If you suspect lymphadenitis in your baby, you should consult a doctor who will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment. Independent home treatment is unacceptable, since home-grown therapy can lead to the development of serious consequences: meningitis or sepsis.