How to strengthen the back of an infant is a pressing question for mothers whose babies are 5-6 months and older. It is not advisable for a child to sit with a round back, especially in the first year of life. If there are ways to prevent the negative consequences of a weak back and even the slightest likelihood of them, then you need to use them. The role of parents in the physical development of a child in the first year of life is no less than the role of doctors, massage therapists, exercise instructors, swimming instructors, etc. Constantly updating knowledge about the life and development of children is very important, especially for those who have their first child. If it is not possible to invite a specialist to work with your child, then you need to learn to work with him yourself, fortunately there is the Internet, although this will not be as effective, but it is better than “it will go away on its own.” In other cases, you need to look for specialists, because... it will be more efficient and faster, and immediately in the right direction. In any craft there are many nuances and little things that we do not notice, but the quality result depends on them.
Why strengthen a baby's back?
- A strong back provides an upright posture, freedom and, most importantly, the possibility of many movements.
- Children with strong backs confidently sit down and crawl, stand on support, and begin to walk.
- Strong back muscles allow a child to sit or stand for long periods of time during games or other activities.
- 4. Strong back muscles of the child prevent static deformations of the spine.
- A balanced and strong muscular corset of a child allows the physiological curves of the spine, lordosis and kyphosis to form correctly.
- The strong muscular corset of the child’s torso, where the back muscles occupy the largest part, is designed and works in such a way that it relieves the spine from the load, due to its uniform distribution over the entire back.
How to strengthen a child's back at 5-6 months?
Closer to 5-6 months, the child can already be verticalized for a short time, but without support on the legs. The baby can be sat down for a few seconds, held vertically in your arms for longer, and the backrest raised higher in the chair. The vertical pose itself for the back is already a kind of strengthening exercise. The first attempts to hold himself up while sitting look very uncertain, the child wobbles in different directions, while sitting he can fold forward, but every day the child holds his back more confidently. By periodically holding the child upright and doing exercises with him, we accustom his body, the spine in particular, to the load, which provides an incentive for bone growth, their compaction, and the replacement of cartilage with bone tissue. The muscular system reacts in a similar way, experiencing new loads, the muscles become thicker and stronger, i.e. grow. The main thing that happens at this age stage is the familiarization of the brain and the entire nervous system with a different body position. The first verticalization of the child, firstly, gives a signal to the brain about the need for structural changes in the skeleton and muscles, and secondly, the brain, vestibular apparatus, muscles and peripheral nerves learn to work in harmony in one circuit. There is a need to maintain a vertical posture for the body, and this is a complex and step-by-step task for the body. In order to keep himself sitting or standing, a chain reaction occurs between the vestibular apparatus, nervous system, and muscles.
So, next we will consider practically how to strengthen a child’s back at 5-6 months, exercises:
1. Toning massage for the back.
2. Tilt the child, fixing his legs. In this case, the bends will be passive-active, because the child most likely at 5 or 6 months will not be able to rise independently from the tilt position, although there are such children. The legs are fixed above the knee, but below the hip joint, the child is turned with his back to the instructor-masseur (mother), the child’s feet are suspended, without support, one adult’s hand supports the child under the chest, the torso leans forward. This exercise is not advisable after eating, or with increased intracranial pressure.
3. Holding in a vertical position. We fix the child, as in the previous exercise, but do not tilt it, but hold it vertically. When the child begins to hold himself upright at least a little, we need to use this and develop this skill. The development or strengthening of the child’s back here is that we begin from the vertical position of the baby by slightly tilting it to the right, left, and forward. More precisely, this will be an attempt to tilt the lower part of the body, and the newborn will reflexively try to keep the upper part vertical. Our task at the moment of such a tilt is not to overdo it with the angle, otherwise the child’s fragile back muscles will not be able to withstand it and he will sharply bend down. You need to find the line beyond which the muscles cannot hold the body, and always bring the tilt close to this line, while holding the safety hand in front of the child, but without touching him, otherwise he will lie on his hand and there will be no back strain. Every day this edge will be further and further and the angle of inclination will be greater, because... the muscles will get stronger. Then you can make it more difficult with an angle, including while bending over and describing a circle in front of you so that the muscles of different groups work in turn.
Diastasis of the rectus and oblique abdominal muscles: causes of appearance
There are many reasons for the appearance of diastasis of the rectus or oblique abdominal muscles, but doctors primarily talk about too much tension, physical activity with emphasis on the abdomen and stretching of muscle fibers.
Among women
In women, the abdominal muscles are paired straight muscles, which are enclosed in a “case” of lateral and tendons. The linea alba is where they meet. During pregnancy, hormonal changes occur in the body, which leads to loosening of connective tissue.
Without this process, not only natural childbirth is impossible, but also the process of gestation itself - the child is actively growing in the womb, the stomach protrudes, and unloosened connective tissue will become an obstacle to the normal course of this process.
a) diastasis; b) after abdominoplasty
As soon as a woman gives birth to a child, the reverse process begins in the body - the connective tissue strengthens itself, and within 6 months everything returns to normal. In some cases, this does not happen due to excessive physical exertion or hard work. Diastasis can also be caused by:
- chronic constipation;
- long/persistent severe cough;
- lifting weights.
In men
Separation of the rectus muscles in men is most often observed due to constant hard physical work and improper training. A man’s weight also plays a big role - obesity, and then sudden weight loss leaves the connective tissue in a loose state, it simply does not have time to contract and strengthen, the protrusion remains.
Sports activities, especially against the background of obesity, should only take place under the supervision of a coach or instructor. A well-designed set of exercises without “Olympic” records is the guarantee that diastasis will correct and disappear.
In children, newborns
Abdominal muscle discrepancy is often diagnosed in children; it is common in athletes when there is a coaching error. It is necessary to select a set of exercises and determine the level of physical activity in childhood on an individual basis.
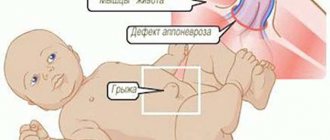
Diastasis in a newborn
If diastasis is diagnosed in newborns, this occurs in two cases:
- the full development and formation of the abdominal wall did not occur in utero;
- the child was born premature and completely unformed.
As a rule, such problems in newborns are easily solved. It will take time, patience and a set of exercises prescribed by a physiotherapist.
During pregnancy
A discrepancy of the rectus abdominis muscles during pregnancy of up to 2 cm is considered normal - this is a physiological process that does not require correction.
When carrying a baby, a woman's abdominal muscles are subjected to strong pressure from the inside - the baby grows, the uterus enlarges and literally “pushes” the rectus muscles along the linea alba. And this is a natural process, because the body has prepared for it and its connective tissue has already loosened in the first weeks of pregnancy.
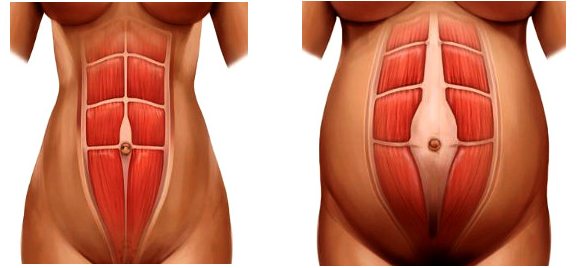
Diastasis during pregnancy
How to strengthen a child's back at 7-8 months?
At 7-8 months, children usually sit up on their own and the issue of a strong back is very important for this age. But it happens, and quite often, that a child is just beginning to make some attempts to support his back at this age. With the right approach, strengthening your back in 7-8 months will go faster than 2 months earlier. Of the exercises to strengthen the back of a 7-8 month old child, you can use the ones described above and add:
1. You can use the exercises described above.
2. Sitting the child down for a short period of time, supporting him by the hand, balancing while sitting.
3. If, when bending forward, the baby cannot yet lift himself up on his own, then at the moment of tilting there should be at least resistance to tilting. It is this back resistance, or you can call it an attempt to stay upright, that will be the most useful “point” from which you can build on and move forward in strengthening the baby’s back. In this case, we simply repeat the tilts, and this resistance will very soon become much stronger and then the child will be able to lift himself from the tilt position.
At 7-8 months, long-term static vertical loads are harmful for children with weak backs, but short-term ones will be useful, because send a signal to the body about the need for additional energy and nutrients for the busiest areas of the body at the time of virtualization. In general, strengthening occurs this way, from the moment a signal is given to the body, and then a response in the form of compaction, growth, thickening of bones, muscles, supply of nutrients in tissues, etc. But the body needs a signal where exactly to focus its “attention”, and in what form. Not a single child will sit down right away without trying; it is at the moment of trying that the most valuable and important things happen, the body learns and gets stronger. If, due to age, it is time to be able to do something, then you can help the child learn it, there is nothing wrong with that, on the contrary, the child will master this stage and “move on” further. You can ask me clarifying questions about how to strengthen a child’s back at 7-8 months by WhatsApp +79266057470. We have an Instagram @happybabymassage.ru and a YouTube channel happybabymassage, where there are videos on the physical development of children at different ages.
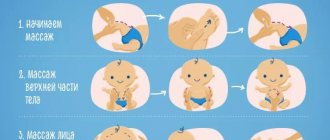
MASSAGE AND GYMNASTICS TECHNIQUES
Starting position: lying on your back.
This exercise helps develop and strengthen the leg muscles. Its implementation consists of the sequential use of light stroking, circular rubbing, felting and tong-like kneading techniques.
The procedure should begin with light stroking along the entire length of the leg, which must be performed 3 or 4 times. Then it is recommended to move on to ring rubbing (3-4 times) and return to stroking again. After stroking, you can begin felting. This technique is repeated 3 times.
During the procedure, the palms should clasp the child’s leg so that one of them lies on the inner surface of the leg, and the other on the outer surface. The exercise consists of moving the muscles with gentle but vigorous movements, which should be done clockwise.
At the end of felting, you need to begin tong-like kneading of the lower extremities. To perform the exercise, you need to place the child’s foot in the palm of your right hand and support it at the bottom of the shin. Using the index finger and thumb of your left hand, you need to grab the outer surface of the shin and move the muscles towards the big toe from the foot to the thigh and back. The procedure should be completed with several strokes.
Starting position: lying on your back.
This exercise helps develop and strengthen the muscles and joints of the legs. To perform it, you should grab the upper part of the child’s shin so that the masseur’s thumbs are on its inner surface, and the rest are on the back surface.
If by the age of 4 months the child’s muscle hypertonicity has disappeared and bending his legs does not bring him any unpleasant sensations, then it is recommended to make several stroking movements under his knees from top to bottom.
Starting position: lying on your back.
The procedure promotes the development of the muscles and joints of the foot. It consists of sequential use of stroking, rubbing and effleurage.
Foot massage begins with stroking. Then you need to do 5-6 rubbings. After rubbing, you need to return to stroking (3 times), and then start beating (5 times). The whole procedure ends with 2-3 strokes. This exercise should be performed on the left and right leg. In addition to massage, it is recommended to do leg flexion and extension daily, which should be repeated 5 times on each leg.
Starting position: lying on your back.
This exercise helps develop and strengthen the arm muscles. Its implementation consists of sequentially applying the techniques of light stroking and circular rubbing of each hand. At the beginning of the procedure, you should perform several light strokes, then move on to ring rubbing, which is repeated 6 times. The procedure should be completed with light stroking.
Starting position: lying on your back.
The procedure promotes the development of the chest muscles. Execution consists of sequential use of stroking and vibration massage.
The procedure begins with several circular stroking movements, carried out in the direction from the ribs to the shoulders. Then you need to do 3 strokes along the intercostal spaces. After stroking the intercostal spaces, you need to start a vibration massage, which must be repeated 3 times. The procedure should be completed with 2-3 strokes.
Starting position: lying on your back.
Carefully spread the child's arms to the sides and smoothly lift them up. Then stretch your arms forward and carefully lower them.
After this, you need to repeat the same movements, only in reverse order. This exercise should be performed 6 times.
Starting position: lying on your back.
To perform the exercise, you should carefully place your thumbs in the child’s palms and make him clench his fists. Then you need to spread the child's arms to the sides and cross them over his chest. The position of the hands should be alternated: first the right hand should be on top, and then the left. Since at 4 months the baby is able to independently hold the fingers of an adult, he should not be supported by the wrists. This exercise must be performed rhythmically, alternating fast and slow tempos. Repeat this procedure 7 times.
Starting position: lying on your stomach.
This procedure consists of sequential alternation of stroking, rubbing, forceps-like kneading and effleurage.
At the beginning of the procedure, you need to make several stroking movements. After stroking, you should begin rubbing the child’s back and buttocks, which is done with your fingertips (2-3 times). After rubbing, you need to do a few strokes again.
After stroking is completed, it is recommended to begin kneading with forceps (6 times). It should be done along the long muscles of the back. Like rubbing, kneading should be completed with light strokes.
At the end of the procedure, you can use the technique of tapping the buttocks. To do this, gently hit the child's buttocks with the pad of your index finger. Then make a few more stroking movements.
Starting position: lying on your back.
To perform this exercise, you need to put his favorite toy on the side of the child and gently ask him to turn in its direction. After this, you should carefully help the baby roll over onto his stomach. This exercise must be repeated 3 times in each direction.
Starting position: lying on your stomach.
Starting position: lying on your back.
The procedure involves a combination of stroking, rubbing, sawing and pinching the skin around the navel.
The procedure begins with circular stroking of the abdomen, which should be carried out clockwise with the palm and fingertips. This technique must be repeated 3 times.
After circular stroking, you can move on to counter stroking and stroking the oblique abdominal muscles.
After stroking, you need to start rubbing the abdominal muscles, which must be done with your fingertips.
Pinching is a good preventive measure against hernia.
Starting position: lying on your back.
This exercise helps strengthen the muscles of the front of the neck and back and stimulates the development of the abdominal muscles. To perform it, you should place your thumbs in the child’s palms and make him clench his fists. The massage therapist should use the remaining fingers to support the child’s wrists.
How to strengthen a child's back at 9-10 months?
Usually, a weak back at this age is indicated by the fact that the child sits with a round back or cannot sit for a long time, but there are also those who still cannot sit down at all. Among the strengthening exercises for the back at 9-10 months and older, I recommend using squats. Why squats? When a child rises from a squatting position, in addition to strengthening the legs, the iliopsoas muscle is strengthened; it is located in the pelvis. This muscle is attached to the lumbar vertebrae and is a very large postural muscle that maintains physiological lumbar lordosis. In addition, when doing squats, the child must keep his back straight, and this is an additional isometric load for the back muscles. Of course, you need to make sure that the child squats with a straight back. This is the main thing that can be added to the exercises described above to strengthen the back of a child aged 9-10 months and older.
For children after one year of age, back strengthening can be done through gymnastics. The older the child, the more difficult the exercises can be. Massage alone cannot strengthen children's backs; massage is used as a method of warming up the muscles, and is done intensively. Corsets also do not strengthen the back; on the contrary, the back does not work in a corset; it is used to accustom the ligamentous apparatus to a certain position, and strengthening is only through gymnastics.