What is such a tumor?
Hemangioma in newborns is a benign formation formed due to changes in blood vessels. In approximately 75% of cases, it disappears on its own by the time the child turns 7 years old.
However, the tumor still needs to be constantly monitored, because if it begins to grow rapidly and change color, you need to urgently consult a doctor. In such situations, as a rule, the hemangioma is removed. They also resort to excision of the formation if the child constantly injures it, which can lead to bleeding .
If the increase in the purple birthmark occurs in proportion to the growth of the baby, it does not pose a threat to life. Such formation causes only cosmetic discomfort .
What it is
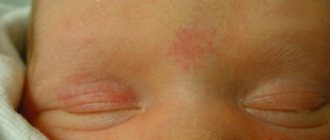
Hemangioma in a newborn is determined after birth. Visually, it resembles a spot that has a reddish color.
This tumor can be classified as benign; it has compactions and uneven edges. Hemangiomas in newborns are a collection of normal and optical cells.
Statistics show that newborn girls have education 2 times more often than boys.
The main characteristics of hemangiomas are as follows:
- There are 4 types of vascular tumors, differing from each other in color and shape. There are cavernous, flat, star and strawberry types.
- Their normal growth involves a gradual increase in size of the spot, corresponding to the growth of the child. In this case, the color should not change.
- In order to make sure that the baby has a vascular tumor, you need to lightly press on it. Confirmation of the guess will be the fading of the formation or the complete disappearance of the previous color.
- The tumor should not cause discomfort to the baby, as well as its growth, the increase of which is caused by stressful situations.
- Hemangioma in an infant has a temperature slightly different from other tissues.
- There are external and internal formations. Quite often, children are born with tumors on the face. They appear in the nasal and frontal parts.
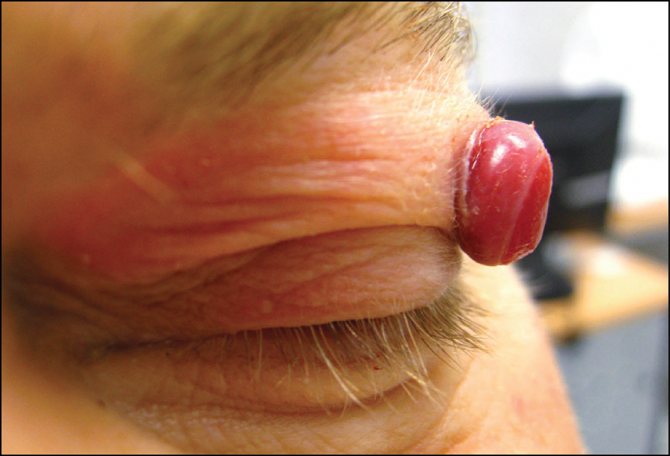
The danger comes from formations located in the eyelid, ear, oral mucosa, and lip, because they may not have the best effect on their functioning.
- As a rule, growth occurs in the first year of a baby’s life, then it stops. The compaction gradually decreases in size until it disappears completely.
- Hemangioma on the head and other areas of the skin in 75% of cases goes away without a trace in children. By about the age of 8, nothing reminds her of her. But there are also 25% of cases in which, unfortunately, treatment cannot be avoided.
Types of hemangiomas in infants
This tumor in newborns can come in different colors and sizes. In addition, it has a different location, everything depends on the type of formation, the degree of damage to the vascular beds and its growth into the tissue. Hemangiomas in children are divided into the following types:
- Cavernous or cavernous . Such tumors consist of dilated large vessels. They affect subcutaneous fatty tissue and can form in bone and soft tissues, as well as on internal organs: spleen, liver, kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Simple or capillary . These formations differ from others in their small size and smooth surface, although sometimes they are lumpy or knotty. Most often they are found in the eyes, forehead and head, affecting mainly only the skin. Such spots are vascular tangles of small capillaries.
- Combined or mixed . Such tumors are considered the most dangerous. They may have symptoms of a capillary neoplasm, but in reality they are a combination of simple and cavernous hemangiomas. Their main difference is that they affect not only capillaries, skin and hypodermis, but also muscle and nervous tissues.
Kinds
Depending on the structure and location of the tumor, the following types of hemangiomas are distinguished:
- Capillary – located on the surface of the skin and consists of small vessels (capillaries). When pressed, it turns pale and then returns to its original color.
- Cavernous - formed by expanded cavities that are filled with venous or arterial blood. If a newborn strains (while crying, coughing), such a hemangioma increases in size.
- Combined - consists of supracutaneous and subcutaneous parts.
- Mixed - contains not only vascular tissue, but also cells of other tissues: lymphoid, adipose, connective or nervous.
Hemangioma of the nose, eye, ear, larynx can lead to disruption of the functioning of the corresponding organ in the infant. The prognosis is also poor for those tumors that are located in the area of constant rubbing with clothing. This can lead to frequent injury to the tumor.
Location of hemangioma
As mentioned earlier, in many cases such formations do not threaten the child’s life unless they develop in the internal organs, causing bleeding. Mostly such tumors are localized on the skin, spoiling the appearance and creating great discomfort for the baby.
According to statistics, hemangiomas affect:
- Internal organs - 1%;
- Face and head - 80%;
- Legs, arms, stomach and neck - 5%;
- Eyelids - 2-3% of all cases.
A hemangioma on a baby's head has one rather unpleasant property - it can spread and destroy neighboring tissues . If the tumor is removed incorrectly, there is a high probability of scarring.
Symptoms and diagnosis of capillary hemangioma
Any irregularities with a characteristic pink or red tint on the body of a newborn may be a manifestation of capillary hemangioma.

Hemangioma in a newborn baby
At birth, the neonatologist will immediately note the type of formation and recommend monitoring it in terms of enlargement. As a rule, the tumor develops before the age of three and completely disappears by the age of five. If a tumor is detected in an adult, you should consult a dermatologist. The branch of medicine - dermatology - studies diseases of the skin, determining whether the formation is oncological or dermatological.
The most common location of neoplasms is the neck and head area. It is impossible to predict how benign cancer will behave. It is possible for the formation to quickly increase to a large size and, in most cases, completely disappear from the skin. Particular attention should be paid to neoplasms in the respiratory tract and organs, as well as the eyes, since rapid growth can lead to problems with hearing, vision and breathing. At the slightest manifestation of unclear rashes on the skin, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Due to the pronounced appearance of skin formations, diagnosis is carried out primarily by visual examination. By pressing on the protruding spot, it is possible to highlight the change in color, from bright to pale.
Before making a diagnosis, the doctor takes a complete history of the woman’s pregnancy to identify the causes.
If there is more than one formation, additional studies are performed using ultrasound, taking into account the likelihood of formations on internal organs. Ultrasound reveals the structure of the hemangioma and its volume.
MRI and radiography help determine neoplasms of internal organs with the accuracy of their location and size. Angiography is performed by injecting a substance under CT guidance to determine the speed and intensity of contrast spread in the capillaries of the formation.
Capillary hemangioma
Detection of internal tumors becomes a direct indication for surgical intervention. Rupture of capillary hemangioma occurs in selected organs, which leads to death.
Provoking factors for the development of hemangioma
Doctors have not yet established the exact reasons for the appearance of such neoplasms in newborns. However, there are still some assumptions:
- Taking strong medications and suffering from illnesses while carrying a baby. For example, if a pregnant woman catches a cold at 3-6 weeks, the risk of hemangioma in the baby increases, since the development of the cardiovascular system occurs during this period.
- A polluted environment has a negative impact on the baby during its embryonic development. Such conditions lead to an increase in tumor cells.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages and smoking during pregnancy also increases the risk of neoplasms in the child.
- Hormonal imbalance in the expectant mother or newborn can also affect the formation of a vascular tumor.
- Multiple pregnancy can also provoke the appearance of hemangioma in a child.
In addition to all of the above, the appearance of such a birthmark can be affected by the age of the expectant mother, especially if it exceeds 38 years. Premature babies with low birth weight are several times more likely to develop tumors than healthy babies.
Hemangioma most often becomes noticeable already at 2 weeks of a child’s life; there are cases when the disease develops during the first year after the birth of the baby.
Not just a defect
The term "hemangioma" comes from the Greek "haima" - "blood" and "angeon" - "vessel" and means a benign vascular tumor. This neoplasm looks like a bright red or slightly bluish spot. This defect is usually congenital or appears in the first weeks of life. Hemangiomas come in different sizes and can be located both on the face and body of the child. Sometimes there are several such spots at once. The reasons for their occurrence are not completely clear, but there is an assumption that this can be caused by colds that the expectant mother suffered from in the first two months of pregnancy, when the formation of the child’s vascular system is underway.
The most common myth about hemangioma is that it can develop into cancer. In fact, such cases are extremely rare. But waiting until everything resolves itself, as, by the way, the second myth advises, is also not always worth it. Indeed, despite the fact that sometimes hemangiomas do go away on their own, this does not always happen. And usually this takes many years (from one and a half to ten or more). Neoplasms located on areas of the body covered by clothing eliminate themselves. And spots on the face, head and neck, as a rule, do not disappear. Hemangiomas grow with the child and especially rapidly - up to six months. They increase in size most quickly in premature babies. It is better to show a baby with such a tumor to a doctor as soon as possible. Indeed, in addition to a cosmetic defect, a vascular tumor threatens with very unpleasant things.
Article on the topic
Cut or leave? 5 signs that it is better to remove a mole
If the hemangioma is located where it is easily damaged, for example by constant rubbing against clothing, it can lead to the development of infected ulcers. Another potential danger is damage to nearby tissues. So, if, for example, the hemangioma is located in the eye, ear, nose or mouth, the baby may experience visual impairment, hearing impairment and even difficulty breathing. In addition, a vascular tumor can begin to grow in width, growing into internal organs. And if the hemangioma is extensive, then it is possible that thrombocytopenia will develop - a deficiency of platelets in the blood, due to which the blood begins to clot poorly.
Diagnostic measures
Before prescribing effective treatment, you will have to pass all the necessary tests. First of all, the pediatrician must differentiate the vascular formation from other pathologies in order to exclude angioma or squamous cell carcinoma. Moreover, this tumor is sometimes very similar to certain types of cysts, nevi, pyogenic granuloma and vascular malformations.
The doctor may order a CT or MRI to determine the extent of skin destruction. If there is a suspicion of malignancy, a biopsy is used. For such a microscopic examination, some tissue will be taken from the baby from the affected area. After an accurate diagnosis is made, subsequent therapy is prescribed depending on the progression of the tumor.
What does a hemangioma look like?
Capillary hemangioma is also called strawberry nevus or juvenile hemangioma. At birth, it may look like a small red dot or tiny speck, but after a few weeks the formation begins to actively grow, slightly changing color, and becomes quite noticeable. Often, upon careful examination of the hemangioma, you can see a vascular pattern on it, and small blood vessels may extend from the spot, which gives the formation a resemblance to a spider vein. The surface of capillary hemangioma is usually smooth, and the formation itself only protrudes slightly above the surface of the skin. When you press on it, it turns sharply pale, and when there is no pressure, it acquires color again.
Vascular formations most often appear on the skin of the face and scalp, on the neck, and less often on the torso and limbs . According to statistics, the occurrence of hemangiomas is two to three times more common in girls, although the reasons for this pattern have not yet been found.
One of the distinctive features of capillary hemangioma is the high probability of its appearance during the first nine months of a child’s life, even if the baby did not have any vascular formations at birth.
Why does a tumor occur?
The exact causes of the occurrence and development of capillary hemangioma are not known for certain. Some people tend to associate the formation of vascular tumors with an unfavorable environmental situation; others tend to name viral diseases of the mother during pregnancy and taking medications as possible causes, and in some cases they blame this on hormonal imbalance in the baby’s body. Another reason for the appearance of hemangioma is also considered to be a tendency to such formations, inherited through the female line, which is probably a logical explanation for the more frequent cases of the disease among girls. However, none of these theories is one hundred percent accurate, and the nature of hemangiomas is still not fully understood.

Capillary hemangiomas in children go through three stages of development:
- Active growth (from birth to six months).
- Slowdown and cessation of growth (6–8 months – 1–1.5 years).
- Involution, or resorption of hemangioma (up to 5–7, sometimes 12 years).
In most cases, a tumor of this type affects only the superficial vessels of the skin, and therefore does not cause discomfort and does not pose a threat to the child’s health. But sometimes hemangiomas can grow significantly and become injured, and in these cases treatment is already indicated.
The main methods of treating hemangioma
For babies under one month old, the tumor cannot be removed surgically. During the neonatal period, the doctor looks at how the vascular tumor will behave. If it does not grow or change color, then it is simply monitored until the child enters kindergarten.
When a vascular formation rapidly increases in size, disrupts the functioning of organs, or threatens the life of the child, its immediate removal is required. Similar operations are performed on infants older than 3 months.
To get rid of hemangioma, the following treatment methods are used:
- Medication;
- Surgical;
- Conservative.
Surgical treatment of tumor
During the operation, the formation is excised completely or partially. It is performed when the disease progresses rapidly, provided that the resection does not cause a severe cosmetic defect.
This method of treatment is used if the vascular tumor is huge. After surgery, a donor piece of skin is taken from another part of the body, especially when the hemangioma is located on the eyelid or in the head area. In infants, such operations are performed only in exceptional cases, while simultaneously performing blood transfusions under local or general anesthesia.
Drug therapy
In some cases, hormonal drugs are used to treat hemangioma. These drugs help speed up the resolving tumor processes. However, such therapy does not bring sufficient effectiveness, and also has many contraindications. Many specialists practice the use of hormonal drugs as an additional means for removing vascular tumors, combining them with sclerotherapy or cold treatment.
Conservative methods of treating hemangiomas
Quite often, such formations in infants are removed by freezing. Cryotherapy is suitable if their size is no more than 2.5 cm. During this procedure, carbon dioxide snow is applied to the spot. After such treatment, a hole appears in the affected area, which then swells, and a blister forms in its place. After some time, a crust of blood appears in place of the water bubble, completely disappearing after 2-3 weeks .
Treatment
Hemangioma of the eyelid differs from tumors localized in other places in that it more often requires medical intervention. Vascular formations resolve spontaneously in half of children over 5 years of age. But the pathology of the eyelid has to be treated, since its rapid growth poses a danger to vision. In addition, the tumor interferes with the child and is often injured.
Taking into account the growth rate of the hemangioma and the possible risks, the doctor decides whether therapeutic procedures are sufficient or whether surgical intervention is required. It is unlikely to do without radical measures if the tumor has reached a large size and penetrated deep into the tissue.
Doctors have various methods of treating eyelid hemangioma in their arsenal:
- drug therapy;
- ligation of the vessel;
- electrocoagulation;
- sclerosis;
- laser or radiation therapy;
- cryodestruction;
- surgical intervention.
A positive result in treatment is achieved through the use of a set of measures. The doctor decides which methods are best to use in each specific case.
Drug therapy
Taking medications is recommended if a child has a large hemangioma of the eyelid. To treat it, glucocorticosteroids, interferons, propranolol, vincristine are used, which blocks cell division and stops tumor growth.
Ligation of the vessel
This method is used when the hemangioma begins to grow rapidly. Ligation of the vessel that feeds the tumor stops the flow of blood. Thanks to this, the size of the tumor is significantly reduced.
Electrocoagulation
The essence of the method is that the area of the hemangioma is injected with a current of the required strength. This method is used as an independent treatment or additional during surgery. The therapy is long-term, but after it there are no scars.
Sclerosis
To reduce the volume of the hemangioma, the formation itself and the surface around it are injected with ethyl alcohol, a solution of betamethasone or quinine. Injection of corticosteroids into the tumor is also practiced. The procedure requires anesthesia; for this, an anesthetic is first injected.
Laser treatment
Laser tumor removal has no age restrictions. The number of procedures required varies depending on the type and size of the tumor. After treatment there are no scars or crusts left.
Cryodestruction
The procedure involves freezing the hemangioma with liquid nitrogen. For the treatment of neoplasms on the eyelid, it is used with caution, since small scars remain. The advantage of the method is that a small tumor can be removed in one session.
Surgical intervention
In world practice, there is a tendency to refuse operations to remove hemangioma. This is due to the danger of using anesthesia in infants, a long period of rehabilitation and possible tumor relapses.
Surgery is resorted to in extreme cases when the tumor threatens the patient’s health. Hemangiomas can be removed from children no younger than six months old.
Laser removal of vascular formation
This therapy is considered to be the most acceptable way to treat this disease. The main feature of the laser is the removal of tumors of any shape and at different stages of its development. In addition, this procedure is painless and low-traumatic. The treatment process, if necessary, can be divided into several stages. The patient undergoes therapy at a time convenient for himself.
Sometimes just one procedure is enough to completely get rid of a hemangioma. When the doctor notices signs of remission during laser removal, he can complete the treatment. But such therapy has its drawbacks; however, compared to other methods, it is considered the most gentle. On top of that, laser removal leaves no scars.
During the recovery period after excision of a vascular tumor, the patient will have to take antibiotics to eliminate inflammation. Even during rehabilitation, it is necessary to care for the skin in the damaged area, treating it with antiseptic agents.
Hemangioma, who needs information, read!!!!!!!!!!!!
I, like probably most mothers, encountered this, here’s what I found
Treatment methods for hemangioma in newborns and children
Two-week-old Sasha’s mother noticed a small red spot on his lower lip.
I got worried: isn’t it dangerous? But the pediatrician, briefly, while running - the area is large, you need to be in time for everyone - looking at the scarlet “blot”, he said that there was nothing wrong, the blood vessels had simply expanded during the birth process, and by the year it would go away on its own. Mom calmed down. But the insidious “spot” - hemangioma - continued to grow almost imperceptibly to the eye, spreading to the mucous membrane of the mouth, and from there to the larynx... After 4 months, Sasha began to choke. For long weeks, which seemed like an eternity to my mother, surgeons fought for the boy’s life. And we won! But if Sasha had gone to specialists as soon as the unfortunate “spot” of hemngioma was discovered, five minutes would have been enough to remove it. SKIN HEMANGIOMA
Hemangiomas of the skin and mucous membranes account for approximately half of the total number of all soft tissue tumors in children.
This is a very big number! The insidiousness of hemangiomas is that, despite their benign nature (they do not metastasize and do not directly threaten life), these congenital vascular formations are capable of increasing in size so quickly that they outstrip the child’s growth. As they grow, hemangiomas destroy surrounding tissues and cause significant cosmetic damage, since they love exposed parts of the body, and in 8 out of 10 cases they are located on the face and scalp. If the hemangioma “has chosen” the eyelids, auricle, or mucous membrane of the oral cavity, there is a danger of disrupting the functions of important organs: vision, hearing or breathing. Therefore, new mothers and fathers should imagine what a hemangioma looks like, and if they find it in a child, do not put the matter off, but immediately show the child to a specialist who, if necessary, will remove the tumor. WHAT DOES A HEMANGIOMA LOOK LIKE?
In 96.2% of cases, simple (capillary) hemangiomas are identified in children.
Capillary hemangiomas consist of many superficial capillaries that appear as four or more red dots, similar to needle pricks. Over 3–4 months, they reach an average of 3–4 cm in diameter, often spreading deep into the tissue, and sometimes new red dots appear around, indicating the rapid growth of hemangioma. A characteristic diagnostic sign: if you press on the hemangioma with your finger, it turns pale and becomes smaller. When the child screams or lowers his head, the swelling increases and becomes brighter. Touching it is painless for the baby, and the skin under the hemangioma is always warmer than the surrounding tissue. Much less common than simple ones (only in 2% of cases) are cavernous, or cavernous, hemangiomas. They are located in the subcutaneous tissue and muscles, causing them to thicken, the skin above them looks red or retains its normal color. Without treatment, a hemangioma can become a source of bleeding or infection. If help is provided on time, there will be no complications. TREATMENT OF HAMANGIOMAS WITH COLD
Small superficial capillary hemangiomas respond best to local exposure to cold - the so-called local cryodestruction.
In contact with a special plate cooled with liquid nitrogen to a temperature of minus 180 o C, the tumor tissue freezes in a matter of seconds and its cells are destroyed. There is no bleeding, and, what is very important, the child is practically not in pain. Therefore, cryodestruction is performed on infants without anesthesia on an outpatient basis. But older children need general anesthesia: the fear of white coats and dangerously shiny instruments overpowers in the child’s mind parental persuasion and promises that it won’t hurt. Anesthesia helps avoid negative reactions that could seriously interfere with the operation. If your child is about to have a hemangioma removed, put aside your worries - there is no reason to worry. True, before the operation you will have to run around for certificates: you will need reports from a cardiologist and pediatrician from the district clinic confirming that mask anesthesia is not contraindicated for the child, as well as general and biochemical tests of blood, urine, stool for dysentery, a throat smear for diphtheria and a chest x-ray . The operation itself lasts on average 5–10 minutes. In order for wound healing to go smoothly, parents must properly care for it. After a few hours, a flat bubble appears at the site of exposure to cold, like after a burn, and a crust forms. In the first 7–12 days, treat the area that has undergone cryodestruction every 3–4 hours with a piece of cotton wool moistened with a 5% solution of potassium permanganate, prepared at the rate of a teaspoon (without top!) of potassium permanganate per 100 ml of water cooled to room temperature. Store the solution under a tightly closed lid in a dark place. Please note that it is quite concentrated (this is necessary not only for disinfection, but also to form a strong crust), so lubricate only the wound itself, without touching the skin around it! When a dry crust forms, under no circumstances tear it off ahead of time, as healing is taking place underneath it. Every day (approximately 2 weeks) until the crust is rejected, lubricate the wound 6-8 times with sea buckthorn or vaseline oil, any nourishing fatty cream - you can use children's cream, or special products prescribed by the doctor. Over time, the crust will disappear without a trace. TREATMENT OF HAMANGIOMAS WITH LASER
In the complex treatment of extensive cavernous hemangiomas, the newest method of so-called puncture destruction (destruction) using a laser is used.
Through a puncture in the skin, a special light guide is brought to the tumor and it is exposed to laser radiation, which in a split second heats a strictly defined area of tissue to the desired temperature. As a result, the proteins coagulate (fold), and the liquid part of the hemangioma cells evaporates. The vessels are “wrapped” without bleeding, connective tissue develops in their place, and the volume of the tumor is significantly reduced: after such treatment it can be “removed” without damaging the patient’s appearance. In particularly difficult situations, laser exposure must be combined with cryodestruction, and sometimes also with radiation and hormonal therapy. X-ray therapy is used to treat large flat hemangiomas, vascular tumors in the eye or meninges, where other treatment methods cannot be used. If the doctor insists on the need for radiation therapy for an infant, do not refuse outright, drawing in your imagination possible pictures of its terrifying consequences - they will not happen. The dose and exposure time are selected so that the radiation affects only the tumor, without affecting healthy tissue. It turns out that it is in infancy – from 3 to 8 months – that the sensitivity of hemangioma cells to ionizing radiation is especially high, which provides babies with an almost one hundred percent cure with complete restoration of the skin. In addition, in children under 6 months of age with extensive hemangiomas, hormonal therapy with corticosteroids has proven itself well, after a course of which the “shrinking” tumor is usually treated with other methods. “PORT WINE STAINS” AND HEMANGIOMA
Parents and doctors, who rarely have to deal with hemangiomas, sometimes mistake them for so-called “wine stains” - pink, red or purple areas (the bright color is given to them by red blood cells, and the dark color is due to under-oxidized hemoglobin), representing hundreds of tiny dilated vessels that approach the surface of the skin. Unlike hemangiomas, such spots are relatively harmless and are not a tumor, but a malformation of blood vessels; they never increase in size, but sometimes bleed and become inflamed. Port-wine stains can be removed using a laser using the so-called selective photothermolysis method. True, you will need to be patient: at one time, using the “point by point” manual scanning method, surgeons manage to treat no more than 20 square centimeters of skin, and repeat sessions have to wait 3–4 months, during which the tissue irradiated by the laser is restored. But when there is hope for recovery, time flies!