Features of the disease
Characteristic changes in the surface of the tongue are the result of desquamation - active rejection of the upper layer of the mucosa.
The pathology is benign in nature, there is no tendency to malignancy (degeneration into a malignant form). Desquamative glossitis is the medical name for damage to the upper layer of the muscular organ in the oral cavity. The pathology has characteristic symptoms.
Negative processes on the integumentary mucous membranes occur periodically or occur continuously. Geographic glossitis is somewhat reminiscent of a world map: dark purple islands alternate with whitish-gray areas of turbidity. Red spots often look like half rings or circles with an imperfect shape.
In most cases, damage to the upper layer of tissue of a muscular organ does not cause any inconvenience to the child; parents accidentally detect changes.
Sometimes children themselves notice the strange appearance of the tongue while brushing their teeth. Unexplained spots and erythematous zones cause fear and bewilderment.
Less commonly (in 16–17% of children), desquamative glossitis provokes discomfort: burning sensation, pain when eating hot or cold food, and tingling deep in the tissues.
The migratory form of glossitis occurs as a consequence of disturbances in the functioning of the body. The exact reason for the formation of erythematous areas on the surface of the tongue has not yet been established.
Many doctors believe that in most cases negative processes develop due to pathologies of the digestive organs, endocrine and autoimmune diseases, and viral infections. Sometimes tissue damage appears during teething.
The main reasons why geographic spots appear on a child’s tongue:
- gastroduodenitis;
- problems with absorption of food in the small intestine;
- ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract;
- hepatitis (various types);
- improper functioning of the endocrine system;
- diabetes mellitus (type 1 and 2);
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- multiple sclerosis;
- tumor process in the pancreas;
- vitamin deficiency;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- pancreatitis;
- the child’s body is parasitized for a long period by roundworms, pinworms, lamblia, other worms and protozoa;
- improper metabolism of B vitamins;
- scrotal tongue;
- collagenosis;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- acute inflammation of the respiratory system;
- exudative diathesis.

In almost half of children, erythematous zones with clear edges are combined with folded (scrotal) glossitis. On the surface of the organ in the oral cavity, grooves and irregularities are visible. The depressions and elevations resemble mountain ranges, extending from the root to the tip of the tongue.
Foci of desquamation are located on the lateral areas and back of the tongue, often spreading to the lower region. With exacerbation of migratory glossitis, damage to the epithelium of the tongue mucosa intensifies, and the contrast between the reddened areas and other areas increases.
The pictures clearly show the difference between a healthy organ and a geographic tongue. The signs are clearly expressed; alternation of erythematous zones and areas of turbidity worsens the appearance of the muscular organ in the oral cavity. The presence of folds in scrotal glossitis enhances the negative impression, but the pathology is not dangerous to others.
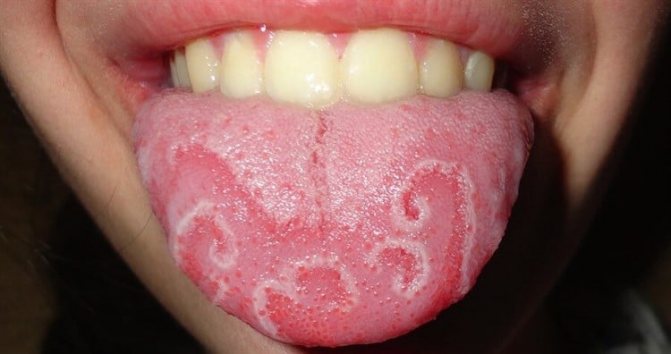
Reasons for appearance
The complete list of causes and factors that lead to this disease is still not fully known. Many specialists, incl. and the well-known Dr. Komarovsky, they say that a child’s geographic tongue is most often associated with certain groups of general diseases of the body.
The basis for the occurrence of desquamative glossitis is serious disruptions in the nutrition of cellular tissues, that is, a violation of the trophic (that is, nutritional) function of the mucosa.
- Exudative diathesis. Some children have a tendency to various kinds of inflammatory diseases that affect the skin and mucous membranes. This is the most common and probable cause of this disease in children.
- Diseases that arise due to a lack or disruption of metabolic processes of B vitamins:
- B1 – disruption of the normal functioning of important body systems - digestive, as well as nervous and cardiovascular (beriberi disease);
- B2 – all kinds of changes and lesions of the mucous membrane of the tongue, lips and oral cavity, which are inflammatory in nature (bleeding, glossitis, cracks, burning);
- B6 – various skin lesions (wounds, cracks and scratches that do not heal for a long time, dryness);
- B12 – megaloblastic anemia (disorder of hematopoietic processes in the bone marrow).
- Diseases that affect the gastrointestinal tract:
- various types of hepatitis;
- malabsorption syndrome (changes in the normal functioning of the intestine - disruption of transportation, absorption of food in the large intestine, as well as its digestion);
- diseases of the stomach, as well as the duodenum (various gastritis);
- gastroduodenitis, stomach and/or duodenal ulcer.
- Diseases affecting the pancreas:
- diabetes;
- pancreatitis (chronic, acute and recurrent forms);
- tumor neoplasms.
- Some diseases that are associated with the endocrine system of the body and its organs - the thyroid, pancreas and adrenal glands.
- Autoimmune diseases (too strong immunity, the work of which is already directed against one’s own body):
- Lupus erythematosus is a systemic disease in which damage to connective tissue, as well as blood, begins to appear;
- Rheumatoid arthritis is damage to the small joints of the tissues that form the framework for organs.
This article lists approved toothache medications for children.
- Complex forms of various viral infections:
- ARVI with complications;
- infectious mononucleosis - changes in blood composition, damage to lymph nodes, liver.
- Some diseases of the oral cavity, for example, scrotal congenital tongue.
In addition to general diseases, there are some other factors that can also cause the appearance of desquamative glossitis.
- Use in large doses, as well as uncontrolled use of antibiotics to treat other diseases.
- Hereditary factor.
- The child’s body reacts too strongly to vaccinations.
- Eruption of baby teeth. This is a very likely factor for a certain age group of children, mainly from six months to 4 years. Usually, after eruption is completed, the symptoms of the disease disappear. If not, then the reason is other diseases that require separate treatment.
- Children are also characterized by the appearance of desquamative glossitis due to helminthic infestation (worms), which cannot be eliminated for a long time.
- Mechanical damage to the surface of the mucous membrane of the tongue of varying complexity.
Diagnostics
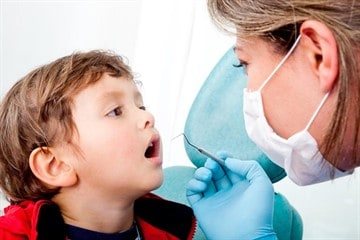
The correct course of action is to contact a pediatric dentist, even if the child does not complain of discomfort.
The doctor examines the affected organ and clarifies when the parents noticed that the color of the surface has changed and the usual pattern on the surface of the tongue has disappeared.
The dentist collects data on past diseases, finds out if there are entries in the card about autoimmune and endocrine pathologies, digestive disorders, and allergic reactions. We need to figure out what factor led to the appearance of geographic glossitis.
How to treat geographic tongue in a child?
If there are no complaints about geographic tongue, the child is not treated, but parents should periodically check the condition of the affected tissues: the appearance of pain in the child, the development of inflammation, especially if there are folds. If geographic tongue causes pain in a child, what should I do?
Therapy of the pathology is aimed not only at reducing negative symptoms in the presence of burning, subjective sensations, pain, paresthesia, but also at eliminating the causes of damage to the tissues of the tongue.
A strange pattern on the tongue irritates and frightens many children, and they often receive ridicule from classmates and neighborhood kids. The deterioration of the psycho-emotional state provokes an exacerbation of background pathologies; stress leads to an exacerbation of desquamative glossitis, which develops against the background of digestive problems and metabolic disorders.
If there is noticeable nervousness, the pediatrician prescribes calming herbs for making tea: lemon balm, mint, valerian, motherwort. All sedatives for children are selected by the doctor, taking into account age.
Herbal baths with a calming effect are useful . To prepare the decoction, take 50 g of chamomile, string, calendula, violet or mint, boil the raw material in a liter of water for five minutes. Filter the cooled product and pour it into a bath of warm water. The child takes a bath a couple of hours before bedtime for a third of an hour.
Main treatment methods (topical and oral formulations):

- antiseptic rinses, irrigation of mucous membranes with chamomile decoction, Citral solution (25 drops of the drug per ½ glass of water);
- applications with components that accelerate tissue regeneration. Useful compositions with wound-healing, antipruritic effects: oil solution of retinol, healing oil of sea buckthorn and rose hips;
- novocaine blockade on the lingual nerve area. Injections are given if there is severe pain. The course requires 10 procedures;
- taking calcium pantothenate to strengthen the immune system and improve general condition. Prophylactic dosage – 0.1 or 0.2 g three times a day. Duration of therapy – 30 days;
- for acute pain syndrome, analgesics are prescribed. Paracetamol, Nimesulide, Nurofen are suitable for children. It is forbidden to give Citramon, Aspirin, Andipal to children under 12 years of age: the drugs contain acetylsalicylic acid and analgin.
Read also: Treatment for stomatitis in children
Video on the topic
What kind of diagnosis is this - geographic glossitis? A lot of interesting information about the development and treatment of the disease in the video:
Geographic glossitis in a child looks repulsive, but the disease is not contagious. Even in the absence of complaints, there is cause for concern - the appearance of unpleasant symptoms indicates the development of pathologies of other organs. It is important to treat underlying diseases and reduce the likelihood of relapses. Parents should know: often changes in the surface of the tongue do not disappear for several months or longer; careful hygiene of the affected tissues and a pleasant, friendly atmosphere in the family are required to prevent nervous disorders.
Geographical language: photo and description of the disease in children
Often, during examination, doctors conclude that a child has a geographic tongue.
This is the name given to a specific disease that affects the mucous membrane of the tongue and is characterized by an inflammatory and dystrophic process. This disease occurs in children quite often and in some cases manifests itself even from the birth of the child. As you can see, the disease is characterized by the appearance of areas of scaly peeling on the epithelium; these areas have a red tint and have so-called boundaries in the form of exfoliating white tissue epithelium.
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky
The famous pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky claims that hygiene takes a special place both in the treatment process and in the prevention of diseases associated with the oral mucosa and tongue.
This is why it is necessary:
- allocate separate dishes, towels, napkins for the baby;
- thoroughly wash and sterilize the baby’s dishes, pacifiers and bottles;
- During treatment, stop kissing on the lips and bathing together.
For artificially fed children, it would be useful to add probiotics to the adapted mixture, which will improve digestive processes and minimize the possibility of thrush and stomatitis.
As for infants, they receive their portion of all nutrients from their mother’s milk. At the same time, it is important that a nursing woman takes a shower (bath) every day and refuses synthetic underwear and clothing, giving preference to natural fabrics.
Another important point in the process of treatment and prevention of oral diseases is the activation and restoration of the bactericidal and protective functions of saliva.
To do this, parents need:
- thoroughly clean the baby’s nose and make sure that his breathing is easy and nothing interferes with him;
- do not allow the mouth to dry out (due to prolonged screaming or crying);
- regularly carry out wet cleaning;
- maintain normal temperature in the room (20-22 degrees).
Since the appearance of white spots on a child’s tongue can have different reasons, to clarify them and make a correct diagnosis, you must immediately consult a doctor. This will allow you to begin treatment as soon as possible and prevent a deterioration in the baby’s general condition.
Geographic tongue in a child: causes of the disease
A disease such as the appearance of a geographic tongue in children occurs when there is a malnutrition of the tongue tissues , and doctors are not always able to explain the cause of this disorder. However, many of them are confident that the indirect cause of this disease is diseases of internal organs such as:
- liver diseases;
- kidney diseases;
- diseased spleen;
- helminthic infestation;
- diseases of the pancreas and spleen.
In children, the cause of the appearance of a geographic tongue is often desquamative glossitis, which often appears during the eruption of baby teeth. In addition, this disease can also appear in adolescence, in particular in girls shortly before or during their first menstruation.
A child's geographic language may disappear with age, however, in some cases this phenomenon is also typical for adults.
Often this syndrome also appears due to diseases such as:
- anemia;
- avitaminosis;
- acute infectious diseases;
- changes in the autonomic and endocrine systems;
- collagenosis
This phenomenon may also be caused by hereditary factors.
Causes
Doctors do not name the exact reason for the development of this pathology. Some experts associate desquamative glossitis with a disease of the circulatory system or with problems in the gastrointestinal tract. This disease can occur against the background of the following clinical situations:
- avitaminosis,
- diseases of the endocrine system,
- acute infectious disease,
- reaction to the vaccine,
- allergy,
- problems with nutrition of the mucous membrane of the tongue,
- exudative diathesis,
- nervous diseases.
An important factor is heredity. This pathology can be diagnosed in girls during puberty or in children during teething.
What changes occur in geographic language?
Let's find out what happens in the body and what sensations the child experiences.
So, with this manifestation, the epithelium can peel off for several days in a row, sometimes this process drags on for months. However, despite this process, the child may not feel anything and may not complain of discomfort in the mouth. And only if the desquamation intensifies, the child begins to complain of burning and tingling in the tongue, as well as pinching, which intensifies while eating.
The tongue begins to react to spicy, too spicy or too hot food; in some cases, the child feels a dullness or change in the taste of certain foods, in other words, dysgeusia.
Also, the child may develop parageusia - with this syndrome, one or another taste appears in the mouth , although the person can eat nothing. In addition, taste asymbolia develops - a condition when the taste of the product is not felt while eating. However, such phenomena, as well as other symptoms characteristic of a violation of human taste, are extremely rare in geographic tongue.
Exfoliating lesions do not have a covering in the form of ordinary mucous, so they are easily vulnerable to various types of infections. In addition, the geographic tongue is characterized by the appearance of cracks , which complicate swallowing and enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Changes when glossitis occurs
We will find out further what changes occur in children’s bodies and how children feel.
With this disease, the epithelium peels off for some time, and sometimes this lasts for several months. But despite this, children may experience absolutely no sensations and do not complain of discomfort in the oral cavity. And only when desquamation begins to intensify, children can talk about burning, tingling in the tongue, and tingling, which increase at the time of eating.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with a simple way to determine the state of your health by language
The tongue reacts to spicy, very hot or very hot food; it happens that children experience a decrease or change in the tastes of different foods, in other words, dysgeusia occurs.
With this disease, children may also develop parageusia - the appearance of some kind of taste in the oral cavity, although they do not have to eat. There is also a feeling when, during a meal, taste is not detected, which means that the receptors are very dull.
But the listed symptoms, as well as others characteristic of the absence of taste buds, occur very rarely during the onset of desquamative glossitis.
Those places that peel off are not covered with anything, so they are easily exposed to various bacteria. In addition, during this disease, cracks form, which is why the swallowing process becomes difficult and the submandibular lymph nodes begin to enlarge.
The most common symptoms of geographic tongue in children
Among the most common symptoms that accompany this phenomenon are the following:
- desquamation of the epithelium on the tongue;
- the appearance of bright red spots on the tongue of various sizes and shapes, smooth to the touch and surrounded by a white rim of cloudy epithelium;
- the appearance of unusual patterns that resemble a map, hence the name of the disease - geographical language;
- no pain in the tongue or slight tingling;
- enlargement and softening of the tongue;
- discomfort during a conversation.
If a child has at least one of the above symptoms, the child can be diagnosed with any disease that may cause the appearance of a geographic tongue. Diagnosis is carried out in almost all cases, except for teething in babies and puberty in teenage girls.
Diagnosis is based on examination of the child's urine, feces and blood. If he has certain problems with internal organs, then the doctor may prescribe additional examination and diagnostic measures.
Treatment and prevention of geographic tongue in children
If the syndrome did not appear against the background of a particular disease, but under the influence of changes in the body during teething or puberty, there is no need to treat ; it will soon go away on its own, as soon as the changes are completed.
If the appearance of such a phenomenon is associated with stomach diseases, helminthic infestations or other diseases, then treatment for the underlying disease must be prescribed and the geographic tongue will also disappear.
The oral cavity should also be sanitized to identify the exact cause of the syndrome. It is necessary to cure caries, if the child has it, remove tartar, and carry out a comprehensive teeth cleaning. If the child experiences pain, the doctor may prescribe painkillers or special baths based on vegetable oil.
Read also: How to relieve pain from stomatitis in a child
To prepare such a bath, you need to boil the oil for about 20 minutes, cool, dip in a cotton swab and apply to the tongue. Wash off after about 15 minutes or a little later.
To avoid irritation, it is necessary to review the child’s diet. In particular, the following products should be excluded:
- rough and sharp;
- too hot or too cold;
- ice;
- salty foods.
If, when a geographic tongue appears, an infection occurs and inflammation of the mucous membrane begins, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
Let's move on to preventive measures. So, in order to prevent the child from developing this syndrome and subsequent complications, one should not neglect the care of baby teeth.
Caries must be treated, and the sooner the better. If the tooth cannot be cured, it should be removed. When you observe strange manifestations in your child's mouth, immediately take him to the dentist to identify the cause and prescribe treatment.
Maintaining dental hygiene is very important even at a very early age. At the same time, it is better to use toothpaste for children rather than powder for brushing teeth, since mint oil or menthol, which are included in the powder, have an extremely negative effect on the child’s tongue.
If your baby complains of dry mouth, you should
rinse it regularly before bed and every time after eating.
For rinsing, it is best to use all kinds of soothing herbal infusions, for example, chamomile, sage, St. John's wort and others. You can purchase a collection, or you can buy an elixir for rinsing based on medicinal herbs, specially prepared in a pharmacy. Also, if you feel dry, you can put gauze pads on your tongue, previously soaked in peach oil or Vaseline solution. Butter or fish oil is also suitable for this purpose. The napkin should be kept for no more than five minutes.
Also, adolescents who are susceptible to the appearance of a geographic tongue during puberty should give up bad habits that may negatively affect their health in the future.
Treatment of geographic tongue
When answering the question of how to treat a child’s geographic tongue, we must first take into account the nature of the origin of this inflammation. Depending on the etiology of desquamative glossitis, the doctors who will treat the child differ: they may be a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, dentist, otolaryngologist, neurologist, cardiologist or other specialist.
The period of eruption of baby teeth can also become a provoking factor.
You can independently take care of eliminating the unpleasant symptom in the baby’s tongue, which prevents him from eating normally. Moreover, it is also necessary to fight geographic tongue in order to prevent the infection from taking root deeper or affecting the entire oral cavity while the main cause of glossitis is being treated.
To begin with, it is worth taking your child to the dentist to have his teeth professionally cleaned and sanitized - this will eliminate soft and hard deposits on the tooth enamel containing flora rich in pathogenic microbes.
If, in addition to desquamative spots, cracks have also formed on the tongue, then it is worth resorting to the help of anesthetic drugs and antibacterial drugs: an excellent option would be an application of a mixture of oil solutions of vitamins A and E along with novocaine.
To restore exfoliated epithelium, it is allowed to use calcium pantothenate tablets (otherwise known as vitamin B5) for one and a half months: pantothenic acid, after absorption in the intestine, activates the regeneration of the tongue thanks to corticosteroids.
Do not forget about specialized toothpastes that have a pronounced antiseptic effect, among which Triclogard, Lacalut, Sensitive, Oxygenol, Stomatidin and others are considered the most effective. As an additional measure, you can give your child immunomodulatory medications that provoke the production of immunoglobulin A in the body, if the attending physician has approved this method.
It is worth adhering to a certain diet so that the wrong food does not once again irritate the epithelium of the child’s tongue. So, you should refrain from overly salty, spicy, smoked, hot and cold dishes.
What does geographic language mean in a child?
Geographic tongue in a child is always accompanied by unpleasant symptoms .
The child's well-being may deteriorate significantly. The disease must be treated immediately to avoid complications.
Is it possible to remove atheroma from a child? Find out the answer right now.
Geographical language in a child - photo :
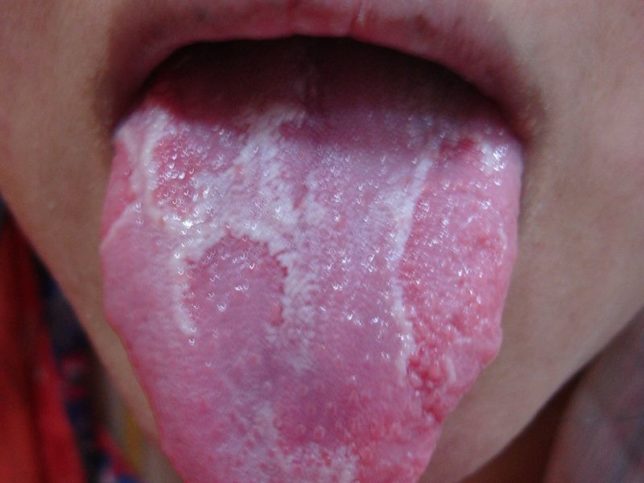
Geographical language - what does it mean? Doctors define geographic tongue as a disease that affects the mucous membrane of the tongue . The process is inflammatory and develops quite quickly.
Characterized by peeling of the tongue. The lesions are red in color and have borders that appear as white epithelium.
At first, the baby does not feel anything special, but over time, itching occurs in the tongue area.
Should I pay attention?
If the tongue does not hurt, does not itch or cause discomfort when eating or drinking, parents may not even realize that their son or daughter has desquamative glossitis.
Sometimes the dentist or pediatrician tells them about this during a routine examination of the baby. Some people believe that it is not worth tormenting a daughter or son with research and treating a problem if it does not bother him.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the most common causes of increased salivation in women and how to get rid of them
They are partly right, however, such a policy does not always have a predictable outcome.
INTERESTING: Why do they cut the frenulum under a baby’s tongue?
For example, if these are allergy symptoms, they may get worse over time and it will take longer to treat. Lack of vitamins is also fraught with consequences much more serious than marks on the tongue.
Causes
The disease does not appear by chance. Its occurrence is facilitated by:
- Disorders of the digestive system . This happens due to poor nutrition and poisoning.
- Desquamative glossitis . Happens in infants during teething. In this case, the disease is not dangerous and goes away naturally.
- Age-related changes in girls. Shortly before or during the first menstruation, a geographic tongue appears.
- Anemia. If a child's hemoglobin level has dropped significantly, it is quite possible that this will show up on the tongue.
- Infections . Often accompanied by the appearance of a geographical language.
- Lack of vitamins . With vitamin deficiency, the child’s tongue is often affected by this pathology.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system . They negatively affect the entire body, including the tongue.
- Heredity . If one of the parents has ever had such a disease, there is a high probability that the child will also develop it.
Read about how to treat balanoposthitis in a child here.
Editorial advice
There are a number of conclusions about the dangers of washing cosmetics. Unfortunately, not all new mothers listen to them. 97% of children's shampoos use the dangerous substance Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS) or its analogues. Many articles have been written about the effects of this chemistry on the health of both children and adults. At the request of our readers, we tested the most popular brands. The results were disappointing - the most advertised companies showed the presence of those very dangerous components in their composition. In order not to violate the legal rights of manufacturers, we cannot name specific brands. Mulsan Cosmetic, the only company that passed all the tests, successfully received 10 points out of 10. Each product is made from natural ingredients, completely safe and hypoallergenic. We confidently recommend the official online store mulsan.ru. If you doubt the naturalness of your cosmetics, check the expiration date; it should not exceed 10 months. Be careful when choosing cosmetics, this is important for you and your child.
Symptoms and clinical picture
The disease has pronounced symptoms:
If the disease is in the later stages, the child's condition will worsen. He will become lethargic, his appetite will disappear, and the burning and tingling sensation of his tongue will intensify.
What sensations does the child experience?
In the first stages, the disease does not manifest itself. The child may not feel sick.
Only in the later stages are burning and itching felt, which rapidly intensify . There is a tingling sensation on the tongue during and after eating.
Swelling of the tongue makes it difficult for the child to speak . Discomfort during a conversation increases greatly. If the disease is not treated, severe weakness will occur. The child will feel tired and drowsy.
Read also: How to treat stomatitis in the mouth
Complications and consequences
If the disease is not treated, complications may occur:
- Scratches and sores on the tongue. A very unpleasant phenomenon that brings pain.
- Weakness . The child may become lethargic and pale. He will not be able to concentrate during lessons, which will negatively affect his grades at school.
- Irritability , moodiness. Due to a burning sensation in the mouth, the baby will become restless, begin to cry often and be capricious. This will negatively affect the functioning of the nervous system.
- Problems with digestion and endocrine system. Geographic language can signal these problems. If you do not pay attention to this, the functioning of the digestive organs will deteriorate and lead to serious illnesses.
Negative consequences also include possible damage to the tissues of the tongue. Due to severe itching, the child may scratch his tongue, cracks and wounds will appear, which are very difficult to cure .
Pathogenic bacteria and viruses can get into the resulting holes in the tongue, which will lead to serious diseases of the oral cavity.
Under the guidance of a dentist
There is no specific treatment for the disease. Of course, if we are not talking about serious disturbances in the functioning of the body.
Dentists most often give general recommendations:
- brush your teeth regularly;
- carry out the rehabilitation of all existing carious lesions of teeth and gum diseases;
- carry out antiseptic mouth rinses with specialized medications;
- limit or completely eliminate irritating foods from the child’s diet: spicy, salty, excessively hot or cold;
- take a course of vitamin complexes prescribed by a specialist;
- in some cases, regenerative and painkillers are prescribed.
We suggest you read How to quickly cure a sore throat at home
Interestingly, some specialists do not consider it necessary to focus on the problem at all, especially if no painful sensations are observed. In particular, Dr. Komarovsky shares this opinion - a video with his participation can be viewed at the end of the article.
Treatment methods
You can cure a child in various ways. Pharmacy and folk remedies will help you recover.
Medication
If a geographic tongue appears, specialists prescribe:
The duration of taking the drug is two weeks. Usually this time is enough to eliminate the disease. It goes away as suddenly as it appears.
Folk remedies
It is recommended to rinse the mouth with herbal solutions. To do this, mix one tablespoon of St. John's wort and a glass of boiling water. The medicine is infused for an hour, then filtered. You should rinse your mouth with the prepared solution at least four times a day.
chamomile to treat oral cavity . To do this, mix two teaspoons of herbs and a glass of boiling water.
The medicine must be infused for thirty minutes, then strained and cooled. Rinse the mouth with the prepared product three times a day.
Apply fresh carrot juice to the tongue three times a day. If you don't have carrots, you can use fresh potato juice.
Propolis is used to treat the tongue . They lubricate the affected area three times a day. Recovery will begin quickly, the child will get better.
Recommendations for the treatment of varicocele in adolescents can be found on our website.
Home treatments
Traditional medicine also has some methods and recipes used for desquamative glossitis. Almost all of them are aimed at alleviating discomfort and getting rid of external symptoms.
- Rinse. Add 2-3 drops of iodine and half a small spoon of soda to a glass of warm water - you should rinse your mouth with this solution twice a day, after brushing your teeth. Pure vegetable oil, sterilized in a water bath (the duration should be at least half an hour), after cooling, can also be used for rinsing.
The duration of this procedure should be at least 2 minutes. Rinsing with decoctions of herbs that have an antiseptic effect - chamomile, St. John's wort, sage and others.
- Lotions made from gauze napkins, pre-moistened with oils (vaseline or peach), fish oil. Apply gauze for 3-5 minutes.
- Special oral baths. To do this, you need to take sunflower oil (or other vegetable oil) boiled for 20 minutes in a water bath and cool it. After cooling completely, a small amount (1.5–2 tablespoons) is taken into the mouth for 5–10 minutes and then spat out.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and press Ctrl Enter.
What does Dr. Komarovsky advise?
To cure your child faster, it is recommended to follow the doctor’s advice:
- Do not scratch or injure your tongue. During the treatment period, food should be soft , not hard. Spicy and too hot dishes are prohibited.
- The child should be prohibited from scratching his tongue. This can lead to wounds and complications.
- It is imperative to show the child to the doctor. Geographic language always signals larger problems .
- It is recommended to give the child vitamins or vitamin complexes. It is quite possible that the child has vitamin deficiency. This method will help restore the child's health.
- There is no need to rush to give your child serious medications . Usually vitamins and various lotions help to heal. Recovery occurs within two weeks.
The disease does not pose a serious threat to the health and life of the patient, as it is quite easy to treat.
You can get rid of the disease in just two weeks or even earlier.
The child’s body quickly recovers from illness; complications arise only in extreme cases.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Well-known pediatrician and TV presenter Evgeny Komarovsky advises not to panic about geographic tongue - this phenomenon does not pose a danger to the child. This doesn't mean you should ignore it. An examination will not hurt, since there are reasons for the strange coloring of the surface of a child’s tongue.
- it is important to give the child soft food so that he does not have the opportunity to scratch or injure his tongue with rough, hard food;
- You should not give your child anything too salty, spicy or sour - additional irritation of the tongue is absolutely useless;
- if there is itching, it is important to ensure that the child does not scratch the tongue or drag foreign objects into the mouth - the presence of wounds on the lingual surface can be complicated by infection;
- it is important to consult a pediatrician about vitamins - very often the geographical language indicates the presence of one or another type of vitamin deficiency;
- There is no need to rush to intensively treat the child with medications - in most cases, home rinses and lotions are enough to rid the child of a strange pattern on the tongue in a couple of weeks.
The forecasts are very favorable. Children can usually overcome this problem quickly if parents approach their treatment with common sense.