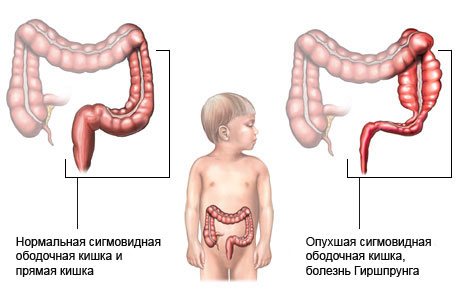
What is it - dolichosigma intestines? This is an abnormal elongation of the sigma, in which the thickness of the walls does not change, the diameter of the intestine also remains normal, and the length increases. In this case, sigma becomes pathologically mobile and does not allow fecal matter to form and move normally, motility and emptying are impaired. Due to its increased length, it can twist and fold into loops. The normal length of sigma is 24-46 cm, with dochilosigma it exceeds 46 cm and forms an extra 2-3 loops.
The essence of pathology
Dolichosigma may not manifest itself in any way in a child, and some doctors attribute this to the characteristics of the body. If such a sigma causes constipation and pain, gas formation and intoxication of the body, then this is already a disease.
Constipation in young children is a very common occurrence and is a problem for parents and pediatricians. But most often this phenomenon is associated with nutrition, this is especially evident in artificially raised people. If constipation becomes persistent, it indicates problems with the lower intestine.
Symptoms of dolichosigma in children
An abnormality in the structure of the sigmoid colon in a child can be judged by various clinical manifestations. The fact is that the disease occurs in 3 phases, gradually replacing each other.
At the compensation stage, symptoms such as constipation for 3 days and severe pain in the lower abdomen are disturbing.
In such a situation, it is possible to empty the intestines only by sitting on a special diet and using mild laxatives.
At the next stage, called subcompensatory, constipation becomes constant, the patient suffers from flatulence and acute pain in the abdominal area.
It is no longer possible to eliminate all these symptoms even with laxatives. The only thing that can be done to improve the child's condition is to give him a cleansing enema.
The last, decompensation stage is characterized by severe clinical manifestations caused by elongation of the sigmoid colon.
Abdominal pain does not subside even for a minute, and the child cannot empty his bowels for a week or more.
At this time, the large intestine becomes greatly inflated, its walls stretch due to accumulated gases and feces.
They, in turn, cause the appearance of pimples on the skin with pus inside, severe nausea and aversion to food.
Symptoms of dolichosigma of the sigmoid colon, such as pain and general malaise, are not as bad as constipation. They often bother children aged 6 months to one year.
This happens as a consequence of feeding the child or transferring him to food with special mixtures that increase the amount of feces and change its consistency.
READ How to cure irritable bowel syndrome?
By the 3rd year of life, constipation appears in 40% of children - at first it occurs as a temporary phenomenon lasting several days.
When constipation becomes prolonged, morphological changes occur in the intestinal tissues, and the reflex to defecate decreases.
Video:
At the same time, the stool increases in diameter, acquiring a resemblance to a “fir cone,” and smells foul.
Passing through the rectum, hard and bulky feces damage the mucous membrane. Because of this, blood appears in the stool.
Dolichosigma of the intestine is manifested by gradually increasing pain in the left abdominal area and near the navel and increased gas formation.
These symptoms become especially unbearable after eating a large portion of food, as well as physical labor.
Clinical manifestations of elongation of the sigmoid colon weaken or completely disappear only when the sick child is able to go to the toilet.
Almost every child suffering from dolichosigma of the intestine exhibits malfunctions in various parts of the digestive tract. The disease is often complemented by chronic gastroduodenitis, dysbacteriosis or colitis.
Dolichosigma, which is expressed in bowel dysfunction, can cause the formation of fecal stones in children, irritable bowel syndrome or iron deficiency in the blood.
Appearance mechanism

So what is it - dolichosigma intestines? It can be acquired or congenital. The second option is typical for children; pathology occurs during embryogenesis. In this case, sigma has 2-3 extra loops.
The acquired variant occurs in adults after 45 years of age, mainly in those who lead a sedentary lifestyle and love fatty foods. Why dolichosigma occurs in a child has not yet been clarified. Some talk about bad heredity. Other occurrences of dolichosigma in a child during the newborn period are associated with infectious diseases during pregnancy or the use of certain medications by the expectant mother. There is also no consensus on whether the pathology is a malformation of the final section of the intestine.
Some researchers consider pathological sigma to be a normal variant because it is often common and is found in 25% of children who do not present any complaints. But in contrast to this opinion, there is another thing - the impaired length of the sigma is often accompanied by an organic or functional deviation in the structure of the terminal part of the sigma and rectum. It is expressed in chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane, intestinal stasis, enlargement of muscle fibers, compaction of mesenteric tissue, damage to the intramural nerve ganglia and disruption of cellular metabolism. In other words, dolichosigma leads to degenerative lesions of the intestine and disrupts its functioning.
Causes of dolichosigma
Dolichosigma can be a congenital or acquired condition in which the sigmoid colon has 2-3 additional loops. The etiological cause of dolichosigma is unclear. It is assumed that congenital disorder of growth and fixation of the sigmoid colon may be associated with heredity; exposure to unfavorable environmental, physical, and chemical factors on the fetus; infectious diseases of the expectant mother, taking certain medications by the pregnant woman.
Acquired dolichosigma occurs as a result of digestive disorders associated with the processes of prolonged fermentation and putrefaction in the intestines. This usually affects people over 45-50 years of age who lead a sedentary lifestyle, are engaged in sedentary work, abuse meat and carbohydrates, and often experience stress. At the same time, some authors believe that dolichosigma is always a congenital anomaly, and digestive problems only cause the manifestation of clinical manifestations given the existing anatomical prerequisites.
To date, proctology has not resolved the question of whether dolichosigma should be considered a malformation of the colon or an individual variant of the norm. On the one hand, dolichosigma occurs in 15% of completely healthy children, which gives grounds to consider it a variant of the norm. On the other hand, elongation of the sigmoid colon is often accompanied by organic and functional disorders of the distal colon, which makes one think about a developmental anomaly. It is likely that dolichosigma is a kind of background for the development of clinical pathology.
Morphological examination of the intestinal walls in dolichosigma reveals structural disorders caused by intestinal stasis and chronic inflammation: sclerotic changes in the mesentery, hypertrophy of muscle fibers, myofibrosis, damage to the intramural nerve ganglia, degeneration of the mucous membrane. Thus, in the intestinal wall with dolichosigma, secondary degenerative changes take place, leading to disruption of its motor function.
Symptomatic manifestations

In 70% of cases, symptoms appear within a year. In 30% of cases, stool disorders occur between 3 and 6 years of age. The first symptoms of dolichosigma in children usually appear at 6 months. Constipation and stagnation of feces immediately occur with the introduction of the first complementary foods, when switching to artificial feeding.
Constipation becomes the main symptom. The rest of the clinic is developing gradually. It manifests itself in moodiness, lethargy, crying, refusal to breastfeed or refuse food, poor sleep and screaming during the day. Symptoms only subside when the child goes to the toilet. A decrease in local immunity is manifested by small pustules on the skin.
There is no stool for 3-4 days, and bowel cleansing becomes a problem. At first, bowel movements occur once every 3 days, then once a week, and later once a month.
Stagnation of feces poisons the body, it thickens, enlarges and acquires a fetid smell of rotting. Hard feces, when moving slowly, injure the mucous membrane, and blood begins to mix with them. The sigma stretches and its walls become thinner. This may result in perforation. If enemas are constantly used, the emptying reflex decreases.
In older children, symptoms appear as follows:
The child seems tired, he often refuses to eat, his heart rate increases, and he refuses to play. Due to constipation and pain, the child is afraid to ask to go to the toilet. Symptoms are especially aggravated after a large meal or physical activity.
Dolichosigma of the intestines in a child: what is it, what are the symptoms, how to treat?
Young children often have a problem when going to the toilet is a real torment.
This fact worries moms and dads greatly, since the reason for stool retention does not always lie in a temporary difficulty in passing feces.
If constipation is persistent and the child feels pain during bowel movements, the presence of dolichosigma can be suspected, and this requires immediate consultation with a doctor.
What it is
Dolichosigma is an abnormal elongation of the large intestine, its sigmoid part. This anomaly causes disruption of motility and natural cleansing of the colon.
The increased length of the intestine has great mobility, which leads to disruption of the formation and movement of feces.
Lengthening, the intestine with the pathology under consideration has the same circumference and the same wall thickness.
This pathology is quite common, but due to the complexity of its diagnosis, it is not always detected. Dolichosigma is found in 40% of children who suffer from constipation.
Types of pathology
Depending on the factors that caused the pathology, there are 2 forms of dolichosigma:
- congenital – formed during the mother’s pregnancy, when the baby’s intestines develop with abnormalities;
- acquired - appears when several new loops appear in the intestines, which is usually caused by poor nutrition, which disrupts the process of digestion of food, which begins to rot and ferment in the intestines.
Pathology has 3 stages:
- Compensated – expressed by periodic constipation with short breaks of 3–4 days. The longest duration of stool retention is 5 days. The child’s health is normal, except for discomfort in the abdominal area.
- Subcompensated – represented by more frequent constipation with a long duration. At the same time, the abdomen hurts greatly, bloating is observed, and gases are formed. Laxatives do not have the desired effect.
- Decompensated – occurs with incessant abdominal pain. Due to retention of feces in the intestines, the abdomen swells and increases in size. Characteristic is the gradual development of intoxication of the body. The child feels unwell and refuses to eat. Nausea, vomiting and even ulcers on the skin may occur.
Causes of pathology
There are a number of reasons:
- heredity at the genetic level;
- pregnancy with complications (infectious diseases, etc.);
- fetal development in poor environmental conditions;
- the use of dangerous drugs while carrying a child;
- exposure to radiation;
- strong ultraviolet irradiation;
- poor child nutrition, consumption of foods containing preservatives, pesticides and other harmful additives, as well as fatty foods that are poorly digested;
- lack of physical activity.
Symptoms in children
The main symptom of this disease is constipation. More often they appear in babies under one year of age due to an increase in the volume and density of feces due to the introduction of mixed nutrition. In 3% of children, this symptom appears later - from 3 to 6 years. The duration and severity of constipation increases over time.
Other symptoms of long bowel:
- hard feces of large diameter;
- presence of blood in the stool;
- abdominal pain, especially on the left side and in the navel area;
- flatulence;
- associated ailments of the digestive system such as gastritis, colitis and pancreatitis;
- presence of bad breath;
- cracks in the corners of the lips;
- brittle nails.
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose dolichosigma in a child, a personal examination is initially performed. In this case, the specialist performs a digital examination of the rectum and palpation of the abdomen. In addition, additional laboratory and instrumental studies are prescribed. The doctor decides which methods are necessary in a particular case.
Laboratory methods
Laboratory methods for determining diagnosis include various types of tests. The child will need to donate blood and stool.
Tests to diagnose an enlarged sigmoid colon:
- UAC;
- blood chemistry;
- coprogram (analysis of the physical and chemical properties of feces, as well as various components and inclusions of various origins);
- stool occult blood test;
- fecal analysis for helminth eggs.
Instrumental diagnostics
Instrumental diagnostics are as follows:
- ultrasound examination;
- X-ray of the intestines;
- irrigography (allows you to determine the condition of the cells and walls of the intestine, determine its size, position and shape);
- colonoscopy (mainly used to diagnose the disease in adults);
- sigmoidoscopy (examination using a tubular device - a sigmoidoscope, which is inserted rectally).
Treatment methods
Treatment for dolichasigma prescribed by a doctor can be conservative (medication) or more radical with surgery. The type of treatment is determined by the clinical manifestations, as well as the stage of development of the disease and the characteristics of the child’s body. Folk remedies can also help, but they should only be used on the recommendation of a specialist.
Conservative treatment
Treatment with medications is prescribed depending on the stage of the disease. Dolichosigma is treated comprehensively; in the presence of concomitant diseases, additional therapy is also carried out.
For abdominal pain, medications are used:
- "No-shpa";
- "Platifillin";
- "Prozerin";
- "Dibazol".
Medicines can be used in the form of tablets or injections. The duration of treatment is 14 - 17 days, then a break is taken for 1.5 - 2 months and, if necessary, they are resumed. In addition, the child takes B vitamins, medications that help populate the intestines with beneficial bacteria, and undergoes physical therapy with abdominal massage.
Surgery
If there is no positive result from drug treatment, surgical intervention is resorted to. The operation involves resection of the dolichosigma and its removal.
After surgery and a rehabilitation period, problems such as constipation and increased gas formation disappear. However, for this, the little patient must follow all the rules and recommendations of the attending physician.
Folk remedies
To treat enlarged sigmoid colon, the following folk remedies are used:
- Mineral water to saturate the body with the trace elements and minerals it needs. With its help, digestion is improved.
- Fermented milk products (kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk) help improve stomach function. You can drink them in the morning and before bed.
- Beet salad with vegetable oil and prunes. You can use boiled and fresh beets. These products have a laxative effect.
- A mixture of honey, prunes and dried apricots is a remedy that helps to improve bowel movements. In combination with dairy products, the effect will be felt immediately.
Diet is very important in the treatment of the pathology in question, when coarse, fatty and spicy foods, as well as sweets, white bread and pastries are excluded from the patient’s diet. Active consumption of fermented milk drinks, fresh fruits and vegetables, lean meat and fish is recommended.
Preventive measures
To prevent the formation of long intestines in children, the following rules must be followed:
- compliance with healthy eating standards;
- sufficient physical activity;
- drinking enough water;
- use of vitamins;
- children's abdominal massage.
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. Prevention of dolichosigma is of paramount importance.
Source: https://RosMedPlus.ru/bolezni/gastro/dolihosigma-kishechnika-u-rebenka-lechenie.html
Course of the disease
Dolichosigma occurs in three stages or forms with different severity of manifestations:
- The compensation stage is the initial and easiest. Constipation is not always a problem, it lasts for 3-4 days, goes away after defecation, the pain is not severe. The general condition does not change, the child is quite active. The stage is easily treated with diet and laxatives.
- Stage of subcompensation - stool is also absent for more than 3 days, but now permanently. The stomach is swollen and hurts. The baby eats poorly, is not gaining weight and is irritable. Laxatives are no longer enough; enemas have to be used. The first signs of intoxication of the body appear.
- Stage of decompensation - all symptoms are vivid and advanced. Constipation is prolonged, intoxication is severe: headaches, poor appetite, skin rashes, nausea and vomiting, anemia and lethargy. My stomach is constantly swollen and hurts all the time. Empty once a week or month. There may be signs of partial intestinal obstruction. Only siphon enemas have to be used. Effective treatment is only surgical.
Diagnostic measures
The diagnosis of dolichosigma in children is made after a comprehensive examination of blood, stool, and instrumental research methods. First, a visual examination reveals the child’s underweight and pallor, peeling of the skin on the fingers due to vitamin deficiency.
On palpation it is felt that the abdomen is full in the loops. Digital examination shows that the rectum is empty.
Irrigography will help to identify the degree and number of loop curls and the sigma value. Additional loops can be in the form of a figure eight, snail, or knot.
CT is used for diagnosis in older children. This technique allows you to determine space-occupying formations. CT scans cannot be performed on young children due to their mobility.
Ultrasound, X-ray, irrigoscopy, colonoscopy, general and biochemical blood tests, stool analysis for worm eggs and the presence of hidden bleeding are also prescribed. On ultrasound, the intestine is clogged with dense feces. What do reviews say about the examination of dolichosigma in a child? Many parents worry that this procedure causes discomfort and pain to the baby. Many mothers categorically do not go for examination precisely because the child is simply unable to tolerate the procedures and is afraid. Others believe that the barium used for barium enema will cause infertility in the girl in the future. Some people consider taking barium disgusting; even an adult wouldn’t drink it.
All these fears are unfounded. Many people tolerate the procedure easily. Moreover, during a colonoscopy, for example, children are given a short anesthesia.
Diagnosis of the disease
The pediatrician should be wary if parents complain of systematic stool retention in the child. Diagnosis of dolichosigma in children is carried out taking into account the description of symptoms and the results of an additional examination. In a small child, pathology can manifest itself from the moment complementary foods are introduced.
The doctor himself must also, by palpation, identify loops filled with feces in the intestines. When the first suspicions arise, in order to clarify the diagnosis, the doctor needs to conduct a digital-rectal examination. If the rectum turns out to be empty, then the child is prescribed an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, which will show the presence or absence of additional intestinal loops.
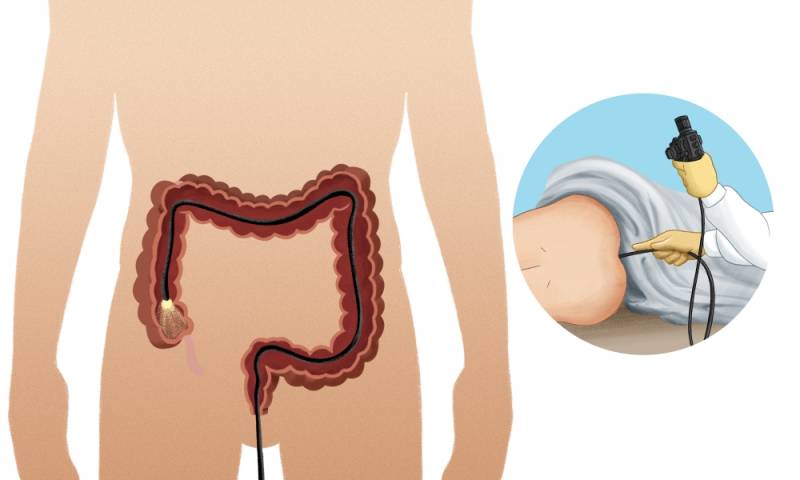
If this pathology is detected, you should understand that it is a feature of the anatomical structure and will not go away on its own as the child ages. Children with identified symptoms of intestinal dolichosigma must be registered with a gastroenterologist. In some cases, it is recommended to take x-rays of the abdominal cavity, which accurately determine the presence and extent of pathology.
Irrigography is widely used in the diagnosis of dolichosigma in children. This is, in principle, the same X-ray, but during this procedure the patient is injected with a special substance, which makes it possible to more clearly examine the clinical picture and make an accurate diagnosis, as well as determine the presence of extra loops in the intestines. You should know that such studies are not carried out on newborn children, since it is still impossible to distinguish between normal and pathological conditions in their bodies.
The colonoscopy method is also used. Using a camera located on the hose, the doctor examines the condition of the intestines: extra loops, tumors, etc. If necessary, a tissue biopsy is taken. Sigmoidoscopy is another method of assessing the condition of the intestinal mucosa using an endoscope.
Additionally, the patient undergoes a number of laboratory tests that complement the overall picture of the disease:
Principles of therapy
The treatment of dolichosigmoid intestines in children is carried out by a pediatric gastroenterologist.
Goal of therapy:
- Normalization of bowel movements.
- Improving stool density.
- Resumption of intestinal function by stimulation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Relieving acute inflammation.
Abdominal massage and therapeutic exercises are used to crush fecal stones. This leads to a rush of blood to the intestines and strengthens the abdominal muscles. To improve the functioning of the intestines, physiotherapy is prescribed. Treatment begins with diet and establishing a diet.
Treatment
At any stage, treatment begins with complex conservative therapy, which includes a strict diet and symptomatically necessary medications. It is strict adherence to the daily routine and a balanced diet that is the key to a positive result and prevention of the development of serious complications.
Treatment for the diagnosis of dolichosigma involves injections of proserin, vitamin therapy, massage, exercise therapy, and electrical stimulation of the intestine. In some cases, mild laxatives (Duphalac, lactulose) are prescribed in individual doses. Sometimes an enema is used as an emergency treatment. But it is strictly forbidden to do enemas independently and uncontrollably, since the reflex to defecation is lost. Spa treatment is also indicated.
Surgical treatment is carried out only in particularly severe cases: in the presence of non-straightening loops, progressive fecal intoxication. Timely examination and adequate therapy can avoid this.
Special diet
It is necessary to ensure water and drinking regime. You should drink at least 10 glasses of water per day. Meals should be fractional - 5-6 times a day, in small portions, strict in time. Lemon water helps a lot as it loosens the stool. Meat is prohibited; a glass of 1% kefir is required.
Menu for a child with dolichosigma: more foods with fiber (berries, greens, fruits). They require heat treatment - boiling or steaming. Anything that is covered with an appetizing crust, as well as fried, smoked, and spicy, is excluded. Also contraindicated are dishes that slow down the movement of feces through the intestines - rice, semolina, millet, pasta, white bread, baked goods, cookies and cakes, coffee, cocoa, strong tea. Animal fats increase fermentation and are poorly digestible. Regarding chocolate: it can be given rarely, not an hour before or after meals.
You can give your child fish, cottage cheese, fermented milk products, buckwheat porridge, salads, and vegetarian soups. Bran is recommended; vegetables and fruits include beets, prunes, carrots, figs, pumpkin, baked apples, apricots, plums, dried apricots. Sweets include compotes, limited honey, marmalade (contains pectins).
Bananas, grapes and pears are excluded. Due to the limited choice of products, the diet for dolichosigma in children is supplemented with multivitamins containing C, A, E, group B, D. They will support the immune system.
Drug treatment

Clinical guidelines for dolichosigma in children include:
- Herbal enemas, laxatives (increase stool volume), prokinetics, stool reducers.
- "Motilium". It speeds up the evacuation of the food bolus. It is prescribed for 2 weeks.
- If there is no effect from the diet, laxatives are used, and they start with minimal doses.
- Abdominal pain and gas formation are relieved with Dibazol and Prozerin injections. “Proserin” also increases the tone of the intestinal walls. The effect increases significantly if it is combined with electrical stimulation of the large intestine.
- Antispasmodics are ineffective, since pain is caused not by spasm, but by intestinal atony.
- An important step is to improve the intestinal microflora, for which pre- and probiotics are prescribed: Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin, Narine, Linex, etc.
- For drug treatment of intestinal dolichosigma in children, to improve well-being, the doctor prescribes Duphalac, Psyllium, Mucofalk (these preparations are made from the shell of plantain seeds), Duspatalin, and Festal. Their effect is multifaceted: increasing the tone of the intestinal wall, diluting stool, increasing intestinal motility.
The effect of treatment can be enhanced with herbal decoctions and infusions, but only after consultation with a doctor. Drugs are also used to reduce flatulence and reduce the smell of feces.
Treatment approaches
Treatment measures are most effective when they begin at stages 1 and 2 of the disease. In these cases, it is possible to use conservative treatment methods. Such therapy includes following a diet with increasing the amount of water drunk, avoiding cereals and fatty meats, baked goods and confectionery products.
Fermented milk products, as well as vegetables, herbs and fruits are added to the diet. If pain increases, antispasmodics are prescribed. Laxatives and enemas are used to cleanse the colon of feces and relieve constipation.
It is extremely rare that surgical interventions are performed if there is no effect from conservative methods. The use of traditional medicine is prohibited, as they have no evidence of their effectiveness and safety.
Dolichosigma in children is diagnosed at different ages. The prognosis if detected early is favorable. Following the diet and other recommendations of the pediatrician allows you to eliminate unpleasant signs of pathology and prevent the development of complications in the form of colitis, intestinal obstruction, etc.
Late seeking of medical help or attempts at self-medication increase the risk of adverse consequences in the child in the early and long-term period.
Using enemas
An enema is done with clean water or saline solution, chamomile decoction. The urge to void occurs as a reflex. The volume of water depends on the age of the child. The temperature of the solution should not differ from the baby’s body temperature.
The baby is placed on his right side, the enema tip must be lubricated with petroleum jelly. After introducing the liquid, the buttocks should be squeezed and the child should be carried in his arms for 10 minutes, after which the baby should be put on the potty.
Enemas, even if they are effective, should be used as rarely as possible; it is better to form a reflex to defecation so that going to the toilet is calm.
What are the benefits of massage?

Massage for dolichosigma in a child is a mandatory component of treatment. It is not done only if there is blood in the stool. Breasts need a back and abdominal massage daily to strengthen their muscles.
The procedures are carried out by placing the baby on his stomach. Using two fingers, carefully make spiral movements along the spine from the lower back and down to the tailbone. The abdomen is massaged in a clockwise circular motion. The massage should be pleasant for the child, otherwise there will be no other results other than screaming and crying.
The beginning and end of the procedure are in the form of stroking and rubbing. Massage movements should be slow and pressing.
In the reverse order, tap with the phalanges of the fingers. The entire procedure lasts at least 20 minutes. It is better to massage in the morning, before feeding.
Physical therapy is indicated for older children. It is better if these are group classes, where the kids look at each other. Then they repeat the movements of their neighbors and learn faster. Jumping in place with a skipping rope, running, and twirling a hoop also stimulate the intestines.
Surgical intervention
If various methods of conservative treatment do not reveal positive results and the disease continues to progress, there is an addiction to enemas, intoxication is severe and continues to increase, radical methods of treatment are resorted to.
The attending physician can recommend surgery for dolichosigma in a child only in extreme cases.
Indications for surgical intervention:
The operation is performed only at stage 3 of the disease. Contraindications to surgery: severe pathologies of the central nervous system and cardiovascular system.
Surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The unnecessary loops of the sigmoid colon are cut off and the ends – upper and lower – are sutured.
The operation to resect the sigmoid is called proctosigmoidectomy. If intestinal obstruction is suspected, the entire intestine is inspected, because twisting of the movable loops compresses and disrupts the nutrition of the intestinal wall, causing tissue necrosis. Then part of the excess sigma and other parts of the intestine are removed.
The duration of the operation is 1.5 hours. Removing excess loops allows stool to pass normally through the intestines. After an illness, sanatorium treatment is very useful for a better and faster recovery.
What to do if a child has dolichosigmoid intestines?
Every child who has been diagnosed with dolichosigma should be observed by a pediatrician and surgeon, and also undergo periodic examinations aimed at identifying complications of this condition. Immediately after the diagnosis is made, the child is taken to the dispensary and the stage of the process is determined.
Dolichosigma is a fairly common condition, which in the vast majority of cases does not manifest itself as anything other than transient constipation. However, even in the absence of complications, annual examination is mandatory for this group.
At the slightest sign of decompensation, the child undergoes a preventive examination twice a year; for dolichosigma decompensation, three times.
If within 2 years after the last episode of constipation (or other complications) the child did not have any pathological manifestations, then he is removed from the dispensary register.
Conservative treatment of dolichosigma in children
It is the main one, and is aimed at reducing the frequency of exacerbations, normalizing stool and restoring normal bowel function. Conducted in repeating courses.
It is necessary to understand that the symptoms characteristic of dolichosigma can return at any time, since the disproportion of the sigmoid colon remains.
The most valuable treatment methods are regimen and diet. The cyclical processes of defecation and nutrition help normalize intestinal function and eliminate the exacerbation of the process that has begun. In addition, herbal medicine, the use of vegetable oils and other traditional medicine methods are quite effective in the early stages of the process.
Diet is one of the most important components of the treatment of dolichosigma
Unfortunately, in many of the observed children, the period of remission when using all these means is 2 months maximum. Basic methods of traditional medicine:
- the doctor prescribes periodic courses of injections or oral forms of proserin. The dose of the drug (prozerin or dibazol (selected strictly according to the age of the child, based on the state of the systems). The break between courses of drugs is, as a rule, 2-3 months;
- Vitamin therapy: group B, E, C;
- Electrical stimulation of the colon (descending section) once a day, in courses of 10-15 days. The essence of the method: electrodes are placed on the skin along the colon, stimulation is carried out with current in the rhythm of syncope. This allows you to achieve adequate contractility of the intestine and interrupt prolonged constipation. This method is good for constipation from 3 to 7 days, since more severe changes in the large intestine make this procedure ineffective;
Prozerin and electrical stimulation complement each other perfectly. For this reason, prozerin is prescribed, as a rule, in the morning, which increases the sensitivity of the intestines to electrical stimulation, which is prescribed in the evening.
- Sanatorium-resort treatment is recommended as part of a program to stabilize the child’s psyche. It is known that dolichosigma most often worsens as a pathological process against the background of constant stress, especially in dysfunctional families. The point of spa treatment in this case is to tear the child away from the conflict-prone environment. When choosing a location, focus on the sea (not in summer) or coniferous forests in the immediate vicinity of the sanatorium;
- Manual therapy is indicated both during the period of exacerbation and for preventive purposes. Effectively helps against constipation, lasting up to 5 days. Massage improves motility, intestinal blood circulation, prevents the development of trophic defects in the sigmoid colon mucosa, and relieves depression;
- Reflexotherapy has a pronounced stimulating effect on the intestines, improves general metabolic rates, and effectively eliminates the neurological part of the symptoms;
- Laxatives are prescribed both when diet and massage are ineffective, and in parallel with them;
- Activated carbon is an excellent detoxifying agent.
Detoxifying agents are activated carbon, food bran, etc. – prescribed for the absorption of toxins during prolonged constipation; - For constipation for less than 3 days, standard microenemas are used. It is good to add chamomile decoction to water. Microenemas are given to young children (up to one and a half years old) with caution to prevent mechanical damage to the rectal mucosa. For longer constipation, a standard enema is used, as well as an Esmarch mug.
If all the above-described remedies do not produce any tangible results, the child is indicated for surgical treatment.
Surgical methods of treatment
There are quite clear criteria for the need for surgical intervention for dolichosigma in children:
- Constant chronic constipation in a child, despite the fact that he is undergoing 3 courses of treatment in a hospital, takes all the medications indicated in this case, uses the services of a massage therapist (reflexologist) and follows a regimen and diet;
- The child has a tendency to form fecal stones. Several consecutive episodes of this complication are a direct indication of the likelihood of obstruction in the future. In order to prevent this rather formidable complication, surgical methods for the treatment of dolichosigma are indicated for such children;
- A clinic of chronic intoxication is observed. The constant reabsorption of toxins from the large intestine, caused by stagnation of feces, leads to quite unpleasant consequences. The child may be significantly delayed in psychomotor development, there is a constant unpleasant odor from the mouth, abdominal pain, pustular skin lesions, severe immunosuppression, even AIDS (a form not associated with HIV);
- X-ray, when examining with a passage of contrast agent, surgeons discover a multi-loop, extremely elongated sigmoid colon with inflamed (thickened) walls. This is a direct warning about the possibility of intestinal obstruction in the future, since it is precisely this anatomical structure of the sigmoid that leads to obstruction in most cases;
- Secondary calorific. As a rule, it indicates a functional deficiency of the sigma. In this case, surgery is necessary, since conventional (conservative) methods will not be able to change changes that have already occurred in the structure of the child’s large intestine.
Contraindications to surgery are severe pathologies of the central nervous system, as well as positive dynamics from the use of any methods of conservative treatment.
The essence of the surgical method of treating dolichosigma is to remove excess loops of the sigmoid colon. If the pathological process mainly affects the final sections of the sigmoid, then it is possible to remove part of the sigmoid and rectum.
The effectiveness of surgical treatment methods
According to statistics, 90% of operated children experience a positive effect - constipation, intoxication, skin manifestations, abdominal pain and other conditions associated with dolichosigma disappear (completely).
Complications, incl. There are practically no deaths in children (there are no data on mortality during operations for dolichosigma in the domestic literature).
Modern conservative approaches reduce the number of children operated on tenfold, but if the doctor strongly recommends a surgical method for treating an enlarged sigmoid colon, agree. This will effectively help get rid of the symptoms of the disease and practically does not pose any risks to the child’s health.
Preventive methods of treating dolichosigma in children
The sooner you start preventing complications or treating dolichosigma, the better it will be for your child. Traditional medicine recommends the following remedies for treating constipation in a baby:
- Flaxseed is poured into 100 ml of boiling water to infuse. Time - about 15 minutes, after which the infusion is filtered and used 2.5 ml (half a teaspoon) with milk, water or other liquid media;
- An infusion of dried hop cones. Pour in bread kvass (1:20), take 2 times a day (morning and evening) ml/kg body weight, for example, for a child weighing 10 kg - 2 teaspoons;
- Older children (from 6 years old) are recommended to try actinidia fruit 100 ml every morning.
Dietary components for children with constipation due to illness
Prunes can be used from the first feeding of a child until old age. A natural laxative, used as a natural addition to almost any diet.
Young children are given prune juice (decoction) in the form of juice. The juice is diluted 1:1. The dose of the fruit depends on age, calculated based on the ratio of 5 ml per kg/body weight for young children.
It is good to give to children from one year of age in the form of puree, or add to porridge.
Dill water, i.e. An infusion of crushed dill seeds is a good mild laxative. 15 ml of seeds are poured into one and a half glasses of boiling water and allowed to brew. Use a teaspoon for children under 3 years of age and a tablespoon for children over 3 years of age throughout the day (4-6 times).
Beetroot with honey is a good laxative for children over 5 years old. A 1:1 ratio is used. Contraindicated if you are prone to allergic reactions.
An excellent element of the diet for dolichosigma in children is homemade yogurt. Constant use of this drink maintains normal intestinal microflora, which protects the child from vitamin deficiency and other manifestations of dysbacteriosis.
What are the forecasts

Diet and taking prescribed medications will definitely help the child in the first two stages. In this case, the stool will become regular.
At stage 3, the decision is individual, it is determined by a number of factors. Complications arise when the process is ignored in any case. Ultimately, fecal masses form, which can no longer pass on their own. At the same time, food waste rots and the body is poisoned. The prognosis in such cases is unfavorable.
Diagnostics
In childhood, a child suffering from constipation experiences the following symptoms: pale skin, weight loss, and delayed physical development. Palpation of the abdomen clearly reveals an intestine filled with feces.
The main diagnostic method for both adults and children is irrigography - an x-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent (barium) into the sigmoid colon. The result is a clear picture of elongation, the presence of additional loops and their turns, expansion and other changes in the sigma.
Additionally, the following studies can be used: ultrasound and radiography of the abdominal organs, endoscopic methods, tomography, electromyography, sphincterometry. General and biochemical blood tests, coprogram, stool testing for hidden blood, the presence of dysbacteriosis, and worm eggs are performed. This is necessary for an objective assessment of the body’s condition, as well as so that the doctor can choose the most effective treatment for a given patient.
For a child with a suspected diagnosis of dolichosigma, it is important to differentiate the disease from other similar pathologies (Crohn's disease, Hirschsprung's disease, chronic appendicitis), which require completely different treatment.