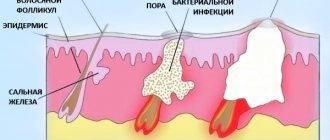
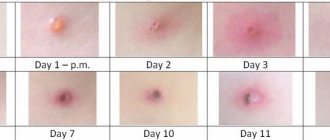
What types of wounds are there?
A wound is a tissue damage that is characterized by a violation of the integrity of the skin or mucous membranes. The wound is accompanied by pain and bleeding.
The first sign is pain. It occurs due to damage to local nerve endings, and subsequently due to swelling, which puts pressure on the nerve and irritates it. In this case, pain can spread not only along the surface of the wound, but also along the damaged nerve.
The second mandatory sign of a wound is bleeding. It occurs as a result of damage to capillaries, veins or arteries. Bleeding can be weak and drip, for example, with a small cut, and severe when the integrity of the vein and artery is damaged.
The third sign of a wound is gaping. However, gaping appears only with deep wounds, for example, with abrasions it does not exist. Gaping is the divergence of the edges of the wound on either side of the axis of the cut. If there is severe gaping, the wound is usually sutured.
There are many types of wounds. For a person in everyday life, it is necessary to know several classifications. The first is based on whether there is an infection in the wound. Wounds may be aseptic, contaminated, or infected.
An aseptic wound is a pure injury to the skin. Usually these are surgical wounds that are performed in order to penetrate the internal organs. Children most often experience contaminated wounds. This means that microbes have entered the area of skin damage. At first, these are relatively safe wounds: local protective mechanisms inhibit the development of microorganisms. If a contaminated wound is not treated, it becomes infected: an infectious process develops, which is accompanied by inflammation, severe pain and suppuration. An infected wound can cause a strong reaction in the child’s body: body temperature rises, chills, drowsiness and apathy appear.
Depending on the nature of the damage, there are the following wounds:
- punctured - they occur when punctured by a narrow and piercing object, for example, when a child falls on a nail. Typically, a puncture wound bleeds slightly and hurts. Outwardly it may seem that this is a safe wound, but this is not so: large vessels, nerves are often damaged, and even an infection occurs;
- cut - occur upon contact with a sharp oblong object: a knife, razor, sharp scissors, a shard of glass and paper. With an incised wound, the tissue is usually slightly damaged. The wound bleeds heavily and hurts moderately;
- Chopped wounds occur when damaged by a heavy sharp object, such as an ax. Usually the bleeding is moderate, but the wound is very painful and gapes. May lead to serious condition;
- a bruise wound appears when struck with a blunt object or falling on asphalt. Most often, the bruised wound is located on the head, elbows and knees. The edges of a bruised wound are uneven and soaked in blood. It bleeds slightly and is moderately painful.
There are also bite wounds that occur when children are bitten by animals or other children. The difficulty with this wound is that in most cases it contains infection from the animal's oral cavity. This is how rabies, insect and snake poison, and putrefactive infection are transmitted.
The wound process consists of several stages:
- In the first seconds after skin damage, local blood vessels reflexively constrict and biologically active substances are produced - platelets, which adhere to the wound area and close the damaged vessel. The blood clotting system turns on, stopping the bleeding. In a healthy child, bleeding stops on its own within 15 minutes.
- Inflammation. Lasts 3 days from the moment of injury. Inflammation is manifested by pain, redness and local fever. Also, swelling in the form of a tumor appears on the wound within two hours.
- 2–4 hours after injury, leukocytes migrate to the area of injury. They absorb foreign particles and cleanse the wound of microorganisms.
- Healing phase. Begins 3–5 days after injury. Bioactive substances arrive to damaged tissues, which restore vascular and skin tissue.
- Epithelization phase. Begins 2 weeks after injury. The wound mark becomes pale and a scar forms. The epithelialization phase may be delayed if bacteria are present in the wound.
Signs of wound infection
In the first stage of the process, redness appears around the infected injury. The pathological area may become crusty, causing the affected area of the skin to look like a burn. The second phase is accompanied by swelling. The redness transforms into a blue or purple bruise and swelling. The feeling of pain around the infected wound intensifies. The general condition of the body worsens.
The influence of radioactive radiation and ultraviolet radiation. It is difficult for the patient to look at the sun, and discomfort occurs in the eye area. At an advanced stage, fever and nausea appear. The condition requires immediate consultation with a doctor with further removal of necrotic tissue flaps.
Wound treatment algorithm
What to do if your child falls, cuts or hits himself:
- Make sure you're safe: you've shooed the dog away, put away the knife, turned off the chainsaw, removed any broken glass.
- Usually, in a situation of injury, the child is frightened: by pain or by the fact of the cut. Reassure him and tell him that nothing bad happened. Make him feel protected.
- Before treating a wound, first wash your hands with soap.
- Remove clothing from the wound site: roll up your shirt sleeve, lift up your T-shirt or pant leg. Examine the wound. Try not to touch the wound with dirty hands.
- If the capillaries are damaged, bleeding is minor. Rinse the wound with warm water, apply hydrogen peroxide and bandage with gauze.
- Gently clean the wound of debris and dirt under warm water. To do this, use cotton swabs or gauze soaked in a disinfectant.
- Disinfect the wound. Usually at home there is always an alcohol solution of iodine, cologne, hydrogen peroxide, alcohol or strong drinks. Dilute alcohol with water so as not to burn the wound. If the wound is extensive, alcohol and iodine cannot be used, they will lead to a chemical burn and the wound will heal more slowly.
- Apply sterile material to the wound and bandage it. You need to bandage so that the bandage covers the wound site. It should not be tight or too soft.
What to do if your child is bleeding heavily:
- Assess the severity of bleeding. If the wound bleeds heavily with dark or scarlet blood, spurts out and the blood erupts synchronously with the heartbeat, the bleeding must be stopped at any cost.
- Call an ambulance. One person provides first aid, the second calls the team. Please note that if the wound is penetrating, that is, a screwdriver or knife is stuck into the body, you cannot remove the object yourself. Be sure to wait for an ambulance.
- Find a tissue or any other tissue in your bag or home medicine cabinet that can be applied to the wound.
- If the wound is on the extremities, place the child on his back and raise the injured limb above the level of the heart, bending them at the elbow or knee. This is temporarily uncomfortable but slows down blood flow.
- Apply a tourniquet. If you don't have one, use a belt, tie, suspender or wire. You need to place a napkin or cloth under the tourniquet so as not to injure the skin. For arterial bleeding, a tourniquet is applied above the wound site; for venous bleeding, a pressure bandage is applied to the wound. Note the time of application of the tourniquet, write it down with a pen or felt-tip pen (not red) on the skin near the tourniquet. Remember that in summer the maximum time for applying a tourniquet is 90 minutes, in winter – 60 minutes. If after this time the ambulance has not arrived, and you have not yet reached the hospital, carefully loosen the tourniquet so that the tissues of the limb receive blood, while pressing the bleeding site with gauze. If the bandage becomes saturated with blood, tighten the tourniquet again until the bleeding stops completely and record the new time on the skin.
It is not recommended to give your child painkillers. This is hampered by the fact that each drug has an expiration date and doctors need to recalculate the doses of a new painkiller or wait for the previous one to expire in order to avoid an overdose. But if you cannot do without pain relief, write down the time and name of the drug you gave your child. Save the empty vials of medication and give them to the ambulance crew so they know what you gave to the victim.
Treatment of infected wounds
Therapeutic measures for wound infections should be aimed at clearing the surface of non-viable and necrotic tissue, eliminating swelling, restoring microcirculation, and suppressing the pathogen. For this purpose, surgical and conservative treatment methods are used.
Surgical treatment consists of secondary surgical treatment, drainage, and suturing.
Treatment of an infected wound is carried out on days 4-5, since during this period secondary necrosis completes its formation.
Surgical treatment consists of dissection of the injury and excision of necrotic tissue. During surgical treatment of wounds, it is recommended to use general anesthesia, especially for extensive purulent injuries, since local anesthesia is not enough to remove all non-viable tissue, perform drainage or apply sutures.
Drainage is done to ensure the outflow of serous exudate and pus. Drainage helps clean the wound and also deprives pathogenic flora of a nutrient medium.
Treatment for a wet surface is as follows:
- Change the dressing as soon as it gets wet, after 5-6 hours;
- Treatment of the wound with furatsilin, Furazol spray;
- Application of 10% sodium chloride solution, 4% sodium bicarbonate, 3% boric acid;
- Use of liquid antiseptics: Miramistin, Miramidez, Betadine, Octenisept, Iodinol.
Treatment of abrasions in children
How to properly treat abrasions in children:
- Wash your hands.
- Clean the skin around the wound from dirt, dust, debris and other objects.
- Disinfect the wound: the abrasion can be treated with the following products: zinc oxide ointment, benzalkonium chloride cream, dexpanthenol cream, chlorhexidine, methyl blue, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green and 5% iodine solution.
- Usually, mild capillary bleeding occurs with abrasions. It is enough to apply a dry cloth or gauze to the damaged skin.
Treatment of infected wounds
If purulent discharge begins to appear in the wound, this indicates that it has become infected. For rapid wound healing, the infection must be suppressed by providing the victim with the necessary assistance. First, you need to ensure the drainage of pus. If it has accumulated under a crust formed on the wound, it is soaked in hydrogen peroxide and removed using a bandage soaked in peroxide or another antiseptic, applied for half an hour. If pus is secreted under the skin, it is squeezed out of the hole, which is made along the edge where the flap of skin has dried.
Mandatory procedures include daily wound treatment with hydrogen peroxide. If necessary, the pus should be squeezed out. Levomekol ointment is a good remedy that promotes the healing of an already cleaned wound. It is recommended to apply a bandage with this ointment to the wound daily.
In case of acute suppuration (phlegmon, abscess), surgical intervention is resorted to. The wound is opened with a scalpel, non-viable tissue is excised, and wound discharge is collected for laboratory testing of the microflora and its sensitivity to antibiotics. The wound is washed and dried several times, then tampons soaked in saline solution are applied to the site of the wound. For some patients with severe pain, saline solution is replaced with novocaine solution. Sutures are placed, which, if healing results are good, are removed on the ninth day.
Doctors very successfully use wipes with immobilized trypsin to heal purulent wounds, thanks to which local manifestations of inflammation disappear after several times of using the solution. On the first day, pain disappears, wound contents peel off, and blood counts improve. The time required for wound cleansing and further treatment after using this medicine is reduced by half. High efficiency, effectiveness and ease of use are the main characteristics of immobilized trypsin preparations.
For certain indications, patients are prescribed analgesics, antihistamines and detoxification agents. Throughout therapy, it is recommended to use immune stimulants. If there is a threat of infection spreading, according to bacteriological tests, doctors prescribe antibiotics. Monitoring the course of the recovery process, treatment and adaptation in the postoperative period is carried out by doctors during dressing procedures.
Much attention is paid to the expressiveness of inflammatory processes on the sides of the wound, studies of wound material and the patient’s blood, as well as studies of the microbial spectrum. Doctors pay special attention to patients with diabetes and people with problems in the circulatory system. Their treatment follows a different scheme and has a number of features due to the complexity of wound healing.
What to do if the wound does not heal for a long time
The wound may not heal for a long time. This occurs due to several factors: the skin is not cleaned after injury, blood flow is complicated due to inflammation, or the regeneration mechanism is disrupted. Because of this, complications arise:
- Seroma is an accumulation of inflammatory fluid (exudate) in the wound cavity. Seromas most often occur when dirt, microorganisms, or foreign bodies remain in the wound;
- wound hematoma. It appears due to the fact that after the wound the bleeding did not stop completely, and drops of blood gradually soaked the surrounding tissue. Hematomas also occur as a result of diseases in which blood clotting is impaired;
- necrosis of soft tissues. Occurs due to severe and massive tissue damage or cutting of blood vessels. Early signs of necrosis: in the first days after injury, the skin is pale, has a bluish tint and is cold to the touch;
- malignancy is a process when tissue cells acquire the characteristics of a tumor. Malignization occurs when a chronically non-healing wound.
In addition, the wound may not heal for a long time with poor immunity, diabetes, long-term use of glucocorticoids and vitamin deficiency. The only correct option is to consult a surgeon: at home it is impossible to assess the condition of the wound and provide proper medical care.
Causes of infected wounds
The source of infection for accidental wounds is primary contamination with microbes. Surgical wound surfaces are often contaminated endogenously (by microbes from the internal environment of the human body) or become secondarily infected by nosocomial infections.
If the patient is in a hospital, then after some time the microflora of the surface changes, gram-negative bacteria appear in it, which predominate over other species. They are resistant to antibiotics and cause secondary infection of any injuries (accidental and surgical).
Factors that predispose to infection:
- Foreign bodies;
- Presence of blood clots and blood clots;
- Necrotic foci;
- Significance of damage in depth;
- The presence of additional side passages or blind pockets.
Illiterate transportation and poor immobilization have an impact on the spread of infection . This becomes an additional source of injury to soft tissues, the condition of the injury worsens, microcirculation is disrupted, as a result of which the hematoma increases in size and the necrotic zone expands.
The general well-being of the victim is of great importance for the development of infection. With decreased immunity, physical and mental exhaustion, and exposure to radiation, the risk of developing a wound infection increases.
Some chronic somatic diseases such as diabetes, obesity, cirrhosis, malignant tumors reduce the body's resistance. In addition, there is a weakening of the body’s defenses when taking large doses of immunosuppressants, steroid hormones, and antibiotics.
When to see a doctor
To protect your child from complications, you need to know in what situations to consult a doctor:
- if after 15 minutes the wound has not stopped bleeding even when applying a pressure bandage;
- if outside the wound the skin begins to become numb, cool, and acquire a pale or bluish tint;
- if you are not sure that the wound is completely cleaned of splinters, rust, dirt and other foreign objects;
- if the injury occurred on the neck;
- if the child was bitten by an animal;
- the wound does not heal within 10 days.
Warning signs also include:
How to bring down a high temperature? an increase in the child’s body temperature, increased swelling, increased pain, a burning sensation and severe redness of the wound.
A wound is tissue damage that requires first aid. However, if you treat the wound according to the algorithm, after 10–15 minutes the bleeding stops, and by the end of the day or the next day the pain goes away. The main thing when a child is injured is not to give in to emotions, calm the child, act quickly and call an ambulance or see a doctor.
When is an urgent consultation with a surgeon necessary?
- At the first sign of wound infection. This is swelling, redness around the affected area, and increased body temperature.
- For cuts (even shallow ones) on the face or head.
- For deep cut wounds if the bleeding does not stop.
- If there is loss of sensation at or below the cut site.
- If the wound does not heal for a long time.
- There is a foreign body in the wound.
- No tetanus shot.
- If tendons and ligaments are cut. Limb movements are limited or absent.
Features of the treatment of weeping wounds on the face, head, legs
If the head is wounded, the hair in the area of the wound must be cut off, and then the wound must be treated and the head bandaged. Wounds on the face should be washed with hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate or furatsilin. To avoid unsightly scars on your face, you should consult a doctor. This is especially important for children. Sores on the lips and mouth should be treated with dental products such as lidocaine ointment, sage, and chamomile. If a child has injured his leg, it should be treated using the methods described above. In case of suppuration, consultation with a doctor is required! Self-treatment of purulent wounds on the legs is fraught with consequences.
If the baby falls, then cuts and wounds may appear on his body. It is enough to wash or treat small abrasions on the knee with an antiseptic, but in difficult situations it is necessary to provide timely assistance to the victim. When a wound is poorly treated, it becomes weeping and does not heal for a long time. How to properly treat wounds and what to do if the injury turns out to be severe?
A calm child or a restless child – no one has ever managed without children’s falls.
Other reasons
Poor wound healing occurs with the following health problems:
- Lack of blood supply at the site of skin injury.
- Inflammatory processes in the body.
- Oncological diseases.
- Obesity or wasting.
These diseases are accompanied by a significant decrease in immunity. Therefore, for rapid healing of skin damage, treatment of the underlying disease is required.
Vitamins A and B take an active part in skin regeneration. A sufficient amount of them stimulates wound healing. , chronic fatigue, as well as bad habits such as alcohol and smoking can cause prolonged healing of damaged skin.
The process of wound healing depends on its nature. Puncture, purulent wounds require more careful care than injuries with sharp edges. The closer the wound is to the heart, the faster it heals.
Long-term non-healing wounds and scratches are a serious problem that signals the presence of pathologies and malfunctions in the body. If skin wounds do not heal well, the reasons may be different - from errors in nutrition to severe disruptions in the functioning of internal organs and systems. You can speed up the regeneration process and avoid the appearance of scars using pharmaceutical and folk remedies.
If skin lesions do not heal for a long time, a blood crust forms on them and they fester - this indicates a lack of certain substances in the body, the presence of infections and diseases of internal organs that disrupt the natural regeneration process.
Main reasons:
- Incorrect or untimely treatment of damaged areas of the skin - pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the wounds, an inflammatory purulent process develops, local temperature rises, swelling and redness appear.
- Chronic non-healing wounds are a sign or consequence of diabetes mellitus. With endocrine pathology, blood circulation in tissues is disrupted, cell nutrition deteriorates, the regeneration process slows down, and the legs and feet most often suffer. In diabetics, any scratch can turn into a large wound that becomes covered with a crust, purulent inflammation gradually develops, pain, itching, and swelling occur. A similar problem occurs with venous insufficiency, psoriasis and eczema, with prolonged compression of a certain area of the body.
- Aging of the body - with age, the immune system weakens, many processes slow down, and the number of chronic diseases increases, which leads to the formation of ulcers, the appearance of eczema, and weeping wounds that are difficult to treat.
- Tooth extraction - against the background of mechanical trauma to the gums or bone tissue, inflammatory processes often develop, wounds heal poorly, the temperature rises to 38 degrees or more, severe pain occurs that does not decrease after taking painkillers, the mucous membranes swell, and the breath smells rotten.
- Lack of nutrition - if wounds heal slowly, this is a sign of a lack of iron, calcium, zinc, vitamin A, C, group B. The problem often occurs in children who adhere to strict diets, during pregnancy and after childbirth. These substances are required for the normal restoration of the epidermis and mucous membranes; if they are deficient, the condition of hair, nail plates, and tooth enamel worsens.
- Ulcers appear on the skin of the hands due to constant contact with chemicals without protective gloves.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the liver, lymphatic system, poor condition of the vascular walls.
The rate of wound healing is negatively affected by long-term use of Aspirin and glucocorticoids, a history of HIV, hepatitis, and malignant tumors. Recovery processes slow down in case of obesity or severe exhaustion due to diets or long-term illness. Lacerated and deep wounds with a large distance between the edges and with signs of necrosis cannot heal quickly even in healthy people; they often fester. Such injuries always leave scars.
Important! The occurrence of chronic wounds and scratches that do not heal for a long time almost always indicate weak immunity, hypovitaminosis, poor blood clotting, and impaired circulatory processes.
Mom-pediatrician

The period of greatest childhood traumatism
Parents and doctors call the age from 6 months to 3 years “the period of greatest childhood trauma.” At this age, children are actively exploring the world with the help of new skills that they have acquired, but are not yet aware of the risks associated with their actions. In this article I would like to draw your attention to the injuries that occur most often in children - various skin injuries, from minor abrasions and scratches to more serious wounds.
First aid for minor wounds in a baby
If your baby gets an abrasion or scratch (for example, he fell and injured his knee), first of all it is necessary to treat the wound with an antiseptic.
Take a cotton or gauze pad (preferably sterile), moisten it with a solution of hydrogen peroxide and treat the wound with gentle blotting movements. Using peroxide, it is also necessary to remove dirt that has got into the wound.
There is no need to generously water your knees with iodine or brilliant green! It is better to treat the skin around the wound with them so that infection from intact skin does not reach the wound surface.
After some time, the wound will be covered with a thin protective crust, under which healing will occur. Your goal during this period is to ensure that the wound area does not become contaminated or re-injured.
When to go to the doctor?
Unfortunately, there are situations when a child receives serious wounds that require medical attention as soon as possible. This may be necessary when:
- deep lacerations, such as dog bites;
- if the wound bleeds heavily;
— burns (a small burn the size of a child’s palm is already a serious injury for the baby and requires medical attention);
- if a child’s hand is caught in a door, etc.
In such cases, it is necessary to contact a children's emergency room. The emergency room employs a traumatologist who can examine and treat the wound and apply a sterile bandage. If necessary, an x-ray or stitches can be taken at the emergency room.
Emergency rooms are open 24 hours a day. If a child has suffered an injury that requires medical attention, do not put off the trip “until tomorrow.” Firstly, the child’s condition may worsen during this time. Secondly, if the wound requires stitches, the doctor can do this within 12 hours after the injury. In case of late treatment, when more than 12 hours have passed since the injury occurred, the doctor will treat the wound, but will not apply stitches, due to the high risk of developing infection in the wound. In this case, the wound will take longer to heal and in the future a scar will form in its place.
The wound does not heal for a long time. Why?
If the wound does not heal for a long time, the skin around it is red and swollen, pus is released from the wound and an unpleasant odor appears, this indicates that there is an infection in the wound that the child’s body is fighting but cannot cope with.
A pediatric surgeon treats such wounds. After examining a wound that does not heal for a long time, the doctor can take a smear to determine the causative agents of the infection and their sensitivity to antibiotics. To treat a wound, antiseptics (to clean the wound) and antibacterial drugs (to kill the infection in the wound) are usually used. In some cases (if the wound is serious or the child is very small), the doctor may additionally prescribe an antibiotic in injections or syrup.
Depending on the age of the child and the nature of the wound, which does not heal for a long time, the doctor may recommend hospitalization in a hospital, or observation in a clinic, in which you need to come for a doctor’s examination and change the bandage every few days.
Cat scratch disease
Children of all ages love to play with animals, which is why they often walk around with their hands scratched by a cat. Unfortunately, cats can be a source of felinosis (cat scratch disease).
Felinosis is manifested by inflammation and suppuration at the site of the scratch, enlargement and soreness of one or more nearby lymph nodes (most often axillary), and increased body temperature. To make a correct diagnosis, it is important to remember the child’s contact with the cat. Cat scratch disease is treated with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
How to avoid childhood injuries?
- Do not leave your child alone unattended.
- Remove all objects dangerous to the baby (knives, scissors, needles, tools, medicines, household chemicals, etc.) from places where the child can get them independently (for example, from the surface of the table or the bottom shelves of cabinets).
- Cook food on the far burners of the stove. Do not place cups of hot tea on the edge of the table so that the child cannot knock them over.
- Do not place irons or other electrical appliances where a child can pull them off by pulling the cord.
- Do not leave your child alone with pets.
author: Anna Sheveleva, pediatrician, source: https://mama-pediatr.com/
The article was published in the magazine “Mom and Me” (3/2014) - read pdf - “If a baby’s wound does not heal for a long time”
Use of article materials is possible with the indication of the author and an active indexed link to the source - the “mother-pediatrician” blog.
You may also be interested in:
1. Antibiotics: from a gun to sparrows
2. What is important to remember when you are prescribed medication
3. Abortion for the benefit of the unborn child?
4. “Don’t smoke, it will harm my health!” 21 creative anti-chicken posters
5. Tick bite: how to avoid and what to do