Causes of low presentation
Symptoms of low presentation
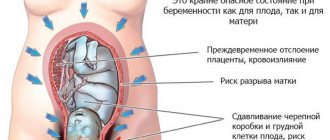
Dangers of low presentation
Detection of low presentation
Correcting behavior in low presentation
During an “interesting” situation, a woman’s emotional state needs understanding, support, and care. Not every pregnancy goes according to plan. Without knowing what a particular message means, it is difficult to find the right actions to solve emerging problems.
Hearing about the low location of the fetus and placenta, panic arises that can interfere with sound reasoning. What do these words mean?
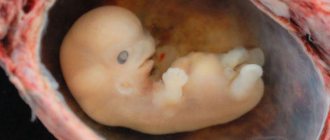
With a low presentation, the baby is located close to the cervix, putting pressure on it. Both the bladder and intestines experience additional weight. This leads to frequent urges, which are not uncommon during this period, and creates the likelihood of a disease such as hemorrhoids.
Why is there a small belly during pregnancy?
It may grow slowly for several reasons.
The size of the uterus may be smaller than expected due to oligohydramnios. Many people believe that the belly grows only due to the fetus, but amniotic fluid plays an important role in this process. If there is not enough water, it looks smaller than expected. Water can be determined using ultrasound. As the pregnancy progresses, the fluid volume also increases. Oligohydramnios is not the norm; it occurs with pathologies, such as hypertension, infectious diseases, gestosis, and others. Therefore, if there is already a small belly, it may well be.
The next reason is that it occurs due to a violation of placental metabolism. Poor maternal nutrition can also lead to slow growth. Under such circumstances, the baby is born weighing 2.5 kg. However, even an ultrasound cannot accurately determine the weight of a child, so it can only be accurately determined at birth; it can change by 500 g in both directions.
The constitution of a woman's body also plays a role. In petite and thin mothers, the bulge is more noticeable than in larger women.
The fertilized egg can attach to the back wall of the uterus, in which case the baby is positioned non-standardly - across the pelvis. Under such conditions, the belly grows deeper and does not stick out, then there will be a small belly during pregnancy, and it may not even be noticeable to outsiders.
Due to hereditary characteristics, it may also be smaller. If the parents are miniature, then the baby will most likely be small, so the belly may increase slightly.
If a woman has a well-trained abdominal press, then the muscles will maintain their shape and tone, and the stomach will not grow much.
Can the position of the fetus change (31 weeks of pregnancy)?
Can things change when it's 31 weeks? Fetal position is the main indicator of these changes. What is breech presentation (31 weeks)? What other secrets does the third trimester hold? All expectant mothers ask these questions before the most exciting moment in life.
Since doctors are also afraid of the incorrect position of the fetus during childbirth. “After the 37th week, the fetus occupies its final position in the uterus and already in this position the baby will be born” - this is what all the obstetrics textbooks say, but the development and growth of the little man and even his position are purely individual. In medical practice there is such a thing as “fetal attenuation.” Just before the birth, for a day or two, the baby does not show vigorous activity, moves little, and accordingly his position will not change radically, partly due to cramped conditions and lack of free space, partly due to hormonal changes. The process of childbirth is difficult not only for the mother, but also for the child himself, he is preparing to disconnect from the mother’s intrauterine nutritional system and become independent. The baby will soon no longer receive all its nutrition exclusively through the umbilical cord that connects it to its mother - this is a vital event in the life of the little person, it is not surprising that he also freezes.
Such “quiescence” is a normal, correct period of development, but nevertheless, consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist is necessary, and tests are required in order to exclude other reasons for the lack of movement, for example, lack of oxygen or a number of genetic abnormalities, many of which are detected only in late pregnancy.
The most responsible period for the location of the fetus is considered to be the second half of the third trimester (28-31 weeks). By this time, the activity of the fetus decreases, both in strength and in quantity, and at the next scheduled examination, the doctor determines the position of the baby, which part of the body he “plans” to be born. Separate cephalic and pelvic presentation. The correct position is considered to be cephalic presentation, which means that the fetus lies head down, towards the pelvis, and this is exactly how it will be born. This position is natural from a physiological point of view; the size of the head in diameter is always larger than the diameter of the rest of the body - arms, legs. And the head, while moving along the birth canal, expands it, allowing the entire body to pass through. In the case of breech presentation, the baby is positioned in the opposite direction - with his head up and, as it were, “sitting”, with his legs in the direction of the pelvis - this position is very difficult for both the baby and the mother, and increases the morbidity during childbirth. In the case of a planned “caesarean section”, fetal presentation loses its significance in the process of childbirth, since the baby will not be born naturally, but thanks to surgical intervention.
As a rule, this method is resorted to when, from the 31st week, it was not possible to clearly turn the baby head down - a planned operation is prescribed. The diagnosis made by the doctor: “31 weeks of pregnancy breech presentation of the fetus” does not mean at all that the child will be in the same position until the 38th week.
There are whole sets of physical exercises that correct the position of the fetus. The woman in labor goes to classes and studies independently systematically. It is important to understand that physical activity should be prescribed under the supervision of a doctor, depending on the physical condition of the mother herself. 31 weeks of pregnancy, cephalic presentation of the fetus is very important, and according to statistics, most cases are still the norm.
In turn, the breech presentation of the fetus (31 weeks) is divided into gluteal, leg and knee. In a breech presentation, the baby is positioned with his head up, his legs are bent, and he enters the pelvic area with his buttocks. In the case of pedicle presentation, one or both legs are below. In the case of knee presentation, the legs are in a semi-bent state, and thus come out. The rarest case is the 31st week of pregnancy, the transverse position of the fetus, that is, the child is not located vertically, but semi-sideways or horizontally.
The reasons for this phenomenon lie in decreased tone and insufficient excitability of the uterus, which invariably reduces its contraction. The female body is endowed with the amazing ability to autonomously and instinctively regulate certain processes in the matter of childbirth. For example, sufficient uterine tone corrects breech presentation (31 weeks). It happens that the baby’s hypermobility also turns him around. The risk group includes women who have an abnormality in the physiology of the uterus that prevents the baby from unfolding, such as septum and tumors, and changes in the size of uterine segments due to pregnancy.
In modern medicine, there are effective methods for maintaining pregnancy, pregnancy and childbirth with all types of presentation that are not the norm.
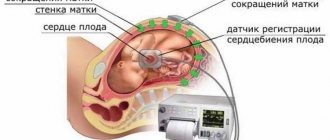
Using computed tomography or x-rays, a set of parameters is determined that together create the support and bed for the growth and development of the baby. There are several ways to diagnose presentation. During the examination, the obstetrician-gynecologist examines the lower segment of the uterus. The diagnosis is then confirmed by ultrasound. The doctor also finds out the location of the placenta and umbilical cord, which is also necessary for a full understanding of the child’s health. It is important to prevent the umbilical cord from entangling the baby's neck in the case of a breech presentation. You can also assume and assess the likelihood of the type of presentation using the pelviometry procedure - measuring the size of the pelvis.
The sooner the doctor learns about the characteristics of the woman in labor or the development of the fetus, the better he can prepare for the most crucial moment. And also in this case, fewer surprises will happen and the more reliable and easier the birth itself will be.
And only in this way, by preventing complications, by being attentive and caring about the pregnancy as a whole, by trusting the leading doctor, will a woman give birth to a happy baby without complications and naturally. It is the observation of a doctor that can help ensure that the child is born healthy.
Types of breech presentation of the fetus
Types of breech presentation of a baby during pregnancy:
- Pure gluteal (incomplete) - when the baby in the womb is with the buttocks down, and the legs are extended along the body - the knees are straight (Photo 1).
- Mixed gluteal - when the baby is “directed” with both the buttocks and legs into the mother’s pelvis - the knees are bent (Photo 2).
Types of leg presentation of a baby during pregnancy:
- Incomplete - one leg is “directed” into the mother’s pelvis, which are not fully bent at the joints, and the other is completely bent (Photo 3).
- Full - both legs are not fully bent (Photo 4).
- Knee - when the fetal knees are presented.
Breech presentations are observed somewhat more often than foot presentations. The latter, by the way, most often form during childbirth. It is known that the fetus in the uterus adapts to its shape and becomes in a position in which it is most comfortable. In most cases this is a cephalic presentation. But in cases where any complications are observed, the child may present in the wrong position - either buttock, or leg, or mixed. Quite often there is a breech presentation and at the same time the child is entwined with the umbilical cord.