Author's rating
Author of the article
Shutofedova Ksenia Yurievna
General practitioner
Articles written
578
about the author
Herpetic sore throat is called differently in medicine. Among the synonyms for it are: herpangina, aphthous pharyngitis, vesicular pharyngitis, herpes sore throat.
The disease is part of a group of ailments of an acute infectious nature, serous in appearance, in addition to the signs related to tonsillitis, it is distinguished by a certain symptom - the presence of bubbles with liquid located on the back of the throat and on the soft palate.
The article contains information about the disease and treatment methods.
Causes, provoking factors
Vesicular pharyngitis is an almost viral type of this pathology, resulting from the entry of pathogenic microflora initially into the oral cavity of a person who has become infected, then there will be contact of the enterovirus infection with the mucous tissues of the pharynx.
Pharyngitis of viral origin is fundamentally different from other forms of the disease in that the symptoms of formation clinically look different compared to bacterial damage to the epithelium of the larynx.
What type of virus caused the disease can only be determined using laboratory diagnostics of smears previously taken from the surface of the pharyngeal epithelium.
- The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets during contact between a healthy person and an infected person.
- Spread occurs due to contact with the environment, which is saturated with pathogenic microflora (viruses).
- Pets may well be carriers of herpetic pharyngitis (dogs, cats, hamsters). If children are in rural areas, livestock, such as pigs, act as the source of infection.
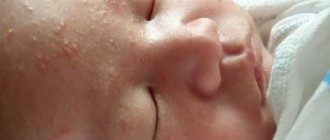
Vesicular pharyngitis in children under one year of age poses a particular danger to their health. Since there is a risk of harmful complications of various forms, which can be predicted by special tests that give a complete picture of the patient’s condition.
The reasons for the formation of pathology in children of different age categories are united by the following factors:
- Not maintaining personal hygiene. During the developmental period, a child virtually all the time comes into contact with objects that were not previously subject to processing. For example, the Coxsackie virus stays in the environment for about a month and its vital activity does not lose activity. If the baby took an object and then pulled his dirty hands into the oral cavity, then there is a high percentage of infection;
- Weak immune system. This is enough for viruses that have penetrated the surface of mucous tissues to easily surpass the level of adaptation and begin to multiply their numbers. In this situation, immune cells fail to cope with their responsibilities to protect the body from foreign biological agents, since the formation of vesicular pharyngitis occurs. The worse the state of immunity, the more pronounced the dynamics of inflammation in the pharynx;
- Seasonal epidemic of viral infection. In the spring-autumn period, due to excessive air humidity and the natural decline of the baby’s immunity, the virus enters the body with the subsequent development of the disease;
- Public places. Prolonged stay in crowded places, where crowds of people pass every day, increases the risk of vesicular pharyngitis, since any of us can be a carrier of various viral and infectious microorganisms, but the disease does not always express itself in an active form. If children go to kindergarten or school every day, travel on public transport, or eat in canteens, they are at risk for developing the disease.
Public places.
Causes
The main cause of the development of the disease is considered to be the penetration of a viral infection into the child’s body (rhinovirus, herpes or influenza virus, adenoviruses and other types of pathogens).
A number of factors are also known that increase the risk of developing exacerbations of the disease.
These include:
- Diseases accompanied by inflammation of the nasal mucosa . As a result of these pathologies, the process of nasal breathing is disrupted, the child breathes through the mouth, which leads to the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the throat area.
- Inhalation of too hot air , leading to burns and inflammation of the throat mucosa.
- Infectious diseases (for example, caries) localized in the oral cavity.
- Poor nutrition and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to frequent heartburn when gastric juice refluxes into the esophagus and pharynx.
- Persistent decrease in local immunity and general defenses of the body.
- Hereditary factor.
- Unfavorable living conditions (staying in a dusty room, passive smoking, prolonged inhalation of aggressive chemicals, poor ecology, living in regions with a harsh climate and high air humidity).
This situation is most dangerous in the cold season, when the risk of local hypothermia increases.
Features of the disease
It is not difficult to make a diagnosis of vesicular pharyngitis. Redness of the back wall of the throat and adjacent tissues, pain in the throat are noticeable - these signs are enough to establish this diagnosis. It is quite difficult to distinguish the viral nature of the disease from the bacterial one.
The cause of bacterial infection is streptococcus, staphylococcus. The presence of a pathological agent can be determined using a smear for culture. Based on the results of the data obtained, the sensitivity of bacteria to antibacterial drugs is revealed, due to this, the correct drug treatment is selected.
Viral pharyngitis has many symptoms (hoarse voice, cough, runny nose). If it is bacterial in nature, a high temperature is often noticeable, the lymph nodes are enlarged, pus is on the back wall of the pharynx and tonsils.
Causes of the disease
The causes of the development of chronic pharyngitis include:
- addition of a secondary infection to acute pharyngitis;
- mononucleosis;
- chronic runny nose , irritating the tissues of the pharynx for a long time;
- constant stay or living in conditions of too dry air ;
- constant exposure of the pharyngeal mucosa to allergens ;
- foreign bodies getting into the throat.
It is the cause that determines the further course of treatment.
Symptoms
Enteroviral pharyngitis mainly affects children, but in special situations adults are also susceptible to the disease. Children under three years of age have a hard time with this pathology.
The disease is characterized by:
- Severe pain in the throat area;
- The body aches due to intoxication;
- Headache;
- Increased body temperature reaching maximum levels;
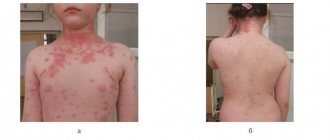
- Skin rash (small dots on the walls of the throat).
The patient may experience abdominal pain and noticeable inflammation in the lymph nodes. Children have seizures. The virus, penetrating the body, adapts in it for some time, and after a couple of weeks makes itself felt. The incubation period ranges from 7 to 14 days. The first sign is weakness, loss of strength. The patient has no appetite. Afterwards, fever, pain and discomfort in the muscles occur.
The main symptom is a sharp sore throat. A person loses the ability to eat normally, even drinking liquid becomes unbearable.
Next comes: discharge from the nasal passage, increased salivation, cough.
In adults, the disease resolves with minimal symptoms, and virtually no complications remain. More severe symptoms in children. The child feels tired and the temperature rises. The disease is accompanied by copious mucus discharge from the nose and severe salivation.
Pharyngitis in children often manifests itself not as an independent disease, but as an additional symptom of ARVI, measles, and influenza. In such a situation, the form and subtype of pharyngitis is determined by an experienced specialist.
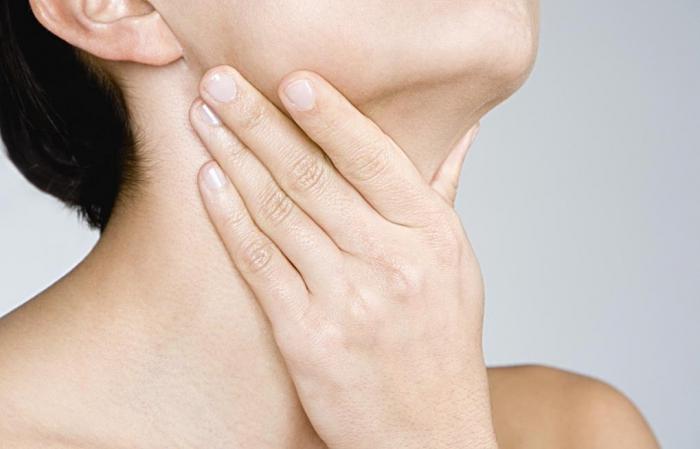
Severe pain in the throat area.
Prevention
There are no specific measures to prevent the occurrence of vesicular pharyngitis. But you can protect your body from viruses if you follow some recommendations:
- Periodically take vitamin complexes and immunomodulating agents.
- Follow some nutritional rules. Food should be rich in vitamins and minerals, easy to digest and assimilate. Alcoholic drinks, spices, herbs, fast foods and semi-finished products are excluded.
- Play sports and do exercises every morning.
- Temper the body with douches, contrast showers, and walking barefoot on grass and stones.
- Always ventilate the room and humidify the air in it.
- Observe hygiene measures. After each return from the street, you should wash your face, hands and nose with laundry soap.
- During seasonal exacerbations, avoid visiting public places.
- In the presence of chronic pathologies, treat the disease in a timely manner.
The Coxsackie virus is an insidious type of pathogen. It can remain in the body for a long time and not manifest itself in any way. The danger is that it is much more difficult to tolerate in childhood and can lead to serious complications. Therefore, doctors give advice: at the first symptoms, contact a doctor immediately and do not self-medicate.
The next video will talk about the disease vesicular pharyngitis.
Diagnostics research methods necessary tests
Considering the fact that the symptoms of vesicular pharyngitis are similar to influenza and ARVI, diagnostic methods must be quite serious. Self-diagnosis should not be done, especially in children.
Diagnostics includes:
- Serological study. To do this, you need to take pharyngeal serum, first days of illness, and then after two or three weeks. This makes it possible to monitor the intensity with which the process of antibody proliferation takes place;
- Virological research. The material used is pharyngeal swabs. They are taken for five days of illness;
- The immunofluorescence method is an accurate method for examining vesicular pharyngitis. The material for analysis must be treated with special fluorochrome antibodies;
- Blood analysis. Able to identify the nature of the viral nature that affects a person;
- Infection of a healthy body. In order to determine Coxsackie viruses, a healthy human body (laboratory mouse) is subject to infection with biomaterial that is taken from a sick patient;
- Nasopharyngeal rinses.
Coping with the diagnosis of vesicular pharyngitis is not difficult for a doctor, but you should not do it yourself.
If you discover signs of this pathology, you should immediately visit a doctor. Timely treatment will protect against possible complications. Because children often suffer from this disease, and their bodies are weak and susceptible to harmful consequences.

Immunofluorescence method.
Complications after illness
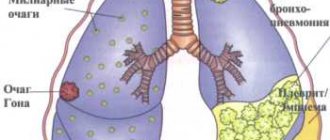
Vesicular pharyngitis can cause serious illnesses, including serous meningitis. This disease is especially dangerous for infants and can even cause death. Therefore, it is very important to consult a doctor at the first signs of the disease and begin treatment immediately.
Herpangina can cause liver disease. The virus can settle in this internal organ and begin its destructive activity, which leads to serious damage to the liver.
As an exacerbation, necrosis of muscle tissue can also be observed.
In children under three years of age, the symptoms of the disease are much more pronounced; it is very difficult for them to cope with the disease; moreover, children can often experience complications in the form of:
- pyelonephritis;
- myocarditis;
- hemorrhagic conjunctivitis.
If complications occur, the patient will need to be urgently hospitalized.
Treatment
Proper therapy for herpangina includes complex treatment. It is worth observing bed rest and following a diet, this will enable the body to overcome the virus. By adding medications to the treatment method, recovery will occur in a short time.
Helpful Tips:
- When diagnosing vesicular pharyngitis, you need to adhere to bed rest, because the temperature may be high;
- Diet: food – warm, solid food is excluded, liquid is preferable. Because the sore throat will not be damaged by coarse particles. Irritable foods – taboo (spicy, sour, fried).
- Drinking plenty of fluids quickly removes viruses from the body;
- Do not strain the vocal cords, this causes inflammation.
Medication
Treatment of vesicular pharyngitis is not complete without taking medications. They eliminate symptoms, eliminate the virus and normalize the condition.
Mainly prescribed:
- Immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs (Arbidol, Cycloferon, Kagocel, Remantadine).
Remantadine.
Remantadine is an antiviral drug that suppresses viruses at the initial stage of the disease. Take the product orally, swallow the tablets whole, do not chew or crush them in advance. Take the required amount of water, dosage and
Duration of treatment is individual.
- Adults - 2 tablets, 3 times a day, on the first day of illness - two tablets 2 times a day, on the 2nd, 3rd days - 2 tablets once a day, on the 4th and 5th - 2 tablets once a day.
- Children from 7 to 10 years old – 2 tablets twice a day; from 11 to 14 years – one tablet three times a day.
Arbidol.
Arbidol - has a certain antiviral spectrum of action, has a direct effect on viruses, promotes the formation of interferon in the body and increases the body's resistance to viral infections.
- Adults – 0.2 g (2 tablets), 4 times a day for three days (before meals).
- Children from 2 to 6 years old – 50 mg; from 6 – 12 – 100 mg, children from 12 years old – 200 mg – once a day.
The course of treatment is from 10 to 14 days.
- Antiseptics for pharyngeal irrigation. They act directly on the site of inflammation (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin);
- Antihistamines. Relieves swelling from the surface of the mucous membranes and normalizes breathing. For children - drops Zyrtec, Zodak. Adults - Suprastin, Diazolin, Tavegil;
- Lozenges. Children over six years old are allowed. They relieve pain and have an antiseptic effect (Doctor Mom, Strepsils, Doctor Theis).
The course of treatment is from 10 to 15 days.
In children, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis, under the supervision of the attending physician. As a rule, children are not prescribed antibacterial drugs, only in addition to a bacterial infection.
If the child has not learned to gargle himself, the procedure is done using a syringe. The baby's head tilts down as much as possible.
Treatment of pharyngitis in children
When a child gets sick with pharyngitis, you should never neglect treatment and hope for an independent recovery. During therapy, several important principles , which largely determine the success of treatment:
- You should avoid food, the consumption of which leads to irritation of the mucous membranes. The diet should not include spicy, sour, salty, extremely cold or hot foods.
- You need to drink a lot, it is better if it is mineral water without gases, milk, weak tea. Drinks must be warm.
- Rooms where the child is present should be regularly cleaned and ventilated.
Cooling compresses are not recommended for treatment if the baby has a fever, as well as ointments for rubbing the neck - in particular, this is what Dr. Komarovsky, a recognized authority in pediatrics, recommends.
Based on the specific type, pharyngitis is treated with various antiviral or antihistamine drugs . Sometimes they are used in combination; the selection of one or another remedy for treatment is determined not only by the severity of the disease, but also by the age of the small patient, so that the therapy does not harm him from the environment. Based on this, independent selection of specific drugs is not allowed.
Acute pharyngitis or exacerbations of chronic pharyngitis are treated by eliminating the main symptoms; for this, treatment is indicated:
- Warm neck compresses
- Antiviral agents, for example, Acyclovir and the like
- If the temperature has crossed the line of 38 degrees, then children's remedies for relieving fever are indicated.
- Mucolytics that thin sputum
- Gargling with various herbal decoctions, both prepared according to folk recipes and the well-known Miramistin
- Rinse the nose with drops with immunomodulatory properties
- Inhalations
- If there is no fever, hot foot baths can be used
To treat viral pharyngitis, Komarovskim recommends gargling with plain warm water to wash away the plaque accumulated there. If pure water seems insufficient, then it is permissible to add soda or salt in the amount of one teaspoon per glass.
Antibacterial agents are used in various forms, these can be absorbable tablets, sprays. Usually, in addition to the antibiotic, they contain contents that irrigate and cleanse the surface of the pharynx.
The use of systemic antibiotics is allowed only if children are diagnosed with complicated bacterial pharyngitis. A specific medication is prescribed only by a doctor.
Inhalations are also very effective in treating pharyngitis in children. It is better to carry them out using a nebulizer, up to four times a day, for this purpose the following is suitable:
- Mineral water Borjomi
- Saline solution with propolis or calendula
- Furacilin in the form of a solution
Inhalation is a very effective and affordable remedy, but treatment with their help must also be approved by the doctor after examining the child. Only under such conditions will it be possible to correctly select a specific liquid that does not cause an allergic reaction or other consequences.
Complications that pharyngitis can cause
In a situation where the child was subjected to inaccurate treatment or it was completely absent, there is a high probability of negative consequences when the upper respiratory tract is affected, with an increased risk of:
- Otitis, when the middle ear becomes inflamed
- Tonsillitis or sore throat
- Lesions of the nasopharynx in the form of sinusitis or rhinitis
- Transition of inflammation to the eyes, resulting in the development of conjunctivitis
- The appearance of meningitis, when the brain is exposed to infection.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is recommended as a complement to drug treatment. Home remedies can help you improve your health.
Rinse
Sanitation of the pharynx with herbal decoctions is one of the simplest methods of treating pharyngitis. For a glass of water - a dessert spoon of chamomile. You need to rinse with warm broth, both before and after meals. Sage - quickly removes the inflammatory process, brew in the same proportions as chamomile, let it brew for one hour.
Mixtures
You will need 10% alcohol, glycerin or peach oil, mix, proportions: 1:2, lubricate the back wall of the throat with a cotton swab.
Propolis – small pieces, slowly chew well in the mouth, after eating, to naturally lubricate the throat.
Inhalations
Inhalations based on pine cones (20 gram cones are placed in boiling water, 250 ml.) will help get rid of the acute form.
Mix mother and stepmother (5g) with string (5g). Throw into a glass of boiling water, then leave for an hour, use for inhalation.
Compresses
Chamomile is useful not only for gargling, but also for compresses on the throat area. One tablespoon of herb is poured into two glasses of water, boiled, then strained and infused. Then soak gauze in the resulting product and apply it to the neck. Keep the compress until it cools.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is provided as an additional procedure in the treatment of vesicular pharyngitis. It is used to eliminate an exacerbation of the disease when there is no fever.
- Electrophoresis with drugs removes swelling and reduces inflammation.
- Laser irradiation and ultraviolet are used in some cases.
7 to 10 sessions are recommended.
Electrophoresis.
Forecast
Herpangina is a representative of severe pathologies. With the right therapy, the patient recovers after 10–15 days.
Next, immunity to viral infections is developed. According to some doctors, relapse is rare.
Others are inclined to believe that infection can occur again, since the infection has different forms. However, the course of the disease will not be long or severe.
Vesicular pharyngitis: etiology
Previously, the diagnosis of herpetic sore throat was extremely rare, but now it is becoming increasingly widespread, especially among children. The infection can be contracted through airborne droplets and also after contact with animals, for example, pigs.
Vesicular pharyngitis is very complex and progresses quite quickly. But if you suffer such a pathology at least once, you can gain, if not immunity, but the body’s resistance to the viral agent.
The disease is most severe in children under one year of age; adults tolerate it much more easily.
Possible complications
With improper and untimely drug therapy, vesicular pharyngitis gradually becomes chronic and entails a number of complications:
- A gradual decline in immunity to a minimum level, then the body becomes sensitive to various infections;
- Transition of the inflammatory process to the upper respiratory tract and other organs, which also join the pathological process;
- The launch of atrophic processes in the pharynx due to the persistent presence of viral foci in it that destroy epithelial fibers;
- Pharyngitis acquires the viral degree of chronic tonsillitis.
Taking into account the severity of the enteroviral disease, the baby may develop other types of harmful consequences. Much depends on the personal characteristics of the body, and on the course of the pathology.

Decline of immunity.
Classification of pathology
Depending on the course and presence of characteristic manifestations, the following types of chronic pharyngitis are distinguished:
- catarrhal , in which there are no changes in the tissues of the mucous membranes of the throat;
- granulosa, which is characterized by compaction of mucosal tissues, the formation on its surface of specific granules-bubbles filled with purulent contents;
- the atrophic form is characterized by thinning of the mucous membrane of the throat and its dryness.
Depending on the area of the lesion, chronic pharyngitis can be limited (the inflammatory process covers only certain areas of the mucous membrane of the throat) or diffuse (the focus of inflammation is more extensive and can also affect the mucous membranes of other organs of the respiratory system).