Probing the lacrimal canal in newborns and children up to one year old: video, consequences of the operation
Probing is a type of surgical intervention, so it requires special preparation.
| Doctor/test | Study |
| Examination of the nasal septum, throat and ears. It is necessary to exclude pathologies of the structure of the nasal and ocular areas. | |
| Exclusion of infectious or bacterial infections, inflammations. Checking your general health. | |
| Identification of internal sluggish pathologies or inflammations. | |
| Examination of the fundus, apple and cornea. This method allows you to detect foreign bodies, retinal tears and pathologies of the optic nerve. | |
| A blood clotting test to rule out the possibility of bleeding or blood clots. | |
| This examination reveals the presence of pathogenic microflora of the eye and mucous membranes. It allows you to select the most effective antibiotic. |
| A tear duct patency test will reveal the extent of the blockage. If the canals have sufficient patency, it is advisable for the child to undergo a procedure to expand them. |
When receiving all the results before probing, it is recommended:
- follow a strict diet 3 days before surgery;
- do not feed the baby 4 hours before;
- stop taking all medications.
To avoid injury or serious complications, the baby's arms and legs must be firmly secured with diapers. It is worth noting that many clinics swaddle children themselves before surgery, so this point will be clarified during consultation.
The operation is performed by a highly qualified pediatric ophthalmologist in a specially equipped eye office or clinic.
5 stages of preparation for the procedure:
- The final diagnosis should be confirmed by consultation with an otolaryngologist to ensure that there is no congenital curvature of the nasal septum.
- A complete blood test is taken to check clotting.
- A few hours before the operation, it is not allowed to feed the small patient to prevent the possibility of regurgitation during the procedure.
- Before the manipulation itself, the baby must be swaddled tightly to eliminate the possibility of chaotic movements of the arms and legs.
- It is better for the child to be well-rested and in a good mood.
Dacryocystitis is quite often observed in infants. During the intrauterine period of development, the fetus has a special film in the lacrimal canal.
It plays a protective role and prevents amniotic fluid from entering the nasolacrimal duct. When the baby is born, this film is torn. But there are cases when it remains intact even after birth.
As a result, the canal becomes clogged, stagnation of tear fluid and inflammation of the lacrimal sac occurs.
The following causes of tear duct blockage in adults can be identified:
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the duct, as well as the face and skull;
- infectious diseases of the eyes and nasopharynx;
- tumors of the facial part of the skull;
- surgical interventions on the organ of vision;
- radiation therapy for oncological diseases;
- abuse of eye drops;
- side effects of certain medications.
Due to a violation of the outflow of fluid, there is an increased proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. An inflammatory process occurs in the lacrimal sac - dacryocystitis.
Symptoms of dacryocystitis in adults at the initial stage of the disease are mild. A person feels only slight discomfort in the area between the inner corner of the eye and the nose. This is where the lacrimal sac is located. But as the inflammatory process develops, the manifestations of the disease intensify:
- Redness and swelling appear in the inner corner of the eye.
- Tears are constantly flowing from my eyes. The fluid may contain blood.
- Mucous and purulent discharge appears.
- The person feels severe pain in the area of inflammation.
- Vision becomes blurry.
If treatment is not started at the acute stage, the disease quickly becomes chronic. Tearing becomes constant and worsens in the cold.
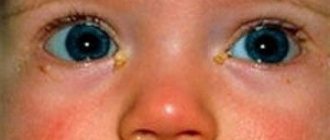
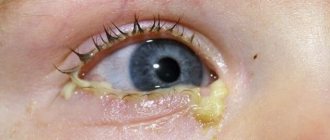
Parents often mistake signs of dacryocystitis in infants for manifestations of conjunctivitis. The child's eyes turn red, purulent discharge appears, which dries out in the form of a crust. Increased tear production occurs.
It is important to carry out differential diagnosis and distinguish dacryocystitis from conjunctivitis. For this purpose, ophthalmologists make a test using a dye.
A dye solution is dropped into the patient's eye, and cotton swabs are placed in the nostrils. If the nasolacrimal duct is passable, then the cotton wool becomes stained. If the tampons do not change color, this indicates a blockage of the duct.
In this case, the diagnosis of “dacryocystitis” is confirmed.
Types of treatment
Treatment of dacryocystitis should be started as soon as possible. Otherwise, the disease can lead to serious complications. Inflammation can spread to the hearing organ and brain.
Probing the lacrimal canal is only one of the methods of treating dacryocystitis. In the initial stages, oral antibiotics, antibacterial and antiviral eye drops, and massage are used. If conservative treatment is ineffective, then surgical methods are resorted to.
Probing must be done in the following cases:
- If the disease has become chronic.
- If the patient experiences severe lacrimation.
- If there is no effect from conservative treatment within 2 weeks.
- For congenital anomalies in the structure of the lacrimal canal.
Probing the lacrimal duct in adults is less effective than in children. This is due to the fact that in mature patients the tear duct is already fully formed and the blockage can be difficult to remove. Usually the operation is performed using bougienage or balloon plasty.
Probing the lacrimal duct in newborns usually gives good results. This is a rather unpleasant procedure, and the baby may cry during this manipulation. However, probing is necessary to prevent severe complications and vision problems in the future.
Before probing the lacrimal canal, you must visit an otolaryngologist. It is necessary to exclude a deviated nasal septum. If a child or adult has such a defect, the operation will be ineffective.
Adults also need to consult a therapist, and children - a pediatrician. You need to make sure that the blockage of the duct is not associated with a general infectious disease. You must undergo a general blood test and a coagulation test.
This will help avoid bleeding during the procedure. If the patient has a large amount of pus discharged from the eyes, then probing is postponed. In such cases, conservative therapy is prescribed.
The operation is performed only when the amount of purulent discharge decreases.
The child should not be fed before the procedure. to prevent him from regurgitating food during surgery. Also, the baby should be swaddled tightly so that he cannot prevent the doctor from carrying out all the necessary manipulations.
Surgery in children
How is probing of the lacrimal duct done? The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Additionally, an anesthetic is instilled into the child's eyes. Then, using rotational movements, the doctor inserts a special probe into the lacrimal canal. This allows you to break through the film and expand the channel. After this, the duct is washed with antiseptic solutions. The procedure lasts about 2-5 minutes.
Probing of the lacrimal duct in newborns is usually performed at the age of 1-6 months. The younger the child, the easier he tolerates this intervention. In addition, after six months of age, the film in the tear duct hardens and is more difficult to get rid of.
The baby’s normal state of health is restored after 4-6 hours. In most cases, one procedure is enough to restore normal tear flow. In 30% of cases, probing has to be repeated.
Surgery in adults
Probing of the lacrimal canal in adults is carried out using two methods:
- Bougienage. This method is the most gentle. If the procedure is carried out on time, this will help avoid surgery to remove the lacrimal sac. Under local anesthesia, special probes called bougies are inserted into the canal through the lacrimal opening. They remove the obstacle and expand the lumen of the canal.
- Balloon plastic. Under local anesthesia, a conductor with a balloon containing liquid is inserted into the canal. It is placed at the site of narrowing. Gradually pressure is supplied to the cylinder. The stenotic area expands.
Sometimes these procedures have to be repeated after an interval of several days.
The procedures are carried out in a hospital setting. Are complications possible after probing the lacrimal canal? The consequences of this intervention may be as follows:
- adhesive process in the canal;
- inflammation of the lacrimal sac;
- bleeding;
- relapse of the disease.
Bleeding is usually the result of a surgical error or improper preparation for the procedure. Other negative consequences usually occur during recovery after the intervention. Therefore, it is very important to properly conduct the rehabilitation period.
If bleeding occurs during the procedure, you must stay in the hospital for another day. After this, the person is discharged home. For 1 - 2 months you need to protect yourself from infectious and colds, which can trigger a relapse of dacryocystitis.
After probing the tear duct, antibacterial drugs should be instilled into the eye. The dosage and duration of use of the drops is determined by the attending physician.
Also, within a week you need to massage the lacrimal canaliculi, after rinsing the eye with a solution of Furacilin. The movements should be directed from the nose to the inner corner of the eye along the canal.
These measures will help prevent the formation of adhesions and inflammation.
Where is probing of the lacrimal duct done? This procedure is carried out in a hospital setting. In Moscow, probing is done in the Ophthalmology Department of the Morozov Hospital (Mytnaya Street, 24).
The smallest infant patients are treated here. For Moscow residents, the procedure is free of charge. However, the queue for probing is quite long.
Pre-registration is carried out approximately a month in advance.
This procedure can be done for a fee at various medical centers. The price of sounding depends on the medical institution. On average, the cost of the procedure ranges from 1000 to 3000 rubles (for one eye).
Reviews about the operation
You can find many positive reviews about probing the lacrimal canal. Parents of young patients report that after the procedure, their children stopped lacrimation and discharge of pus, their eyes became clearer, and inflammation and pain disappeared.
Probing the lacrimal duct in newborns
| Life is designed in such a way that from the very first days we are susceptible to various diseases. Some of the newborns begin to suffer from eye diseases, and the most effective way against this is to probe the tear ducts in infants. |
This procedure is a fairly safe operation, but it is still worth taking a closer look at it and finding out why it is dangerous, because there are other methods of treatment.
Problems with the tear duct from birth arise due to the fact that the film that protected the baby’s eyes in the womb did not break during his first cries, so the fluid began to accumulate and suppuration formed.
It is a fairly normal thing for newborns to develop some eye problems. The reason for this can be hidden in many things, be it allergies, infection or problems with the tear duct. Sometimes the symptoms are revealed in the maternity hospital: lacrimation, redness, discharge of purulent masses, souring of the eyelids. But, most often, the cause of all this is conjunctivitis, which can be treated with simple rinsing and some medications.
But if this is not the reason, then most likely it’s all in the child’s lacrimal duct. To find out the diagnosis, you need to contact a pediatric ophthalmologist, who can easily determine the cause and prescribe the appropriate treatment. As a rule, probing of the lacrimal canal in newborns is prescribed.
Checking for problems with the tear duct is carried out as follows. The doctor drops a harmless solution, colored in a noticeable color, into the baby's eye, after which a cotton swab is inserted into the baby's nose. If there are no problems, the tampon will turn the color of the solution, otherwise there is a blockage, so you will have to treat it with probing.
Video: Obstruction of the tear duct
Aznauryan Igor Erikovich, MD, pediatric eye surgeon, pediatric ophthalmologist, head of a specialized system of children's eye clinics.
Risks
In fact, the procedure is quite safe, because everything is carried out under anesthesia; all you need to do is take care of the child after the operation, that is, do not forget about massages, drips of antibacterial drugs and monitor the condition of the eyes. Parents can also choose a more experienced attending physician, so that he definitely does not misfire.
If the child catches a cold in the near future after the operation, then the suppuration will recur, otherwise there are practically no relapses. Therefore, eye probing in newborns is considered the most effective, fastest and safest method.
Carrying out the procedure
Some people don’t know how to probe the lacrimal canal in newborns, so it’s worth talking about it in more detail. So, the beginning of the whole procedure begins with a visit to an otolaryngologist, who will give an accurate diagnosis, because similar symptoms can be observed in other diseases. The attending physician advises trying to get rid of the problem using improvised methods, this is a massage; if it works, the gelatin plug will break through on its own, and no operation will be necessary.
But if the operation is still planned, then before probing, blood is donated to determine its coagulability, everything takes place under anesthesia. The procedure is performed by a doctor who puts on gloves and takes instruments. The head is fixed in one position so that nothing happens during insertion of the probe. Now is the time to open the eye and instill painkillers. Next, the film is pierced with a tool and washed with an antiseptic. This action will take no more than five minutes. This is how this operation is performed.
Video: Probing the nasolacrimal duct
Balasanyan Victoria Olegovna, PhD, deputy head of the specialized system of children's eye clinics.
Consequences of probing
After the procedure, the baby can go home with his parents, who must monitor the condition of the baby’s eyes for two months. The fact is that sometimes eye probing does not help due to insufficient depth or incorrect diagnosis, but this happens very rarely. But if, nevertheless, the situation turns out in such a way that you will have to consult a doctor again, who will either prescribe repeated probing or another way to solve the problem.
After probing, if the operation was successful, then after a few hours the result will be noticeable, because the eye will no longer show signs of the disease. But to prevent any infections from getting into the eye, it is necessary to instill antibacterial devices for some time. If you don’t want any recurring problems to arise, then do massage to get rid of all the partitions.
Alternative to probing
As mentioned above, doctors sometimes advise massaging the baby’s eyes before surgery, because sometimes this method works and allows you to refuse intervention. The goal is to try to break through the film, which will be removed using a probe.
How is massage performed:
- the accumulated moisture is carefully squeezed out of the lacrimal sac;
- a heated, warm furatsilin solution is instilled into the eye;
- pus is removed with a cotton swab;
- after this you can begin the massage itself;
- Once the massage is completed, a disinfectant solution is instilled into the eye.
This procedure can be performed up to five times a day; the massage itself consists of light pushing movements. During a consultation with a doctor about solving problems, try to inquire about how the massage is performed, because it is the specialist who will be able to accurately tell you and show you this procedure. The procedure is carried out only at those moments when the child is crying, because the chance of tearing the film increases. Every movement must be calculated and done as carefully and carefully as possible so as not to harm the baby.
Video: Probing the nasolacrimal duct
A very important note is that the sooner you perform the operation, the less painful it will be for the child, because during the growth of the body, the very film that prevents tears from flowing out strengthens. So if you notice this problem in a child, then immediately go to a specialist who will prescribe treatment and tell you about all aspects, try to find out as much information as possible from the doctor.
Monitor your baby carefully to ensure that pus does not leak into the other eye or ear before surgery. So to the question “How to avoid complications?” everything is simple: the sooner the probing is carried out, the better.
After the operation, a massage is prescribed, which is aimed at removing the remaining membrane walls.
clinic2.ru
Contraindications for surgery
When a child is born and screams for the first time, the film bursts from tension. In rare cases, this process still does not occur. Due to the fact that it maintains its integrity, there is no way for tears to escape; they accumulate in the lacrimal sac and cause an inflammatory process. The described phenomenon is the cause of dacryocystitis.
- with light pressure on the lacrimal sinus, pus flows out of the eye;
- continuous flow of tears in any condition of the child or their absolute absence;
- pus is released without stimulation.
If these symptoms are present, in order to make a final diagnosis, the doctor resorts to the following manipulations: a special coloring liquid is poured into the child’s eye. Before the procedure itself, cotton strands must be placed in the nostrils. You need to wait 5 minutes and let the solution flow down the entire tear duct.
The absence of violations is indicated by colored cotton wool, since normally the liquid overcomes the lacrimal canal and enters the nose. If staining does not occur, the doctor diagnoses obstruction of the canals and prescribes probing of the lacrimal canals. It is worth considering that it is better to carry out intervention for children who are already 2-3 months old, not earlier.
If the situation is urgent and alternative treatment methods have not helped, probing can be done earlier. Parents must definitely find out information about why the eyes of a newborn are festering. Timely implementation of recommendations will help avoid serious vision problems.
- inflammation of the tear ducts and sac has acquired chronic status;
- alternative treatment methods (drops, massage) do not help;
- continuous flow of tears;
- the doctor questions the normal development of the lacrimal duct.
If all of these symptoms are present, probing of the lacrimal canals in infants is inevitable, otherwise dacryocystitis in newborns will lead to more dire consequences, including loss of vision.
There are 2 reasons for refusing surgery:
- deviated nasal septum;
- acute purulent inflammation of the lacrimal sac and surrounding tissues (phlegmon).
If a child was born with an already deviated nasal septum or has congenital anomalies in the structure of the lacrimal canals, probing simply does not make sense, since other surgical interventions are needed.
In these cases, it is undesirable to perform the procedure, since the course of the operation may be unplanned and the consequences may be disastrous. But, nevertheless, in some cases, doctors still perform the operation with contraindications, since each case is individual. If you try to carry out probing during purulent inflammation, you can aggravate the situation even more.
There are not many reasons for the development of obstruction and inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct.
In most cases, pathology is detected immediately after birth and occurs due to:
- abnormal structure of the nasal septum;
- underdevelopment of the lacrimal canal;
- preserving the film that should have broken through during the first breath and cry of the child once after birth;
- genetic pathologies of the structure of the bones of the skull or face;
- eye infections;
- entry of a foreign body into the lumen of the canal;
- tumor formations.
The most common cause of blocked eye ducts is the baby's lack of prolonged and strong crying immediately after birth.
Surgical breakthrough of the protective film is prescribed only after conservative treatment. If there are no positive results or the condition worsens, the ophthalmologist gives permission to perform the procedure.
Indications for surgical intervention are also:
- profuse lacrimation;
- increase in the inflammatory process;
- change in color of purulent contents from yellow to green;
- ineffective treatment with massage;
- disturbances in the formation of the lacrimal canal;
Probing the lacrimal canal in newborns has a number of contraindications, including:
- abnormal structure of the optic ducts;
- acute sinusitis;
- chronic sinusitis;
- allergic manifestations in the form of cough or runny nose;
- curvature of the nasal septum;
- hemophilia;
- altered blood composition;
- diabetes;
- infectious diseases;
- leukemia;
- conjunctivitis;
- facial injuries;
- increased sensitivity to painkillers;
- pneumonia;
- asthma;
- tumors;
- heart failure.
The eye festers after probing the lacrimal canal
Our sore subject with a happy ending. My daughter had her first sounding done at 4.5 months. Before that, a bunch of different massages, from gentle almost stroking to painful pressure. Every day torture, burying. After probing, nothing went away; on the contrary, the lower eyelid was inflamed, the eye was completely poor. A week later they came for an examination and said that it was impossible to do it again, since nothing and only “meat” had healed there. A week later they did it again, but “nothing happened,” since everything was inflamed and the doctor said that she would send us to Morozovka. At that time, I was already so nervous, and I felt sorry for my daughter, and there was no choice but to take her to the hospital. I've read so much about how mothers are nervous at the door, how no one stands on ceremony with their children. I couldn't pull myself together. The doctor said that once a week after the operation has not passed, it means there is no chance of self-recovery. They also advised me to drip vasoconstrictors into my nose, because there was swelling of the nasal mucosa. It seems like the tubule will not open any more. I don't like drops and all kinds of medications. Well, I came up with the idea that since my daughter can’t breathe dry air normally, I’ll try to relieve the swelling with round-the-clock hydration. After two days there was an improvement, then 3 days later, and dacryocystitis was as if it had never happened. At 5.5 months it was all gone. Of course, probably not from the humidifier, but this is what happened to me. Maybe it just helped a little, or maybe it all went away on its own. And yes, we also had not just lacrimation, but also suppuration. My daughter was wearing anti-scratch guards all this time, as she was constantly scratching her eyes. A friend of her daughter decided not to do it, but to wait, since in 90% everything goes away on its own before a year, when the tubules simply expand with age. It's been 10 months. But they didn’t have such a degree, their eyes just watered all the time. In mine it was 2 times smaller than the second one.
This page contains the most popular posts and comments from our users on the topic “Pus after probing.” This will help you quickly get an answer to your question, and you can also take part in the discussion.
Girls, who had your children have their tear ducts probed, on what day did your eyes stop festering after the operation? A week has passed, and there is still a little pus... will we really have to go through this terrible procedure again?