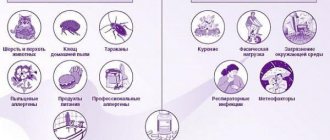
Causes of cough in children
The entry of foreign particles into the respiratory system provokes bronchospasm. This is the body’s protective reaction against viruses, bacteria and dust particles that are invisible to the naked eye. A child may develop a severe cough for the following reasons :
- Ingress of viral microorganisms. They actively multiply on the mucous membranes, causing swelling of the larynx, runny nose and chest pain. If the child has a severe cough, the child should be taken to the pediatrician, especially when the child is under three years old. At this age, children are not able to independently expectorate mucus in which viruses multiply.
- Bacterial infections are always accompanied by a sore throat and yellow-green nasal discharge.
- Allergy - a very severe cough occurs when the child is near an irritant. Allergens are often pet hair, household dust, powders and fabric softeners, fluff in pillows or plants. In this case, a cough occurs without phlegm, but the eyes begin to water and the nose becomes red.
Sometimes children can get a foreign body into their respiratory tract - we must not forget about this. From the outside it looks like a sharp attack of coughing; the child experiences a feeling of suffocation; it is necessary to urgently provide first aid and go to a medical facility.
Treatment of a severe cough in a child is prescribed only after the pediatrician determines the type of spasm . There are two types - wet and dry. In the first case, mucus comes out during an attack. Therapy in each case is selected individually, taking into account the age of the young patient and the presence of chronic diseases.
A child’s cough does not go away - what to do?
Awareness of what a cough is and the nature of its origin largely determines treatment tactics and sets the direction if examination is necessary.
So, we know that cough, like fever, is the body’s response to the penetration of external irritants. Thus, a physiological cough appears due to saliva, dust, crumbs, and mucus that accumulated during night sleep entering the respiratory system. As a rule, such a cough is episodic, it should not cause concern and there is no need to treat it either. A pathological cough that does not go away for two weeks or more is a completely different matter. It can develop as a result of a history of acute respiratory viral infection or act as an independent symptom of any disease. To determine the cause of such a cough, it is necessary to take into account that cough receptors are located not only in the respiratory system, they are also present in the outer lining of the heart, in the esophagus and even in the mucous membrane of the stomach.
In other words, coughing is a reflex that occurs under the influence of irritating factors. To decide what to do if a child’s cough does not stop, you need to thoroughly understand the reason for what is happening.
Causes of persistent cough in a child
If your baby has recently had a cold, the cough, as a residual phenomenon, can last up to two weeks, in rare cases up to a month. There is no cause for concern if, in addition to such a persistent, always wet, cough, the child has no other symptoms of the disease.
Things are different if there are no noticeable improvements in the baby’s condition for a long time, and he is tormented by a dry, hacking cough. Then we can assume that the disease did not go away without a trace and the baby developed complications, for example, bronchitis, pneumonia, laryngitis, pharyngitis, tracheitis; whooping cough, as well as roundworm migration, cannot be ruled out. As a rule, these diseases are accompanied by fever, general weakness, loss of appetite, and headache. How to treat such a dry persistent cough in a child must be decided by the pediatrician based on the diagnosis, the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the little patient.
It is impossible to speak unequivocally about the causes of a dry, persistent cough in a child without fever. Especially in cases where the appearance of the latter was not preceded by any disease of the upper respiratory tract. In this situation, we cannot exclude the possibility of cough as a symptom:
- left ventricular failure;
- gastroesophageal reflux;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- adenoiditis;
- tuberculosis;
- the presence of a laryngeal cyst;
- developed initial stage of cystic fibrosis.
Also, a persistent cough in a child without fever can be caused by an allergy.
What to do if a child’s cough does not go away for a long time?
Based on the above, it follows that before starting to treat a cough, its etiology should be clarified. Usually, when a cough arises against the background of an inflammatory process occurring in the respiratory tract, the parents’ task is to transform the unproductive dry cough into a wet one and help the child get rid of phlegm. In such cases, doctors prescribe medications with a mucolytic effect, then, when the cough becomes wet, they are replaced with expectorants. These medications are used in combination with antibacterial therapy, inhalations, foot baths (in the absence of fever), mandatory drinking plenty of fluids, and massages.
Of course, when answering the question of how to treat a child’s cough that does not go away, one cannot be guided by general rules. Since there are many reasons for the appearance of this symptom, and only a doctor can prescribe competent and adequate treatment.
Why does a child have a dry cough?
In children, severe coughing causes chest pain. The child sleeps restlessly at night and experiences a constant feeling of fatigue. If measures are not taken, pneumonia or bronchitis may occur. At an appointment with a pediatrician, you can find out why bronchospasms occur without phlegm:
- A cold is the most common reason why a child suffers. A cough accompanied by a runny nose is treated with antiviral or bacterial drugs and medications that help remove phlegm from the lungs;
- whooping cough is a rare disease, but if a child has a strong cough for a long time and the appropriate vaccination was not given at a certain time, then the disease cannot be ruled out;
- measles - bronchospasm is always accompanied by elevated temperature, the patient also complains of a sore throat;
- false croup - the disease is accompanied by a runny nose, sore throat, high fever and attacks that suffocate the baby, causing vomiting. Therapy is carried out only under the supervision of specialists in a hospital;
- pharyngitis and laryngitis - the disease begins with a sore throat, bronchospasm and hoarse voice, which disappears after 2-3 days.
A child has a wet cough without fever - what to do?
A well-known doctor claims that such a symptom cannot be ignored - a wet cough without fever stimulates the removal of phlegm accumulated in the bronchi. The manifestation itself is not very dangerous, but it can cause severe irritation and lead to serious consequences.
Additional symptoms that should alert you:
- attacks occur in the evening hours, worsening at night;
- wheezing is clearly audible between breaths;
- greenish discharge with blood clots is possible.
In such cases, Komarovsky does not recommend the use of cough suppressants. More useful here will be drugs that stimulate expectoration ( bromhexyl
). The instructions for the drugs detail the dosage and method of use; exceeding the specified standards or giving the baby syrup more often than indicated by the manufacturers is strictly not recommended.
A mandatory stage of treatment is long walks in the fresh air. In the cold season, you should dress warmly, but not allow the body to overheat - the child should be comfortable.
Cough in a child without fever - how to treat it

Before treating a child’s cough, it is necessary to determine the exact cause of this symptom. It is important to understand that reflex contractions of the chest occur as a result of irritation of receptors caused by various factors. Don't focus on respiratory infections or viruses. If there is no fever and other accompanying manifestations of acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, then a possible source of breathing problems may be the external environment or an allergic reaction.
How to treat dry cough in a child Komarovsky
The peculiarity of Dr. Komarovsky’s method is that he recommends wisely combining the use of medications and the body’s natural resources. Moreover, Dr. Komarovsky speaks of cough as a symptom, which is often only worsened due to improper treatment or the use of unnecessary medications.
It is due to the fact that the discharge is insufficient or it is very thick, which is why the child cannot cough it up. Classic treatment regimens suggest the use of mucolytics and expectorants for a speedy recovery.
A famous Ukrainian doctor, the main character of this article, has a different opinion. First of all, Komarovsky draws attention to the following facts:
- for children under 2 years of age it gives more side effects than benefits;
- This was confirmed in France back in 2010, when a high-profile situation arose: after treating young children with mucolytics, the latter developed serious complications. After this, doctors banned the use of these drugs to treat children under two years of age;
- Later, the Italians came to the same conclusion, banning drugs based on bromhexine, acetyl- and carbocysteine, ambroxol and several other common active ingredients (sobrerol, erdostein, neltenexin, telmestein) for the treatment of children of this age;
- In our country, such drugs are sold without a prescription, and television advertising constantly convinces people that they are necessary;
- To date, there is no convincing evidence that mucolytics help better than drinking plenty of fluids, rinsing the nose and gargling, humidifying and cooling the air. Dr. Komarovsky notes that mucolytics are drugs of unproven effectiveness, and the course of the disease depends only on the conditions in which the child is;
- In many cases, the initial illness is not serious, but symptoms intensify due to the use of mucolytics. The doctor thinks that the disease is progressing, he prescribes other drugs, including hormones and antibiotics, although there is no reason for this.
Dr. Komarovsky insists: under no circumstances should unproductive tissue be treated with a mucolytic. In older children, this is also not necessary, since the effectiveness of the drugs has not been proven.
There is no better remedy for cough in children than moist air, airing the room, drinking plenty of fluids and walking (if there is no fever or feeling unwell). Drug therapy is required only in the case of bacterial inflammation, when the situation is really serious.
Komarovsky also describes the causes of a child’s night cough as a consequence of insufficient humidity in the room, high temperature in the room (above 20-21 degrees). If a child is absolutely healthy, but coughs at night, it means that external conditions are not good enough for his respiratory system. If the baby has signs of illness (pain, fever, etc.), you need to contact your pediatrician for help and still improve the conditions in which the child is located as much as possible.
Causes of chest muscle spasms in children
The only correct decision when a child develops a severe cough is to visit a medical facility. Consultation with a pediatrician is required. Self-diagnosis often leads to the wrong choice of therapeutic actions and the disease becoming chronic.
The kid choked. If a child has a spasmodic cough without fever, you need to make sure there is free access of air to the lungs. Often, while playing, children swallow small toys or other found objects. In this case, the respiratory lumen is blocked, and the body tries to cleanse itself of the foreign body. You can help the patient by patting him on the back and performing a drainage massage. If necessary, call an ambulance.
Barking cough . Dry spasms usually indicate the emergence and development of a disease such as laryngitis. In most cases, the disease occurs with an increase in body temperature, unmotivated weakness and other symptoms of the pathological condition, but under certain conditions (immunity problems), inflammation can only be detected by reddened vocal cords.
Prolonged chest spasms . A prolonged, persistent cough without fever in a child is considered a sign of chronic respiratory diseases. A sluggish infection is rarely accompanied by a sharp deterioration in health and causes weak but frequent reflex chest contractions (coughing). Doctors recommend treating rhinitis, tracheitis, pharyngitis.
Cough with runny nose. When a baby constantly “thumps” and has a runny nose, pediatricians recommend undergoing a comprehensive examination for adenoids. The growth of the pharyngeal tonsil can be manifested by a persistent cough without a sharp increase in temperature. It would also be useful to exclude sinusitis as a source of an unpleasant symptom.
Spasms for no apparent reason . If irritation of the mucous membrane is not accompanied by obvious signs of acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, you should make sure that the baby does not have a predisposition to allergic reactions. Treatment of this condition comes down to taking antihistamines and avoiding contact with external irritants.
Separately, it is necessary to mention such a common cause of a dry non-productive cough without fever as the consequences of bronchitis, pneumonia and other diseases of the respiratory system.
It is important to know that residual spasms may bother the child for several months after the end of treatment. It takes time to restore the normal state of the mucous membrane.
If there are productive reflex contractions of the chest in a child (with sputum discharge), it is necessary to exclude the occurrence of tracheitis of allergic or infectious origin.
What to do if a child’s allergic cough does not go away?
If a child has been coughing for more than a month, nothing helps, and does not get better, it is worth considering whether an allergic reaction is causing the attacks. Typical signs of cough due to allergies:
- It begins abruptly and has a paroxysmal character.
- An allergic cough is always dry and is often accompanied by rhinitis (runny nose).
- The attack can last a very long time - up to several hours.
- The cough does not bring relief.
- Sputum, if it is released, is transparent, without green or red impurities.
- Itching or sneezing may be present.
If your child is coughing, you need to find out why as quickly as possible. An allergic cough without timely treatment can cause asthma or bronchitis. And this is already fraught with serious consequences.
Coughs of allergic origin are relieved with the help of inhaled corticosteroids (Beclomethasone, Beclazone, Budesonide, etc.), the prescription of which is entirely within the competence of the attending physician.
We tried to imagine at least part of what to do if a child’s cough does not go away. Given the number of possible causes of a prolonged cough, parents should not risk their children’s health - seek medical help in a timely manner.
Found an error? Select it and press Ctrl Enter.
Almost all parents are concerned about the situation when a child’s cough does not go away for a long time. In this situation, it is necessary to seek help from a medical facility as soon as possible. An exceptionally qualified worker will be able to determine the root cause of the ailment that has arisen, accompanied by a symptom in which a dry or wet cough occurs in a child without fever, and prescribe optimal therapy.
A persistent cough in a child can be physiological or pathological. A child’s cough does not go away due to various reasons.
Common causes
- diseases of infectious origin (for example, bronchitis, pharyngitis, whooping cough);
- the beginning of the development of the tuberculosis process;
- cystic fibrosis;
- bronchiectasis, which causes coughing in children;
- inflammatory processes occurring in the chest area and/or diaphragm;
- benign or malignant neoplasms of the respiratory system or localized in the chest cavity or diaphragm area;
- disturbance of the microclimate in the room where a small child spends most of his time (for example, dry air, heavy dust).
The reasons for the development of a situation where a child’s cough with mucus discharge (protracted wet cough) does not go away for a month are:
- previous acute bronchitis;
- bronchitis with symptoms of obstruction;
- pneumonia;
- sinusitis;
- sinusitis;
- bronchial asthma;
- a pathological condition that develops when exposed to a specific allergen;
- pathologies of internal organs.
After suffering from an acute respiratory infection, acute respiratory viral infection, influenza, parainfluenza, a cough can occur without mucus discharge (dry), or a wet cough may occur.
A lingering cough in a child without fever is diagnosed when parasites - roundworms - are detected in a small patient.
A prolonged cough in a child is accompanied by heart failure and papillomatosis.
The causes of a child’s prolonged cough are hidden behind a diagnosis such as underdevelopment of the swallowing reflex, which is usually observed in infancy.
Incorrect or insufficient drinking regimen becomes the cause of such a pathological process as a constant cough in a child without fever. Lack of water or milk causes a dry cough in a child without fever, drying out the mucous membrane of the mouth or throat.
Abuse of nicotine in a room where a child is located can also cause a long cough in a child without fever.
The psycho-emotional state of the patient cannot be discounted. If a child is constantly in a stressful situation, is nervous a lot, worries about and without reason, this may also be the answer to the question why the child’s cough does not go away for a long time or a prolonged cough occurs without fever.
Physiological messages, if a child has been coughing for more than a month or the child has been coughing without fever for a month, may include:
- Excessive salivation.
- Microscopic remains of food accidentally lodged in the windpipe.
- Accumulation of mucus in the bronchi during night rest.
A persistent cough in a child can be caused by the presence of candida fungi and pulmonary chlamydia. Detection of cytomegalovirus can also cause this pathological process.
How to treat cough without fever in children
An unpleasant symptom can be eliminated by treating the underlying disease. Most often, the pediatrician prescribes therapy for the original source of the problem, and the painful symptoms disappear as the patient’s general health is restored. The exception is a severe cough in a child. Such chest spasms can be eliminated with the help of special medications and traditional medicine recipes.
How to choose the right medicine
The choice of an effective cough medicine should be made by a doctor. The pediatrician assesses the patient’s condition, studies the symptoms and only then recommends adequate treatment. Most often used:
- expectorant syrups that enhance the cough reflex (“Amrogexal”, “ACC”);
- mucolytics, thinning mucus and accelerating sputum discharge (“Mukaltin”);
- bronchial dilatator inhalers that relieve allergy symptoms (“Eufillin”);
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory substances that eliminate swelling in the tissues of the upper respiratory tract (“Ibuprofen”);
- natural medicines that have a general effect (“Gerbion”, “Gedelix”);
- drugs that suppress impulses at the peripheral level (“Prenoxdiazine”).
How to treat residual cough in a child Komarovsky
After a respiratory tract illness, the symptom of cough may remain for some time. The child is already healthy, eager to go to kindergarten or study, and active. What to do?
How to treat Komarovsky says: no way. Hydration, drinking, nasal rinsing and gargling, walking, fresh air. All this will help the symptom disappear faster.
But if the baby sits in a hot, stuffy room with dry air because of the obsessions of his parents and grandparents (“He still has a cough, where should he go for a walk!”), then the cough will not go away.
And finally, some advice from a doctor on cough treatment:
- Almost all cough remedies are either mucolytics or antitussives. They are indicated only in a limited number of cases and this can only be decided by a pediatrician. These include acute bronchitis and pneumonia. In other situations, they will only aggravate the illness and confuse the symptoms of the disease;
- In most cases, a child's cough occurs when there is an infection in the nose or throat. Do not give mucolytics or expectorants. They will only increase the amount of mucus and worsen the situation;
- Expectorants help only if there is wet sputum. Otherwise, they intensify the unproductive tearing cough. On the other hand, if the child drinks a lot and the air in the room is moist and cool, then the sputum itself will go away just fine without medication;
- Obstructive bronchitis and – frequent complications due to the use of mucolytics and expectorants. The amount of mucus and the urge to cough increase, but the child is simply unable to cough up due to insufficient physical development. Sputum accumulates in the bronchi and lower parts of the lungs;
- Don't believe product advertisements on TV. The best remedies: warm clothes for the child, room temperature 16-20 degrees, rinsing the nose and gargling, humidifying the air, lots of warm drinks, walks (if health allows).
No need to heal the child! Be prudent and appropriate when treating any disease.
Parents often
, thinking that a child’s cough is a problem that can be easily dealt with on your own. They simply go to the pharmacy and buy cough syrup, unaware of the harm it can cause to the baby.
“For an hour I was in a room with a working TV. Within an hour, I saw 8 times advertisements for medications that, according to the manufacturer, should be swallowed immediately when a cough occurs. My nerves can no longer stand listening to this scam! People, pay attention!
, says Dr. Komarovsky.
General recommendations for prolonged cough without fever
You need to understand that a cough always indicates breathing problems. This symptom occurs as a result of the negative impact of external or internal factors. Treatment of the pathological condition should be aimed at eliminating the root cause of mucosal irritation. Simply suppressing reflex chest contractions is not enough.
An integrated approach is considered the most correct. If necessary, medications are prescribed by a pediatrician; parents can provide the most comfortable conditions for recovery. The child's room should be moderately warm and slightly humid. This can make breathing easier and speed up the removal of mucus. Hiking in the fresh air will not be superfluous.
If during treatment the patient develops nausea, vomiting, wheezing when inhaling and exhaling, or a sharp increase in body temperature, you must immediately call an ambulance. Such manifestations are characteristic of pneumonia and false croup (these diseases can cause suffocation).
What to do if your child has a severe coughing attack
What to do if a child’s severe cough manifests itself as an attack? Is it possible to get rid of attacks in the future? Many parents are concerned about coughing attacks in their children. Treatment of severe cough in children is a whole range of measures, they can improve immunity through vitamins, medicines, and folk remedies. The disease can occur in case of inflammation of the trachea, with allergic reactions to something. Doctors recommend treatment with medications, traditional medicine, massage and rubbing procedures, and aromatic therapy.
What is a cough
The baby reacts to inflammation, allergies, and viruses by coughing: the body tries to remove harmful viruses and cleanse the main respiratory organs of mucous, purulent sputum and secretions. The cough reflex can appear as a result of inflammation of the throat mucosa; it can be short-term, acute, protracted, or chronic. Wet is treated with expectorants, and dry with drugs that suppress it. Dust, foreign microparticles entering the respiratory tract, inflammation processes, dry stale air can trigger coughing attacks.

Pathological cough
A pediatrician cannot always immediately tell what is the cause of a lingering cough. In addition to household “pathogens,” there are a number of diseases that can provoke the appearance of symptoms. Most often, a dry cough without fever does not go away for a long time due to the fault of the parents.
When the child had problems with the respiratory system, the parents found out from the doctor how to treat the disease, but did not complete the therapy they started - after the first improvements in the patient’s condition, they simply stopped giving the medication, unable to complete the prescribed course of medication.
Because of this approach to treatment, pockets of infection and inflammation remain in the body, which gradually become chronic. They weaken the immune system and can cause a persistent cough, although there are no other symptoms. However, if you follow the instructions of your doctor and take the course of medications to the end, then such problems usually do not arise.

Another cough can be caused by:
- Tuberculosis. The initial symptoms of the disease may not be accompanied by an increase in temperature. However, subsequently in the child it will be steadily increased to 37 °C.
- Bronchitis. If the acute form of the disease is accompanied by a high temperature, up to 39 °C, then the chronic form, which develops with incomplete treatment, can be practically asymptomatic.
- Laryngitis or pharyngitis. Due to severe swelling of the larynx and constant shortness of breath, air circulation is disrupted and a cough develops. It occurs with adenoiditis and regular overstrain of the vocal cords, for example in children who sing.
- Whooping cough. In a mild form, the disease can affect even a vaccinated child. At the initial stage, there is a dry cough without fever, which does not go away for a long time. However, subsequently the symptoms intensify, and only a doctor is able to identify the problem and tell how to treat the disease.
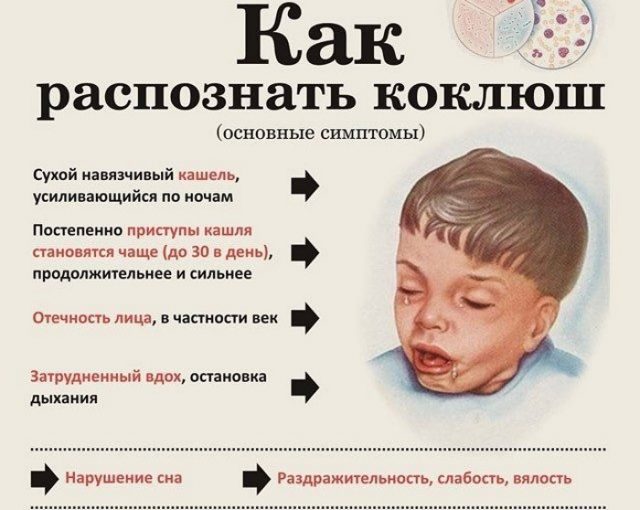
Among the diseases that can provoke a chronic dry cough, there are not only problems with the respiratory system. If the ENT specialist could not detect anything, you should contact other specialists, because such a symptom may be a consequence of:
- Helminthiasis. Roundworms and other parasitic worms can cause a sore throat and chronic cough.
- Gastrointestinal diseases. Reflux in the chronic stage, swallowing abnormalities, fistulas in the esophagus and a number of other pathologies provoke irritation of the bronchi, nasopharynx and coughing attacks.
- Oncopathology. In very rare cases, a cough may be the result of a tumor in the area of the larynx and pharynx.
- Poisoning. When mercury and other heavy metals and chemicals enter the throat, they corrode its tissues, causing coughing attacks.
- Stress. Cough is one of the psycho-emotional defenses in an unfavorable environment at home and at school. Sometimes coughing becomes a sign of prolonged depression in adolescents.
In any case, you can get rid of a lingering dry cough only by dealing with its cause.
Causes of cough in children
Your baby may be coughing due to:
The baby's lungs fill with a mucous substance, and the body tries to free itself, provoking a cough reflex. It can be dry and moist, appearing only at night or during the day. One of the main causes of the disease may be a cold. When the body is infected with viruses, coughing can become prolonged and cause a gag reflex. To prevent vomiting, you can give your baby cough suppressants.
Child has severe cough at night
At night the child coughs when he sleeps and is in a horizontal position. Mucus and phlegm quickly collect in the nose and throat, do not dissolve, making breathing difficult, provokes a cough reflex and requires long-term treatment. A change in the climate in the room where the baby sleeps can cause coughing. At night, the air cools down and becomes dry, which negatively affects the mucous membrane of the throat, irritating it. A warm drink at night, a well-ventilated room, and also humidification will help.
Accompanied by vomiting
To avoid the gag reflex, it is possible to alleviate the attack with the help of tablets, inhalation, applying a compress, massage, and manipulation by rubbing. Attacks contribute to the occurrence of vomiting, and vomiting can also be provoked by severe irritation of the mucous membranes of the throat when:
- A dry cough reflex is observed, as a result the baby breaks into a painful cough. The gag reflex is caused by tension in the throat and irritation of the vomiting centers.
- A wet cough reflex is observed, the baby's respiratory organs are so congested that mucus and phlegm provoke vomiting (symptoms of bronchitis).

Dry cough
A severe dry cough in a child (non-productive cough) can manifest itself as a sore throat when the air masses in the room are dry and cold. It is best to give the baby a warm drink with a spoonful of honey added to it and well ventilate the room where he is. The cause may be irritation of cough receptors in the trachea, bronchi, and laryngeal mucosa. Breathing becomes difficult, coughing becomes exhausting and intrusive. It is observed with irritation of the respiratory tract, ARVI, allergic manifestations, colds, sore throat.
What to do if your child’s cough with sputum does not go away for a long time
source
Any cough in a baby should not go unattended, and if the process is protracted, a visit to the pediatrician becomes a necessity. A cough can be a reflex to an external influence, but quite often it becomes a symptom of a serious pathology, and not only of the upper respiratory tract. Such an abnormal phenomenon cannot be triggered, and measures must be taken as early as possible.
Let's go to the doctor
Before going to see a doctor, make sure that the air in the apartment where the child lives is not too dry. And the baby had no contact with allergic substances. Methods for treating a prolonged cough without fever depend not only on the identified cause. The type of cough syndrome is also important for the doctor:
- With a dry cough, the child has difficulty expelling mucus (it is too thick and viscous and the baby is unable to cough it up). In this case, medications are prescribed that can thin the mucus and remove it from the bronchi and lungs.
- A wet cough is productive. In this case, the doctor prescribes medications that help remove phlegm.
When prescribing therapy, the pediatrician takes into account the age of the small patient, the tendency to allergies, the condition of the body and previous diseases. What does the pediatrician prescribe?
Antibiotics. Antibacterial therapy is prescribed when a persistent cough develops due to infectious diseases of the respiratory tract (sore throat, otitis, sinusitis) and goes away with fever. Cough with whooping cough, pneumonia and bronchitis also requires taking antibiotics.
Attention! Self-prescription of antibiotics for children is strictly prohibited! These medications are aggressive and can be harmful to health.
Antitussive drugs. Medicines that dilute mucus and promote its removal are prescribed by a pediatrician to relieve a lingering dry cough in a child without fever. The following drugs are most often prescribed:
- Glaucine. Alkaloid of plant origin. An anti-inflammatory, bronchodilator that does not suppress the cough center.
- Butamirat. A medicine that affects the central cough center, reducing its ability to be excited. Butamirate relieves inflammation in the bronchi, actively saturating them with oxygen.
- Tusuprex. The medicine is prescribed for debilitating cough caused by a number of viral diseases (pneumonia, bronchitis, ARVI, laryngitis, whooping cough).
- Libexin. Eliminates throat pain by expanding bronchopulmonary lumens. The action of libexin is aimed at converting a dry cough into a wet, productive one.
- Delsim. A medicine that helps relieve attacks of dry cough at night, relieving the allergic manifestations of cough syndrome. Delsim affects the cough center, blocking its work.
- Robitussin. It has a vasoconstrictor effect, relieving swelling and inflammation of the bronchi. This medicine is prescribed for prolonged cough caused by colds.

Mucolytic expectorants. Mucolytics help with a prolonged wet cough without fever with thick, viscous sputum. This treatment helps remove mucus. Mucolytic drugs are divided into drugs that thin sputum and drugs that help quickly remove it. Mucolytics include:
- Ambroxol. Increases the amount of mucus produced and thins it, making it less viscous, helping to quickly remove phlegm.
- Carbocysteine. Accelerates regeneration and normalizes the functioning of the bronchial and lung mucosa. Helps form and remove mucus.
- Bromhexine. Effectively reduces the viscosity of sputum, increasing the activity of the epithelium of the bronchial mucosa.
- Fluimucil. Reduces inflammation, has an antioxidant effect, helps thin and remove mucus.
- Ambrobene. Helps in the fight against inflammatory diseases. Effective for long, wet coughs with purulent sputum. The medicine reduces the viscosity of mucus and promotes its rapid removal.
- Lazolvan. The active component of the product reduces the viscosity of sputum and activates the work of the ciliated epithelium of the lungs, which helps to quickly stop coughing.
Attention! Mucolytics should not be taken simultaneously with antitussives! This combination leads to the development of complications, which leads to a deterioration in the child’s condition.
Folk remedies
Traditional recipes are not able to rid a child’s body of the causes that cause a prolonged cough without fever. But they become an excellent help in complex treatment. To use recipes correctly, you need to know the cause of a lingering cough and its type.
Dry cough. The following methods will help alleviate the painful and painful cough syndrome in your baby and eliminate heavy breathing:
- Inhalation from pine cones. Steam pine cones (10 g) with a glass of boiling water. Cook the mixture over low heat for half an hour with the lid closed. The baby should breathe over the healing steam for 10-15 minutes. Make sure your baby doesn't get burned!
- Milk drink. Boil a glass of fresh milk and dissolve a pinch of soda and a teaspoon of butter in it. Give the product to drink warm, a tablespoon 4-5 times daily.
- Onion drink. Add a glass of sugar and two large onions to a liter of boiling water. The mass should be cooked for 1-1.5 hours. Then remove the bulbs and give the baby one tablespoon of the broth to drink 3-4 times a day.
- Radish juice. Take a small black radish and cut off the top. Make a niche hole in the fruit. As soon as the cavity is filled with radish juice, add honey there. After infusion for 10-12 hours, the medicine is ready. The child is given a teaspoon of juice to drink 3-4 times daily.
Black radish juice is also good to give as a preventive measure during the off-season (the preventive course is 3 weeks).
Moist cough. Delicious and healthy syrups can help in getting rid of a lingering wet cough without fever:
- Viburnum. Mix viburnum berries with sugar (a tablespoon of each). Bring to a boil and simmer over low heat for 1-1.5 hours. Drink aromatic syrup 3-4 times a day.
- Onion. Finely chop a medium onion, mix it with honey (2 tablespoons) and a teaspoon of lemon juice. Bring the mixture to a boil and cook for half an hour. Give the syrup to drink warm 2-3 times daily.
An excellent way to combat a lingering wet cough are decoctions of medicinal herbs. To prepare them, use one or a mixture of the following herbs: chamomile, sage, coltsfoot, elderberry and linden blossom. Steam 2-3 tablespoons of dry herbs with a glass of boiling water and leave for 30-40 minutes. Give your child a tablespoon to drink 4-5 times a day.
Rubbing is considered the best method in the fight against a lingering wet cough without fever. It is better for your baby to do them before bedtime. For rubbing, use lard, badger or goat fat. These methods will help your baby sleep well without debilitating nighttime bouts of prolonged coughing and wheezing. They are suitable even for one-year-old children.
Heat compresses have also proven themselves well:
- Potato compress. Boil unpeeled potatoes (2-3 fruits). Mash the potato mass with a fork, add vegetable oil (1-2 tbsp) and iodine (2-3 drops). Form a cake from the mixture and place it on a cotton towel. A cloth with potato cake is placed on the baby’s chest and secured with a warm scarf. Remove the compress when the cake has cooled.
- Cabbage with honey. The elastic cabbage leaf is softened with a rolling pin and immersed in boiling water for 5-6 minutes. While the cabbage leaf softens in boiling water, melt the honey in a water bath. Make sure that the temperature of the honey does not exceed 50⁰ C (at higher temperatures, honey loses its beneficial properties). Warm honey is applied to the baby's chest or back and a heated cabbage leaf is applied. The compress is covered with film and insulated with a long woolen scarf. Keep the compress on all night.
Hardening. Temper your baby with air baths and water procedures. Rinse your feet with cool water every day. In the summer, it is very useful to run barefoot on the grass, and in the winter, let the baby jump in the mornings and evenings on a terry towel soaked in warm salt water. Dissolve a tablespoon of salt in a liter of water and wet the cloth.
Don't overheat! Do not put a lot of warm clothes on your baby. Focus on your palms and feet - if they are warm and dry, the clothes are chosen correctly. You should walk with your baby every day in any weather. But during the cold season, especially during an outbreak of respiratory diseases, avoid visiting mass events and crowded places.
Complete nutrition and vitamins. A diet rich in vitamins improves children's health. During the off-season, be sure to give your baby a course of multivitamins with micro- and macroelements. During the period of exacerbation of acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections, pediatricians recommend giving children herbal preparations aimed at strengthening the body’s protective qualities.
Give preference to products made from Echinacea purpurea, radiola rosea, ginseng, eleutherococcus and zamaniha. The course of prophylaxis lasts 3-4 weeks and is recommended for all babies starting from one year of age.
Inhalations. Inhalation procedures are effective therapeutic methods used in the treatment and to prevent a child from coughing without fever. Inhalations are best done using a special nebulizer device.
A nebulizer breaks down medicinal solutions used for inhalation into tiny microparticles. In this way, an aerosol effect is created, and medications penetrate into the lower parts of the respiratory system, which improves the effect of the procedure.
Inhalation with saline solution. Saline solution is a mixture of table salt and water. During the procedure, particles of the mixture settle on the mucous membranes, improving the formation and discharge of mucus. Saline solution is used in inhalations in its pure form and for diluting herbs and medicines for inhalation.
Saline solution for inhalation can be bought ready-made, or you can make it yourself: dilute finely ground table salt (10-12 g) in a liter of boiled water.
Hyperthyroidism with goiter
- Goiter is a nodular or more often diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland, provoked by a number of exogenous and endogenous factors.
- In this case, cough develops as a result of compression of the trachea and bronchi by an overgrown endocrine organ.
- Excessive pressure leads to irritation of the lower respiratory tract.
- The result is the formation of an intense reflex that will not go away until the operation is performed.
Diagnostics
As a rule, the doctor first listens to the bronchi and lungs. Specific tapping is also used to determine the disease, and in difficult cases, X-rays and bronchoscopy are used. When diagnosing a cough, many factors are taken into account:
- Acute coughing is typical in the presence of a virus in catarrh of the upper respiratory tract in bronchial asthma, bronchitis, tracheitis, laryngitis, pneumonia, and sore throat.
- Signs of ARVI: a child has a hoarse, low voice, breathing is difficult, and the nasopharynx is stuffy.
- A lingering cough for more than 10-12 days is accompanied by acute bronchitis and the presence of a virus in the respiratory tract.
- A wet and severe night cough in a child occurs during purulent processes in the lungs and bronchi, accompanied by the release of sputum, mucus, and pus.
How to treat
In cases of damage to the bronchi by a viral infection, when the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract are inflamed, the normal functioning of the lungs and bronchi is disrupted in the child’s body. It can be eliminated with the help of medications and agents that suppress the cough reflex. The pediatrician prescribes antitussive drugs, depending on the child’s age, his physical condition and the danger of the disease. Antibiotics are given when there is a wet cough to remove phlegm, when the throat is inflamed, and fluid collects in the lungs and bronchi.
Medicines
Coughing can be effectively treated with drugs that promote expectoration and remove phlegm and mucus from the body. For children, such medicines are available in the form of tasty syrups. Prospan syrup is a leader in the treatment of infants and is intended for babies under one year of age. Antibiotics are used for purulent sputum in the bronchi and nasopharynx. It will relieve pain, help you recover and will not cause allergies, a medicine from the penicillin group Ampiox: the drug helps reduce coughing and helps relieve bouts of barking.

Massage
If the cough starts to get worse, it means it's time to use chest massage. For inflammatory diseases, massage should be done for several days, before starting, give the child an expectorant, apply protective baby cream to the skin, and then massage the baby’s chest, back, sides, shoulders, rubbing, pinching those parts of the body where phlegm and mucous secretions accumulate . Any adult can master the massage procedure, which is very helpful in combating wet cough.
Aromatherapy
When a baby has been bothered by a barking cough, runny nose, or pathological cough accompanied by mucus for a whole month, aromatherapy works great. Therapy with aromatic oils is also necessary for other characteristic symptoms of a cold:
- For colds, essential oils of chamomile and calendula will help cure coughing in infants.
- For older children, orange, lemon, and mint oil can be an effective treatment.
- For signs of bronchitis, orange and eucalyptus oils work well on the mucous membranes of the throat.
How to treat a severe cough
When a child has a runny nose, cough and fever, this is an upper respiratory tract disease. Why increase the amount of mucus in the lungs when the baby just has a runny nose or sore throat?
2. Expectorants are sometimes needed for certain diseases of the lower respiratory tract: bronchitis, pneumonia. These products must be of plant origin.
! But all diseases should be treated by doctors, not by people who have watched enough TV.
3. Children's cough is much weaker than that of adults. After taking expectorants, children are often unable to cough up the increased amount of mucus. It is not surprising that in many countries it is not recommended to give mucolytics to children under 5 years of age, and prescribing them to children under 2 years of age is generally a crime. 4. How to treat dry cough?
Carrot juice is perfect, always freshly squeezed, in a one-to-one ratio with milk. Give this mixture 4-5 times a day. Also brew tea from viburnum berries.
5. Remember that an effective effect on sputum even with the most modern drugs is impossible without meeting two mandatory conditions: clean, cool air (+18 ... +20 ° C) in the room where the child is, and a sufficient amount of warm liquid to drink.
Monitor the air humidity in your child's room! It should be 40–70%. After all, a stuffy room is the easiest way to organize complications. And if, in addition to this, the nose is stuffy and the body temperature is elevated, the chances of turning a common cold into a monthly treatment for pneumonia are maximum.
6. It should be noted that self-medication with antitussive drugs can be very dangerous. Cough, as you know, is not just an unpleasant symptom. This is one of the body's most important ways to cleanse the lungs.
Suppression of cough can lead to the accumulation of sputum in the lungs, which in turn is highly likely to lead to bronchitis or pneumonia, impaired ventilation of the lungs and other troubles. Also, abuse of antitussive drugs leads to deterioration of liver and kidney function.
7. Use of antitussives to treat wet cough
contraindicated.
As mentioned above, suppressing cough will only make the disease worse, as these drugs promote mucus sedimentation. It’s a banal truth, but where can one go from it: don’t self-medicate
! It is not the cough that needs to be treated, but a specific disease, one of the symptoms of which is cough.
Cough in children is mainly either viral or allergic. When a virus or allergen penetrates the bronchi, inflammation of their mucous membrane occurs. The body actively fights, producing mucus, which should neutralize the virus. And expectoration is an attempt to remove mucus accumulated in the lungs.
The appearance of a cough in a child, of course, worries his parents. They are especially confused by the absence of any other symptoms - fever, redness in the throat, weakness, runny nose. What happens to the baby in this case? Komarovsky and a number of other pediatricians consider a cough in a child without fever to be a signal that some kind of illness is developing in the child’s body. All that remains is to find out what kind of disease we are dealing with.
Traditional medicine methods
Traditional medicine has many effective recipes for treating cough in children:
- For acute bronchitis and signs of pneumonia, doctors prescribe treatment with warm milk and honey.
- Frequent coughing can be cured and suppressed well by using black radish with honey, the juice of which is great if a child coughs a lot at night.
- In case of complications, decoctions of medicinal herbs - chamomile, calendula, linden flowers - work well on the mucous membranes of the larynx in case of complications. They are able to suppress an attack and disinfect the mucous membrane.
Rubbing
In case of dangerous diseases, the child is bothered by difficulty breathing, elevated body temperature, and sometimes the disease is accompanied by swelling of the larynx. You can cure your baby with generally accepted medications and by rubbing:
- Rubbing with bear and goose fat helps a lot, as it improves immunity and prevents dangerous complications. You need to rub your legs, feet, back, sides, chest (excluding the heart area).
- Honey or vodka are very effective and help the body warm up well. After rubbing the baby, you need to cover it with a warm blanket. The procedure is indicated for children from 6 months.

Water treatments
Warm or hot baths with the addition of medicinal herbs are indicated for any cold and will help relieve irritation. All herbs and flowers must first be brewed with boiling water and infused:
- Raspberry leaves, chamomile inflorescences, calendula, linden blossom, mint are plants that have soothing bactericidal properties.
- Water treatments with lavender, valerian, and mint relax the baby’s nervous system and promote healthy sleep.
Features of the treatment of children's severe cough
Treatment before recovery has its own characteristics and should be carried out in combination:
- antibiotics to destroy viral infections and pathogenic microorganisms;
- expectorants;
- inhalations for colds, inflammatory processes of the throat mucosa, sore throat;
- compresses on the chest and back to warm the body;
- rubbing to improve blood circulation;
- massage;
- water treatments in the form of baths, foot baths with medicinal plants and herbs;
- aromatherapy;
- use of traditional medicine methods.
Quick treatment of cough in a child at home
The baby coughs, and this is always bad. If it is not a cold or an infectious disease, then you can eliminate this unpleasant phenomenon at home using proven methods that were used by our grandparents. Parents are undoubtedly interested in how to quickly cure a child’s cough at home, but they should be warned that this cannot be done in one or two days. It will still take some time, because the components used for this must, first of all, be safe for children.
Causes of cough in children
The coughing process is completely physiological, as it is protective in nature, protecting the respiratory tract from the accumulation of dust particles, microscopic foreign objects, and also mucus. If a child coughs periodically throughout the day, this does not mean a serious illness. In this way, infants get rid of maternal milk or saliva from entering the respiratory system.
It is important for parents to pay attention to whether the cough is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms, for example, fever, runny nose, headache. Sometimes even the absence of a fever in a child does not guarantee that a cough is not a sign of some disorder in the body.
It could be:
- pneumonia;
- bronchial asthma;
- inflammation of the trachea and other diseases of the respiratory system;
- respiratory diseases;
- dysfunction of the digestive organs;
- reaction to allergens of plant, animal origin, chemicals, if the child is taking any medications.
In all of these cases, as a rule, a wet cough is observed, the symptoms of which are the quality of the sputum. It is this biological substance that can indicate the origin of the cough:
- if it is watery, almost transparent, this indicates inflammation of the mucous tissues of the respiratory canals;
- when there are bloody impurities in it, most likely there is tuberculosis or functional heart failure;
- when the sputum has a putrid odor and contains pus, it is an indicator of an abscess.
- with asthma and bronchial inflammation - sputum is heterogeneous, viscous, containing clots and lumps;
- when the sputum has a putrid odor and contains pus, it is an indicator of an abscess.
A dry cough can occur with diseases such as diphtheria, false croup, influenza, inflammation of the pharynx and larynx, and whooping cough. It is usually abrupt, reminiscent of a dog barking.
When a child needs medical help
Even when sputum is discharged with a wet cough, self-medication can worsen the child’s well-being.
Parents need to know in what cases it is impossible to do without a doctor:
- if after coughing the child begins to vomit;
- if a cough occurs during sleep and such attacks cannot be stopped;
- in addition to the fact that the baby coughs, wheezing and wheezing can be heard when he breathes;
- pain in the child’s chest accompanied by a cough is a dangerous combination;
- the sputum has a greenish tint or contains blood;
- the baby develops shortness of breath;
- The cough remains for a long time (15-20 days) with intensive treatment.
As for the phenomenon of coughing after sleep, which occurs in the morning, in infants this is a natural action to get rid of mucus and tears, but in other cases, the prerequisites for it may be diseases of the nasopharynx, bronchial asthma, disruption of the gastric pylorus, allergic the body's response to stimuli.
Cough often becomes a residual symptom of past diseases, however, if this pathology is ignored, various complications are possible. That is why it is important to consult a doctor for any infectious or cold-related ailments, especially when it concerns children whose immune systems are not yet perfect.
However, quite often the baby simply coughs up unnecessary “garbage” in his lungs, or this phenomenon remains after suffering from laryngitis. How to quickly cure a child’s cough at home, and with the help of what means that will be harmless to him?
There are several such treatment methods and all of them are worthy of the attention of parents, since it is advisable to act comprehensively.
How to quickly cure a child’s cough at home
When a child has a coughing attack, parents can easily help him cope with this trouble, and sometimes even prevent its onset. There are several methods to quickly get rid of a cough at home.
There are some helpful steps you can take to do this:
- the air in the nursery should not be too dry, since coughing is caused by insufficient humidity; for this, you can put a three-liter jar of water in the corner of the room or buy a special fountain;
- When putting him to bed, you need to make sure that the baby’s upper body is at some elevation compared to his legs - this will make it easier for the baby to breathe.
When the baby coughs, you need to place your face down on your lap and give a light massage to the back, kneading and gently tapping on it. Sometimes it is enough to induce the gag instinct by touching the inner wall of the throat with a spoon - this will stop the attack.
Many people do not know how to treat a child’s cough. Various procedures and folk remedies are suitable for these purposes.
These can be compresses, inhalations and wraps.
- Inhalation is convenient to carry out at home, and this method is extremely simple - the child inhales steam over a bowl of hot water, to which plant ethers, medicinal herbs, and special products prescribed by a doctor can be added.
- Herbs such as linden with oregano, chamomile and sage, or eucalyptus with menthol and calendula are great for warming up the nasopharynx.
- A simple way is to mix a few drops of iodine tincture and a spoonful of soda into hot water - the recipe is suitable for thinning phlegm and noticeably making it easier for the baby to breathe.
But moms and dads need to know that this procedure cannot be performed if the baby has a high fever, heart and vascular disease, or an allergy to herbs or ethers. This method should also not be used by children who have a tendency to bleed or are suspected of having bronchitis.
For infants, wraps with a diaper or towel, previously soaked in diluted mustard, are used. The solution must be squeezed out and the cloth wrapped around the baby’s chest and back. Then you need to wrap the baby in a warm blanket or blanket. The whole procedure takes about four minutes, after which the mustard is washed off the skin, wiped dry, and the child is put to bed. For preschool and older children, you can simply place mustard plasters on top of gauze to prevent burns.
As a compress, potatoes are boiled in their jackets, mashed to a puree and mixed with turpentine, alcohol and any vegetable oil, one spoon per three medium potatoes. Two flat cakes are molded from the cool mixture and placed warm on the chest and back. They must be kept for at least 60 minutes.
How to cure a child’s cough using traditional methods:
- Chamomile brewed with honey or a drink made from heated milk with the addition of natural honey and baking soda are good for coughs;
- You can give children who are one year old a mass of grated onion pulp with honey or a small piece of butter mixed with it - this softens the mucous membranes of the throat, the onion disinfects the tissues of the pharynx, and attacks quickly pass;
- the same positive effect is observed if you infuse honey with radish juice, placing it inside the vegetable and letting it stand for half a day in the dark; children drink the resulting juice in a small spoon three times a day;
- Half an hour before each meal, children can be recommended to drink a tablespoon of steamed plantain leaf, steeped for five hours.
Barking cough in a child without fever - what is it?
You can observe a barking cough in a child without fever quite often, and Komarovsky does not advise premature panic. Usually attacks occur at night and pass by morning. Doctors find it difficult to give an exact explanation for the phenomenon, but the parents' favorite claims that it is simply the baby freeing the bronchi and lungs from dust microparticles accumulated during the day.
What to do in such cases? The children's doctor is categorical in his recommendations - medications are completely excluded here. Fresh, cool air (walking during the day, ventilating the room in the evening) will help you quickly forget about your cough.
If you have a nebulizer, you can inhale several times a day using alkaline mineral water. In the absence of this useful device, you can simply drink the liquid in small portions throughout the day.
Komarovsky suggests treating a barking, prolonged cough in a child without fever with plenty of fluids. It doesn’t matter what exactly it will be, the main thing is to drink at least one and a half liters of drink per day. Perfect for these purposes:
- compote (with a minimum amount of sugar);
- tea (preferably green);
- juice (you can even store-bought);
- liquid jelly;
- fruit drink
The main rule is that drinks should be at room temperature; cold liquid can only intensify attacks.