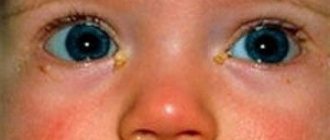
When a child's eyes cross, it worries parents very much. And everyone, without exception, is concerned about the question of when the strabismus will disappear, and whether it is dangerous for the baby.
Parents are worried for good reason. Strabismus is a serious problem that requires close attention. Fortunately, this problem can be treated, but if this is not done, then the quality of the child’s vision will suffer quite severely in the future.
In this article we will look at very important questions: why strabismus occurs, how to diagnose it and how to get rid of strabismus.
Eyelids swell in infants: symptoms
Have you noticed that the child’s eye is swollen and the upper eyelid is red, and the baby himself is restless: does he cry a lot and does not sleep? In such a situation, consultation with a specialist is necessary. You should not try to relieve swelling on your own and wait for improvement within a few days. After all, a symptom such as swelling of the eyelids is a clear signal from the body about the presence of allergies, the development of an infection or serious systemic pathologies, or kidney problems. An experienced diagnostician, after a visual examination of a child whose eyelid is swollen, will prescribe an additional consultation with an ophthalmologist, allergist, etc. Only if the diagnosis is correct can the disease be dealt with quickly and its recurrence prevented.
Baby's eyelids swell - symptoms:
- the baby's eyelids are swollen - if the baby's two eyelids are swollen at once, and the eyes are red and itchy, it is possible that the baby is developing an allergy;
- swollen lower eyelids - the lower eyelids in children often swell due to prolonged crying, poor sleep, such swelling can be physiological and is present in many infants, but it is also observed with an allergic reaction, kidney disease, etc.;
- the newborn’s eyes are red, swollen and watery - if the swelling of the eyelids is bilateral and is accompanied by lacrimation and redness, this indicates the development of viral or bacterial conjunctivitis;
- only one eyelid swells, the lower one - severe swelling under one eye may indicate a problem such as dacryocystitis, obstruction of the tear duct;
- a child's eyelid is swollen and painful - this can be a symptom of stye, which causes itching and pain during the ripening period.
In many cases, swollen upper and lower eyelids in infants are the result of prolonged crying and an uncomfortable position during sleep. Such conditions are not dangerous and pass quickly. If you have been observing swelling in your child for several days, be sure to visit a doctor, since frequent swelling is not the norm.
Why the lower or upper eyelid may swell in a baby - possible causes
A doctor must determine the exact cause of any ailment or unstable condition in an infant. If your baby's eyelids are swollen, you should first visit a pediatrician. If necessary, he will either prescribe an additional examination by a specialist - an ophthalmologist, an allergist, a cardiologist, or propose a correct treatment plan.
Why do the upper or lower eyelids of a baby swell - possible reasons:
- physiological swelling of the lower and upper eyelids - observed in newborns in the first weeks of life, if the swelling persists longer, consultation with a pediatrician and additional diagnostics are necessary;
- trauma, foreign body - the upper or lower eyelid may swell, since the child’s eyes are very sensitive, and even a small speck or eyelash that gets into the eye can cause swelling of the eyelids, in this case the process will be one-sided;
- conjunctivitis - newborn children are prone to conjunctivitis, since in the first months of life their eyes do not produce enough tears, and are therefore vulnerable to bacterial and viral infections;
- allergies - at risk are children with weak immunity, those on artificial nutrition, as well as those whose parents are allergic (with allergies, two eyes usually swell);
- dacryocystitis - if a baby’s lower eyelid is swollen and does not go away, it may be a blockage of the lacrimal canals, which leads to the appearance of edema; the disease can be congenital or acquired (often a one-sided process);
- barley - with barley, usually one eyelid swells - the upper or lower one, turns red and localized inflammation is visible on it; after the barley ripens, with adequate treatment, the swelling of the eyelids goes away.
If a child has a cold that lasts a long time and the eyelid is swollen, this may mean that the disease is complicated by inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. If your baby has been sick for several days and his upper or lower eyelids begin to swell, contact your pediatrician. It is possible that the child develops sinusitis, which, in the absence of adequate treatment, can become chronic and complicated by inflammation of the jaw, lower and upper eyelids, and orbit.
Contact a specialist
Standard situations with a hair getting into the eye and removing it using improvised means go without complications. If you cannot remove an eyelash from your eye yourself, you will have to go to the clinic to see an eye specialist. He will help you get rid of foreign material using tweezers and other professional devices.
You should consult a doctor if one of the symptoms appears:
- pain and burning appeared in the eye;
- the cornea is red;
- lacrimation increased;
- vision has deteriorated;
- there was pain when blinking;
- there were unpleasant painful sensations from the presence of an extra object;
- light sensitivity increased.
If you ignore the doctor, severe inflammation may occur with undesirable consequences.
How to remove an eyelash from an eye (video):
What to do if something gets under the upper or lower eyelid (video):
Eyelids are swollen - what examinations are needed?
Despite the similarity of the symptoms of diseases in which the lower or upper eyelids swell, there are still significant differences that can be used to preliminarily assume the presence of one or another disease. During a visual examination of the child, doctors take into account how often the eyelids swell, whether the process affects both eyes or only one, whether the baby is breastfed or on artificial nutrition, and also examines the medical history, including that of the parents.

Swelling of the lower or upper eyelids - diagnosis:
- visual inspection;
- allergy tests;
- scraping from the eyelids for microbiological examination;
- blood and urine tests;
- consultation with an ophthalmologist, allergist.
What to do if a baby's upper eyelid is swollen? What is the reason for this condition? Among the unobvious reasons why a newborn's eyelids may swell are diseases of the stomach and intestines, diabetes mellitus, and weakened immunity. Therefore, parents should react as quickly as possible to any changes in the child’s health and seek help from specialized specialists. Remember that you cannot ignore a painful condition for a long time if a child’s eyes are swollen, trying to cure, for example, compresses, allergic swelling. Without specific treatment for allergies, there is a high threat to the child’s life.
How to get a speck out of your eye
Having determined the location of the foreign body, take a mirror, open your eye wide and look again to see if it is exactly it. If yes, and the speck has not yet reached his mucous membrane, hook it with the edge of your nail and pull it closer to the bridge of his nose. Then take a clean handkerchief, wet it a little in water and apply it to your eye. Then press it hard and remove it slowly; the speck will have to be removed along with it.
If after a visual examination the foreign body is not detected, we can say that it has entered under the lower or upper eyelid. In this case, I advise you to turn out the first one, and then the second one. To remove the speck, apply a sterile paper napkin to its outer side, fold it in half and moisten it a little. This way, what needs to be removed from the eye will quickly stick to it. After this, slowly move it from left to right and remove it from your face.
In my experience, another effective method is to use a sterile ear stick. Soak it in warm water, stand in front of a mirror and run it along the outside of your lower eyelid. Then repeat the same thing, only this time with the top one. After removing a foreign object, to avoid redness and allergies, place a warm cloth over the eye.
Allergic eye swelling in infants: symptoms and treatment
Allergies in newborns can manifest themselves in the form of swelling of the eyelids, rashes, and redness on the skin. Since the child is still too young, parents do not have information about intolerance to certain substances, nutritional components, or medications that can cause unwanted symptoms. Those at risk of having swollen eyes due to allergies include not only formula-fed children, but also those who are breastfed. Allergies to breast milk are not uncommon. Also among allergic agents: pollen, dust, washing powder, pet hair, creams, shampoos, soaps and other hygiene products.
If a child has allergies, the upper and lower eyelids may swell. Allergic swelling of the eyelids may appear periodically. This is due to the type of allergen and how often the child comes into contact with it. If this phenomenon is left unattended, the allergy may intensify, which will lead to a worsening of the condition. With allergies, not only the eyelids often swell, but also the throat, tongue, and lips, which makes breathing difficult and threatens the child’s life.
Symptoms of allergic swelling of the eyelids in children:
- redness of one or both eyes;
- severe itching - the child will show anxiety, older children rub their eyes;
- swelling of the eyelid, narrowing of the palpebral fissure.

If a child's upper (or lower) eyelid is swollen, this should alert parents. In the first hours after symptoms appear, the baby needs help. Allergies are treated by an allergist who, taking into account the severity of the disease, draws up a treatment regimen. It includes antihistamines, as well as preventive measures to strengthen the immune system.
The baby's eyes are watery and the eyelids are swollen - what to do?
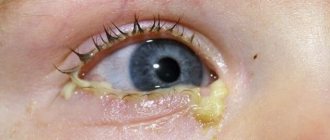
Young children often have swollen and watery eyes when conjunctivitis develops, and purulent discharge may also be present. This happens if a bacterial infection occurs due to infection or improper care of the newborn. What should you do if your baby’s eyelids are swollen and conjunctivitis begins? It is necessary to follow all stages of treatment prescribed by the doctor.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in newborns:
- cleansing the eyes of pus - if the eyes are swollen and there is pus, you need to use a warm antiseptic solution based on boiled water;
- antibacterial therapy - for microbial infections, eye drops with an antibiotic are prescribed; for infants, drugs with the least degree of toxicity are selected;
- antiviral and antimicrobial ointments - depending on the type of infectious agent, the drug is prescribed in the form of an ointment, which must be carefully placed behind the newborn’s eyelid.
To wash the eyes, you can also use decoctions of herbs that have an antiseptic effect, but first you need to make sure that the child is not allergic to one of the components of the herbal collection. Decoctions of herbs such as chamomile, calendula, and sage are best suited for cleansing the eyelids of pus.
The lower eyelids of a newborn baby are swollen due to dacryocystitis - what to do?
Is your baby's lower eyelid swollen? This could be dacryocystitis. Blockage of the tear duct in infants can be congenital or acquired. In the fetus in the womb, the tear ducts are closed and protect the respiratory system from the ingress of amniotic fluid. Normally, at the birth of a child, the tear duct should open - the baby cries, and under pressure the film breaks and the ducts open. If this does not happen, the newborn may develop dacryocystitis due to tear stagnation - the lower eyelid will swell. Secondary dacryocystitis, in which the lower eyelid swells, develops in older children against the background of prolonged illness or injury.
Film on the eyes of a newborn: cause of appearance and methods of elimination
Inexperienced parents are often frightened when they discover film on their newborn's eyes. It’s true that little babies’ eyes look very clouded within one or two months after birth, but there are physiological reasons for this.
It’s just that the baby’s vision does not immediately adapt to new conditions and continues to actively develop after birth, and not just in the prenatal period. But when does the film pass on the eyes of a newborn and in what cases does this indicate the development of the disease?
Typical clinical picture A film on the eye of an infant is a fairly rare phenomenon that occurs in only 5% of cases. As a rule, this indicates a congenital disease such as dacryocystitis - stagnation in the lacrimal canaliculi and subsequent inflammation. The main manifestation of the disease is purulent discharge from the eyes, which appears by the second week of life. The area of the lacrimal sac may swell, and with light pressure, pus is released from there. In the morning, the eyes may become sour and difficult to open. The inner corner of the eye may become red and watery. General symptoms of malaise (fever, drowsiness) are usually not observed, but the child may be capricious.
The pathology usually affects only one eye of the baby. This is the main sign by which dacryocystitis can be distinguished from conjunctivitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the inner surface of the eyelid. If the disease is viral, a film appears on the eyes of the newborn. Parents may notice swelling, irritation and redness of the mucous membrane, and tearing.
In newborn babies, conjunctivitis can appear with a weakened immune system if the infection is transmitted from the mother. The pathogen can enter the body of a newborn if the mother is infected with oral or genital herpes, if a foreign body or dirt gets into the eyes, or if simple rules of hygiene and care of the baby are not followed.
Causes of the appearance of a film A clearly visible film on the eye of a baby is most often a symptom of some ophthalmological disease. In some cases, we are talking about a regular accumulation of secreted fluid at the inner corner of the baby’s eye. If this does not bother the baby, this is a normal option, in which it is enough to rinse the baby’s eyes with boiled water every time after waking up. You can use drops prescribed by your pediatrician. Typically, this disorder goes away on its own and does not require treatment.
If, in addition to the film on the eye, the child has other symptoms of the disease (redness, tearing, discharge of pus, sticking of eyelashes, pain and anxiety), you need to contact a pediatrician and ophthalmologist. The causes may be congenital obstruction of the lacrimal canaliculi or an infectious lesion, damage to the face by obstetric forceps during childbirth, abnormalities in the structure of the nose and lacrimal canaliculus, underdevelopment or complete absence of lacrimal canaliculi. To understand the process of eye formation and its further development.
When the film normally disappears During the prenatal period, a protective plug was located near the nose to prevent amniotic fluid from entering the lungs. Normally, this film disappears immediately after birth (it breaks and is rejected at the first cry) or during the first two weeks of life. By this time, the inflammation subsides and the disease disappears without any dangerous consequences. If this does not happen, then intervention by a pediatric ophthalmologist is necessary.
When does the film come off from a newborn's eyes? As it has already turned out, if this is a film that for some reason did not break with the baby’s first cry, then it is possible that it will come off closer to two full weeks of life. But babies’ eyes remain cloudy for up to a full month, or even a month and a half. This is due to the peculiarities of vision adaptation.
Necessary therapeutic measures If the film on the eyes of newborns bothers you, then it is necessary to begin treatment. Usually parents start putting drops into their baby’s eyes on their own, and this helps. All unpleasant symptoms disappear, and the child becomes much calmer, because he is no longer bothered by pus and irritation. But with the abolition of such treatment, all signs of the disease return. This clearly indicates that the problem should be addressed to a pediatric ophthalmologist.
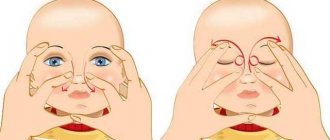
Massage of the lacrimal sac In cases where dacryocystitis is involved, massage of the lacrimal sac is indicated. To understand, an adult can feel the lacrimal sac on his own. This is a lump in the inner corner of the eye. Parents massage the newborn after each feeding. It is enough to make six to ten up and down movements with light effort. If the amount of purulent discharge increases, then the massage is performed correctly.
Gentle and regular physical impact on the problem area is the most important procedure in the first stage of treatment, because it helps improve the patency of the lacrimal ducts. To remove accumulated pus, you need to rinse the eye as necessary. It is best to do this with a solution of furatsilin. To prepare the solution, one tablet is diluted in a glass of boiling water. You need to wipe your eyes with a sterile piece of cotton wool in the direction from the temple to the nose. Afterwards you need to instill an antibiotic solution prescribed by your doctor.
Rinsing the tear ducts Long-term treatment does not help in some cases. The film on the eyes of a newborn does not go away, and the accompanying symptoms cause more and more discomfort to the baby. In this case, it is necessary to rinse the lacrimal ducts. To do this, the ophthalmologist, under local anesthesia, inserts a special probe into the lacrimal canal and passes it through the lacrimal ducts. Afterwards everything is washed with an antiseptic. Usually this procedure leads to a complete cure.
Washing is quick and quite easy. The protective film on the eyes of newborns is removed in one procedure. Local anesthesia is enough so that the baby does not feel pain, but you need to prepare for pain relief. A blood test is first taken to determine clotting time. You will also need a certificate from a general practitioner about the possibility of carrying out the procedure. After rinsing, the ophthalmologist will prescribe antibacterial drops. To avoid inflammation, you must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations.
A film on the eye of an adult A film can appear on the eyes of an adult. It does not cause discomfort as long as it does not affect most of the eye. Otherwise, the sharpness of vision may be significantly reduced. Modern medicine cannot give a definite answer to the question of why such a protective film forms on the eyes of an adult, although it is possible to identify certain factors that can provoke such a phenomenon.
The eyes are swollen, a child has stye - what to do?
The appearance of a small reddened bump on a child’s eyelid may indicate the development of a stye. Usually, the eyes swell and a boil appears in a child when his immunity is weakened, and also if the baby is overheated or frozen. Staphylococcal infection can also provoke the development of barley. If you notice that your child's upper or lower eyelid begins to swell and a stye appears, consult a doctor so that he can prescribe a suitable ointment that will soften the skin and speed up the ripening of the stye.
How to treat stye in a newborn:
- cleansing the surface of the eyelids from secretions - if the eyes are swollen and there is mucus and secretions, use a warm solution of furatsilin; cool liquids can be harmful, since cold provokes stagnation;
- warm compresses based on herbs with an anti-inflammatory effect (provided the child has no allergies) - for barley, decoctions of chamomile and dill seeds help well;
- antibacterial ointments are placed behind the lower eyelid - this way they are evenly distributed on both the upper and lower eyelids; the ointment is necessary to prevent bacterial infection;
- eye drops are prescribed if the eyes are swollen and conjunctivitis develops with stye.
What to do if the upper or lower eyelid swells and hurts? In the case of a child, visiting a doctor is mandatory, and adults should not ignore such dangerous conditions. It is better to seek advice in a timely manner. The choice of drugs for the treatment of barley in infants is small, so their selection should be carried out by a specialized specialist who will take into account the child’s age, his tendency to allergies and select the optimally suitable medications.
How to remove a speck (eyelash, hair) from your eye

And this can happen if action is not taken to remove it in time. Therefore, today I will tell you on the website izbavitsya.ru how to remove specks from your eyes, as well as eyelashes and hair. In order for everything to work out for you, it is very important to act according to the instructions I have proposed. Before proceeding with the removal of a foreign body, I recommend determining its location. To do this, wash your hands with soap and press your fingers first on the lower eyelid, and then on the upper. Take your time, move from left to right and vice versa. Since the skin in this area is very thin, you will definitely feel the speck.

Prevention of eyelid swelling in children
Hand hygiene by a mother who constantly interacts with her baby significantly reduces the likelihood of developing a bacterial infection, which is what causes the baby’s eyes to swell. The better the care of the baby is organized, the optimal microclimate in the house is constantly maintained, the less the risk that the eyes will swell due to conjunctivitis.

How to avoid recurrence of eyelid swelling in infants:
- gently washing the child with warm boiled water, caring for the surface of the newborn’s eyelids;
- scheduled dry and wet cleaning of the room where the child is located;
- regular ventilation of the room, timely hygiene procedures;
- balanced diet, healthy sleep, massages;
- air humidification during the period of central heating operation - due to dry air, the mucous membranes of the eyes are irritated, they become vulnerable to various infections, and may swell;
- Walking in the fresh air strengthens the child’s immunity, which helps prevent allergies.
A baby's eyelids may swell and hurt due to improper diet, unbalanced nutrition of the mother, etc. Remember that swelling of the upper or lower eyelid is not the norm; they are often a symptom of dangerous pathologies: anemia, thyroid diseases, problems with internal organs. Therefore, try to get advice from a qualified specialist as quickly as possible.