Cardiotocography is one of the most important diagnostic procedures during pregnancy., which allows you to timely identify certain deviations during its course. Thus, it makes it possible to study the condition of the fetus, as well as the contractile activity of the uterus of the expectant mother.
And if you are recommended to undergo CTG, and you have some doubts about this study, we will be happy to tell you in detail about it. What this procedure is, how and from what week CTG is performed on pregnant women, what its values are considered normal during pregnancy, and whether it harms the fetus - read on.
What is CTG
CTG, or cardiotocography, is a research method in which the fetal heart rate is recorded and how it changes depending on the activity of the baby itself, external factors and uterine contractions. Along with ultrasound diagnostics and doplometry (Doppler ultrasound), CTG is an integral part of assessing the condition of the baby in the womb.
Using this method, you can identify and promptly prevent the negative consequences of such unpleasant phenomena.:
- intrauterine infection;
- hypoxia;
- oligohydramnios or, conversely, polyhydramnios;
- placental insufficiency;
- pathologies of the baby’s cardiovascular system;
- premature aging of the placenta;
- premature birth;
- umbilical cord entanglement;
- true umbilical cord knot, etc.
What is fetal cardiotography (CTG) during pregnancy?
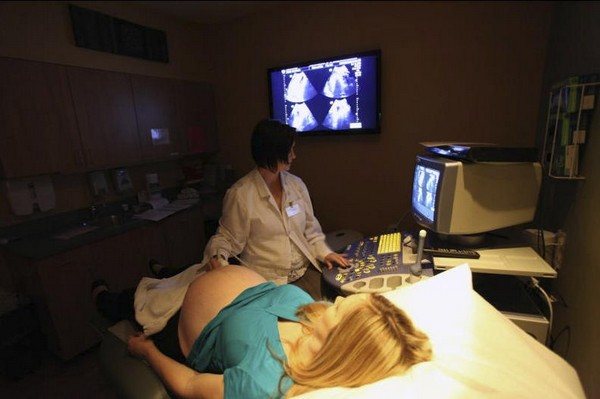
This method is used everywhere due to its ease of implementation, information content, harmlessness and painlessness, and stability of results. It is used to monitor the well-being of the fetus both during pregnancy and at all stages of labor.
We will consider the topic question by question. For convenience, we will highlight the most important ones.
The first question is what is fetal cardiotocography. This is an examination based on the Doppler effect, that is, the reflection of ultrasonic waves from moving objects. A sensor that generates high-frequency sound is placed on the front wall of the pregnant woman's abdomen in the place where the baby's heartbeat can best be heard with a stethoscope. This signal is reflected from the working heart of the fetus, comes back in a modified form, and is again perceived by the sensor.
The program processes the changed signals, analyzes which signals were received from the uterus and which from the fetus. The result of computer processing is sent to the monitor in the form of a graphic, light or sound signal, reflecting the number of heart contractions per minute.
Also, many CTG devices display uterine contractions and fetal movements as a separate graph. Modern devices are also equipped with a remote control with a button that the pregnant woman presses when she feels the movement of the fetus.
If the unborn baby is not feeling very well, fetal cardiotocography, ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound allow obstetricians to determine the tactics and timing of delivery.
A cardiotocogram taken during childbirth makes it possible, if necessary, to begin more active actions without delay. This means either stimulation of labor, or obstetric assistance, and, if necessary, a transition to surgical delivery.
CTG for pregnant women is an opportunity, using ultrasound diagnostics, to find out whether the baby is suffering: whether there is a lack of oxygen, whether there is low or polyhydramnios. Before birth, a normal CTG (in the absence of other changes on the part of the mother and child) means that the baby is able to undergo a natural birth.
Why is CTG performed on pregnant women? A cardiotocogram should also be done during a physiological pregnancy in order to find out the condition of the fetus. This study is mandatory to be carried out three times during physiological pregnancy.
If indicated, fetal cardiotocography may be done more often. These are the following states:
- urgently - when the pregnant woman has stopped feeling fetal movements for 8-12 hours, or, conversely, the baby begins to move actively (this can signal that something is wrong with him)
- in post-term pregnancy
- oligohydramnios
- polyhydramnios
- with gestosis, when swelling appears on the legs (especially if they are on both the face and body), blood pressure rises and/or protein is found in the urine
- multiple pregnancy
- Rhesus conflict
- for hypertension, maternal anemia, diabetes mellitus
- if before this pregnancy there were miscarriages, abortions, “frozen” pregnancies, premature births, fetal cardiotocography will show how the baby feels in the uterus
- with intrauterine growth retardation
- there is a scar on the uterus
- umbilical cord entanglement detected on ultrasound
- problems with the placenta, as determined by ultrasound examination
- there were abnormalities on the previous CTG
- threat of premature birth
- If there is a suspicion of circulatory disorders in the mother-placenta-fetus system, Doppler echocardiography of the fetus is indicated.
Only from the 19th week do the nerves of the parasympathetic nervous system approach the heart, and then the baby’s motor activity affects the frequency of heart contractions, reducing them. The branches of the sympathetic department of the autonomic system begin to sprout only by the 28th week, then the opposite reaction is observed: the movement of the fetus stimulates its heartbeat.
It is possible to perform a CTG of the fetus from 23-24 weeks, but it is impossible to evaluate it correctly during this period.
During this period, an increase or decrease in heartbeat will be associated with the entry of various hormones or substances from the mother into his blood; with the help of CTG you can only hear that the child is alive. In addition, this early there is no clear cycle of activity and rest for the child.
Only from the 32nd week does the baby’s cyclicity of rest and wakefulness and the dependence of the heart rate on movement begin to form.
Preparation for CTG during pregnancy is not required. The CTG examination is carried out 2-3 hours after eating, but not on an empty stomach; the pregnant woman simply comes to the office, and a fetal cardiotocography is taken within 40 minutes to 1.5 hours.
Since you will need to be semi-sitting or lying down during the procedure, it is worth asking in advance whether you need to take a small pillow and blanket with you. You may also need to take food rich in carbohydrates (chocolate, cookies) with you: this is how, in some cases, they stimulate the motor activity of the fetus if it suddenly falls asleep during the study.
Before the procedure, you should definitely visit the toilet.
Is it possible to eat before CTG? 1.5-2 hours before the test. It lasts quite a long time (you still need to get to the destination and from it), but the child needs nutrition. During the procedure, in agreement with the doctor performing it, you can have a snack. Sometimes this is even necessary to cause fetal movements.
You shouldn’t overuse this study either: you don’t need to do a CTG as soon as you want to listen to the melodic sound of your own child’s heartbeat. There is a scientific opinion that indicates that the fetus hears ultrasound in the form of a very unpleasant loud noise, and this disturbs its calm.
The device takes into account the resting heart rate, acceleration or deceleration of the rhythm depending on the child’s activity and uterine contractions. The diagnostic accuracy using this method is about 88.5%.
However, the result must be assessed by a doctor, since there are errors in the baby’s sleep, in the increase in his motor activity, in recording the mother’s heartbeat, if for some reason the device does not detect the contraction of the fetal heart.
PSP points mean the following:
- from 0 to 1.0 is normal, but if this result is -0.7-1.01, a fetal CTG must be done again after a week
- from 1.01 to 2.0 points: there are initial signs that the fetus is suffering; treatment and repeat CTG is required after 5 days
- 2.01-3 points: the child suffers greatly, the pregnant woman needs to be hospitalized in a hospital
- more than 3 points: the condition is critical, hospitalization should not be delayed, emergency delivery may be necessary.
The resulting conclusion is not a diagnosis. If high numbers are obtained, this means that the pregnant woman must be hospitalized, undergo an ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound, be examined by a specialist obstetrician-gynecologist, and only on the basis of the totality of all data should any decision be made.
Where to go for CTG during pregnancy
The study can be carried out in a maternity hospital or antenatal clinic, as well as in the offices of medical centers that are specially equipped. The obstetrician-gynecologist leading your pregnancy should advise you where to do fetal cardiotocography is best in your situation.
If your doctor determines that a test should be performed before each visit, this is most likely dictated by the obstetric situation and not by any other criteria.
Doppler echocardiography of the fetus allows you to study the speed of blood flow, the patency of blood through the vessels and heart of the child, as well as blood flow in the placenta and uterine vessels.
Indications for its use are as follows:
In the photo: three-dimensional ultrasound of the fetus in late pregnancy
- If the mother has high titers of antibodies to the rubella virus, toxoplasma, cytomegalovirus (those microbes that can provoke the appearance of heart and vascular defects, fetoplacental insufficiency).
- If a pregnant woman or the father of a child has a heart defect, since some diseases can be inherited.
- The mother suffers from lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes.
- During the ultrasound, a suspicion of fetal heart disease arose.
- Suspicion of fetoplacental or uteroplacental insufficiency.
- Oligohydramnios, polyhydramnios.
- Signs of early aging of the placenta on ultrasound.
- Taking medications during pregnancy that affect the formation of defects in the baby’s cardiovascular system: lithium, sodium valproate, carbamazepine, trimethine; maternal alcohol intake.
- Arrhythmic activity of the child’s heart, listened to with a stethoscope, CTG, or detected during an ultrasound.
- Genetic diseases in the family: Espers-Danlow syndrome, Marfan syndrome, glycogen storage disease.
Doppler echo CG of the fetus is performed at 18-22 weeks of pregnancy (less often through a vaginal sensor at 12-14 weeks). If fetal cardiotocography shows how the baby absorbs oxygen, Doppler helps to visualize what the vessels of the uterus, placenta and fetus itself look like, and what the blood flow is like in them.
On average, how much does a fetal CTG cost: 800-1200 rubles. A Doppler study can be done for 800 rubles.
Thus, you have learned what CTG is during pregnancy: what are the indications for it, how often it can be performed, and how necessary it is. Since the test is harmless and can be performed quite often, you should not delay it if it was prescribed by your obstetrician-gynecologist. There will be no harm, but both you and the doctor will be sure that the baby is comfortable and his blood supply is not affected.
Watch a video in which a woman at 35 weeks filmed the process of a CTG in the diagnostic room.
Based on materials from uzilab.ru
Pregnancy for a woman is undoubtedly a pleasant and happy period. Every expectant mother wants her child to grow and develop healthy and strong in the womb. In order to monitor the comfortable and healthy development of the baby, the mother must undergo various tests and do an ultrasound. But medical workers highlight another important method of examining pregnant women, which allows them to see a complete picture of the condition of the fetus. This method is called cardiotocography or CTG.
CTG is an ultrasound diagnostic that makes it possible to assess the condition of the fetus by the nature and frequency of the heartbeat. This diagnosis allows you to obtain the following important information about the intrauterine baby:
- his activity;
- the frequency with which the uterus contracts;
- cardiac activity.
During pregnancy, CTG is optional, but by making this diagnosis, the following important and dangerous conditions of the baby and mother are confirmed or refuted:
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- a lot or little water;
- fetal hypoxia;
- aging of the placenta or its premature maturation, which leads to premature birth;
- abnormalities in the development of the fetal cardiovascular system.
Thus, the method of diagnosing a pregnant woman using CTG allows us to determine (even in the early stages) deviations, illnesses or other types of disorders in both mother and baby. After undergoing CTG diagnostics, disorders can be prevented so that a healthy and strong child is born.
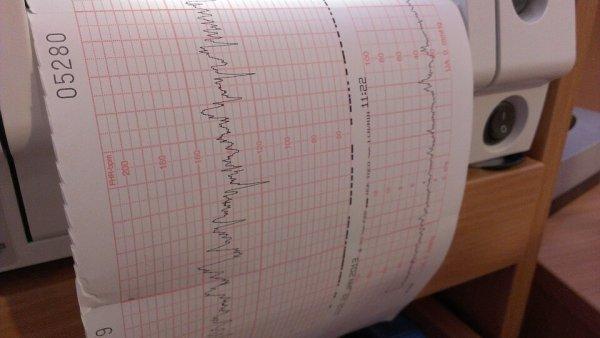
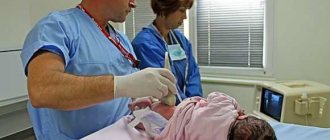
The CTG diagnostic device consists of two sensors and a recording device. One of the sensors (ultrasonic) is used to take readings of the fetal cardiac activity. The second (tensometric) is designed to record readings of uterine activity, and also additionally removes the baby’s reaction to uterine contractions. These sensors are attached using belts to the belly of the expectant mother. During the diagnostic procedure, a woman can take any of three comfortable positions:
The pregnant woman herself decides which position is comfortable for her. A special button, which is given to a pregnant woman during a CTG, serves to inform the movement of the fetus. At the moment when the fetus moves, the woman must press a button, thereby making it possible to record changes in heart rate. The procedure takes from 30 to 60 minutes. All information is recorded on paper, which is displayed in the form of a tape. (Useful to read: HCG for ectopic pregnancy).
Tips before the procedure! A pregnant woman needs to prepare, for this it is recommended:
- sound healthy sleep;
- eat chocolate to increase fetal activity;
- don’t worry, don’t be nervous, don’t worry.
During pregnancy, the optimal period for performing cardiotocography is the third trimester. It is at the end of the second - the beginning of the third that the formation of the “activity-rest” cycle occurs. It is during this period that diagnostics are most effective and, more importantly, reliable. This procedure is allowed at earlier stages, but the accuracy and reliability of the readings is questioned, which requires re-diagnosis. (We recommend reading: X-rays during pregnancy).
Important! The optimal time for CTG is 32-34 weeks.
If pregnancy proceeds without abnormalities, which are recorded using ultrasound and tests, then cardiotocography is optional. The doctor himself decides whether the pregnant woman needs to undergo this examination or not. Indications for prescribing a CTG procedure are various abnormalities (entanglement of the fetus with the umbilical cord, a scar on the uterus, delayed labor, etc.). If the pregnant woman does not complain of various ailments, and the results of tests and ultrasound are normal, then conducting a study of the fetal cardiac activity is unnecessary.
Preparation for the cardiotocography procedure is very important, since there is a high probability that the child will be asleep at the time of diagnosis and it will be impossible to obtain the result. In order for the child to be in an active state, it is necessary to try to wake him up before the procedure: slightly jump or walk around. Important! But under no circumstances should he be harmed in this way. But eating chocolate gives the baby a greater chance of activity. It is when the baby does not sleep that cardiotocography is performed during pregnancy.
Important! If the fetus is not active during CTG, then results will not be obtained, so preparation is very important.
This is the most important thing a pregnant woman expects. If the procedure was successful, then a conclusion is drawn based on the analyzes performed. The results are recorded on paper tape and represent a curved line (like a heart cardiogram!). Results are most often assessed using two indicators: the Krebs and Fisher scales. Some doctors may evaluate using one of the indicators.
Based on these scales, a conclusion is made. Let's take a closer look at decoding the Fisher scale, which is often used. So, the data is controlled according to the following parameters:
- Basal rhythm. The fetal heartbeat is recorded and does not change within 10 minutes. Depending on the number of hits, a certain score is given (from 0 to 2).
- Variability. Amplitude of heartbeat per minute.
- Heart rate per minute.
- Acceleration. An increase in heart rate by 15-20 beats per minute from the base value, which occurs during fetal activity or mobility.
- Deceleration. Decreased heart rate with activity or contractions of the uterus.
The table contains the main indications on the Fisher scale, according to which scores are assigned.
Based on these data, scores are assigned, which are ultimately summed up, and a conclusion is drawn. According to the Fisher scale, the score should not exceed 10 points. Based on the values, the doctor makes a conclusion:
- At 6-7 points - the condition is pre-pathological. In this situation, a repeat examination is scheduled after a while.
- From 6 and below - the results are unsatisfactory. Immediate hospitalization will be required until a certain time of resolution of the problem.
- From 8 to 10 - the result is normal. Results in this range in the third trimester of pregnancy confirm the healthy development of the child.

The CTG procedure during pregnancy is absolutely harmless and does not carry any consequences or contraindications. If for some reason there are concerns about carrying out this procedure, then be completely sure that the device operates without the use of negative phenomena that could adversely affect the development of the fetus. Even if the doctor prescribes the diagnosis repeatedly, and perhaps more than once, the frequency of repetition of the procedures is also unable to negatively affect the unborn child.
In addition, CTG during pregnancy is a key factor in identifying fetal heart failure and abnormalities in its development. Identifying such ailments in the early stages allows you to apply timely remedies to eliminate them. The general picture of the course of pregnancy is compiled on the basis of all tests, ultrasound and cardiotocography results.
PSP is an indicator of the condition of the fetus, which is obtained after a CTG procedure. The doctor determines PSP, which during normal development should be less than 1. When the PSP value corresponds to the range from 1 to 2, then this is a sign that the fetus is developing with some disturbances. If the PSP indicator is more than 3, then a full examination should be immediately carried out and measures should be taken, as this is a sign of a critical condition of the fetus. If, after a full examination, the sign of a critical condition is not confirmed, then this indicates that the readings taken are incorrect. To prevent such situations from arising, it is necessary to do the diagnosis again to verify the results.
It is also important to know that the indications of a CTG test during pregnancy are auxiliary, but not essential. Only by combining the readings of cardiotocography with other tests can a general conclusion be made about the course of pregnancy.

The CTG procedure during pregnancy must be carried out as prescribed by the leading doctor. If the doctor has not prescribed such a procedure, then there is no need to look for where this examination is performed and diagnose yourself. If you want to check yourself, consult your doctor before doing so. The doctor gives directions and tells where there are rooms with such equipment.
Although medicine has reached heights in our time, this does not mean that any examination is free. Thus, cardiotocography during pregnancy will cost 1000-1200 rubles. But at the same time, the person accepting the client for examination devotes time from 30 to 80 minutes to him.
Thus, knowing all the intricacies of cardiotocography research, you can confidently undergo diagnostics and be convinced of a positive result.
If the doctor sent you for a CTG, then don’t despair - he’s just a good doctor who decided to make sure there are no abnormalities.
Based on materials from krohapuzz.ru
Modern pregnant women have a unique opportunity to receive maximum information about the fetus, even in the early stages. So, you can find out the sex of the unborn baby, track its development and even record the frequency of contractions of a tiny heart using CTG. Decoding the abbreviation - cardiotocography. This procedure allows you to identify deviations during pregnancy and take action at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus.
Cardiotocography is a very useful analysis that allows you to determine the following dangerous points:
- oxygen starvation of the baby;
- intrauterine infection;
- amount of amniotic fluid;
- deviations in the structure of the heart and blood vessels;
- the likelihood of premature birth;
- condition of the placenta.
We found out what CTG is in pregnant women and why this analysis is needed. But at what stage of pregnancy should such a study be carried out?
Gynecologists recommend performing fetal CTG at 32 weeks. It is by this time that the child has already formed a cardiac reflex, there is a relationship between the movements of the fetus and the frequency of its heart contractions, and the sleep-wake cycle has been determined. If cardiotocography is done at an earlier stage, the results may be unreliable.
CTG during pregnancy does not require any special preparation. Unlike other tests, cardiotocography is not done on an empty stomach and you do not need to drink large amounts of water before it. The only thing that many expectant mothers who have undergone cardiotocography advise is:
- visit the toilet before the test;
- Bring a light snack (fruit, candy bar, bottle of water);
- Grab your favorite pillow or bolster from home to make it more comfortable to sit.
A woman comes to an appointment and sits on a chair or lies down on a couch (depending on what is more comfortable for her). She can put a brought pillow under her back. Special sensors are attached to the belly of the expectant mother, which during the analysis will record the reaction of the uterus, the activity of the fetus and its heart contractions.
Another feature: the woman is given a button, which she must press as soon as she feels the fetus moving. This will enable the devices to obtain the most complete picture of the child’s life and cardiac activity.
What is CTG from the point of view of a medical procedure and how harmful is it? This is a question all mothers ask. The answer is simple: cardiotocography does not pose anything dangerous for either the woman or the child, because the body does not receive any radiation. CTG is almost like an electrocardiogram, which can be done every day if necessary.
Cardiotocography is usually recommended by the gynecologist based on questionable ultrasound results at 32-33 weeks. If a woman herself feels some deviations, then the initiative can come from her. Most pregnant women, who for some reason feared for the health of the fetus, after the analysis realized that it was very important for them to carry out such a procedure as CTG, that this was a good opportunity to correct the pregnancy and give birth to a healthy child.
If the indicators turn out to be normal, then this allows mothers to breathe a sigh of relief and calmly wait to “meet” the baby.
Based on materials from mamsa.ru
When is cardiotocography performed during pregnancy?
As a rule, cardiotocography is carried out no earlier than 30–32 weeks, since by this time the fetus is already developing:
- contractility of the heart muscle;
- the relationship between motor activity and cardiac muscle activity;
- cycle of activity and sleep.
In exceptional cases, cardiotocography can be carried out from the 28th week (if any pathologies are suspected), however, it will only be possible to record the direct presence of a heartbeat in the fetus. Also, this study can be carried out directly during labor.

CTG, like ultrasound, should be done by all pregnant women without exception in the third trimester of pregnancy, and no special indications are needed for this study. As a rule, cardiotocography, starting from the third trimester, on average, is carried out once every 7–10 days . However, it can be carried out more often if:
- various chronic diseases of the mother;
- Rh conflict between mother and fetus;
- oligohydramnios;
- suspicions of congenital defects in the fetus;
- post-term pregnancy;
- a noticeable decrease in the baby’s intrauterine motor activity;
- premature aging of the placenta;
- umbilical cord entanglement, etc.
In the presence of some of the above circumstances, CTG can be performed even several times a day.
Decoding the results
CTG interpretation should be done only by a specialist. This is a complex process that requires knowledge and experience. The cardiotocogram consists of two types of graphs - tachogram and hysterogram. The tachogram reflects changes in the fetal heart rate. The time is measured horizontally, and the number of beats per minute is measured vertically. Thus, the graph deviates downwards when the heart rate decreases, and upwards when it increases. When measuring fetal motor activity, the indicators are displayed under the tachogram. The second graph, usually located at the bottom of the cardiotocogram, displays the force of uterine contraction.
The first step is visual interpretation of the CTG. However, to reduce the subjectivity of the assessment, it is customary to use rating scales. There are two methods: the Gauthier scale and mathematical analysis.
The ten-point Gauthier scale is a questionnaire where the doctor is asked to evaluate the basal rhythm, variability, number of accelerations, decelerations and fetal movements. Each indicator is given a score from 0 to 2 points.
Based on the sum of points, a conclusion and recommendations for further observation are formed. This scale has many modifications.
The second assessment method is mathematical. When interpreting computer-processed data, the fetal condition indicator (FSI) is used.
- 1-2 - signs of initial violations
- 2-3 - pronounced violations
- >3 – critical condition.
Scores above 2 indicate a dangerous condition that requires hospitalization in a maternity hospital.
The CTG method, like any other, has its disadvantages and errors. In some cases, fetal oxygen consumption may decrease regardless of the presence of pathology. For example, fetal compression of the umbilical cord causes short-term disruption of blood flow. In this case, cardiotocography will register fetal hypoxia. However, these changes are temporary and when the position of the fetus changes, blood flow will be restored. Therefore, the conclusion based on the results of CTG is not a diagnosis, and only a doctor should evaluate and interpret the cardiotocogram data.
Preparing for CTG during pregnancy
You can get the most reliable CTG result only when the baby is awake and not asleep. That is why the task of the expectant mother is to wake him up before conducting this study. Of course, the use of such barbaric methods as tapping on the stomach is prohibited, because such actions can cause stress in the baby.

It is recommended:
- show acceptable physical activity (jumping on a fitball, climbing stairs, etc.);
- eat something sweet shortly before the procedure;
- perform breathing exercises, as the child reacts to minor breath holdings (in this case, the main thing is not to overdo it, so as not to harm the baby).
It should be remembered that CTG is not a procedure that should be performed on an empty stomach, nor within an hour after the administration of glucose (if indicated). An equally important factor for obtaining reliable results is the psychological state of the mother, so you will have to calm down and relax as much as possible during cardiotocography. You should also go to the toilet and empty your bladder before the procedure.
How is CTG performed?
To undergo this examination, the woman is placed on a couch, lying on her left side or sitting (the examination in the supine position is not recommended, since the uterus can press on important blood vessels, and its results will be less reliable). After this, the doctor, applying a stethoscope to the abdomen, determines the place where the heartbeat can be heard best. He then attaches a special ultrasonic external sensor to this very spot.
A strain gauge sensor, which records uterine contractions, is placed in the area of the uterine fundus. Also, the expectant mother is given a special remote control with a button that she needs to press every time the baby moves in the womb. The received data is recorded by the device on a paper tape (cardiotocogram), which slowly comes out of it.
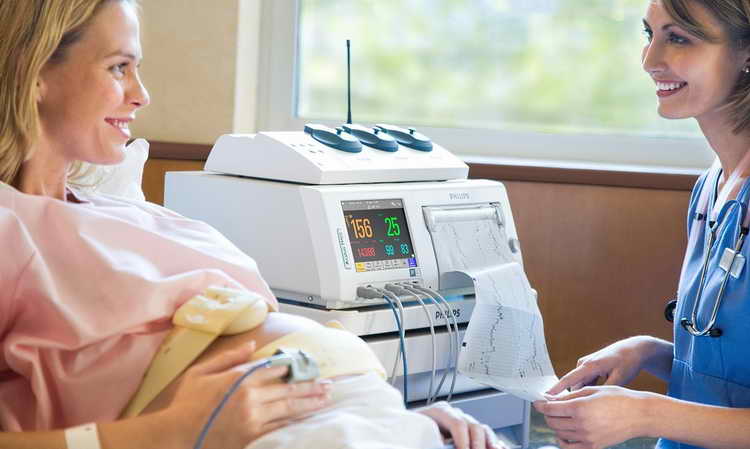
A fairly common question is: how long does a CTG study take during pregnancy? The duration of such a procedure, on average, is 30 - 40 minutes, however, when obtaining stable and positive data, 15 - 20 minutes may be quite enough. Conversely, if the results of the study are doubtful, then it can last more than an hour.
Reasons for prescribing CTG
Clinic specialists prescribe fetal cardiotocography to all late-term pregnant women and women whose previous pregnancies had unfavorable outcomes. Our clinic specialists recommend regular CTG for pregnant women with high blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease.
CTG devices allow you to monitor the condition of the fetus, both during pregnancy and during labor. Modern equipment for conducting cardiotocography allows you to make the right decision: continuation of pregnancy or its artificial termination, natural birth or cesarean section, etc.
Also, at the earliest stages, using CTG, it is possible to determine whether there are risks of hypoxia, anemia, and disturbances in the development of the fetal cardiovascular system.
Interpretation of CTG results
When deciphering a cardiotocogram, the doctor takes into account 5 main indicators, each of which is given a score from 0 to 2:
- Fetal heart rate (basal rhythm): 2 points – 120 – 160 beats per minute, 1 point – 100 – 120 or 160 – 180 beats per minute, 0 points – less than 100 and more than 180 beats per minute.
- Rhythm variability (the average value of its deviation from the basal): 2 points - 10 - 25 beats per minute, 1 point - 5 - 9 beats per minute, 0 points - less than 5 and more than 25 beats per minute.
- Frequency of rhythm deviations from the basal (oscillation frequency): 2 points – more than 6 per minute, 1 point – from 3 to 6 per minute, 0 points – less than 3 per minute;
- Accelerations (significant accelerations of the heart rate, which are displayed by high teeth on the graph): 2 points - occur frequently, 1 point - occur periodically, 0 points - absent.
- Decelerations (rhythm slowdowns, which are displayed as long teeth downwards): 2 points - absent, 1 point - occur periodically, 0 points - appear frequently.
All points obtained from the results of deciphering the cardiotocogram are added up, and an assessment of the fetal condition is given:
- 8 – 10 points – normal condition;
- 6 – 7 – initial signs of hypoxia;
- 5 or less is a clear threat to the baby’s life.
It should also be understood that deciphering a cardiotocogram cannot make it possible to clearly make a particular diagnosis. Such data is needed only to assess the general condition of the fetus, and becomes a reason for further medical measures.
Interpretation of CTG during pregnancy
The doctor can show the results of CTG during pregnancy on a paper tape on which graphs-curves are depicted, or say, naming the number of points scored.
Deciphering CTG during pregnancy is not an easy task. It’s good if the graphs do not raise any suspicions at all. Then the doctor and the expectant mother will not have to worry about anything. However, in life there are different cases. CTG results may be alarming. In such a situation, it is very important not to make a mistake. Any decision must be carefully thought out by a doctor, because every action and word affects the child.
Here is a clear example taken from life: a young doctor who had not yet gained experience did not like the results of cardiotocography of one patient. He told the pregnant woman about his concerns, but she categorically did not believe the results of fetal CTG during pregnancy. You can easily imagine how the woman felt at that moment. The specialist called an ambulance because he was worried about the patient’s condition and the life of the fetus. In the maternity hospital, in the pathology department, it later turned out that the pregnant woman had absolutely no abnormalities. What mood will this patient be in next time at the antenatal clinic?
It would be nice if the expectant mother learned to interpret the results of cardiotocography in general terms. This way it would be possible to avoid unnecessary waste of nerves and a collision with the incident described above.
When interpreting cardiotocography and making a diagnosis, many factors must be taken into account, because the results are influenced by weather conditions, the mood of the pregnant woman, sleep or active wakefulness of the children. Based on the results of a poor CTG during pregnancy, it is not recommended to draw conclusions about the condition of the child in the tummy, because even an absolutely healthy baby may have “suspicious” graphs.
When deciphering a cardiotocogram, doctors take into account several basic parameters: the basal rhythm, amplitude, as well as the frequency of deviations from it, slowdowns and increases in heart rate. Each parameter is awarded 0-2 points. At the final stage, the points received are added up, and the condition of the fetus is assessed based on their sum:
- 8-10 points – normal CTG during pregnancy;
- 6-7 points indicate the possible presence of initial signs of fetal distress. The doctor may order additional tests;
- A score of 5 or less is an indicator that the pregnant woman urgently requires hospitalization and assistance.
Heart rate assessment
The basal fetal heart rate should be 110-160 beats per minute. The graph clearly shows that ups alternate with downs. However, the doctor is not interested in the minimum or maximum values. It estimates the average.
A woman can independently evaluate what CTG shows during pregnancy. To do this, you need to move the printout to an arm's length and run your finger along the graph, as if drawing it in the form of a straight line. The level to which the line on the vertical axis will correspond will be the basal rhythm.
Study of denticles and teeth
The next parameter that doctors evaluate is the variability of the child’s heartbeats. Having determined the basal rhythm, you can begin to study the frequency and amplitude of deviations from this rhythm.
The graph clearly shows that the curves have many small teeth and several large teeth. Small denticles indicate deviations from the basal rhythm. It is advisable that there be no more than 6 of them per minute - this is the norm for CTG at 32-39 weeks of pregnancy. However, counting the number of small cloves is not so easy. Doctors often evaluate the amplitude of deviations - changes in the height of the teeth on average, which normally should be 11-25 beats per minute.
Doctors may not like it if the change in the height of the teeth is 0-10 beats per minute. However, this may be completely normal if the baby feels comfortable in mom's tummy and sleeps or the pregnancy does not exceed 28 weeks. When the estimated rate of 25 beats per minute is exceeded, medical professionals begin to suspect the presence of umbilical cord entanglement or fetal hypoxia.
Assessment of increases and decreases
When assessing increases and decreases in CTG at 32-38 weeks of pregnancy, you should pay attention to the large teeth shown on the graph. Doctors, doing cardiotocography on old devices, ask pregnant women to press a special button when the baby moves. Modern models no longer require this. They themselves are able to register the activity of the fetus. When your baby kicks, his heart beats faster for a few seconds. This will be represented on the graph as a large tooth growing upward. This is called acceleration. If there are at least 2 of them on the chart over a 10-minute period, then this will be considered a good sign.
Increases may not be detected during the study. There is no need to panic ahead of time because of this. Perhaps the baby has not woken up yet.
Decreases are the exact opposite of increases. On the CTG chart for 35-39 weeks of pregnancy, they look like teeth growing downward. There is no cause for concern if the increase on the graph is followed by a short and shallow decrease, after which the curve returns to the level of the basal rhythm. High-amplitude decreases can be alarming. However, before drawing a conclusion, you should pay attention to the 2nd graph available on the printout. Contractions of the uterus that are noted on it can influence the occurrence of contractions.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that the CTG method has several undeniable advantages. Firstly, thanks to this procedure, you can learn about the condition of the fetus and the nature of labor, quickly identify existing problems and find ways to solve them, and secondly, when CTG is done during pregnancy, no unpleasant sensations arise. The procedure is completely safe for the mother and fetus. Thus, if expectant mothers are concerned about the question of whether CTG is harmful during pregnancy, then the answer is always clear - it is not harmful.