Hydrocele in children: treatment
Only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis, because a visually enlarged scrotum looks like an inguinal hernia. A distinctive feature of hydrocele is that upon palpation, the volume of fluid gradually decreases. If the pediatrician finds it difficult to make a diagnosis, you will be prescribed an ultrasound or diaphanoscopy, when the quality of the accumulated fluid is examined using a special device.
One testicle may be larger than the other from birth; this pathology does not require treatment once the child reaches two years of age, since during this time the duct connecting the abdominal cavity with the testicles heals on its own. Afterwards, the child undergoes a simple operation to dissect the membranes. When the swelling in the newborn becomes too severe and the testicle increases in size, a puncture is performed to pump out the fluid. The procedure is repeated if the deviation appears again.
Hydrocele of an infectious nature is treated with antibacterial medications, which are also prescribed by the doctor. In this case, no self-medication should be allowed. Parents should not be afraid of surgical intervention, since after the procedure the testicles remain healthy and do not lag behind the norm in development.
In advanced cases, when the mother neglects the doctor’s recommendations, the child may experience testicular atrophy, which leads in 80% to infertility and low sexual function.
There are several folk methods to reduce testicular swelling. One of the fastest-acting compresses is a compress based on sunflower oil, which needs to be boiled, cooled, moistened in a soft cloth and wrapped around the scrotum. The procedure is carried out 3 times a day for a course of 2-3 weeks. During this procedure, the boy needs to wear tight-fitting panties so that the testicles do not sag. To improve the passage of fluid through the ducts, during evening bathing, massage the scrotum in warm water for 1-2 minutes for the procedure to be effective; it also needs to be done daily.
Treatment
False cryptorchidism, in which the gonad “walks” from the scrotum to the scrotum, does not require special treatment. It usually goes away after 7-8 years, when the inguinal ring shrinks. But this form of pathology requires constant monitoring by the surgeon. You will have to visit this specialist more often.
True cryptorchidism can be treated with both medication and surgery. Treatment with medications makes sense when the testicle has only slightly reached its destination and is located next to the scrotum. Any conservative therapy helps the gonad advance to the scrotum by only 30-50%. Therefore, doctors can guarantee a probability of successful treatment of 60-90% only when the testicle has a short journey ahead of it.
The best results are achieved if therapy begins at 6 months and 1 year of age. However, it makes no sense if the child has already entered the ranks of adolescence, when testosterone levels naturally increase.
For treatment, Choriogonin or Pregnil (hCG preparations) are used; injections are given in courses in the age-specific dosage prescribed by the doctor. Statistics show that in every fifth child who was cured with the use of medications, cryptorchidism returns after some time. Reviews from parents who decided to treat their child with medication indicate that these statistics are higher, and the disease returns much more often than official sources say.
Surgery is considered a more reliable treatment method. It can be done on children from 9-10 months of age, however, surgeons are often in no hurry and wait up to 2 years. After 7-8 years, there is no point in undergoing surgery, since the processes of puberty begin in the body. The younger the child is at the time of the operation, the greater the likelihood that the testicle that is returned to its place will function normally, produce sperm of proper quality and provide the boy’s body with male sex hormones.
If the disease was first discovered after the child was 8-10 years old, then the “lost” testicle must be removed. Even if it has not atrophied, then in any case it will not perform its functions, and the risk of developing malignant tumors in it increases significantly. The operation is performed using laparoscopy, this can significantly facilitate and shorten the rehabilitation process.
The first changes begin during the period of intrauterine development. The seminal function is disrupted, the composition of the tissue changes, because the temperature in the scrotum is lower than in the abdominal or subcutaneous area.
During the rehabilitation period, the child is prescribed antibiotics, dressings, and after the stitches are removed, a special massage.
This pathology is less scary. There is a temporary appearance and absence of testicles in the scrotum. Regular monitoring by specialists is recommended; therapy is not prescribed, let alone surgical intervention.
This reaction of the body causes the testicles to fall and rise from time to time. Most often, such changes appear in a child at the age of two years. It goes away over time, upon reaching the age of 11. It is during this period that puberty occurs, the testicles enlarge and remain in the scrotum forever.
In rare cases, children do not outgrow it; this reaction of the body remains with them all their lives. The phenomenon is not terrible, it has no effect on sexual function, moreover, it is considered normal.
Such changes in the development of children are quite common. About 30% of babies have testicular pathology. As a rule, most of these are premature babies. In only 5% of children, this pathology requires treatment and surgical intervention. Basically, it returns to normal in the sixth month of the boy’s life.
Neglected pathology remains dangerous; without timely surgical intervention, it leads to cancer in the future.
Readers already know that until the age of 12 months, parents can calmly wait for the baby’s testicles to drop. If after this period an important event in the life of the future man has not occurred, then the pediatric urologist chooses a method of treatment. It depends on the location of the testicles and the reasons that caused cryptorchidism. Assigns:
- hormonal therapy;
- surgical intervention.
Hormonal therapy is carried out by two doctors - a urologist and an endocrinologist. There is no need to be afraid of this treatment. Some parents believe that hormone therapy will cause their child to experience premature puberty. But there is not an iota of truth in this. Since, contrary to expectations, after the examination the baby will be prescribed gonadotropin. This hormone promotes the natural descent of the testis.
In other cases, the most effective treatment method will be surgery. To get lasting results, the best age to carry it out would be a period of 3-4 years. This method is chosen when cryptorchidism arose due to a mechanical barrier. The surgeon lowers the organ into the scrotum and at the same time takes a piece of tissue for analysis to rule out gonadal dyskinesia, as well as tumors of malignant origin.
What to do if a newborn’s testicle has not descended: causes and treatment
At the birth of a boy, attention is paid to what kind of testicles babies should have. When examining the baby, they monitor the condition of the organ and its position. Various pathologies associated with the small size of the genital organ, its atrophy, displacement of one or two testicles, and dropsy are identified. It happens that one testicle in a newborn does not descend into the scrotum. The neonatologist will immediately determine the pathology. But the disease can develop later, so the mother should be attentive to her son.
Non-descending of one or two testicles is common and is called cryptorchidism. The problem disappears when the child reaches six months. If the pathological process is prolonged, then surgical intervention will be required.
The situation when in newborns the testicle is not in the scrotum, but is hidden in the peritoneum or inguinal canal, is called false cryptorchidism. This condition is provoked by the baby’s muscle tension and being in a cold room.
The reasons that a newborn has one testicle much larger than the other lie in the filling of the cavities with serous fluid. The danger of dropsy is its development into a hernia.
A hernia in the groin can be felt visually. It can be discovered by a mother while bathing her son. Education causes anxiety for the child, and the hernia must be removed.
Untreated pathologies lead to organ atrophy and reduction in size. The disease develops after the baby has had infections.
If redness of the testicles is detected in a baby, then the cause of the disease is non-compliance with hygiene rules. Diaper rash in the groin leads to irritation of the skin of the scrotum. But serious pathologies such as hernia, torsion, dropsy, and organ injury are accompanied by redness of the affected area. The appearance of a rash on the scrotum is a consequence of an allergic reaction
Source
At what week of pregnancy do the testicles descend into the scrotum?
The main research method is palpation. For a non-palpable testicle, ultrasound is used. If the testicle is absent even on ultrasound, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed.
The most effective surgical treatment for cryptorchidism. It is carried out when the child is between one and a half years old. Before the operation, the baby is observed by a pediatric urologist.
As a preparation before surgery, hormonal therapy can be carried out.
Correct development of the sex glands is possible only in the scrotum. Other cases lead to various complications, including:
- disturbance of spermatogenesis;
testicular torsion;
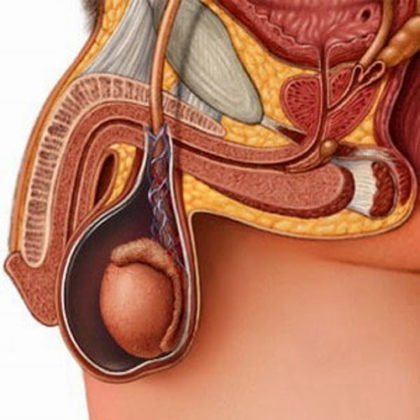
- Sometimes the testicle lies in the inguinal hernia and is strangulated along with it.
- Traumatic orchitis with cryptorchidism develops as a result of generic grass in newborns and is called idiopathic testicular infarction.
- The above conditions have a similar clinical picture and are called “acute scrotal syndrome”.
The risk of developing cancer of an undescended testicle is 20 times higher. And it does not depend on whether treatment was carried out or not.
If the operation is performed on time, the prognosis is often favorable.
With pseudocryptorchidism, the scrotum is symmetrical. On palpation, the testicle easily sinks to the bottom of the scrotum, but due to the strong cremasteric reflex it returns to its original position. This condition goes away during puberty.
With pseudocryptorchidism, the functions of the boy's testicles are not impaired.
Testicular pain is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
Reasons why boys have testicular pain:
- testicular torsion;
- strangulation of the testicle in the inguinal hernia;
- traumatic orchitis;
- inflammatory orchitis.
These conditions have a similar clinical picture (signs) and are united by the term “acute scrotal syndrome.”
The clinical picture includes the following symptoms:
- sharp pain in the scrotum and testicle, radiating to the groin area;
- swelling of the scrotum, its hyperemia (redness) on one or both sides;
- enlarged, dense testicle;
- fever, nausea, vomiting, pale skin.
Let's look at diseases that cause pain in the testicles.
Testicular torsion and strangulation in an inguinal hernia are described above.
In traumatic orchitis, the severity of the lesion depends on the strength and type of injury. There is a bruise, dislocation, rupture and separation of the testicle.
If there is a bruise, the pain goes away after a while, bruising, hyperemia, and swelling are visible on the scrotum. In case of severe injury, vomiting and fever may occur. Upon examination, a hematoma (bruise) of soft tissues, hyperemia, swelling, and tenderness of the scrotum are visible. The testicle is enlarged and painful.

Torsion, strangulation of the testicle, rupture, and separation of the testicle are treated surgically.
For inflammatory orchitis, bruise and dislocation, treatment is conservative. It includes bed rest, a fixing bandage on the scrotum, antibacterial therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs, and glucocorticoids.
The development of the testicles begins in the second month of pregnancy, and if there are no genetic abnormalities in the fetus or other difficulties during pregnancy, then the formed testicles descend into the scrotum at 9 months, or in the first weeks after the birth of the child.
The testicles descend along the inguinal canals and are supported by the spermatic cords (schematically shown in the photo). If the inguinal canals are too narrow, or the spermatic cords do not release their tension, cryptorchidism (undescended testicles) may develop.
In about 4% of boys, only one testicle (usually the right one) may descend before birth, with the other one doing so a little later. At risk are those children who were born prematurely, have too little birth weight, or have congenital and genetic diseases.
Usually mothers worry whether this is painful for the baby. Doctors say that the process of lowering the testicles normally does not cause severe pain in the child, especially if everything happened in the womb. Crying and whims before the age of 6 months usually provoke colic and adaptation of the digestive system to new operating norms.
Reading reviews of expectant mothers after undergoing the second and third screening, I would like to once again emphasize some points:
- When boys' testicles descend, this is clearly visible on an ultrasound. An ophthalmologist can also determine whether there are any pathologies in the structure of the genitourinary system. This information is provided to mothers not for unnecessary worries, but for proper preparation for care during the postpartum period.
- The third screening showed the absence of any abnormalities in the structure of systems and organs, but the testicles did not descend? No problem. It is normal for the testicles to descend in the first 6 weeks after birth (for full-term babies).
- Don’t be afraid to consult with your doctors about any issues you have doubts about. Consultation is not a treatment, but it helps you stop worrying in time or start taking action in the interests of a speedy recovery.

You can independently find out whether everything is in place by simply bathing the baby in warm water: the testicles are easy to find by touch or even see two small balls.
Neonatologists carefully examine newborns and are the first to notice the problem. If any deviations from the norm occur, observation until 3 months of age, hormonal tests, and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity are recommended.
Radical treatment methods are resorted to after 6 months of life, or even 12 (individual developmental characteristics are taken into account). If the testicles cannot descend on their own, then surgical methods should be resorted to. Otherwise, the ability to produce sperm will be lost.
Also, in the absence of adequate treatment, the following may occur:
- inguinal hernia and, as a consequence, removal of one testicle;
- the appearance of a malignant tumor;
- hormonal imbalance in a child upon reaching adolescence.
Treatment for cryptochristism is usually performed only with surgery. The laparoscopic method greatly simplifies the postoperative period. And traditional methods can only aggravate the situation, or create another problem.
You should also carefully consider doctors’ proposals to use hormonal medications. Hormones can greatly disrupt the functioning of the entire endocrine system; their use must have strict medical indications.
Also note that failure of the testicle to descend on its own may indicate Klinefelter syndrome, a chromosomal change that causes delayed sexual development and subsequently infertility. To eliminate this problem, a series of tests will be required.
Very attentive parents may also have other “testicle questions” because the appearance of the genitals may seem strange. Adults are most often concerned about two problems: a change in the size of one or both testicles, or their disappearance for a while.
As for the situational disappearance of one or both testicles, this “behavior of the testicles” is a variant of the norm; sometimes they can be retracted into the abdominal cavity, and after some time return to the scrotum. Retraction has no detrimental effect on future sexual health.
But a testicle that is too large may indicate problems. And not only because it can be difficult to visually determine the presence of both testicles in the scrotum if one testicle is significantly larger than the other in size.
Such changes may indicate the following diseases:
- the presence of an inguinal hernia - it can be unilateral or even bilateral. In essence, we are talking about protrusion of the abdominal wall and intestines, which threatens strangulation and the development of peritonitis. In this case, surgical treatment is recommended;
- hydrocele - the sac around the testicle cannot quickly empty itself of fluid during the descent of the testicles from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum. Doctors do not recommend considering this condition a problem until one year of age. Most boys are born with hydrocele (various degrees of severity), but usually the fluid resolves on its own. Surgery is appropriate if swelling blocks normal blood flow. Parents can determine this themselves when the color of the scrotum changes to a stable burgundy, or even bluish.

Pediatricians Joan Liebman-Smith and Jacqueline Nardi Egan recommend that parents be attentive not only to the search for the testicles, but also to the general condition of the scrotum:
“An overly painful, swollen and hard scrotum may be evidence of testicular torsion. This condition blocks the normal flow of blood to the testicles and scrotal tissue. Without surgical intervention, the testicle can completely lose its functionality within a few hours.”
An immediate visit to the hospital cannot be avoided if even a small inguinal hernia greatly increases in size, vomiting and severe pain are observed.
This is how pinching of the intestines by the abdominal wall manifests itself. Most often, such hernias occur in children under 6 months of age and are treated exclusively through surgery.

This word refers to a disease when boys' testicles do not descend on time. This phenomenon occurs quite often. They can navigate the canals on their own during the first year of life. If this does not happen, then surgical removal is prescribed. The operation is mandatory, because if descent does not occur, the testicles will lose their reproductive function.
Initially, the testicles are formed in the body at 6-7 weeks of life in the womb. They are located in the abdominal cavity of the fetus. Their growth and development is influenced by hormone levels.
After 30 weeks, they begin to descend into the scrotum.
However, quite often there are cases when boys’ testicles do not descend immediately.
The diagnosis is made immediately after birth. During the first year of life, no treatment is required, as everything can return to normal on its own. If deviations are also noticeable during the annual examination, then treatment is prescribed. It is selected depending on the course of the disease and the general condition of the child.
So, these could be hormonal drugs to stimulate the development of the testicles. Surgery is also often recommended. The age of a boy for surgery varies from one to five years.
The reason for the occurrence of the disease may be different. This list contains a lack of androgen and gonadotropin hormones. In cases where boys' testicles immediately descend due to their underdevelopment, treatment is carried out with hormonal drugs. This gives tangible results and promotes rapid recovery.
There are cases that during the course of infections inside the womb, a boy develops adhesions in the canals through which the testicle moves. This is diagnosed during laparoscopy and corrected immediately.
It is often found that when boys' testicles descend, one remains in the abdominal cavity or in the canal on the way to the scrotum.
This variant of the disease is diagnosed and treated in the same ways as in the case when both testicles do not descend.
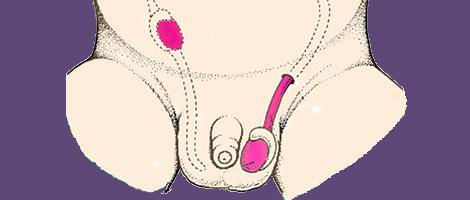
The details and characteristics of each child are revealed strictly during examination by a doctor.
Ultrasound is often used to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. This allows you to accurately determine where the testicles are located in boys.
The child’s body is designed in such a way that at the slightest suspicion of danger, a defensive reaction is activated. The most important male reproductive organ is attached to special muscles. Thus, the testicles in boys can retract when the ambient temperature changes or when touched.
In such cases, no treatment is required. The scrotum will be completely filled as soon as the time is right. The fact is that her muscles also have several layers and must mature in order to provide reliable protection to the testicles.
There is a lot of disagreement on this issue. Some argue that the operation should be performed as quickly as possible after a year. The argument is that the testicle, while in the abdominal cavity, is subject to overheating, and this may affect its further functioning. There are also observations that, while in the peritoneum, it changes its membranes.
Another opinion is that until the age of 5, it does not matter whether the testicle descends a year earlier or later. That changes in their cover are a normal physiological process. And operations at an earlier age are more difficult to tolerate. According to these recommendations, intervention should be performed at 4 years.
Thus, it is clear that there is no clear answer to the question of at what age the testicles descend. It depends on the heredity and physiology of each child. The main indicator in this situation is time.
That is, the longer the changes persist, the more surgical intervention is indicated. Monitoring the baby by a specialist and parents will be key.
Thanks to this, it is possible to adjust the treatment at the right time and save the boy from problems in the future.
What to do if the testicle does not descend after taking a course of medication? Surgery to correct the position of the testicles can be of two types:
- Open type - one medium-sized incision is made on the abdomen. Then they find the desired element and direct it into the scrotum.
- Laparoscopy - the operation consists of several small punctures in the abdominal cavity, special tubes are inserted into them, with the help of which the testicle is sent to the desired place.
Cryptorchidism in adults
The displacement of one or two testicles can occur in both adolescent and adult men. As a rule, this becomes a consequence of some kind of injury or illness.
So, if the testicle has been in the abdominal cavity for some time, it may have to be removed. Such an organ loses its viability, and if it remains, there is a risk of developing tumors.
This happens due to impaired blood circulation and exposure to elevated temperature.
But even if the operation was performed on time and the testicle was saved, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations. This is necessary to identify various complications in the early stages.
A rare pathology, occurs in 4% of healthy children, 30% of premature children. As a rule, when the child reaches 1 year of age, it goes away; 3-4% of children need treatment; for 2%, surgery is extremely necessary.
Testicles begin to form in the womb, during the first trimester of pregnancy. They will remain in the boy’s abdominal cavity for six months, and will begin to descend a few weeks before birth.
They are located near the kidneys, descending through the inguinal canal. Mothers can figure out for themselves whether their baby’s testicles are back in place. You just need to examine and feel the scrotum.
This examination is carried out when the baby is calm and not upset by anything. If you cannot figure out for yourself whether everything is normal, consult a doctor. Only an experienced doctor can figure it out and give the correct conclusion.
It is not always possible for a mother to distinguish a false pathology from a real one.
It happens that mothers assess the situation not entirely correctly. For example, they touched the scrotum, and it instantly became as if empty, and they immediately begin to get nervous. This reaction occurs due to the fact that during touching, the testicles react to the temperature difference, reflexively rising to the groin. Such a child needs to be monitored. The baby is relaxed, if the testicles are in place, tell the doctor.
If you cannot find them in a relaxed state, then you need to worry. But as a rule, they take place within 1-1.5 years.
The testicles descend in stages. The first time they reach the tummy, they remain there for a while. The second time they travel a longer distance, move through the inguinal canal and are fixed in the scrotum.
They travel this entire long journey while the baby is in the mother’s tummy, just before birth. As a rule, in 80-85% of children this process is completed before birth.
For the rest, upon reaching the first year.
After birth, the baby must be examined by a doctor. He gives a conclusion, all data is recorded in the child’s card. If something is wrong, you will be sent for the first ultrasound in the maternity hospital. Upon discharge, all recommendations will be noted, and your local doctor will be able to give timely referrals to specialists.
Very rarely, there are cases when the testicles have not descended, or only one has descended, and the second wanders. This deviation from the norm is called cryptorchidism. The diagnosis is made immediately after the baby is born. If the doctor cannot feel the testicles, he should perform an ultrasound examination to have an idea where they are stuck. Very often, over time, they fall into place on their own.
It is generally accepted that it is normal for the testicles to fully descend before the baby's sixth week of life. It takes 12 months to correct this pathology naturally.
If by this time the testicles have not descended on their own, then by the second year of the child’s life, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Laparoscopic interventions are considered to be more gentle, although a regular operation also does not take much time, children tolerate it normally.
Men's health is the key to a stable psyche and the absence of complexes. Therefore, mothers of boys should be very attentive to all changes in the genitourinary system. Due to the absence of one of the testicles, boys may develop psychological problems, and later more complex mental disorders.
Investigative reasons associated with the behavior and habits of the mother:
- Drinking alcohol, even low-alcohol drinks, during pregnancy;
- Smoking;
- Drug therapy. It makes no difference whether you take medications before or during pregnancy;
- The mother’s hormonal state, disruptions, disturbances in the production of hormones, especially androgens.
- Diseases of the endocrine system;
- Increased blood sugar levels;
- Problems with digestion and metabolism of the mother;
Because of this, as a consequence, the manifestation of the following pathologies is possible:
- The spermatic cords , along which the testicles should descend, are underdeveloped. Moreover, due to their length, the testicles constantly stretch upward. With such a pathology, surgical intervention is inevitable. And the sooner it is carried out, the better.
- Pathology of the inguinal canals , which does not allow the testicles to descend and attach to the scrotum.
The baby’s development may also be affected by:
- Premature birth;
- Hereditary factors;
- Congenital, acquired umbilical or inguinal hernias.
- Hydrocele of the testicle;
Such changes in the child’s body have not been fully studied. Therefore, all changes require control and observation by specialists.
Failure to perform surgical intervention entails unpleasant consequences, a malignant tumor. Which carries a huge risk to the life and health of the child.
Undescended testicles in boys are called cryptorchidism. This phenomenon is a consequence of pathology, accompanied by the absence of a testicle in the scrotum. The child does not feel any discomfort. A very rare occurrence is the pathology of non-descendancy of two testicles, mostly it is only right-sided.
There are three subgroups of this pathology:
- Lack of hormonal components in the baby's mother during pregnancy. Human chorionic gonadotropin is responsible for the development of boys. They belong to the hormonal subgroup.
- Endogenous subgroup . Changes in the development of the baby even before birth, the consequence is not prolapse of the testicles.
- Changes in the inguinal canal, which prevents the descent of the testicles, followed by surgery. Belongs to the mechanical subgroup .
Therefore, it is very important to figure out with your doctor what exactly is wrong and at what stage the pathology occurred. After determining the diagnosis, treatment is prescribed according to the subgroup of the disease.
The opinion of the famous pediatrician Komarovsky agrees with the opinion of leading doctors in Russia. Surgical intervention for such a pathology is inevitable and is the only correct solution. Komarovsky recommends referral for surgical intervention from the age of 10.
The main indication for this will be the conclusion of the ultrasound examination. It allows you to determine where the testicles are located, whether they can descend into the scrotal cavity on their own, and how urgently the operation needs to be performed.
It is also important to decide on the choice of surgeon and anesthesiologist; a competent approach to this issue will help to avoid complications after the administration of anesthesia in the postoperative period.
Children's pediatrician Komarovsky recommends not to rush into taking hormonal medications. Moreover, their effect on an unformed organism has not been fully studied. They can cause much greater complications than surgery.
This pathology entails a number of specific consequences. Prolonged presence of the testicle in the abdominal cavity can affect the ability to have children and potency. After all, the temperature in the tummy is higher.
Possible concomitant diseases:
- Boy's infertility;
- Hormonal imbalances;
- High risk of impotence;
- Predisposition to inguinal hernias;
- Increased risk of injuring or pinching a testicle that is out of place;
- Increased risk of developing cancer.
Surgical interventions are recommended from six months to 1.5 years. At the age of up to six months, the amount of hormones responsible for voluntary descent of the testicles is increased. After this period, there are much fewer of them, so it is pointless to wait further for a miracle.
When a child reaches the age of one and a half years, changes begin to occur in the genital organs and blood vessels form. After the child reaches the age of three, changes in the genital organs become irreversible, treatment is largely unsuccessful.
This happens, as a rule, due to the fact that the cords along which the testicles should descend into the scrotum cannot be stretched.
After all, the smaller the baby, the better the quality of the operation, the shorter the distance from the kidneys to the groin, and the operation ends in one stage, the cords are not injured. The older the child, the more difficult it is, he grows, but the cords are not there, they need to be stretched a little during the operation.
There is a risk of damaging them; the testicle will stop growing over time and become deformed. The lower the testicles are, the higher the chances of success. The higher, the greater the risk.
If surgery is not performed, the testicle will need to be removed when the child reaches 10 years of age. Otherwise, in the near future, the undescended testicle will degenerate into a cancerous tumor.
There are several types of this pathology:
- Unilateral pathology occurs in approximately 15% of patients. Typically, for most cases, it is a right-sided non-descent;
- Bilateral, extremely rare. Approximately 5% of patients have this diagnosis;
The testicles are formed in the mother's womb; at the time of birth they are already formed and descended.
The process of descent occurs in the last weeks before birth:
- In full-term children, this pathology occurs in 3-4% of children. When the child reaches the third month of life, they fall into place in 74%;
- In preterm infants, the pathology rate is higher, 10-15%. But when the child turns three months old, they fall into place in 95% of cases;
- Pendulum , it only needs observation. The testicles react to temperature changes and rise and fall on their own;
- Inguinal . When the testicles wander, they stop in the inguinal canal. Their location is easily determined by hand;
- Abdominal . Their location can only be determined using an ultrasound examination;
- Unstable. The testicles are located high up, but from time to time they descend and go back. They can also snap into place when pressed, then move away again;
- Ectopic. When lowered, they can be located under the skin, located side by side in the same channel. There is a combination of ectopic changes and inguinal hernia, this occurs often, in approximately 95%.
This pathology is less scary. There is a temporary appearance and absence of testicles in the scrotum. Regular monitoring by specialists is recommended; therapy is not prescribed, let alone surgical intervention.
This reaction of the body causes the testicles to fall and rise from time to time. Most often, such changes appear in a child at the age of two years. It goes away over time, upon reaching the age of 11. It is during this period that puberty occurs, the testicles enlarge and remain in the scrotum forever.
In rare cases, children do not outgrow it; this reaction of the body remains with them all their lives. The phenomenon is not terrible, it has no effect on sexual function, moreover, it is considered normal.
Such changes in the development of children are quite common. About 30% of babies have testicular pathology. As a rule, most of these are premature babies. In only 5% of children, this pathology requires treatment and surgical intervention. Basically, it returns to normal in the sixth month of the boy’s life.
Neglected pathology remains dangerous; without timely surgical intervention, it leads to cancer in the future.
Immediately after the baby is born, the pediatrician conducts an examination and feels the genitals. Conclusion Inguinal cryptorchidism is not a fatal diagnosis. It means that the testicle has been discovered and is located in the groin area. If you couldn’t feel it with your hands, an ultrasound will help identify its location.
In most cases, groin pathologies return to normal closer to the first year of the baby’s life.
Until the baby's sixth month of life, undescended testicles only need regular monitoring. If from the sixth month to a year, the changes have not returned to normal, they need to be eliminated.
There are two treatment methods:
- Treatment with hormones;
- Surgery;
You make this decision together with your doctor. In most cases, hormone therapy does not produce results; surgery remains the only solution. In addition, during this period the child will be frightened by injections. Therefore, surgical intervention is considered the only and correct solution.
During the operation, an experienced surgeon will put the testicle in place and perform local fixation. This will take on average 30 minutes. The lower the testicle is located, the better and more effective the operation; the higher it is, the more difficult and time-consuming such intervention is needed.
After the operation, the baby quickly recovered. Such intervention is justified, although there is always a risk. It is possible to carry out intervention later, when the child is older. But this increases the risk, the cords may be too short, and the postoperative condition will be more severe.
Therefore, you should not take risks, listen to the recommendations of doctors. Take care of your children's health.
Therapy for cryptorchidism pathologies is possible only with specialist consultation and regular examination. To avoid inflammatory processes, infertility, relapses and complications, it is necessary not to self-medicate. Follow all recommendations of your attending physician. This is the key to your baby’s health and a bright future.
source
newborn one testicle is larger than the other
Despite the fact that the length of stay in the hospital was minimal and the operation was simple and minimally invasive, Lekha is not recovering very quickly. It’s been three days now and he’s still pale and sleeps a lot. He is less mobile, has lost weight - his facial features have sharpened, but gradually everything goes away. So, even such a small operation is not a small burden on the body. I’m not doing well either - I’m constantly dizzy and very drowsy. I don't want to do anything. I decided that we at least need to eat well.
Or what is sex? I understand this is a well-worn topic. It’s just that the child has recently become very active with questions. He generally asks me 100 questions a minute, a lot of philosophical reasoning. And I like it. But one of the topics that, apparently due to their age, they actively discuss with the guys is gender topics.
I've been feeling really sick the last few days. The worst thing about the mood is irritability, impatience, you want to be left alone. I feel sick almost all day, but only go away in the evening. The only time I don't feel sick is when I eat. I feel bloated and not wet at all. I’m also constantly worried that something is wrong. That I will do something wrong. This has never happened before, it usually happens with the first child. I'm worried that something will go wrong and everything I've already gone through will be in vain. Don't know.
Source
Testicular diseases in newborn boys
No health problem causes as many complexes and grief in men as problems in the sexual sphere. In order, on the one hand, to avoid unnecessary worries, and on the other, not to miss the symptoms of an impending problem, mothers of boys simply need to have an idea of the peculiarities of the functioning and development of the male reproductive system and be aware of what the testicles of a newborn look like normally. It is also important to know what to do if a newborn's testicle has not descended. We invite you to talk about this in more detail.
Boys' testicles begin to form in the first trimester of pregnancy. They are initially located in the abdominal cavity, and the process of their descent into the scrotum occurs just before birth. Therefore, in babies born at term, the testicles are already in the scrotum. But there are cases when a newborn boy’s testicles have not descended into the scrotum or only one has descended. This phenomenon is called cryptorchidism and, as a rule, is diagnosed during the first medical examination of the baby.
In pediatric urology, undescended testicles in newborn boys is the most common congenital anomaly, which occurs in 4% of full-term and 10 - 20% of premature babies. During the first six months of life, in 75% of newborns, the testicles descend on their own, which is associated with a gradual increase in testosterone levels in the body.
According to experts, this disease often goes away on its own before the child’s first year of life. But there are some points that parents should pay special attention to in order to prevent its complications.
Along with cryptorchidism, the opposite situation is often observed when a baby is born with enlarged, swollen testicles. In this
Source
Types of pathology
There are three types of anomalies based on the location of the testicles:
True anomaly
With this form of pathology, the testicle does not descend into the sac due to delayed migration. It can be located in the inguinal canal, near its rings or in the abdominal cavity. If the testicles are located in the groin, no special diagnostic measures are required. Since this is determined by simple palpation, when the doctor presses on the groin area. But, if they are in the abdominal cavity, then an ultrasound machine is used, which will show the picture of the disease more informatively. Some people think that the testes are capable of bursting - this opinion is completely wrong.
False anomaly
When the testicle periodically descends into the scrotum and takes a natural position, like in all boys, they speak of a false pathology. This happens because from time to time the muscles that depress the testicle become tense. The reasons for this are usually hypothermia or severe stress.
This form of the disease occurs in boys under five years of age. This pathology is not treated, since the testicle can descend on its own and become fixed in the scrotum. False cryptorchidism disappears by the time of puberty.
Is it dangerous if one testicle is larger?
Testicles are the most important part of the male reproductive system. They produce sex hormones and sperm. The weight and size of the testicles vary among men. It happens that one testicle is slightly higher than the other.
In most cases, this arrangement of the gonads does not affect their functionality, and, therefore, men’s health does not suffer from this. However, the abnormal position of the gonads, a sharp increase or decrease in one of them, indicates serious problems with men's health.
Normally, in right-handed people, the left egg is lower than the right one, and in left-handed people it’s the other way around. A reasonable explanation for this phenomenon is as follows: with such an arrangement, these organs are not compressed or injured when walking. There are no other explanations for this.
Malignant tumor. This is the most serious reason for an increase in the size of the gonad, requiring immediate treatment.
Inflammation of the appendage occurs in men at any age. Characterized by enlargement of one of the testicles and severe pain.
Varicocele, that is, varicose veins of the spermatic cord located in the scrotum. Because of this, the nutrition of the organ is disrupted and its size decreases.
Undescended testicle at birth (cryptorchidism). If the sex gland has been retained in the abdominal cavity for a long time, then its size is smaller, despite corrective operations.
Taking anabolic steroids often leads to atrophy of an important organ. In this case, one of the testicles begins to quickly decrease in size. The production of male sex hormones and sperm is significantly reduced.
A hydrocele is a dropsy of the testicle. With it, there is excessive formation of fluid and its accumulation in the membranes of the gonads. In this case, the left testicle is larger than the right one, sometimes this is a
Source
Why two testicles?
This pair of oval glands is responsible for the production and storage of sperm, as well as the production of male hormones.
If for some reason one testicle is missing, problems with conception may arise. According to statistics, when a child with cryptorchidism undergoes surgical treatment after reaching the age of seven, the ability to fertilize is reduced by 25%. That is, the absence of one testicle can only be considered as a psychological barrier or an external defect.
a newborn has one testicle larger than the other for reasons
The testicles are the most important organ for reproduction and procreation. This is a paired gland that produces sex cells and male hormones. The main function of germ cells (sperm) is the delivery of hereditary information to the egg. Penetrating the egg, they stimulate its development. Spermatozoa cannot develop at temperatures above 35⁰ C, so nature provides for the location of the testicles outside the abdominal cavity. The testicles also produce hormones that enter the blood and stimulate the development of male characteristics: mustache, beard, body hair, size of the genitals and male body structure.
The testicles (testicles or testes) are located in the perineal area in leather sacs - the scrotum. They are located behind the base of the penis, the left one is slightly lower than the right one. The scrotum has two separate chambers for each testicle. The weight of each is in the range of 20-50 g. One is always a little larger; there is no ideal symmetry in the body. Their size and mass depend on the individual characteristics of the organism. Large, tall men are thought to have slightly larger testicles. Although there are exceptions. Scientists still cannot determine the reason for the size.
The outside of the testicle is surrounded by a whitish-colored membrane called the tunica albuginea. Underneath it is the testicular substance, consisting of many cone-shaped lobules. The cone is directed towards the center. Each lobule contains 2-3 seminiferous tubules, which merge into a duct in the central part. There can be up to 300 such lobules in each testis.
Already in the 4th month of pregnancy in utero, the child develops epididymis, which secretes hormones for the development of sexual characteristics of the unborn child. The testicles descend into the scrotum from the groin area in 96% of newborn boys
Source
Hydrocele of the testicles in infants: is it dangerous?
Nowadays, it is quite common for young children to be diagnosed with hydrocele - hydrocele of the testicle in a newborn. Therefore, for many parents it will be useful to understand the following questions: what kind of disease this is, what are the causes of this disease, is it dangerous for the child’s health, what is the treatment, and what its consequences may be.
Hydrocele of the testicles or hydrocele occurs only in boys and is characterized by a large amount of serous fluid in the membranes of the testicles, while the scrotum is often significantly enlarged (unilateral enlargement of the scrotum is possible if fluid accumulates near one testicle in newborn boys).
This disease is diagnosed in approximately 10 - 16% of newborns and in 75 - 85% of cases goes away on its own, without any treatment. Therefore, this disease is also called physiological hydrocele of the testicles.
Why does communicating hydrocele occur? Usually, in a male child, just before birth, the testicles descend into the scrotum. As they pass through the inguinal canal, they take with them part of the peritoneum (called the processus vaginalis). Then this part of the peritoneum becomes overgrown. Due to this, organs and fluid from the abdominal cavity will not be able to enter the space in which the testicles are located. If certain reasons arise and the appendage is not overgrown, then fluid accumulates in the membranes of the testicles and hydrocele of newborns develops.
heredity (if the father had testicular hydrocele in the family, then there is a high probability that the baby will develop a similar disease);
increased intra-abdominal pressure in newborns, which usually occurs due to excessive excitability of infants and problems with the gastrointestinal tract. At the same time, in addition to dropsy of the testicles, hernias may form in the groin;
Non-communicating dropsy occurs when
Source