Reasons for the appearance of acetone in the urine of a child
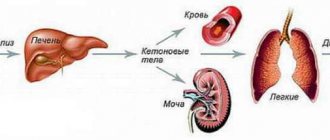
To do this, you first need to figure out how ketone bodies can get into the blood, and why this is so dangerous. Acetone should not be detected in the child's blood. If proteins and fats break down, ketone bodies begin to form; they first oxidize the tissue almost to the level of non-hazardous products, then exit through the urine and the air that we exhale.
As the rate of ketones increases, the rate of their release begins to exceed, and along the way they begin to harm cells, and most importantly, brain cells; are irritants to the digestive tract, which is why the child vomits. So the child begins to lose a very large amount of water, because he spends it on vomiting, urine and breathing. Metabolic processes also begin to progress, and it all ends in metabolic acidosis. If the child is not treated promptly, he may fall into a coma and die due to heart problems or dehydration.
The main reasons for the appearance of acetone in a child’s urine
1. The concentration of glucose in the blood decreases, this happens if the child remains hungry for a long time or is constantly on an unbalanced diet.
2. With enzymatic deficiency, when carbohydrates are poorly digested.
3. If the child consumes a lot of glucose (after experiencing stress, an infectious disease, increased mental or physical stress, experiencing trauma, after exacerbation of chronic diseases and after surgery).
4. Proteins and fats enter the child’s body in large quantities, because of this, the process of their digestion is disrupted, and the body is forced to urgently dispose of them.
5. Diabetes mellitus is the main reason for the appearance of acetone in the blood; the level of glucose in the blood is increased, but it cannot be used correctly because there is not enough insulin.
What is acetone syndrome and crisis?
Acetone in the urine of a child has syndromes that are caused by an acetone crisis. In cases of repeated crises, the child begins to develop acetonemic syndrome.
The syndrome can be either primary or secondary. Secondary occurs on the basis of such diseases:
1. After suffering severe injuries and operations.
2. After suffering an infectious disease, which was accompanied by high fever, vomiting (sore throat, ARVI, influenza and intestinal infection).
3. Somatic diseases, liver diseases, kidney diseases, anemia, diabetes mellitus, thyrotocycosis).
Primary acetone syndrome is typical for children who suffer from uric acid diathesis. With this disease, the metabolism of fats and proteins is disrupted, a lack of enzymes appears, and the child is very excitable. Such children are very thin, but at the same time they move quickly, are excited, and often go one step ahead of their peers in mental development. They are characterized by emotional instability, they do not suffer from enuresis, and they have almost no stuttering. But they suffer from metabolic disorders. Therefore, they often complain of pain in the bones, joints and abdomen.
Diagnosis of acetonemia
Diagnosis of exceeding the acetone norm is carried out based on the results of urine and blood tests in the laboratory. The blood is examined based on the results of general and biochemical analysis. The degree of acetone syndrome is assessed by the manifestation of characteristic signs.
At home, the presence of acetonuria can be determined using standard test strips. The end of each strip is coated with a composition that changes color upon contact with acetone. The acetone level is determined by comparing the color of the strip after contact with urine with the color scale placed on the packaging. The intensity of the color gives an idea of the concentration of acetone in the urine.
The test result can be negative (-) or positive, with a different number of characters ( ). Standard decoding scale:
- receipt (-) - acetone content not more than 0.5 mmol/l;
- receiving ( ) - 1.5 mmol/l, which corresponds to a mild degree of acetonuria;
- presence ( ) - up to 4 mmol/l, characterizes the average degree of pathology - treatment can be carried out at home, but in consultation with a doctor;
- presence ( ) - up to 10 mmol/l, indicates severe acetonemia, which requires hospitalization of the child.
What symptoms accompany the appearance of acetone in the urine?
1. The child vomits very often, taking both liquid and food. She becomes of an indomitable character.
2. The child constantly feels sick, loses his appetite, and refuses water and food.
3. Spastic pain occurs in the abdominal area.
4. What are the symptoms of dehydration and intoxication? The amount of urine produced decreases, the skin becomes pale, dryness, general weakness and a coated tongue appear.
5. Damage to the nervous system, first very strong excitement, then lethargy, drowsiness and falling into a coma, convulsions may also occur.
6. Body temperature rises significantly.
7. The smell of acetone comes from the child’s mouth, the same is observed in the urine. It resembles the smell of rotten apples. Such a smell can be either strong or light, but this does not mean that your child is well.
8. With acetone in the urine, the child’s liver enlarges.
Symptoms of increased acetone in children
At first glance, acetonemic crises occur suddenly. However, if you carefully analyze and remember, then each acetonemic crisis is preceded by precursors of an attack, which include:
- general malaise,
- refusal to eat,
- nausea, weakness,
- lethargy or agitation
- migraine-like headache,
- stomach ache,
- pale colored stool (gray, yellow),
- stool retention,
- There may be a peculiar “fruity, vinegary” smell from the mouth.
Parents may also notice that the baby is pale or slightly jaundiced, has a lack of desire to play, or has an apathetic facial expression.
In this period:
- the child is pale,
- with a characteristic unnatural blush on the cheeks,
- signs of intoxication are increasing,
- the acid-base balance of the blood is disturbed,
- the temperature rises to 37-38.5C,
- liver enlarges
- the child is worried about dizziness,
- headache (moderate),
- cramping or persistent pain in the abdomen, often without specific localization,
- stool retention,
- nausea,
- then repeated, uncontrollable vomiting develops over 1-5 days with frequent, repeated attacks.
Actually, this is why in foreign literature this syndrome is called “cyclic vomiting syndrome.” As vomiting becomes more frequent, fluid loss increases and body weight loss occurs. Often the vomit contains bile, mucus, and even blood - that is, the child has nothing to vomit with. The skin is dry, pale, sometimes with a bright unnatural blush.
At this stage of the disease, parents make the most mistakes in “treating” their children. They do not understand what is happening to the child, they do not know what to feed him or whether he needs to be treated.
Most often, worried mom and dad try to force-feed the weakened baby with meat or fish broth, cottage cheese, sour cream, kefir, egg, steam cutlet, chop and other ketogenic products.
But it is precisely this food load that aggravates metabolic disorders and contributes to the progression of the crisis. Gradually the little one's condition worsens. The child first becomes nervous, excited, runs and screams, then becomes lethargic, adynamic, apathetic, does not want anything - does not eat or drink.
Trying to feed or drink a child also provokes repeated episodes of vomiting. In most cases, a strong odor of acetone is felt in the vomit, urine and exhaled air. In severe cases, in the absence of adequate treatment, acetonemic coma may develop.
Among the deviations from the norm in the child’s condition, doctors consider the appearance of acetone in the urine, which causes symptoms such as lack of appetite, severe vomiting, high fever, and abdominal pain. The combination of these symptoms is called acetone syndrome. Under normal conditions, the child should not have acetone in his urine at all.
Since the list of causes of this disorder includes problems with the functioning of the digestive system, as well as dehydration and toxic poisoning, one of the generally accepted methods of alternative medicine is treatment with soda, namely, a soda enema with acetone in children.
Special test strips that are dipped into the baby’s morning urine help determine the level of acetone in urine. According to the attached instructions, you can determine whether there are deviations from the norm or not. As a general rule, the brighter the color of the test reading, the higher the acetone level.
Reasons that can cause the appearance of acetone in the urine include:
- eating fatty and smoked foods;
- binge eating;
- stressful conditions;
- excessive physical activity;
- infectious diseases;
- long lasting increase in body temperature.
Soda enema is the enemy of acetone
The basis of therapeutic therapy is a soda enema with acetone in a child, which is recommended to be done only for certain demonstrations:
- If vomiting does not stop for a long time.
- When fluid loss due to dehydration is more than 10%.
- In case of disruption of water exchange processes.
- If the child has a disturbance of consciousness.
- A neurological deviation is observed, as a result of which the process of replenishing fluid in the child’s body is disrupted, i.e. the baby cannot drink on his own.
- If the cause of acetone is an infection that needs to be removed from the intestines.
Therapeutic enemas must be given according to age indicators:
- from birth to 6 months, 30–60 grams of solution is taken;
- from 6 months to a year – up to 150 grams;
- from one to 2 years, 200 grams are recommended;
- from 2 years to 5 years the dose is 300 grams;
- from 5 to 9 years old you need 400 grams;
- from 10 years, dose 500 grams.
- It is necessary to prepare a soda solution with acetone in children, the proportions of which should include 1 tsp per 1 glass of boiled water. baking soda.
- Fill a clean, disinfected syringe with the prepared medicinal composition heated to 25 - 27 degrees.
- By pressing on the expanded part of the bulb, remove excess air until liquid appears from the tip.
- Lubricate the tip with Vaseline oil or baby cream.
- Place the baby on his back and raise his legs; lay a child over one year old on his side and, bending his legs, pull them towards his stomach.
- The tip of the enema is carefully inserted into the rectum 50 mm for infants and 80 mm for older children.
- Gradually squeeze the enema and very slowly introduce the soda solution.
- Without stopping pressing the bulb, we remove the tip from the child’s body.
- Briefly squeeze the baby’s buttocks to hold the solution in the rectum.
- It is recommended not to lift the child for 10-15 minutes.
- The baby must go to the toilet after the procedure.
During soda therapy, the child should drink liquid per day at the rate of 120 ml per kg of net weight. If it is impossible to carry out a sufficient rehydration process, fluid is administered intravenously in the form of saline solution, glucose solution, ascorbic acid, etc. But as soon as the patient’s condition returns to normal, the injections are replaced by drinking fluids in the normal way.
In combination with soda enemas, it is necessary to carry out a complete treatment of acetone in children, which includes:
- It is necessary to adhere to a gentle diet, which provides for a sufficient amount of fluid consumed - raisin decoctions, compotes, not very sweet herbal tea.
- Taking medications that improve carbohydrate and fat metabolism - Motillium, Metoclopramide.
READ MORE: Yeast fungus on the nails of a child
If a child experiences an increased gag reflex, it is worth limiting it in food, but do not stop giving drinks - 1 tsp. every five minutes. If there are no contraindications, you can give soda solutions - 0.5 tsp per 1 glass of boiled water. soda In case of severe vomiting, the solution is given in drops using a pipette.
Severe vomiting can also be caused by an elevated temperature, which, with constant drinking, can only be normalized with a decrease in the level of acetone.
Before performing an enema on your baby, you must consult a doctor and test the pH level and electrolyte balance.
As a rule, acetonemic syndrome can be observed in children up to 13 years of age, so parents should, if there are special symptoms characteristic of it, undergo a medical examination with clinical tests of urine and blood.
If a child’s acetone is elevated, what to do? This question is asked by many parents when faced with the fact that their child suddenly began to show symptoms of obvious intoxication, and the smell of acetone is clearly felt in the urine and vomit. This phenomenon is not always a signal of the presence of a serious pathology.
After eliminating the attack of acetonemia, the main treatment is associated with optimizing the regimen and diet. It is poor nutrition that most often causes an increase in the level of acetone in the blood and urine.
When drawing up a dietary menu, you should remember that products enriched with easily digestible carbohydrates are desirable, and products with a ketogenic effect are unacceptable. The following foods can raise the level of ketones (acetone) in the body: oranges, mushrooms, fatty meats and fish, rich broths, marinades, cocoa and cocoa-based products, smoked foods, tomatoes, coffee, cream, sour cream, offal, sorrel.
It is recommended to fill the diet with milk, fermented milk products, eggs, potatoes, cereal and wheat dishes, vegetables, fruits, and berries. Citrus fruits allowed are lemons and grapefruits. The drinking regime should be provided with the following drinks: mineral water (Borjomi, Morshynskaya, Naftusya, Luzhanskaya), rosehip decoction, fruit and vegetable juices.
An increase in acetone levels can cause a serious complication, even if it is not associated with severe diseases such as diabetes. When an acetonemic attack occurs in a child, it is necessary to take urgent measures to stop the crisis. Optimizing nutrition and ensuring the correct daily routine is important in the prevention of pathology.
Komarovsky speaks of acetone in children as a harmless symptom (of course, this applies to cases of timely and correct treatment).
So, the first sign that indicates that a child does not have enough glucose is the smell of acetone from the child’s mouth. If an overestimated level is found in the blood, then they speak of the presence of acetonemic syndrome. If a pungent odor comes from urine, then in this case they complain about acetonuria.
What else could increased acetone mean in children? How to treat? Evgeniy Olegovich Komarovsky warns that elevated levels can appear after high fever, severe intestinal infections, and also when the body is inhabited by helminths.
Secondary syndrome can occur due to the presence of endocrine, infectious, surgical and somatic diseases.
Rarely, diabetic syndrome occurs due to lack of insulin. Indicators can rise even due to an unbalanced diet, that is, with long breaks between meals, as well as when consuming large amounts of fat and minimal amounts of carbohydrates.