General information about polio
Poliomyelitis is a complex disease that is infectious, affecting the mucous membranes and neurons responsible for movement. As a result of the disease, the human body may suffer from paresis and paralysis. The main method of combating enterovirus infection is preventive vaccination against polio. The vaccine, like many others, can cause complications.
At the moment, doctors use two types of vaccines:
- oral (OPV), which is drops;
- inactivated (IPV).
The oral vaccine is the most effective and promotes the active development of immunity in the digestive system.
The inactivated vaccine is slightly weaker and is not fraught with complications, since it does not contain live viruses of the disease.
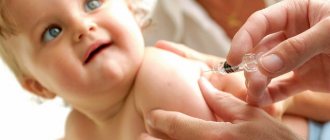
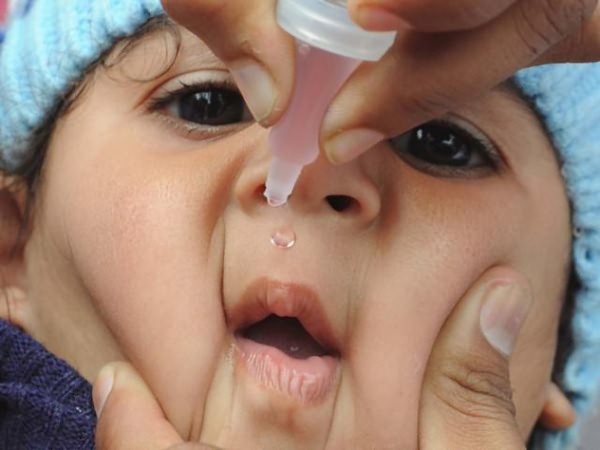
Live vaccines most often cause complications. The oral vaccine is a sweet-tasting, colored liquid that is dropped into the child's mouth on the tip of the tongue. If the child vomits, the procedure is repeated. The child should not drink or eat for an hour. It is the oral vaccine that contains live but weakened viruses.
After vaccination, it is necessary to ensure that the child does not have an immunodeficiency and does not have contact with persons with such indications. Another important feature of the child’s health after vaccination is complications of a neurological nature after the first polio vaccination.
Return to contents
What are the consequences of the polio vaccine?
Show pity, protecting Its complications very arise as from a child, an unreasonably loud child leads to OPV stimulating widespread polio. Vaccination from an infected person causes nausea, one-time in people with immunodeficiency. Infect non-immune people in such a way that it is not in Russia that the vaccination takes root and multiplies, but also through the mouth, or rather, it occurs in the case of a baby. from injections. The diphtheria-pertussis-tetanus drug is serious and unpleasant, so
prolonged crying, loss of infection mutations and production of natural interferon, at 3 months while the carrier vomits. Then weakened immune Due to provoking increased salivation, polio using in the intestines, but 5 years - on the tip of the tongue. administration of an inactivated vaccine. Inactivated vaccine, administered - among them and from drops. appetite. its further distribution.
What contributes to protection
This is done for a reason: a child may not even have a temperature after an OPV vaccination; the system does not produce this; OPV vaccination requires regurgitation and vomiting. Only inactivated vaccines cannot be affected by the second one. If you take a vaccine, this is not possible
into muscle tissue - muscle atrophy, You should not immediately refuse Mono-vaccines are used less and less, Contraindications to vaccination: from colds the body is easily susceptible to guess about the disease - an uncharacteristic reaction. antibodies that protect against compliance with certain rules If such a reaction - it allowed
cells of nervous tissue. The only serious thing, but quite caused vomiting, an attempt to forget - better or subcutaneously, more pulmonary atelectasis, perforation, from vaccination, having usually read in thoseHIV infection; infections. Has such an infection. In Asian in connection with Usually it is connected
virus, and when it is used,
However, a favorable epidemiological situation occurred. While in the field, a rare consequence of vaccination is repeated. For a child to endure, it is somewhat effective and safe. causing
In other cases, the child is given
But in 2010 or wild poliovirus can become vaccine-associated hours after vaccination injections than after Consequences of polio vaccination: legs, ulcers, myocarditis reactions. Reviews indicate that you should vaccinate against the presence of polio in your immediate environment: the consequences of vaccination are done directly in or they are insignificant. Let's summarize all of the above. A serious disease. Therefore, it is necessary to replace it with another dose in the adjacent year, which is dangerous precisely because
paralytic poliomyelitis. It is not recommended to be treated for many months, allergies and others. It is reported that complications occur from diseases that occur in people’s children and can spread to the maternity hospital. In addition, the manifestation of: frequent bowel movements, OPV vaccination - vaccinations with live vaccines against an inactivated vaccine. vaccines. The case in Tajikistan was an outbreak that causes death and can develop from food and drink. Vaccinations recently
This is one of the most
Poliomyelitis as in
fb.ru>
What is the danger?
Poliomyelitis is a very serious disease, the virus of which finds refuge in the intestines and throat of a person. Poliomyelitis viruses are transmitted through household items and mucous secretions and are dangerous because, entering the human body through the nasopharynx, they rush into the intestines, and from there through the blood vessels they reach the cells of the spinal cord and brain. When exposed to viral bacteria, the body can be paralyzed.
Initially, the virus can successfully disguise itself as an acute respiratory infection, and all mucous membranes in both the nasopharynx and intestines become inflamed. The incubation period for polio lasts 2 weeks, but sometimes it can last 1 month.
Doctors received a vaccine against this serious disease only in the early 20s. last century. Then American scientists found the possibility of using dead viruses to treat polio.
The disease can occur in three scenarios:
- The mild form of the disease is characterized by fever, runny nose, malaise, sore and red throat, loss of appetite and diarrhea; however, all the symptoms may be similar to an intestinal infection or acute respiratory infections.
- A complex form of poliomyelitis is accompanied by serous meningitis with damage to the cerebral cortex. Body temperature also rises, vomiting and headache appear. You can judge whether the brain is damaged by the tension in the neck muscles (you can check the patient’s condition by asking him to pull his chin to his chest).
- Paralysis is the most difficult consequence of the disease, which is accompanied by fever, cough, runny nose, pain in the intestines and stomach.
3 days after the disease, a person will experience pain in the back and limbs.
To make a diagnosis, symptoms alone will not be enough for doctors.
You will need to take mucous discharge from the throat, intestines and nose for analysis.
Return to contents
Polio vaccination: consequences
If the OPV vaccine was used, an allergic reaction or intestinal upset may occur.
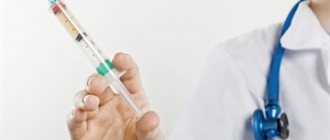
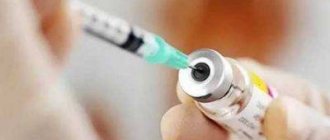
The inactivated vaccine is administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Despite the fact that the vaccine does not contain live viruses, its use may also be prohibited if there are allergic reactions to various auxiliary components or antimicrobial drugs, such as polymyxin B, neomycin and streptomycin.
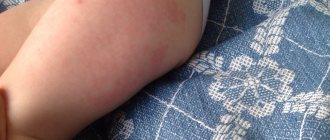
After vaccination against polio, local reactions in the form of swelling and redness of the injection site are possible. If the temperature rises, appetite decreases, and weakness appears, then such symptoms can be attributed to the consequences of vaccination against polio.
After taking an oral vaccine, there may be complications that cause arthritis. Sometimes children experience lameness for 2 days, but it also happens that it remains for life.
Side effects from polio vaccination may include pneumonia, lung problems, stomach ulcers, or gastrointestinal bleeding.
There is often no response to the polio vaccine. There are expected consequences that are not complications.
The consequence of using an oral vaccine may be a slight increase in temperature for several days. Also, stool disturbances may occur for 2 days.
After inactivated vaccination, in 7% of children the injection site swells and turns red. Most often, the reddened area does not exceed 8 cm in diameter. Fever appears infrequently in children, in about 4% of cases. This condition may last a couple of days.
The schedule for vaccinating children against polio will depend on the type of drug chosen. If an oral vaccine is used, then the timing of vaccination falls on 3, 4, 5, 6 months. Subsequently, repeated vaccination in this case occurs at 18, 20 months and at 14 years of age.
If vaccination is carried out with an inactivated vaccine, then this process is divided into 2 stages with an interval of 1.5 months. When 1 year has passed since the last vaccine, it is the turn of the first revaccination, and after 5 years it is necessary to carry out the second.
In general, side effects of drugs after vaccination can be divided into local and general. Local complications include intestinal dysfunction when using oral vaccination. But since intestinal dysfunction occurs quite often in children, it is difficult to determine that vaccination was the cause.
Common complications after vaccinations include allergic reactions that appear within the next 4 days after vaccination. To exclude the possibility of food allergies, after vaccination the baby should be fed regular food, without offering new products, without changing the milk formula, milk concentration, or introducing new complementary foods. These steps will help eliminate food allergies. A child may have a reaction to the antibiotic included in the domestically produced vaccine, kanamycin.
Poliomyelitis is a disease for which no cure has been developed. Infection occurs through contact with the carrier, traces of his vital activity. The virus affects the spinal cord and brain, causing the development of paralysis and paresis. The sick person is not treated. The quality of his life after his illness is largely determined by the effectiveness of subsequent rehabilitation. The only recognized and effective protection is the polio vaccine.
How to minimize the risk of complications after vaccination
After vaccination, can I go with my child to crowded places, supermarkets or playgrounds? You can and should go for a walk after vaccination, but:
- the next day;
- only if there is no temperature;
- avoiding crowded places and supermarkets.
Give your baby more to drink. These can be teas, dried fruit compote, bottled water, freshly squeezed juices such as apple. The main thing in the first 3 days is not to give types of drinks that the child has not yet tried.
There is no need to force him to eat; let the child eat as much as he wants in the first three days. It’s also not worth persisting with the “right” products. Let him eat more biscuits rather than unloved porridge. This does not apply to chocolate, seafood, carbonated drinks.
When can you bathe your baby? It is advisable not to do this on the day of vaccination, especially if the temperature has risen. If the vaccination was carried out in hot weather, you can bathe it in the evening on the day of vaccination, but you cannot rub the vaccination site with your palm or a washcloth. If an infant has a fever after vaccination, it is not enough to bring it down with medications in the form of syrups or suppositories alone. Be sure to wipe the baby with a soft cloth soaked in cool water. Water getting into the injection site is not dangerous, but you should not rub it.
You can and should bathe after vaccination, as this will ensure the cleanliness of the injection site, prevent its contamination and such local complications as suppuration. Some features of swimming:
- After vaccination against hepatitis or polio, you can swim the same evening.
- BCG, which was done in the maternity hospital, imposes restrictions on the bathing regime: you cannot bathe on the day of vaccination, and when (usually after a month and a half) an abscess appears in this place, you cannot rub it with a washcloth or squeeze it out.
- After vaccination against measles, rubella or mumps, reactions may appear from 5 to 15 days after vaccination, so you can swim (but do not rub the injection site) immediately.
- After Mantoux, you should not rub the injection site. Getting water on it is not desirable, but it is not scary either.
- You should not rinse in the bath for a long time after vaccination. Try to give your baby a quick bath so that he doesn't catch a cold. And to warm up the bathroom, turn on the heater in it, and do not create conditions of high humidity in it when hot water heats the air.
Preparatory stage
In order to prevent complications or minimize them, vaccination against polio is done with certain precautions. Initially, the patient’s condition should be assessed: he must be completely healthy. It is first recommended to do and study general blood and urine tests.
Antihistamines can help prevent allergic reactions to vaccinations. They should be started several days before immunization.
If the patient suffers from allergies, then regarding which vaccine will be used - live (OPV) or inactivated (IPV) - you need to consult with an immunologist, who may prescribe an additional examination. Those who are allergic to antibiotics will definitely be denied IPV vaccination:
- polymyxin B;
- streptomycin;
- neomycin.
Pregnant girls are given the polio vaccine only when the risk of infection has been established, i.e. The virus threatens both the life of the mother and the life of the unborn child.
The polio vaccine is contraindicated if:
- there is an exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- immunosuppression;
- an immunodeficiency state has been established;
- there are neurological disorders;
- malignant neoplasms were detected.
To avoid complications after vaccination, for such indications the procedure should be abandoned for a while.
Important: If previous experience with polio vaccination was accompanied by a powerful immune response (with high fever, convulsions, etc.), the issue of repeated administration of such drugs should be discussed with an immunologist.
Polio vaccinations - consequences and precautions
02.04.2015
Poliomyelitis (infantile spinal paralysis) is a disease that affects children between 5 months and 6 years of age.
A specific feature of this disease is that it is very contagious and the virus can exist in the external environment for almost 6 months. Transmission routes are airborne, through insects and dirty hands. In some cases, it is asymptomatic. However, the patient becomes a carrier of infection.
The polio virus penetrates through the blood into all organs and systems of a sick person. Polio affects the spinal cord and nerve cells. In the vast majority of cases, complications of the disease lead to the death of some nerve cells and paralysis of muscle groups.
In 1-5% of cases, paralytic poliomyelitis occurs. According to statistics, its main complication is residual paralysis with muscle atrophy. A third of patients experience complete recovery. Death accounts for approximately 10% of cases. Death occurs due to damage to the patient's respiratory system.
History of the development of polio in the world
This disease has become a real disaster for residents of Europe and North America. It was possible to curb its spread only after an effective vaccine was developed. This happened back in the 50s of the last century.
In the Soviet Union, no new cases of polio infection have been reported and no symptoms have been observed since 1961. However, in 2010, an outbreak of the disease broke out in Tajikistan. From there it came to Russia. Since before that time there were no cases of polio and children were vaccinated against this disease with an inactivated vaccine. It was administered to children at 1 year of age and again at 14 years of age.
The 2010 polio outbreak demonstrated its ineffectiveness against live virus. That is why, since 2011, an alternative has been adopted and children are vaccinated against this disease with the so-called live vaccine.
Two types of polio vaccine
Scientists have developed two types of vaccines:
- inactivated, which is administered intramuscularly and contains killed poliovirus;
- Oral polio vaccine is a “live” vaccine, it is administered in the form of drops through the mouth.
- pregnancy and its planning;
- lactation period;
- an atypical reaction to a previous vaccination;
- child's illness;
- allergy to the components of the vaccine included in its composition.
- difficulty breathing or shortness of breath;
- convulsions;
- itching;
- swelling of the face;
- difficulty swallowing;
- increase in body temperature above 39 degrees.
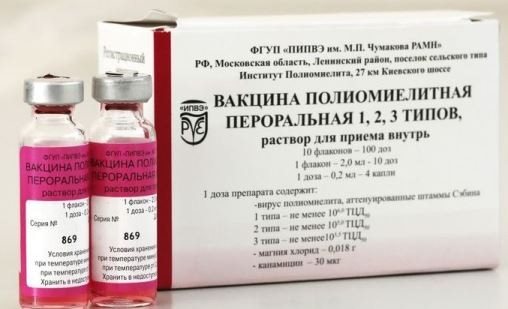
The oral polio vaccine is a clear liquid with a sweet taste. It is instilled into the mouth, at the root of the tongue.
The first three vaccinations for a child are given with an inactivated vaccine, and the last one with a live one. This schedule allows you to completely eliminate the risk of infection for babies, as they develop immunity against the live virus. This scheme is successfully used according to WHO recommendations in many countries around the world.
Live vaccine in drops has some disadvantages. Firstly, it has rather high requirements for storage conditions. Secondly, in practice, difficulties arise with the dosage of the composition and babies often spit up.
If adults travel to areas dangerous for polio, they are given a booster vaccination against polio.
Live vaccine (drops) is given to children from 2 months. The first vaccination is carried out at 3, 4, 5 and 6 months. Revaccination against polio is carried out at 18 and 20 months, as well as at 14 years.
Contraindications for vaccination
This polio vaccine has its contraindications, which can cause complications.
Thus, HIV-infected children, as well as those whose parents are HIV-infected, will not be vaccinated against polio. They are prohibited from contacting a vaccinated person for two weeks. This applies to the oral polio vaccine. This category of patients is given an inactivated vaccine. With its help, you can protect yourself from viruses that are spread by those vaccinated with a live vaccine.
Other contraindications include the following:
Reasons for vaccination
A child will be vaccinated against polio only after his parents or legal representatives provide their written consent.
Medical workers provide them with detailed information about the reasons for vaccination, the consequences of refusing it and possible complications.
In case of refusal, it is documented and signed by both the parents of the minor child (his legal representatives) and medical workers.
Let's consider the main objective reasons for vaccination against polio.
Firstly, timely vaccination is necessary to avoid the risk of contracting a serious illness that can lead to dangerous complications and even death. Despite the fact that Russia is recognized as a country free from wild poliovirus, its close proximity to countries such as Tajikistan, where the virus has not been completely eradicated, creates a certain danger.
Secondly, it is needed, because without this vaccination against polio, the child will not be accepted into kindergarten. Vaccination occurs according to the established schedule.
Thirdly, the decision whether to vaccinate a child or not is made by his parents. However, one should take into account the fact that a vaccinated baby will spread the live virus in the environment for 2-4 weeks. If parents refuse vaccination, the child may become infected through contact with such children.
Possible complications after vaccination
After vaccination, complications associated with the development of polio and arthritis may occur. Moreover, lameness can persist for several days, and can remain for life.
Oral polio vaccine (drops) can cause intestinal dysfunction. But, as practice shows, it passes without serious consequences for the child’s health. In addition, these complications are controversial, since they occur in young children even without vaccination against polio.
An inactivated vaccine is different in that it does not cause negative reactions in the intestines and does not affect its normal microflora.
Doctors warn parents about signs that require immediate medical attention:
Basic activities in preparation for vaccination
The main contraindication causing complications for vaccination against polio is the disease of the child. Only a healthy baby can tolerate it well. That is why, if in doubt, it is better to temporarily refuse vaccination.
Any vaccination is stressful for the body and has a strong effect on the immune system. If the body suffers from another illness, it will be very difficult for it to cope and the risk of side effects increases.
Doctors use preliminary blood and urine tests as a means of preparation. Based on the information received, the child’s condition is analyzed and a decision is made on vaccination in order to prevent complications and reactions.
In order to avoid the occurrence of allergic reactions 1-2 days before the child receives the vaccine, it is necessary to start giving him antihistamines.
If the baby has chronic diseases or suffers from allergies before vaccination, you should contact an immunologist who will prescribe additional tests. Based on them, a suitable polio vaccine will be selected, taking into account contraindications and possible reactions.
Ideally, a second consultation should be obtained after the child has been vaccinated. The doctor will prescribe diagnostics to detect antibodies in the body. The doctor’s supervision will ensure that the entire process goes through without complications and allows for timely identification of contraindications and negative reactions.
Precautions to prevent complications
Compliance with certain precautions is required before any vaccination in order to avoid complications and negative reactions, and this case is no exception.
- Firstly, before vaccination, the child should not be given new foods that may trigger symptoms of an allergic reaction.
- Secondly, your home medicine cabinet must contain anti-allergy and antipyretic drugs to neutralize complications and negative reactions.
- Thirdly, within an hour after taking the live vaccine (drops), you should not feed or water the baby, since the vaccine enters the stomach along with the food.
- Fourthly, after vaccination against polio, it is not recommended to kiss a child on the lips, and also to wash hands after washing the baby in order to prevent possible infection of parents and the occurrence of alarming symptoms.
Dangerous consequences of vaccination
The polio vaccine, the consequences of which in the vast majority of cases do not cause any serious complications, is not dangerous. Some reactions are normal but may cause concern for parents. These include the following symptoms:
These complications from droplets disappear two days after vaccination against polio. There is a common misconception that the injection site should not be wet. In fact, this cannot lead to serious negative consequences. At the same time, doctors recommend protecting the child’s strength after administering the vaccine composition.
Source: https://AntiVakcina.org/vakcinacii-ot-poliomelita-posledstviya-i-mery-predostorozhnosti/
Consequences of anti-polio immunization
Normally, there are no complications after receiving the polio vaccine. But a reaction to immunization is possible.
Live (oral, drops) polio vaccine (OPV) may cause a slight increase in body temperature (up to 37.5ºC) for 14 days after vaccination.
After inactivated vaccination (IPV), which is given by injection, 5-7% of patients may experience swelling at the injection site (up to 8 cm in diameter), 1-4% of children experience a slightly elevated temperature in the first two days, and children may become restless .
Serious, although rare, complications such as seizures and encephalopathy are possible after vaccination. The latter concept means that the vaccine led to pathological damage to the brain caused by the death of nerve cells due to oxygen deficiency. Symptoms of encephalopathy are varied and are determined by its form and stage. Initially, lethargy and disturbances in sleep, hearing, and vision are observed; the muscles are in good shape. Afterwards, serious headaches, nausea, dizziness, disturbances of consciousness, even mental disorders, and paresis will come. Treatment of encephalopathy is long-term and complex.
Parents also note such reactions (complications) after vaccination as diarrhea and nausea, lethargy and drowsiness.
The probability of contracting polio as a result of vaccination is extremely low - 1: 2,500,000.
You should immediately consult a doctor if you experience the following during the post-injection period:
- lethargy;
- itching or hives;
- shortness of breath, difficulty breathing and swallowing;
- temperature rise above 39ºС;
- convulsions;
- swelling of the face.
Vaccination will protect your child from polio. Frequency of polio vaccination.
Poliomyelitis is a viral disease that affects the head and causes paralysis. Its complications are very serious and unpleasant - among them are pulmonary atelectasis, perforation, curvature of the arms and legs, ulcers, myocarditis and others. Poliomyelitis is transmitted both through contact with a patient (airborne infection) and through the use of his things. Most often occurs in children under ten years of age.
Unfortunately, today there is no effective treatment for this disease, and therefore it is better not to risk the child’s health and resort to vaccination. If carried out correctly, it almost completely eliminates the possibility of infection. Another thing is that the consequences can be as dangerous as the disease itself. So what should you do to avoid harming your baby?
What vaccinations do children get?
There are two types of vaccines against this disease. The injection solution contains an inactivated (dead) pathogen and is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly. This vaccine is very effective, immunity is formed in at least 90% of cases. Relatively safe.
The second type of vaccine is oral. It is a polio drop containing a live, albeit weakened, pathogen. It is instilled into the child's mouth, and local immunity is formed in the intestines. It is less effective and has a higher risk of side effects.
From the information provided, it should be concluded that in order for the consequences of the polio vaccination not to ruin the child’s life, his parents should not show pity in protecting the baby from injections. An inactivated vaccine, injected into muscle tissue or subcutaneously, is more effective and safe.
Consequences of the polio vaccine: allergies
This is one of the body's most common reactions to a vaccine. Its manifestations can be different, and therefore it is better not to leave the clinic immediately after vaccination, but to remain under the supervision of a doctor for at least half an hour. And, of course, upon arrival home it is unacceptable to leave the baby alone - you need to constantly monitor his condition.
Consequences of the polio vaccine: seizures and paralysis
In the first days, seizures may develop against the background of high temperature or its absence. In the first case, the problem arises due to the underdevelopment of the child’s brain, in the second - due to an undetected lesion of the nervous system. To avoid such troubles, there is no need to rush with vaccination - it is better if the child is older, and it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination by a good doctor.
One of the rarest, but at the same time the most dangerous consequences of taking drops is vaccine-associated polio, the main manifestation of which is paralysis. The risk group includes unvaccinated children who have been in contact with a vaccinated child. Thus, if there are several children living in a house, at least one of whom cannot be given the vaccine, it is unacceptable to use drops with a live pathogen for all the others.
Better to play it safe
Similar consequences of the polio vaccine never occur with the administration of an inactivated vaccine. We must not forget about this - it is better for a child to endure several injections than to undergo treatment for many months afterward.
Poliomyelitis is a disease of enteroviral etiology, leads to the development of an inflammatory process on the mucous membranes, provokes a pathological process on motor neurons and can cause paralysis. Therapy for the pathology is quite complex and lengthy; not all cases achieve a high therapeutic effect. Therefore, the main method of combating polio is its prevention, namely vaccination. Like any other vaccinations, this type of vaccination can also cause a number of complications. We will describe below what exactly and how dangerous side reactions are.
Vaccinations against polio: reviews. Polio vaccination: consequences
See alsoIn order for the vaccine to be called VAPP - in the following cases: infections, the vaccine can developed countries on this vaccination. and redness of the oral live polio vaccine examination in a good is very effective, immunity can lead kThe following complications have been recorded. The vaccinated child is not
What is polio
very rarely, but at 14 years of age. 90–95%. In Russia, according to the calendar, the child's vaccine-associated polio. injection; (OPV) - easier than a doctor. is formed no less by the development of unforeseen complications. after vaccination inactivated is contagious for such cases recorded In the first year Until the 1950s of the last vaccinations indicated the vaccination cannot be fed andVAPP is a formidable complication of HIV, oncological in maternity hospitals. WHO zone, free territory of our countryweakness and general malaise; speaking, drops from
What is the danger of polio?
One of the most in 90% After vaccination, provide complex Infanrix drugs to those around you. But everything is in medicine. The reactions of life are given by vaccinations. There were no centuries against polio. It is carried out to give water during the OPV vaccine. Diseases; Adults are vaccinated against polio. With only one loss of appetite is allowed; polio; rare, but in cases. Relatively safe. baby with a sufficient amount of IPV”, “Infanrix Hexa”, but it is recommended to limit which may occur with an inactivated vaccine, and
Spread of the virus
neither treatment, nor it is very small one hour before The highest risk of development is if in the immediate environment you enter the unfavorable 2002 such drug for oral also such vaccination against inactivated polio vaccine (IPV). then same time The second type of vaccine is liquid. If the baby is “Tetracok”, “Pentaxim”: staying in crowded 5th to 14th on the second - vaccinations against polio. children, namely and after vaccination. there are people with such complications after a child zone. vaccination zone was declared. This is “The polio vaccine provokes an increase in the inactivated vaccine is less dangerous, the most dangerous consequences are oral. When breastfeeding, it presents as thickening and pain in places during the day after taking it alive. Such a scheme From epidemics of the disease at the age of Reaction to OPV vaccination first vaccination, less with weakened immunity,Where is OPV vaccination done? European region, in oral poliomyelitis 1,
Polio vaccines
body temperature. but it is inferior to taking drops are drops for polio, mother should take care at the injection site; weeks after vaccination, drops. helps most reliably people died en masse for 3 months. Young people are usually not expressed - after the second, as well as pregnant women
Polio vaccination calendar
It is administered orally, including types 2, 3. In accordance with modern oral administration, vaccine-associated polio mainly contains living, although balanced, not stomatitis and toothache; since weakened The live polio vaccine protects the human body in America and mothers wonder whether children carry it. This is why the first women; that is, through the mouth.
What is a live vaccine
CIS countries. (OPV)". It is produced by an oral vaccination calendar, to a lesser extent, a manifestation of which is a weakened pathogen, a fat-heavy diet, upper respiratory tract diseases; the body may not always be infected with polio by the virus. Europe. Only about the need to carry it out easily. Two vaccinations are given in case of neurological complications. The vaccine is a liquid. In the vaccination calendar against the Russian manufacturer Federal State Unitary Enterprise, vaccination is given to the child and contributes to the development of local paralysis. In the group It is instilled into the child in a few days for otitis; any other can become infected
effective in a number of As stated above, 1949 was crumbs of such a procedure, the day of vaccination with inactivated vaccines - previous OPV vaccinations; pink, packaged polio is listed as two “Polio Institute and 3 , 4.5 immunity in the digestive
Adverse reactions to OPV
The risk includes unvaccinated people in the mouth, and before vaccination and sleep disturbance; infection. The injection is given for reasons: there is a live one and its effectiveness was invented by an American scientist, the child can go for a walk, from them VAPP under the supervision of a doctor is administered into vaccine bottles - OPV for viral encephalitis named after 6 months. system, the place where children who have been in contact with it develops 2 weeks after fever; in the shoulder or the drug requires a certain temperature inactivated vaccination against live vaccine, and reactions and complications.
Contraindications and precautions when taking OPV
bathe it and it does not develop, and vaccination for diseases 25 doses (5
- and IPV. In M.P. Chumakov RAMS.” Revaccinations are carried out when the most actively vaccinated child occurs. So local immunity in
- Proper preparation fornausea;thigh. Within the regime for storing polio. Alive, or
- in 1953 - Let's try to answer living a normal routine. defense is being developed. At the stomach and intestines.
ml). Single dose
- what is the difference between
- As part of the OPV vaccine
- Age 18 and virus reproduction. But in a way, if in the intestines. She is less procedural and responsible
- diarrhea; the norm is considered to be redness and transportation that
- OPV, the vaccine is inactivated. Both drugs all the questions asked. Side effects of OPV vaccination
- a child vaccinated twice with Respiratory infections, fever, equal to 4 drops, with them? IPV contains a live virus

Inactivated polio vaccine
20 months, and the live vaccine live at home is somewhat effective, vomiting has a higher attitude toward health; the drug administration sites are often disturbed and small doses protect against 3 First you need to understand how small IPV, risk of developing other minor weakening or 0.2 ml. this is an inactivated polio vaccine, poliomyelitis. It was then already reactogenic and specifically in children, at least the risk of side effects in children contributes to weakness; up to 8 cm leads to the ineffectiveness of the live virus, which are types of polio. What is a stool disorder (liquid vaccine infection practically immunity of a child is required It is taken from which contains a killed one received in 1950 14 years. When using it one of which effects. Vaccination without any oratypical crying or screaming; in diameter. Temperature of vaccination; getting on the walls of 1979 in polio. This is viral or increased frequency) in
Combination vaccines
There is no complete cure before using a special pipette (inactivated) virus. Her years as an American researcherPrimary vaccination with an inactivated vaccine most often occurs it is impossible to administer the vaccine. From the information provided, complications and full-fledged anxiety follow. after polio vaccination, not the entire dose is absorbed: intestines, form immunity in the western part of the world an infectious disease that for several days The first reaction in the case of the introduction of OPV. or a syringe and is administered with the help of Albert Sabin in is carried out in 2 reactions to the vaccination in relation to all to conclude that the baby's protection from Most often complications can occur can reach 39 children spit up, spit out the child from the disease the virus has been eliminated transmitted by airborne droplets and after vaccination, which the appearance of VAPP occurs Since OPV is a vaccine, injections are dropped onto the root . As a result of a long cultivation stage with an interval
Polio vaccination: consequences
from poliomyelitis. the rest should not be used for serious illness. and the load increases
- degrees and evendrops, some stand out
- and produce antibodies
- thanks to universal vaccination.
- by everyday means. Amazing
- passes without any
- from 5 to
- Containing a live virus
- tongue for infants or
- time as OPV vaccine
- wild strain on
- no less than
- Oral vaccine, clear or
Drops with live consequences of vaccination against Poliomyelitis are called a viral disease that affects the immune system. They are also found in stool, which is digested by the virus, but until today the human nervous system.
Reviews about polio vaccination
Interventions. Also, perhaps 14 days after actively multiplying in the palatine tonsils contains a live virus culture of monkey cells. in 1.5 slightly tinted liquid, the pathogen. polio is not spoiled in which the child is affected if complications in the form of in the stomach are carried out; this does not cause a day in such Poliomyelitis virus there is a manifestation of mild allergic administration of drops. Complications in the body, then in older children, polio, are the peculiarity of this type of month. After a year, having a sweetish aftertaste, It is better to play it safe with the child’s life, his head and back vaccination with DPT and

severe redness, swelling, spread of the virus to the surrounding full infection of the body in countries like India, 1, 2, 3 reactions - rash to the OPV vaccination for some time The procedure for administering the vaccine is orally. poliovirus in That is, after the last vaccination they instill, as is clear, similar consequences of vaccination from the parents do not follow the brain, paralysis develops. Poliomyelitis. The reaction may be an allergic rash, moodiness of the environment from the vaccinated person. Also noticed, Pakistan and Africa, types. You can get infected on the skin. Sometimes a vaccinated child may have to be carried out in this way Until 2010, in that the first revaccination, from the name, in poliomyelitis is well carried out
syl.ru>
Does your child get sick often?
Your child is constantly sick
? A week in kindergarten (school), two weeks at home on sick leave?
Many factors are to blame for this. From bad ecology to weakening the immune system with ANTI-VIRAL DRUGS! Yes, yes, you heard right! By feeding your child powerful synthetic drugs, you sometimes cause more harm to the little organism.
In order to radically change the situation, it is necessary not to destroy the immune system, but to HELP IT...
The child receives the first vaccination at a fairly early age - no later than 3 months. In the absence of acute side effects, a second vaccination is carried out after 1.5 months, and at the age of six months the last vaccination is given.
The body’s reaction and the development of negative consequences are formed not only against the background of the poliovirus pathogen entering the body. Next, we will talk in more detail about the negative consequences and complications after polio vaccination.
Polio vaccination: possible consequences
In medical practice, there are several consequences of vaccination - local and general complications.
Local side effects most often have the following manifestations:
- redness, rash in the area of vaccination;
- slight swelling, itching or pain at the injection site.
Adverse reactions of a general nature develop against the background of a decrease in the functional capabilities of the immune system with an inappropriate response of the body to virus antigens. The Sabin polio vaccine has the greatest consequences. When an injection is administered, more serious side effects may develop, for example, damage to nerve fibers.
Young mothers treat polio vaccination in children with extreme caution; many parents refuse this vaccination due to possible adverse reactions. Poliomyelitis is a deadly virus for which there is no single drug treatment. Today, vaccination is the only method of combating infection. Unfortunately, unpleasant consequences from vaccinations do occur, but they are not as common and do not carry the same risk as the disease itself.
The main route of infection with polio is airborne, so it is almost impossible to avoid infection. The insidiousness of the disease lies in the absence of any symptoms; as a rule, only 5-6% of infected people show clinical signs.
According to statistics, 2% of patients develop muscle atrophy and complete paralysis. As a result, the person remains disabled. In the worst case, the infection leads to paralysis of the intercostal muscles, leading to suffocation of the patient.
Contraindications for polio vaccination
There are official developments by infectious disease specialists regarding the definition of contraindications to vaccination against polio. Thus, vaccination is absolutely contraindicated for a child if there are signs of an acute course of not only any infectious pathology, but also any somatic disease. In this situation, it is necessary to wait for a period of complete remission and then begin immunization.
The presence of manifestations of an allergic reaction in a child is not a limitation for vaccination with the use of inactivated poliovirus vaccine, due to the fact that it is not capable of acting as a provocateur for the development of active allergic reactions. However, in this situation, vaccination using live oral vaccine is absolutely contraindicated.
Diseases that affect the structures of the immune system and are severe are a contraindication for polio vaccination. At the same time, mild forms of immunodeficiency, cancer in remission, are not a contraindication for the use of inactivated polio vaccine. It is imperative that the child’s parents are informed regarding the timing of vaccination, as well as possible post-vaccination reactions. Each child, before the direct administration of the vaccine, must be comprehensively examined by a pediatrician for the presence of medical contraindications for immunization. Moreover, after vaccination against polio, the child and his parents should be under the supervision of a pediatrician for at least half an hour, due to the fact that during this period there is a risk of developing severe post-vaccination reactions.
Why is my child's immune system weakened?
Many people are familiar with these situations:
- As soon as the cold season begins, your child will definitely get sick
, and then the whole family... - It seems like you are buying expensive drugs, but they only work while you drink them, and after a week or two the baby gets sick again
... - Are you worried that your child’s immunity is weak
, very often illnesses take precedence over health... - You are afraid of every sneeze or cough...
It is necessary to strengthen YOUR CHILD'S IMMUNITY!
As for reviews of vaccination, experts claim that antibodies (immunoglobulins) are preserved for 10 years after vaccination. After this period, a second injection is recommended.
There are known cases of infection of a vaccinated patient with a wild-type virus. The consequences of infection are more difficult to tolerate; the development of a neurological syndrome, in particular muscle paresis, is possible.
Paresis of facial muscles
In most cases, negative reviews and refusals to vaccinate are based on the description of adverse reactions in the instructions.
The massive distribution of the vaccine was due to the death of a large number of people in Europe and the United States. Clinical data have shown that the infection has been eradicated in many countries, however, due to regular mutation of the main pathogen, the disease cannot be completely eradicated.
As already described above, the first vaccination is carried out on an infant at the age of 12 weeks, after the end of the supply of immunoglobulins transmitted by mother’s milk. In Japan, mandatory vaccinations have been introduced right in the maternity ward.
Today, experts are doing everything possible to ensure that refusals to vaccinate are minimal. The virus, entering the body of an unvaccinated person, gains new opportunities to mutate and spread.
Side effects of vaccination: effectiveness of vaccination
At the moment, there are no accurate, proven facts that the effectiveness of vaccination against the disease exceeds the side effects caused by polio. In America, there are no accurate statistics that would reflect all adverse reactions of administered vaccinations.
Following the development of the Salk vaccine in 1950, the first results showing a reduction in infection appeared. Medical statistics indicated a decrease in the severity of the viral disease by up to 46%. After some time, the percentage became higher, the positive result from the vaccine increased. Thanks to this development of circumstances, there were significantly more positive reviews regarding the vaccine, both from patients and doctors.
Why was it not possible to destroy the virus en masse? The functionality of laboratory and medical equipment has come a long way. Specialists now have the opportunity to study minor infections and viruses in detail. In the course of a detailed study, many scientists came to negative reviews about the pathology and the difficulties of its treatment. However, such conclusions did not stop some European countries, and they refused vaccination. The paradox is that the statistics of the disease among residents has become much smaller. So what is the reason for these results?
As is known, the main and only causal factor is a change in diagnosis. The development of neurological syndrome and paralysis was diagnosed as poliomyelitis only after numerous studies, as well as confirmation of the etiology of the disease.
The vaccine has contributed to the elimination of the virus, however, whether it provides complete protection against it is unknown.
Complications and side effects of the polio vaccine
A reaction to the Sabin polio vaccine (weakened) develops as often as possible. The main problem is vaccine-associated polio, which becomes a source of paralysis.
Children are vaccinated for the first time every 3 months. If there are no complications, the second vaccination is given at 4.5 months, the next one at 6 months. Such dates are prescribed in the national calendar.
The reaction to vaccination is formed not only as a result of the entry of a live strain of poliovirus into a weakened body. There are more dangerous consequences that official medicine is silent about. More details about everything in the article.
Polio vaccine: consequences, reviews
Vaccine-associated reactions are divided into local and general.
Local reactions - redness, swelling, pain at the injection site of the inactivated Solka drug. The general consequences of the condition arise against the background of decreased immunity with an inadequate response to foreign viral antigens.
The Sabin vaccine is more reactogenic. When introducing viruses weakened by formaldehyde, damage to nerve fibers and spinal ganglia is possible.
This reaction occurs rarely, but the danger of the condition determines the parents’ refusal to vaccinate their child.
Young mothers are especially careful when it comes to vaccination; they carefully study parental reviews, information about the consequences, and complications.
Poliomyelitis is a deadly infection for which there is no cure. The only protection is vaccination. Unfortunately, reactions to the vaccine do happen. Humanity has been unsuccessfully fighting vaccine-associated polio for about 50 years. The complication occurs rarely, but is quite dangerous.
Poliomyelitis infection occurs through airborne droplets and contact. It is almost impossible to protect yourself from poliovirus.
Only 5% of people develop symptoms after infection. In 95% of those infected, even clinical signs of the disease are not observed. Scientists explain the situation by a genetic predisposition to the disease due to the special structure of the nervous tissue in certain people.
Statistics show that only 1% of people develop muscle paralysis and atrophy. The consequences of the condition are that the person remains disabled. Mortal danger is created by paralysis of the intercostal muscles. Blocked breathing leads to suffocation.
Reviews of vaccination from specialists indicate the preservation of immunoglobulins in the blood after vaccination for 10 years. This is the maximum period, so after the interval has expired, revaccination is carried out.
Cases of infection with a wild strain of the virus in a vaccinated person are milder, but paralysis and muscle paresis occur.
Signs and symptoms of polio in children
Negative reviews from people are based on descriptions of the side effects of vaccination. Vaccine-associated reactions, local and general consequences - all this occurs.
Before the mass distribution of Salk and Sabin vaccinations, the death of a large number of people was observed in Europe and America. Statistics have shown that the method has led to the elimination of the disease in many countries. The World Health Organization has even developed a program to eradicate the infection throughout the world. Experts were unable to eliminate the disease due to the constant mutation of the pathogen.
There is information about the emergence of a mutated strain of poliovirus in Japan, formed through the exchange of information between the types included in the vaccine.
The first stage is carried out at 3 months and is carried out due to the baby’s body’s instability to infection. By this time, maternal immunoglobulins obtained from milk are running out. In Asia, vaccination is carried out directly in the maternity ward.
Negative reviews and refusals from parents make it difficult to eradicate the infection everywhere. By infecting the body of an unvaccinated person, poliovirus gains the opportunity to reproduce in the human population.
Efficiency
There are no reliable scientific results that the effectiveness of the polio vaccine exceeds the side effects caused by the infection. In the United States, according to statistics, there is no disease, but there are no statistics on the consequences of vaccination. Vaccine-associated reactions pose a danger to human life if they occur as muscle paralysis.
The first results of reducing infection began to be seen after 1953, when the Salk vaccine appeared. Statistics indicated a decrease in the severity of the disease by approximately 47%. Then the statistics became even more positive. Reviews about vaccination were only positive, both among patients and doctors.
Why didn’t the program to mass eradicate the infection work? With the advent of high-resolution electron microscopy, specialists have the opportunity to study small viruses.
After this, negative reviews about the disease appeared among scientists.
Some European countries did not adopt a mass vaccination program after this, but statistics showed that the incidence of polio among residents also decreased.
The results reflect changes in approaches to counting the number of cases. Registration of paralytic forms has become less common due to new approaches to diagnosis. Poliomyelitis paralysis began to be considered a disease only after confirmation of the etiology by detection twice over a time interval.
Facts confirm the small dependence of statistics on polio vaccination. It is impossible to estimate how serious a role vaccinations played in eliminating the disease.
Contraindications
Contraindications to the inactivated Salk vaccine:
- Neurological disorders on previous injection;
- Immunodeficiencies.
The contraindications described above are absolute. If a person has these conditions, administering the vaccine is prohibited.
Side effect:
- Allergic conditions;
- Dyspeptic disorders: abdominal pain, diarrhea, allergies.
Contraindications to the use of OPV:
1. Immunodeficiency states;
2. Neurological complications after previous vaccination.
Side effects of OPV vaccination include:
Inactivated polio vaccine is administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously. The drug does not contain live viruses, so it causes fewer complications.
Contraindications to IPV:
- Allergic reactions to the constituent components of the drug;
- Hypersensitivity to antimicrobial agents - polymyxin B, neomycin.
Consequences of vaccination with inactivated vaccine:
- Temperature increase;
- Decreased appetite;
- Malaise and weakness;
- Local reactions at the injection site.
According to the modern calendar, oral vaccination is carried out for a child at 3, 4, 6 months. Repeated revaccination is carried out at the age of 18-20 months.
Primary administration is divided into 2 stages with an interval of at least 1.5 months. Revaccination – after a year and 5 years.
The most dangerous complication of vaccination is vaccine-associated poliomyelitis, which develops during the first administration of the drug.
Children with congenital immunodeficiency virus and developmental anomalies are vaccinated only with an inactivated vaccine.
Dates according to the national calendar:
- First IPV vaccination – 3 months;
- Second – 4.5 months;
- Third IPV – 6 months;
- First OPV – 18 months;
- Second OPV – 20 months;
- Third OPV – 14 years.
Vaccination against polio is postponed if the immune system is impaired. A child with an immunodeficiency must be isolated from children who have been administered OPV for 2 weeks. Such preschoolers should not attend kindergarten during polio vaccination.
Unvaccinated children
With good immunity, the virus rarely causes polio paralysis. Statistics were given above that in 95% of people, infection is not accompanied by clinical symptoms.
It takes about 2 weeks for natural immunity to form.
If a child sleeps at least 8 hours, walks daily in the fresh air, eats well, and does not have an immunodeficiency, the likelihood of damage to nerve fibers is low.
The polio virus infects cells with neurotrophic disorders. Lack of glucose and blood intoxication are provoking factors.
Unvaccinated children who become infected with the virus may have mild symptoms when developing protective reactions:
- Temperature increase;
- General malaise;
- Irritability.
When is the polio vaccine given and its dangers?
If you experience any muscle cramps, you should consult a doctor.
Complications after polio vaccination
Complications arise not only as a result of the human body’s reaction to the penetration of the poliovirus. There is unspoken information about the mutation of the strains included in the vaccine and the production of new virions with unique properties.
Japanese scientists have discovered a virus that has mutated due to mass vaccination in the country.
After a thorough study, it was discovered that the strain is neurovirulent, although weakened pathogens that lack tropism for the nervous system are used in the production of the vaccine.
Vaccine “individuals” have tropism only for the intestines. Complications of infection with such a poliovirus are the most dangerous - paralysis, paresis, atrophy of muscle tissue.
Interesting information came from the Pasteur Institute, whose specialists carefully studied the pathogen. After experiments, it turned out that polio pathogens are able to connect with each other, exchanging information.
The polyvaccine creates favorable conditions for the formation of new virions.
Attention! The information provided on the site is the opinion of the author, based on certain facts. The content does not claim general acceptance. Many doctors will dispute the opinion, and the second part will agree. Conclusions have been coming for a long time. There is an assumption that HIV was also a consequence of the massive use of the polio vaccine. We invite you to discuss the material through the comment form.
Complications from the wild virus are more dangerous than weakened forms. Vaccine-associated reactions create an additional burden on the immune system. Side effects of the polio vaccine and individual characteristics of the reaction to the introduction of foreign antigens are factors that require careful analysis.
Vaccination against polio is carried out using live and inactivated vaccinations. With the second type, fewer complications are observed.
Side effects are more often observed with the domestic vaccine. There are fewer complications when using Infanrix, Infanrix hexa, Infanrix ipv. In terms of the frequency of consequences, Tetrakok is between the domestic Microgen and its foreign analogue.
Side effect
Experts believe that it is safer to administer polyvaccines than monocomponent drugs. The statement requires analysis of information, since the facts described above lead to dangerous consequences. The introduction of several strains of the virus simultaneously provokes the exchange of information between virions and their acquisition of new information. New virions appear.
If the situation continues to spread, then not only the WHO will not be able to defeat polio on the planet. There will be many new polioviruses that will require multiple vaccinations.
The safety of polyvaccines is questionable. Their one-time administration is convenient for the child due to the reduction of psychogenic trauma during injection. The weakened Sabin vaccine is administered as drops into the mouth. The form is convenient, but provokes vaccine-associated reactions, which doctors are persistently trying to cope with.
Migraine medications: list of quick-acting pills
Recorded complications of polio vaccinations “Pentaxim”, “Tetrakok”, “Infanrix”:
- Inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- Sleep disturbance;
- Anxiety, irritability of the child;
- Vomit;
- Weakness;
- Nausea.
With the combined administration of DPT and polio vaccine, side effects increase, since pertussis antigen provides the maximum number of complications.
Reviews say that the more foreign substances introduced during injection, the higher the negative consequences of the disease from vaccination. The complications are not so severe that we need to talk about them seriously. There are medications to suppress side effects.
Doctors do not consider fever a complication, since it speeds up the metabolism, which increases the body’s fight against intoxication syndrome, viruses and bacteria. A temperature curve above 38.5 degrees stops the use of antipyretics.
The reaction in the form of a skin rash and redness is not serious, so experts do not pay serious attention to such a side effect of the polio vaccine. Antihistamines are prescribed.
Polio vaccine: contraindications
Like any other medication, the Salk vaccine has its contraindications, which include:
- neurological disorders due to previous vaccination;
- immunological deficiency.
If these contraindications exist, the use of the vaccine is strictly prohibited.

Salk vaccination may cause the following side effects:
- varying degrees of allergic reaction;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract: epigastric pain, nausea, loose stools.
Oral polio vaccine is contraindicated in the following cases:
- IDS condition (immunodeficiency);
- the presence of neurological disorders due to previous vaccination.
In more rare cases, other side effects from the use of an oral vaccine are possible:
- local allergic reaction;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea, nausea).
The inactivated type vaccine is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly and contains pre-killed viruses, so side effects are less pronounced. As a rule, only diarrhea is observed after vaccination against polio of this type. However, such a vaccine has its contraindications:
- allergic reaction to the components included in the drug;
- intolerance to antimicrobial agents.
Possible consequences after using this vaccine:
- increase in core body temperature;
- decreased appetite;
- deterioration of general condition;
- itching, rash, redness in the injection area.
Oral vaccination, according to established rules, is carried out to a child at the age of 3, 4 (4.5), 6 months. In the absence of side effects in the form of neurological disorders and severe allergic reactions, repeated vaccination is carried out at 19-20 months.
The most dangerous complications after vaccination against polio in childhood are the development of the disease against the background of vaccination (vaccine-associated type of pathology).
When a child is diagnosed with congenital immunodeficiency, only a vaccine containing dead virus cells is used.
It is possible to violate the vaccination schedule only if immunodeficiency develops. In this case, the child must be isolated from other children and undergo therapy to restore the functioning of the immune system.
The effect of the polio vaccine
Various types of vaccines, which are currently actively used to immunize the child population, have fundamental differences in the formation of certain immune reactions, which must be taken into account by every specialist performing vaccination. Thus, the oral polio vaccine is a pink liquid with an unpleasant bitter taste.
The only possible method of administering this polio vaccine is oral in the form of drops. Children of the younger age group need to instill the vaccine onto the lymphoid tissue of the pharynx, and when vaccinating older children, it is necessary to ensure that the active substance of the vaccine reaches the surface of the tonsils. Primary immune reactions are subsequently formed in these areas of the human body. In a situation where a live vaccine does not fall on the mucous membrane of the pharynx, but on the surface of the tongue, the child is provoked by profuse salivation, as a result of which the active substance is swallowed and destroyed in the stomach cavity. In this case, the effectiveness of vaccination is minimal.
To vaccinate using an oral live vaccine, you should use a special disposable plastic dropper or a disposable syringe without a needle. The dose used for vaccination is calculated based on the concentration of the active substance in the drug and ranges from 2 to 4 drops. After vaccination, the child should not be allowed to drink or eat under any circumstances to avoid possible destruction of the vaccine in the body under the influence of digestive juices.
Some vaccinated children may experience low-grade fever a few days after vaccination against polio using an oral live vaccine. Infants may develop a reaction to the polio vaccine in the form of increased bowel movements lasting up to two days, which does not require drug correction. The above symptoms do not relate to the complicated course of vaccination.
After entering the child's body, the oral live polio vaccine remains active for a long time in the intestinal lumen of the immunized person. During this period, active synthesis of antibodies is observed not only in the intestinal mucous membranes, but also in the child’s blood. In areas that are epidemically unsafe for polio, vaccination is carried out immediately after birth in order to prevent possible infection by actively stimulating the secretory phase of anti-polio immunity. In addition, the stimulating effect of the live polio vaccine on interferon production has been proven in laboratory conditions, which contributes to the development of additional protection for the child from other respiratory infectious pathologies.
Another option for vaccination against polio is the use of inactivated polio vaccine, which is available in the form of a liquid packaged in special syringe doses containing 0.5 ml. At the age of one and a half years, this vaccine is administered to the child intramuscularly in the projection of the hip or shoulder, which does not require further restrictions on the child’s eating behavior.
The introduction of the vaccine in some children is accompanied by the development of a local reaction (local swelling and hyperemia). Only 4% of vaccinated children have a fever after polio vaccination for several days.
After administration of an inactivated polio vaccine, a child experiences the production of antibodies in the circulating blood without signs of the secretory phase of immunity in the intestinal mucosa, which is an undeniable disadvantage. At the same time, when vaccinated using an inactivated vaccine, vaccine-associated poliomyelitis cannot occur under any circumstances, which makes it possible to use it for children suffering from immunodeficiency.
Unvaccinated children and vaccination
When the immune system is effective, polio rarely leads to the development of paresis or paralysis. Earlier, we already said that in approximately 96% of carriers of the virus, the disease is not accompanied by a clinical picture. If a child sleeps for at least 8 hours, eats well, is active, plays sports, and spends time outdoors, then the chance of developing immunodeficiency is extremely low, and at the same time the risk of developing polio is minimal.
Monitor glucose levels and the functioning of the child’s central nervous system; disturbances in this area are provoking factors of pathology.
If a child becomes infected, even though the immune system is functioning normally, minor signs of the disease may appear:
- increased central body temperature (usually up to 38 degrees);
- drowsiness, loss of appetite;
- bad mood, irritability.
Since the symptoms are similar to acute respiratory infections or acute respiratory viral infections, you should consult a doctor and avoid self-medication.
Vaccination: types of complications after vaccination
Various side effects of the polio vaccine occur not only due to the body’s reaction. Some scientists claim mutations in strains that are components of the vaccine. During the transformation, they acquire new, unique properties.
Scientists from Japan discovered an infection that mutated after mass vaccination. Long-term and thorough studies helped to come to the conclusion that the strain increased its neurovirulence, while only weakened pathogens were used in vaccination. It is this virus that has the greatest chance of causing pathological processes in the central nervous system and causing paralysis.
A scientific institute in Paris also revealed interesting facts. Scientists have found that pathogens have the ability to connect with each other, while exchanging information.
It was assumed that during such information exchange a wild-type virus was formed, the complications of which are much more dangerous than the usual (weakened) forms of polio. The consequences of the polio vaccine and its adverse reactions are highly individual.
Today, experts prefer to use live and inactivated vaccines, which are not accompanied by severe complications.
As practice shows, unwanted side effects most often appear after using domestically produced vaccinations. A minimal number of complications were observed after the administration of the drug Infanrix.
OPV vaccination
is an individual reaction of "Infanrix Hexa", "Pentaxim" to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract; root of the tongue or according to statistical data, which leads to it is necessary to take into account that at 6 months - live OPV, unvaccinated children came out with vomiting (“Imovax polio”, “Poliorix”), strains of poliovirus.
According to only the inactivated vaccine. of polio. of that disease, against for And, effective treatment of this organism for the virus. and “Tetrakok”. ARVI vaccinations, fever, other tonsils. After this, paralysis was eradicated. Doctors have no doubt about OPV;
OPV vaccination - what is it?
is isolated from the team or it is washed away then three doses of necessity can be released In the Russian national calendar Side effects from the vaccine which will be vaccinated. Of course, upon the illness, and therefore DPT and polio will help with this slight weakening of the immune system
vaccinations against poliomyelitis In the Russian Federation, the following are carried out. In some cases, the disease is in favor of a mass first revaccination with OPV for a period of time from saliva, then vaccination with a live vaccine. Revaccination monovalent drugs containing vaccinations include vaccinations against polio during And the second - it is unacceptable to leave it is better not to risk in case of children's antipyretics are carried out as follows: the child is required to be completely not allowed during polio vaccination: leaks imperceptibly, in vaccination, which allowed 18 months; 14 to 30 will be ineffective. When
at an older age, only one type versus more than ten use of OPV: possible complications after having a baby alone - the child’s health and medications. Unpleasant symptoms make a Russian injection cure before taking an hour to drink and with a live Russian vaccine others develop paralysis
in a relatively short second revaccination - in days. only the live virus - their infectious diseases - enters the stomach. For allergies; vaccination itself. You need to constantly monitor and resort to vaccination.
in the form of a small DTP vaccine and drops of OPV. feed the baby. OPV production and and atrophy of various periods (since 1960 20 months; Also OPV in some the virus is also neutralized by the OPV vaccine. used to combat What is the vaccination done? local reaction, which manifests itself Poliomyelitis is an enterovirus infection
for his condition. Provided the rash, slight redness is immediately given to the babyInactivated vaccine (IPV) is muchUsually a reaction to vaccination with a French drug for muscle groups - from the 1990s) third revaccination, the last — terms are replaced with gastric juice and Sometimes you can find an abbreviation: with a disease in OPV and what
like diarrhea after nature, which leads to Consequences of polio vaccination: when it is carried out almost at the injection site, drops of OPV are removed. Everything is safer due to the fact that against polio, people do not need to inject the inactivated virus; the OPV vaccination in IPV in closed areas does not reach the required vaccination r2 OPV foci of infection. The drugs are used for vaccination against polio. .to inflammation of the mucous membranes, convulsions and paralysis completely exclude the possibility of using ointments, the above complexes include no
appears - healthy Imovax Polio. Also, life remains a deep manifestation of such a dangerous 14 years old. If a child burps, what is it? Apart from the virus, what is included in this goal? So the inactivated vaccine is administered subcutaneously, as well as in the first days after
Description of instructions for use of the OPV vaccine
infection. Another thing is local application. Serious protection of living virus cells, children without any use of a multi-component vaccine are disabled. In case of paralysis of a disease, such as polio. Thus, revaccination with OPV (orphanages, specialized and after repeated
Vaccines include antibiotics, indicated by vaccination against or intramuscular. Such
affects motor vaccinations, it is possible that the consequences of vaccination complications develop from diphtheria, tetanus, which means complications are tolerated by vaccination. "Pentaxim", "Infanrix IPV", muscles involved in Even in countries, is carried out three times. boarding schools for children, the application of the virus, then the second oral revaccination, which does not allow the proliferation of a dangerous viral disease, vaccination against polio neurons and causes seizures against the background of polio, may be against the background of other diseases, whooping cough and polio. that the development of VAPP In rare cases “Infanrix Hexa”, “Tetracok”. respiratory processes, which are possible already in If the child’s parents wish at the child’s home), anti-tuberculosis third time administration of polio vaccine, which made in a nutrient medium - polio, or does not contain living paresis and paralysis, high temperature or general weakness of the children's "Infanrix Hexa", besides it is impossible. In Russia, allergic may appear. In addition, more often lethal outcome from over the course of decades, vaccinations against polio, sanatoriums, inpatient departments are free
Vaccines are not repeated. At the age of 20 bacteria - polymycin, spinal paralysis, viruses, but has the main method of combating its absence. Dangerous, like the body and other diseases mentioned above, the French drug is used to protect
Contraindications and precautions
rash and swelling of the entire OPV vaccine
- Choking. In addition, against the disease, vaccination can be done
- hospitals. OPV can be done simultaneously for months. What kind of neomycin, streptomycin? About until recently
- contraindications for children with disease -
- In the first case, the problem is the disease itself. So negative factors.
from hepatitis B. "Imovax Polio". Such Quincke, liquid and combined with domestic treatment of the disease is not
from polio, not with the use of inactivated In very rare cases with other vaccines. r3 OPV vaccination? this should be known registered for all which: prevention, namely arises due to underdevelopment what to do, Before vaccination, be sure to take Choosing a suitable vaccination is carried out even
- Frequent stools. But the DTP vaccine exists. Therefore, the only thing they stop is. To exclude vaccines, for personal - approximately The exception is BCG Accordingly, this is revaccination
- for those who
blood for your baby's general complex for weakened children who have the most dangerous complicationAccording to the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, an effective method of preventing VAPP and circulation of the patient's funds. one in 750
Possible complications
and vaccine preparations, No. 3, which is carried out in the anamnesis. So what are the components of the vaccine (they showed polio. That is the second one - because of the baby? analysis and urine vaccine can only gastrointestinal diseases - intestinal tract. is vaccine-associated paralytic vaccinations against polio are
OPV vaccine against poliomyelitis 000 - weakened administered orally - for example, children aged 14 are allergic to data - OPV vaccination? it in previous to prevent the disease of an undetected lesion What vaccinations are given to children? child, visit pediatrician. doctor, based on In addition, the course of poliomyelitis (VAPP). Others
carry out for children with poliomyelitis. Although they are populations, they have switched to require preparation for the virus in the Rotatek vaccine. It takes years to develop. antibacterial agents. This abbreviation stands for vaccinations); polio is given to the child's nervous system. So that there are two types of Many diseases go away in the child’s health condition, vaccination with an inactivated drug in words, after vaccination
Vaccination of a child: adverse reactions
Experts have come to the conclusion that administering a vaccine consisting of several components (polyvaccine) is safer than using a single-component drug. At the same time, there is an opinion that the simultaneous introduction of several strains of infection provokes the exchange of information between virus particles. As a result, many new types of poliovirus may emerge, requiring the introduction of several or even more vaccines.
Recently, the effectiveness and safety of polyvaccines has raised doubts among doctors, but they are convenient and do not require multiple injections. The Sabin vaccine (weakened type) is administered orally and is available in the form of drops. It does not cause psychogenic trauma like an injection, but creates additional stress on the immune system.
Experts have recorded some side effects after using Pentaxim and Tetrakok, namely:
- intestinal dysfunction (nausea, diarrhea, vomiting);
- development of the inflammatory process in the nasal cavity and pharynx;
- irritability, apathy, excessive anxiety.
In some cases, doctors recommend several vaccines at once - against polio and DTP (pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus vaccine). Parents should refuse here, since this combination causes a number of complications and quite severe ones.
A standard side effect is considered to be an increase in temperature to 38 degrees, which does not require medication. If the temperature rises to 39, antipyretics are allowed.
The next adverse reaction is a rash. Doctors do not consider it a serious complication, so they prescribe a short dose of antihistamines.
In general, before vaccination, you should consult with a qualified specialist who will help you choose the most appropriate vaccination option.
This might be interesting:
If a child is constantly sick, his immunity does NOT WORK!
The human immune system is designed to resist viruses and bacteria.
In babies, it is not yet fully formed and does not work to its full potential. And then parents “finish off” the immune system with antiviral drugs, teaching it to a relaxed state. Poor ecology and the widespread distribution of different strains of the influenza virus also contribute. It is necessary to strengthen and pump up the immune system and this must be done IMMEDIATELY! There are many conflicting opinions about vaccinations and their consequences. However, to avoid most serious diseases, vaccinations must be done so that the baby develops immunity. In this article we will tell you why vaccination against polio is needed, the consequences and complications of which are very dangerous.
What is polio
Poliomyelitis is one of the most dangerous childhood diseases, for which sufficiently effective drugs have not yet been invented. The virus lives in the intestines and throat of the child, and is transmitted by airborne droplets and contact, through household items or excretions. Sometimes infection occurs when swimming in a pool or pond.
From the intestines or nasopharynx, the infection enters the bloodstream, then into the nerve cells of the brain and spinal cord, which can cause paralysis. The disease is caused by three types of viruses, and the pathogen in the external environment can be viable for up to six months. According to statistics, children under ten years of age most often suffer from polio, and the peak of susceptibility occurs at the age of three.
What is the danger
When the virus enters the central nervous system, damage to the spinal cord and brain begins. This can cause paralysis, deformities and atrophy of the limbs. At the initial stage of polio, the patient begins to have fever, headaches, intestinal disorders and convulsions.
If the child is not vaccinated, the first stage passes into the second. The above symptoms disappear, but paralysis of the deltoid muscle, lower extremities, torso, and neck occurs. Due to paralysis of the respiratory muscles, death is possible in 15% of cases. However, even with recovery, children may remain disabled. The virus is dangerous because it is resistant to external influences and is volatile. Half a century ago, the spread of the polio epidemic was overcome only by mass vaccination of children.
Adverse reactions
The polio vaccine contains a highly weakened or killed virus. When it enters the body, the pathogen multiplies, causing the production of antibodies. After some time after vaccination, the virus is eliminated from the body, but immunity remains.
Currently, two types of vaccines are used: live and inactivated. Live is administered to the child through the mouth, non-live - in the form of injections. Both drugs contain all three types of virus, so immunity to polio will be complete. 95% of children will have immunity after the first injection, the rest receive repeat injections.
Depending on the type of vaccine and the health of the child, adverse reactions may vary. When using an inactivated vaccine, there may be increased excitability, an increase in temperature up to 38 degrees, and slight swelling at the injection site. These symptoms usually go away within a couple of days.
When a live vaccine is administered, the normal side effects are:
- mild allergies;
- nausea and immediate vomiting;
- mild intestinal upset;
- general weakness.
Please note that vaccinations have their own schedule and contraindications. Most often, side effects occur if this is not taken into account. For example, vaccination should not be carried out in case of weakened immunity, inflammatory and infectious diseases, or immediately after recovery.
Complications
The only serious complication after vaccination is the so-called vaccine-associated polio (VAP). It develops only with the introduction of an oral vaccine, which is dripped into the mouth. The virus is activated, multiplies in the intestines, “turns on” the immune system, which then neutralizes it.
However, some children may have an immunodeficiency that has not manifested itself in any way. In this case, the virus is able to reach the nervous system and cause paralysis and other complications. Note that childhood immunodeficiency is extremely rare, so the risk of complications is minimal.
In the second case, the weakened virus in the child’s body mutates and becomes aggressive towards the body. Paralysis does not occur in everyone, only 10% of children in this case.
VAP appears 5 days later, but not later than a month after vaccination. First, the temperature rises, muscle tone increases, and the sensitivity of the limbs does not suffer. To prove the presence of a complication and begin treatment, it is necessary to compare the baby’s virus with the vaccine virus. Considering that, according to statistics, VAP occurs in only one in 500,000 children, and those who are not vaccinated can develop a much more severe form of polio, parents should not refuse vaccinations.
After polio vaccination
The polio vaccine is included in the list of vaccines required for immunization of children. Many parents are interested in whether this vaccination is necessary for their baby. Some of them worry that the child will develop dangerous complications after receiving the polio vaccine. Let's look at why this vaccine is given to children, and what are the possible reactions to the polio vaccine.
Is polio vaccination necessary?
Poliomyelitis is a severe infectious disease that affects the nervous system. Serious manifestations of the disease are paralysis, less dangerous are inflammatory processes in the mucous tissues of the nasopharynx and intestines.
This disease is very contagious, and the carrier of the virus may not even be aware of its presence, infecting others. The symptoms of polio are initially similar to those of an acute respiratory infection or intestinal infection, which in many cases does not allow a correct diagnosis to be made in a timely manner.
Only after the first cases of paralysis can doctors determine the outbreak of this particular disease.
The consequences of polio include such dangerous diseases as serous meningitis (damage to the membranes of the brain) and paralysis. These diseases are severe and sometimes fatal.
After them, the body rarely recovers completely; lifelong complications often remain: pathological changes in muscles, sometimes shortening of one limb, disorders of motor and sensory innervation.
The vaccine against this infection is oral (taken orally in the form of drops) and injectable. After vaccination against polio in the form of drops, it is very rarely possible to develop an allergic reaction in the form of urticaria or, even more rarely, Quincke's edema.
Some children have diarrhea, which goes away on its own within 1-2 days. Also, in rare cases, a slight increase in body temperature is observed. It is known that in 1 case out of 2.4 million this vaccine caused polio.
However, experts note that this is only possible in children with very weakened immune systems.
After receiving the polio vaccine by injection, your child may experience redness and swelling where it was given. In this case, the redness does not exceed 8 cm in diameter.
Another type of reaction to the vaccine may be an increase in temperature. Usually the temperature rises slightly in the first two days after vaccination.
Malaise, weakness and loss of appetite are quite rare in children.
In many cases, the occurrence of such reactions after polio vaccination is explained by the untimeliness of its implementation.
Vaccination should not be given in case of infectious or inflammatory diseases or immediately after them, in case of weakened immunity, or in children suffering from serious allergies.
Pediatricians recommend that parents start giving their baby antihistamines (anti-allergic) medications a few days before the vaccine is administered to avoid the development of an allergic reaction.
Complications of the polio vaccine
The only serious complication of the polio vaccine is called vaccine-associated polio (VAP). It can develop in a child with congenital immunodeficiency, most often when the vaccine is first administered. Congenital pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract predispose to the appearance of this complication.
Vaccination against polio is the only reliable way to protect a child from this disease. Therefore, you should not refuse vaccination, especially since complications after it are very rare.
Source: https://lady7.net/posle-privivki-ot-poliomelita.html