What is the normal blood sugar level during pregnancy?
In healthy pregnant women, average fasting glucose levels are 3.8-4.2 mmol/L. An hour after eating, glycemia should remain in the range of 5.8-6.0 mmol/l. If a woman has diabetes or develops hypertension, the goal of treatment is to bring glycemic levels as close to normal as possible.
According to doctors’ recommendations, pregnant women with diabetes or HD need to achieve the following glycemic values:
- Fasting glucose – ≤5.3 mmol/l.
- An hour after eating – ≤7.8 mmol/l.
- 2 hours after eating – ≤6.7 mmol/l.
Another important indicator of the presence of sugar metabolism disorders in pregnant women is glycosylated hemoglobin HbA1c, which displays average glycemic values over the past 6-8 weeks. Normally this figure is below 6%. In diabetes or hypertension it increases.
Increased glucose levels
Many pregnant women suffering from hypoglycemia wonder what foods increase blood sugar in pregnant women and what they need to eat in order for their blood glucose levels to return to normal. The consumption of carbohydrates is responsible for high sugar levels during pregnancy. It is they that increase the indicators and therefore are contraindicated for diabetics who have high sugar during pregnancy.
Carbohydrates are found in all foods, but in varying quantities. Therefore, some foods affect the indicators significantly, while others less. The easiest and fastest way to normalize low sugar is to eat simple carbohydrates, which are easily digestible and have a significant effect on blood glucose levels. These are carbohydrates contained directly in candy. But if the norm of sugar from a vein or finger during pregnancy is constantly reduced, then you need to consult a doctor to prescribe treatment.
In what cases are deviations observed?
During pregnancy, blood sugar can go beyond normal limits in one direction or the other. This is due to the fact that during pregnancy, the metabolism of carbohydrates in the female body is changed.
Many pregnant women experience hypoglycemia, that is, a decrease in sugar below normal limits . This is manifested by increased hunger, sweating, weakness, dizziness, fatigue, hand tremors, and irritability. One of the causes of hypoglycemia is drug therapy for diabetes or HD, in which case it can be very severe and life-threatening.
Very often, due to hormonal changes, mild hypoglycemia may occur in pregnant women without diabetes, especially at night. In this case, women wake up in the morning with headaches and fatigue, which are relieved after eating food.
The cause of hyperglycemia - increased blood sugar - is most often diabetes or hypertension.
Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which the amount of glucose in the blood is increased. The cause of this disease is a lack of insulin due to the destruction of the pancreatic cells that produce it. These cells are destroyed by the body's own immune system due to autoimmune processes.
As a rule, type 1 diabetes mellitus appears in childhood and young adults, so this form of the disease is more often observed in women at the time of pregnancy. Heredity and environmental factors, such as viruses, bacteria, toxins, and the nature of feeding in infancy, play a role in the development of diabetes.
Doctors believe that gestational diabetes is caused by hormonal and metabolic changes during pregnancy, combined with genetic susceptibility and environmental factors. These factors contribute to the development of insulin resistance, which appears in all women in the 2-3 trimester. Due to insulin resistance, the need for insulin necessary for glycemic control increases.
Like type 2 diabetes, HD is associated with excess weight. Another factor that increases the risk of this disease is a family history of diabetes, which emphasizes the role of heredity.
The risk of developing gestational diabetes is increased in women:
- over 25 years old;
- having a close relative with diabetes;
- obese;
- having polycystic ovary syndrome;
- taking corticosteroids (to treat autoimmune diseases), beta blockers (for hypertension and tachycardia) or drugs to treat mental disorders;
- having HD in a previous pregnancy;
- who gave birth to a high birth weight child during a previous pregnancy.
Since changes in the body's hormonal status usually subside after childbirth, gestational diabetes disappears over time in most pregnant women.
Exposure to hyperglycemia in utero increases the child's risk of developing obesity or type 2 diabetes later in life.
Gestational diabetes
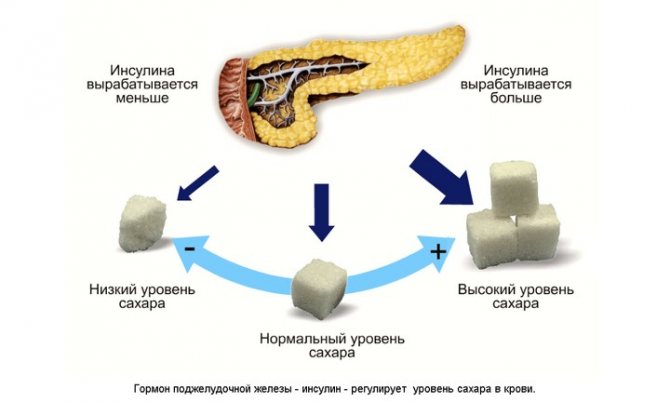
This type of diabetes means disruptions in metabolic processes caused by hormonal changes in the body during pregnancy. The main symptom of GDM is high sugar levels in the body. The disease is diagnosed mainly after a glucose tolerance test, since the fasting values of most expectant mothers are within the normal range.
The beginning of such a pathological process is explained quite simply. After all, after conceiving a baby during pregnancy, hormones begin to be strongly produced and by 5-6 months they reduce the sensitivity of cells to insulin, which is why sugar increases.
Insulin is a hormone responsible for transporting glucose, resulting in a person receiving energy. With its deficiency, hyperglycemia occurs, and then diabetes. The reasons for the gestational type of this pathology are the same, but this disease does not occur in everyone and for convenience, you can familiarize yourself with the risk groups:
- Childbirth after 30;
- Hereditary predisposition, especially on the maternal side;
- Overweight;
- Having 3 or more abortions;
- Gestational diabetes was already diagnosed last time;
- Abundant amount of amniotic fluid;
- Last time a child was born with a pathology or there was a miscarriage.
Doctors usually advise expectant mothers to think about it if they have 2 or more factors that can lead to GDM. In such a situation, the girl will need to undergo examination by an endocrinologist, and at the same time begin to monitor the concentration of glucose in the blood. The only positive thing that doctors are encouraging about is the disappearance of GDM after childbirth. This does not happen in all cases, and if you do not go on a diet and do not control the course of the disease, the pathological process can develop into full-blown diabetes.
How to get tested?
All pregnant women should be screened for diabetes and hypertension at 24-28 weeks.
For this purpose, the following is carried out:
- Fasting blood test for glucose levels.
- Glucose tolerance test.
- Determination of HbA1c.
The test is taken on an empty stomach. Blood is taken capillary, from a finger, using a small injection with a scarifier. To determine the HbA1c level, blood is drawn from a vein. When performing a glucose tolerance test, a woman first drinks a certain amount of a sugary drink, and the sugar levels are measured 1 and 2 hours later.
Signs of high sugar in women
A woman should immediately consult a specialist if she has a pathological thirst, the number of trips to the toilet has increased, or she has a feeling of dry mouth. A rash may appear periodically, which does not go away for a long time, and visual acuity decreases.
Important! Pregnant women often do not pay attention to the symptoms of hyperglycemia, because they consider them to be manifestations of an “interesting situation.”
To confirm that sugar is really elevated, the patient’s complaints will be few. The doctor will definitely prescribe laboratory diagnostic methods, including the following methods:
- capillary blood test for sugar;
- biochemistry;
- glucose tolerance test (sugar load test);
- determination of glycosylated hemoglobin indicators.
In addition, the woman is advised by a neurologist, ophthalmologist, surgeon, and cardiologist.
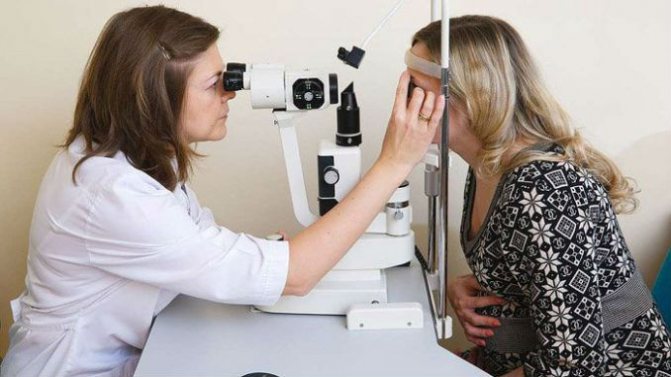
Fundus examination is one of the stages of ophthalmological examination during pregnancy.
How to normalize blood sugar?
During pregnancy, treatment for high blood sugar depends on the type of condition. If a woman has type 1 diabetes diagnosed before or during pregnancy, she will likely need insulin injections. However, it is very important to carefully control glycemia, as pregnancy can greatly affect blood glucose levels.
In pregnant women with gestational diabetes, drug treatment is necessary in only 10-20% of them; in other cases, blood sugar can be brought back to normal through lifestyle changes.

Regardless of the type of diabetes, diabetes mellitus or gestational, all pregnant women with this disease need to:
- Monitor your blood sugar carefully.
- Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables and whole grains, while limiting foods with easily digestible carbohydrates.
- Engage in moderate intensity physical exercise.
If these measures do not help normalize blood sugar during pregnancy, patients need therapy with insulin.
A very important part of treating diabetes in pregnant women is to carefully monitor the condition of the baby, its growth and development inside the uterus. Elevated levels of sugar in maternal blood lead to the presence of hyperglycemia in the fetus.
Because of this, if diabetes is poorly controlled during pregnancy, a woman may have a baby with the following problems:
- High birth weight increases the risk of childbirth for mother and baby.
- Hypoglycemia immediately after birth.
- Respiratory distress syndrome, manifested by respiratory failure.
- Increased risk of death after birth.
- Jaundice.
Such children are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes and obesity in the future.
An increase in blood sugar levels above normal is a common condition, occurring in approximately 10% of pregnant women. It is very important to identify it in the early stages of gestation, before the baby is harmed. That is why all pregnant women must undergo screening for diabetes mellitus or gestational diabetes.
Author: Taras Nevelichuk, doctor, especially for Mama66.ru
Glucose tolerance test
The glucose tolerance test (GTT) is used to determine the degree of sugar absorption, and it is its indicators that doctors focus on when diagnosing diabetes. It is carried out for any suspected pathology, including in a prediabetic state, as well as during pregnancy. The goal of GTT is to detect the presence of the disease in time and begin treatment or prevent further development.
The tolerance test is carried out after a basic fasting blood test and it is advisable that the patient does not have any health problems before the examination. After all, any cold can slightly change the composition of the blood, and even more so the medications that are taken to eliminate it. If it is not possible to fix the problem, you will have to take into account some errors when obtaining test results.
When the results of the first test become known, the girl will have to drink glucose dissolved in water in order to do another test an hour later. Next, a control blood sample is taken and from this it will be clear whether the pregnant woman has GDM or not. The essence of this process is that after taking dissolved glucose, a healthy person’s sugar will jump sharply, but after 2 hours it will return to normal. In GDM, this does not happen, since the cells are less able to perceive the insulin produced by the pancreas.
The endocrinologist will be forced to make such a terrible diagnosis as gestational diabetes mellitus with the following results:
- After taking the morning test on an empty stomach – 5.2>;
- During GTT after 1 sampling - 10>;
- After 2 fences – 8.5>.
Despite the disappointing forecasts, after the first series of tests the diagnosis is not yet accurate and it will be finally made only after repeated procedures in 2-3 days. GTT is performed 2 times due to possible disorders in the body that affected the results:
- Failure to comply with the rules of preparation before the study;
- Eating fatty foods or alcohol shortly before blood collection;
- Endocrine disruptions;
- Potassium deficiency.
If both tests show results close to each other, which are above the permissible norm, the doctor will diagnose gestational diabetes mellitus. A pregnant woman in such a situation will need to consult an endocrinologist, as it will be necessary to prescribe a course of treatment and adjust the diet. In many cases, physical education is also added to this, because sport has a positive effect on metabolic processes in the body.
Once you have received all the instructions, you will need to see your doctor regularly and it is recommended that you purchase a glucometer to monitor your sugar levels at home. In addition to the mother, the child will also need to be examined, since it is important to know whether the fetus is growing correctly and whether there are any abnormalities.
5-6 months after the baby is born, the new mother will have to undergo GTT again. The results of this test will be very important, since it will be based on them that it will be possible to judge whether the pathology has gone away or whether diabetes mellitus remains permanent.