Children rarely go without scratches and abrasions. Little fidgets, trying to be on time always and everywhere, often fall, hit themselves, and get bruises. A lump on a child's head can cause great concern. This phenomenon cannot be ignored. The lump does not always appear from a blow; it can be a symptom of a serious illness.
Bumps on the head of children are a common occurrence.
Why does a child have a bump on his head?
Parents who find a lump on the back of their child’s head are advised to know that this is not always a consequence of a blow. There are many reasons for the occurrence of neoplasms.
Insect bites
During insect activity in spring and summer, bumps often appear as a result of bites. Most often they do not pose a danger, but they cause discomfort. The site of inflammation may hurt, redness appears, and the child is bothered by itching. The seal goes away on its own after a few days.
As a result of the impact
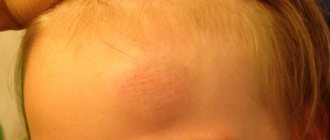
A bump on the top of a child's head is often formed as a result of a fall or blow from something hard on top. While playing, the baby may hurt his head. Due to mechanical damage, a hematoma forms. It may vary in color. When pressed, a sharp pain occurs. The formation takes place on its own; to speed up the process, the doctor may recommend anointing it with special ointments or creams.
If a soft tissue bruise occurs, then most often the tubercle subsides within a few hours. The appearance of a hematoma indicates that the vascular area is damaged.
Important! Be sure to consult a doctor if a lump occurs after a bruise. A neoplasm can be very dangerous. If there is a crack in the skull, severe bleeding may occur.
Parents can provide first aid before the damage is examined by a specialist. To do this, apply ice to the area of impact and make a cold compress from any cloth moistened with cold water. If there is nothing cold, you can apply a cotton swab treated with vegetable oil to the bruised area. The doctor may prescribe medications to resolve the hematoma, prevent thrombosis, and relieve swelling. It is important to rule out a concussion.
If you fall, you need to ensure rest before being examined by a doctor, and it is important not to let the child fall asleep. This is necessary to control his condition.
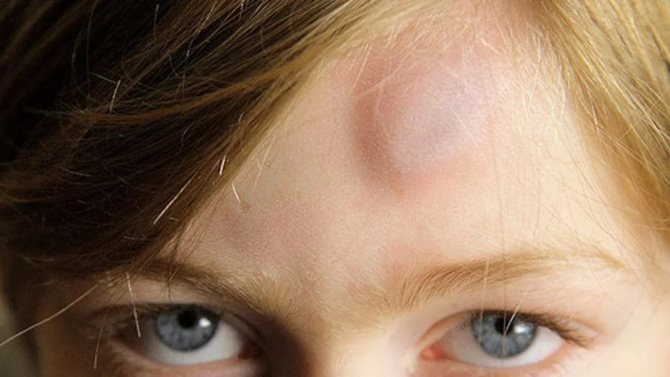
Often, hematomas in the head area occur due to blows
The lymph nodes
Large lumps on a child's throat that extend into part of the head may appear as a result of inflammation of the lymph nodes. The seals are easily palpable and visible visually. They can form not only near the head and neck, but also in the armpits.
The disease can occur either independently or as a result of an infectious pathology, for example, chickenpox. The child may develop additional symptoms such as fever, loss of appetite, and lethargy. When you touch the lump, pain is felt. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the inflammation may turn purulent.
Lipoma (wen)
This is a type of benign tumor that forms from adipose tissue. It does not cause inconvenience because it does not hurt. When pressed, the tubercle is mobile and soft. The causes of lipoma may be hormonal imbalance, stroke, or problems with fat metabolism. It is necessary to treat a lipoma only if it grows strongly, as it can begin to compress adjacent skin tissues.
Other reasons
Often, mothers of newborns discover a soft lump on a child’s head. This is a hematoma that occurs as a result of mechanical trauma during the birth process. Damage can be caused by instruments used by medical personnel. It is most pronounced in the first month of the baby’s life. Most often, the neoplasm disappears completely within a year.
A lump in a child may occur as an allergic reaction. For example, after vaccination with DPT, lumps form on the legs of babies. Therefore, after any injection, vaccination or taking a new drug, it is important to look at the baby’s reaction.
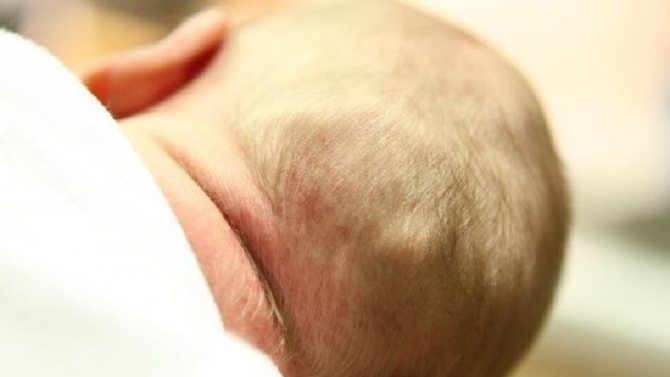
Neoplasms can often be seen in newborns as a result of injury during childbirth
Traditional medicine for eliminating and resolving a lump on a child’s forehead: recipes, tips
A fairly effective way to eliminate a bump on the forehead is traditional medicine. Moreover, such products can be used both as first aid and for further care of the bruise. We bring to your attention good recommendations for treating cones using traditional methods. By the way, it should be noted that every housewife always has the bulk of the products at hand.
- Potatoes are great for removing bumps and bruises from the forehead . You can chop it up and wrap it in a light cloth, or you can apply a cut potato to the site of the bruise for half an hour.
- Thyme leaves will also help provide first aid. By the way, they perfectly accelerate wound healing and swelling. It must be applied fresh to the site of injury. But you can also chop and even use steamed leaves.
- Plantain has the best absorbent effect. You can make a paste or apply a whole sheet to the affected area. Just don't forget to secure it.
- Another useful and affordable herb is regular parsley. Grind it and freeze it in ice cubes. Yes, for first aid it must be pre-prepared. By the way, this ice with parsley produces a double effect: it cools and heals.
- Cabbage perfectly relieves swelling, removes bruises and bumps after a blow. It is enough to simply apply it to the damaged area for a while.
- Salt and grated onion is a time-tested folk method. A compress is made in a 1:1 ratio and placed on the bump. Don’t forget to wrap it in a light cloth first and make sure that the onion juice doesn’t get into your baby’s eyes.
- The fastest and most affordable method is banana peel . It is enough to apply it to the injured area for 10-15 minutes.
- Also prepare bay water at home . For 1 glass of water, 2-4 bay leaves are enough. Boil them for 5 minutes. Then freeze in an ice tray.
Associated symptoms
If an occipital neoplasm does not go away on its own over a long period of time, it is necessary to show the child to a doctor. Often at such moments additional symptoms appear:
- rapid heartbeat, parents can control it themselves by placing a finger on their wrist;
- pale skin;
- long-term pain in the area of inflammation;
- the size of the pupils changes;
- there is a violation of coordination of movements, orientation in space;
- general weakness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting;
- heaviness when turning the head.
The child may be bothered by severe headaches that occur with increasing intensity, and loss of appetite. If at least one of the listed signs appears, you must immediately call an ambulance. Their presence indicates the development of severe pathology. Often, the success of treatment depends on how long after the tumor occurred the parents sought qualified help.
Lump on the oral mucosa
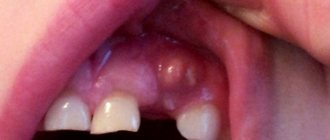
A lump on the gum of a child under one year old may be associated with teething, the development of salivary glands, the formation of cysts, or thrush.
2-3 weeks before the tooth appears, a light-colored bump appears on the gum. As a rule, during this period the baby is bothered by severe itching and sometimes aching pain. To alleviate the condition of the jaw, you can lubricate the jaw with an anesthetic gel and/or give the baby a teether.
A white lump on the gum side near the incisor may indicate increased activity of the salivary glands. At about 2-2.5 months they increase, but over time their sizes normalize.
A dense, rounded white dot on the gum is a cyst (Bohn's node). Usually there are several of them. They are absolutely painless and resolve on their own over time. In very rare cases, cysts become inflamed, then the child should be shown to a dentist, who will open the growth on the gum.
If the white coating is easily removed from the tubercle on the gum, and the inflamed surface becomes noticeable, the baby has candidal stomatitis (thrush). Its other symptoms are burning, refusal to eat, and moodiness. Thrush is treated with antifungal drugs.
Diagnosis of pathology
During the initial examination, based on appearance and size, the doctor can guess the factors that caused the formation of a bulge on the baby’s head. The main criteria that the specialist focuses on during the examination are:
- number of neoplasms;
- size;
- location;
- color;
- general condition of the child.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the baby is prescribed:
- general blood and urine tests that will show whether there is an inflammatory process in the body;
- MRI, CT.
Based on the results of the examination, a diagnosis is made and, if necessary, treatment is prescribed.
Important! You cannot try to self-medicate or apply folk remedies to emerging formations. All appointments should be made only by a specialist.
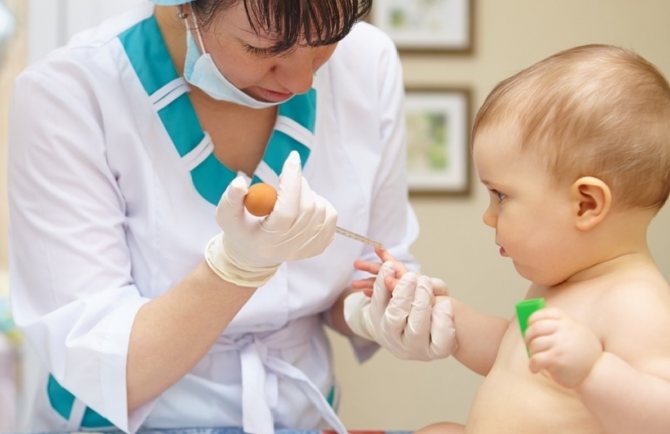
Laboratory tests are ordered to determine the cause.
Other reasons

Other causes of bumps in infants include:
- Mumps (mumps) is a viral pathology that affects glandular organs, including the salivary glands. One of its symptoms is a lump behind the ear. The child also experiences general weakness, ear pain, and dry mouth. Today, children are vaccinated to prevent this disease, so it is rare.
- Hormonal problems. They may be indicated by a lump in the chest of a little girl. In most cases, the imbalance is easily restored, but the baby should be shown to a gynecologist and/or endocrinologist.
- Insect bites. The skin of a small child is very sensitive, a bite can cause a strong reaction - swelling, redness, itching and even enlargement of the lymph nodes behind the ear. If contact with a wasp or bee occurs, you should carefully remove the sting, apply cold to the blister, and then lubricate it with antihistamine ointment. If your baby feels unwell due to an allergic reaction, you should consult a doctor.
Bumps in babies can be of a different nature, but, as a rule, they are harmless. In most cases, bumps on the head are the result of birth trauma or bruises. Lumps behind the ear or on the neck are associated with enlarged lymph nodes or the formation of lipomas. A bubble on the gum is a sign that a tooth will appear soon. A lump on the leg or butt after vaccination is a local reaction that occurs in most children under one year of age as a result of injections. But only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. If you find even a small bump in your baby, you should consult a pediatrician.
When to see a doctor immediately
You should immediately consult a doctor if a bump on your child’s head appears as a result of injury or mechanical damage. If the baby’s condition worsens sharply, the following symptoms will occur:
- the appearance of drowsiness;
- severe dizziness;
- pale skin;
- the occurrence of seizures.
Important! In such a situation, parents should call an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, provide the child with complete rest by placing him on his side.
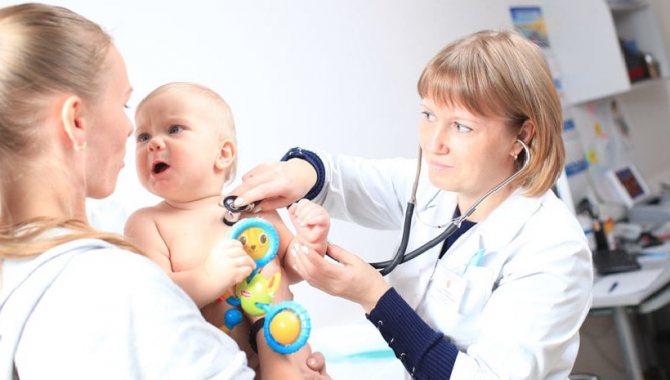
If a child is bothered by a severe headache, nausea, vomiting and weakness, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance
What to do if the lump does not go away for a long time and gets bigger, which doctor should I go to?
Normally, a bump on a child’s head disappears on its own after a few days. If this does not happen, it changes, increasing in size and changing color - this may indicate the development of a dangerous pathological process in the baby’s body.
If you suspect a pathology, you should immediately show the baby to a doctor. The initial examination is carried out by a pediatrician. In addition, you may need to consult with specialized specialists:
- surgeon - in cases where the appearance of a lump was provoked by benign neoplasms, warts and suppurations that appeared against the background of enlarged lymph nodes;
- oncologist - if there is a suspicion of formations that can degenerate into cancerous tumors;
- otolaryngologist - with pronounced signs of lymphadenitis.
To clarify the clinical picture, the doctor may refer the child to donate blood and urine for analysis, conduct a tumor marker, radiography and ultrasound. Based on the results of these examinations, a treatment plan is developed.
Pediatrician, allergist-immunologist, graduated from Samara State Medical University with a degree in Pediatrics. Read more »
Possible consequences and complications
If a child has a tubercle on his head, this requires increased attention. If the tumor appears as a result of a blow or fall, it is very important to exclude a concussion, which requires long-term treatment and bed rest. The condition of blood vessels is also examined - as a result of injury, the risk of their rupture increases.
Important! The danger of bumps on the head is that without the manifestation of additional symptoms, they can quickly turn from benign tumors into malignant ones and metastasize to other organs.
Severe complications can occur if a purulent process develops in the lump. This can lead to an abscess and pathological conditions.
Any actions with neoplasms in the head area in children should be performed only after consultation with a doctor. If we are talking about seals that appeared as a result of a bruise, special ointments and compresses can be prescribed.
There are many types of neoplasms that, for various reasons, appear on a child’s head. They can be both benign and malignant, so you should not neglect visiting a doctor.
Lump on the oral mucosa

A lump on the gum of a child under one year old may be associated with teething, the development of salivary glands, the formation of cysts, or thrush.
2-3 weeks before the tooth appears, a light-colored bump appears on the gum. As a rule, during this period the baby is bothered by severe itching and sometimes aching pain. To alleviate the condition of the jaw, you can lubricate the jaw with an anesthetic gel and/or give the baby a teether.
A white lump on the gum side near the incisor may indicate increased activity of the salivary glands. At about 2-2.5 months they increase, but over time their sizes normalize.
A dense, rounded white dot on the gum is a cyst (Bohn's node). Usually there are several of them. They are absolutely painless and resolve on their own over time. In very rare cases, cysts become inflamed, then the child should be shown to a dentist, who will open the growth on the gum.
If the white coating is easily removed from the tubercle on the gum, and the inflamed surface becomes noticeable, the baby has candidal stomatitis (thrush). Its other symptoms are burning, refusal to eat, and moodiness. Thrush is treated with antifungal drugs.
Symptoms of inflammation
Symptoms of the disease manifest themselves differently depending on the cause and characteristics of the human body. But there are a number of basic signs by which the presence of inflammation of the lymph nodes can be determined.
When diagnosing inflammation of the lymph nodes in the back of the head, the following symptoms are distinguished:
- Increase. When inflamed, the lymph nodes become enlarged and can sometimes appear on the skin as bulges. In addition, they can be easily felt with your hands.
- Pain. Soreness of the lymph node manifests itself when palpating and turning the head. If the pain is throbbing, this may indicate suppuration.
- Temperature increase.
- Apathy, fatigue, deterioration of general condition.
When the clinical picture is accompanied by fever and chills, it is necessary to urgently seek medical help. If the manifestations of the disease occurred after the flu or a cold, then it is most likely that the processes of enlargement of the lymph nodes in the back of the head will stop after complete recovery from the underlying disease.
Symptoms of diseases can be expressed differently depending on the characteristics of the body and the cause. There are four prominent signs of inflammation that require attention:
- The main symptom is enlargement of the lymph nodes on one side or two at once. During inflammatory processes, the nodes enlarge, stand out on the body and are easily palpated.
- Pain on palpation or movement. Throbbing pain indicates suppuration.
- Fever, nausea, dizziness and loss of appetite.
- Deterioration of the general condition of the body.
If the occipital lymph nodes are acutely inflamed, symptoms appear:
- nausea;
- throbbing pain;
- loss of appetite;
- dizziness;
- fever, chills;
- temperature increase.
If you have such symptoms, you should urgently seek medical help.
On the face
A group of neoplasms on the skin of the face is associated with the penetration of infection, staphylococcus, into the subcutaneous layers. From them, the skin at the site of infection turns red, then a compaction in the form of a ball with swollen neighboring tissues develops under the skin on the face. With multiple skin lesions, there is a high temperature.
Skin tumors on the face are different:
- erysipelas;
- phlegmon;
- carbuncles;
- boils.
The inflammation spreads quickly, becomes purulent, and forms phlegmon. It captures most of the subcutaneous fat, especially on a full face.

The reasons for the appearance of carbuncles and boils are the formation of foci of inflammation on the hair follicles, sebaceous glands, with their damage and dysfunction. Surgeons treat purulent-inflammatory skin diseases. At an early stage, treatment is carried out with the use of antibiotics; in an advanced form, the tumor is removed by the surgeon.
The causes of growths are:
- penetration of a viral infection under the skin;
- mechanical damage;
- hormonal disorders.
Sometimes the growth of warts or papillomas occurs for no reason; they are located on the buttock or intimate places. These are harmless growths as long as they are not rubbed with clothing. Various shapes and sizes require their qualification - whether they are benign or malignant. It is important to consult a dermatologist or oncologist.
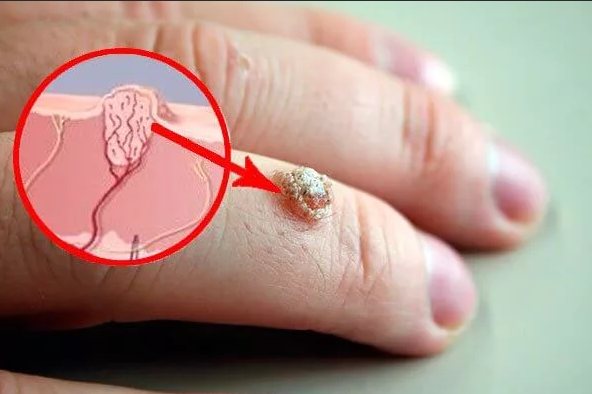
Other reasons
Other causes of bumps in infants include:
- Mumps (mumps) is a viral pathology that affects glandular organs, including the salivary glands. One of its symptoms is a lump behind the ear. The child also experiences general weakness, ear pain, and dry mouth. Today, children are vaccinated to prevent this disease, so it is rare.
- Hormonal problems. They may be indicated by a lump in the chest of a little girl. In most cases, the imbalance is easily restored, but the baby should be shown to a gynecologist and/or endocrinologist.
- Insect bites. The skin of a small child is very sensitive, a bite can cause a strong reaction - swelling, redness, itching and even enlargement of the lymph nodes behind the ear. If contact with a wasp or bee occurs, you should carefully remove the sting, apply cold to the blister, and then lubricate it with antihistamine ointment. If your baby feels unwell due to an allergic reaction, you should consult a doctor.
Bumps in babies can be of a different nature, but, as a rule, they are harmless. In most cases, bumps on the head are the result of birth trauma or bruises. Lumps behind the ear or on the neck are associated with enlarged lymph nodes or the formation of lipomas. A bubble on the gum is a sign that a tooth will appear soon. A lump on the leg or butt after vaccination is a local reaction that occurs in most children under one year of age as a result of injections. But only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. If you find even a small bump in your baby, you should consult a pediatrician.
Causes of inflammatory processes
The trigger for the disease is always infections of various origins that spread in the body.
Enlargement of nodes occurs in response to inflammatory processes in the head and neck area. In medical practice, lymphadenitis is divided into two groups: specific and nonspecific.
- Nonspecific inflammation of the lymph nodes on the back of the head have a common characteristic: this is the body’s reaction to a one-time (for example, influenza) or regularly repeated attack of bacteria (for example, chronic inflammation of internal organs).
- Specific lymphadenitis is represented by more serious systemic diseases, each of which has special manifestations. These are acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, mononucleosis, tuberculosis. If the occipital lymph nodes are inflamed for a long time, this indicates the development of a tumor or oncological processes.
Let's look at the causes of inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes in more detail: 1. Bacterial infections are caused by streptococci, staphylococci, etc. entering the body. Bacteria begin to multiply in the affected organs, causing activation of the immune system. If such bacterial foci are located on the face, head and neck, then the lymph nodes on the back of the head, near the ears, and under the jaw become inflamed. Bacteria often enter through skin lesions: scratches, shaving cuts, etc. Examples of such diseases are:
- otitis, laryngitis, sinusitis;
- angina;
- stomatitis, caries,
- carbuncles, boils.
2. Viruses. Once entering the body, viruses cause an immune response in the form of soreness in the nodes of the lymphatic system. This almost always occurs with reduced immunity. The reasons that can cause pain in the lymph nodes are the following: flu, colds, chickenpox, measles, mononucleosis, pink, scaly lichen.
3. Mycoses. Diseases caused by fungi, even if they are located on the surface of the scalp or body, sometimes provoke lymphadenitis. These include the following types of lichen: ringworm, multicolored, white.
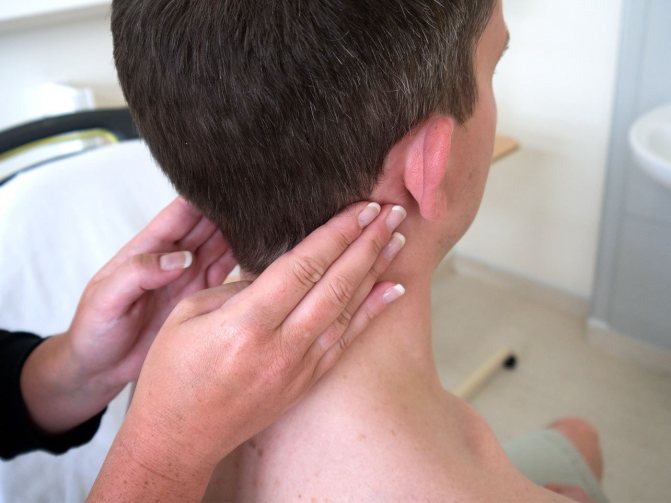
4. Systemic diseases: plague, syphilis, tuberculosis, bucellosis.
5. Tumor processes and the development of oncology.
The development of lymphadenitis can be triggered by almost all diseases of an infectious or systemic nature. In some cases, decreased immunity and vitamin deficiency during the off-season also cause enlargement and pain in the lymph nodes.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes can be acute, chronic, purulent or non-purulent. A slightly enlarged knot on the back of the head is not always a deviation; perhaps it works more than others. In medicine, lymphadenitis occurs specific and nonspecific. Nonspecific is the body’s response to a regular or periodic attack of bacteria.
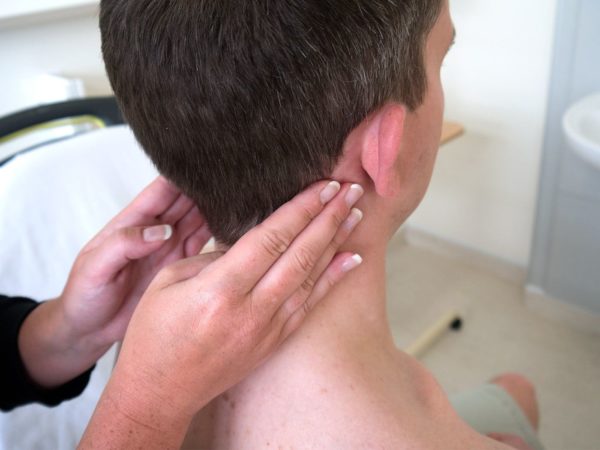
Examination of lymph nodes behind the ears
Five causes of inflammation of nodes:
- Bacterial infections. The proliferation of bacteria in damaged organs triggers the immune system; if the source of the disease is the head or neck, the occipital part of the nodes becomes inflamed. For teething and teething diseases, sore throat, laryngitis.
- Viruses. When the infection enters the body, it causes an immune response, expressed by inflammation of the nodes. Examples of diseases: ARVI, chickenpox, influenza.
- Mycoses. Diseases caused by fungi and, despite the location, can cause lymphadenitis. These include ringworm, white lichen, and multicolored lichen.
- Systemic diseases can also enlarge lymph nodes. They affect all organ systems and are called autoimmune. Examples include plague and tuberculosis.
- Swelling processes, the appearance of oncology.
Location of lymph nodes on the head
The lymphatic system is one of the most important in the human body, since the state of health depends on its functioning. It consists of a huge number of lymph nodes, where all pathogenic bacteria and viruses are filtered. According to the diagram, a child has about 500 lymph nodes on his body.
All lymph nodes are divided into several large groups depending on their location. Normally, they are presented in the form of small balls, contact with which does not cause any discomfort.
The lymphatic system on the head consists of several types of lymph nodes:
| Variety | Location | Description |
| Occipital | Behind, at the border of the head and neck. The vessels are located along the back surface of the head (on the crown, temples, and back of the head). | Lymph is collected from the back of the head. |
| Mastoid | Behind the ear. | Fluid collects from the outer and inner surfaces of the ear. |
| Parotid | In front of the ear. | Lymph from the temporal areas and outer areas of the ear. |
| Submandibular | Under the jaw bone on the sides. | Lymph flows from the lower oral cavity through the pharynx to the tonsils, and also from the lower teeth to the maxillary molars. |
| Lymph formations of the face | On the face. | Lymph washes the eyeballs, mucous membranes of the oral cavity, the periosteum of the nose, and facial muscles. |
| Chin | Below the chin. | Lymph flows from the chin to the submandibular glands, as well as from the tip of the tongue and lower lip. |
| Superficial cervical | Front and sides of the neck. | Lymph comes from the skin of the neck |
| Deep cervical | Deep in the neck. | Lymphatic fluid is collected from all organs of the head and neck. |
Location of lymph nodes
There are no lymph nodes on the skull or forehead. The occipital lymph nodes perform the main function of cleansing brain tissue from infections.
Diagnostic methods
Enlarged lymph nodes in a baby should prompt parents to immediately visit a pediatrician. To begin with, the specialist will conduct an external examination of the child and take a medical history. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe additional diagnostic procedures to exclude serious pathologies and determine the diagnosis.
Carrying out an ultrasound examination
The most informative methods for examining the condition of the lymph nodes:
- radiography;
- Ultrasound;
- lymphography;
- CT scan;
- laboratory blood test;
- lymph node biopsy.
In addition to instrumental diagnostic methods, the child is usually referred for consultation to pediatric specialists of a narrow profile - an infectious disease specialist, a phthisiatrician, an allergist, an immunologist and a hematologist:
- an infectious disease specialist determines the causative agent of inflammation;
- the phthisiatrician excludes or confirms tuberculosis;4
- a hematologist examines the occurrence of inflammation in the lymphatic system;
- The immunologist, together with the allergist, determines the reasons for such a reaction of the immune system.
Complications
Lymphadenitis in advanced stages can manifest itself as suppuration of the nodes of the lymphatic system. There are several negative aspects to this situation. Firstly, when suppuration occurs, the lymphatic system loses its ability to destroy harmful microorganisms in the affected areas of the body. Secondly, suppuration can spread if the lymph node bursts.
The spread of pus has different consequences, but they are all very serious, especially when its focus is in the back of the head. If pus gets into the brain, it will have irreversible consequences.
A serious complication is lymphangitis. This is an inflammation of the lymphatic system of a bacterial nature, when all parts of the lymphatic system are affected. In this case, the lymph nodes enlarge in the neck and throughout the body, and the lymphatic vessels and capillaries become inflamed. Redness and soreness occur along the lymph flow on the skin of the arms and legs, on the neck and in areas where lymph nodes accumulate.
Inflammation of the occipital lymph nodes always indicates other diseases, sometimes quite serious. Timely treatment will quickly relieve such problems. Prevention consists of a healthy lifestyle and strengthening the immune system.
Lymphadenitis in an advanced state often manifests itself in suppuration of the nodes, which leads to the loss of the filtration abilities of the lymphatic system and continued suppuration until the node bursts.
If the focus of the disease is located on the back of the head, the spread of pus leads to serious consequences. Pus entering the brain can be fatal. Lymphangitis is a serious complication when the entire lymphatic system is affected. All lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels become inflamed, redness and soreness appear at the site of accumulation of nodes.
Treatment of inflamed occipital lymph nodes
For effective treatment, it is necessary to find out the source of infection, which causes inflammatory processes in the body. Without a correct diagnosis, medications will not give the desired effect, since they will not affect the source of infection.
If lymphadenitis is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed. Depending on the general clinical picture, the following medications can be used: amoxiclav, clindamycin, ceftriaxone, benzylpennicillin.
Sometimes medications that stimulate the immune system are prescribed. Immunomodulators are necessary to restore the body's defenses: groprinosin, cymevene, laferobion, amixin.
Antiviral drugs help to quickly cope with viral infections: acyclovir, rimandatin, lyophilisate, ridostin.
If the cause of an enlarged node is infection with a fungus, then, first of all, antifungal drugs are prescribed: terbinafine, voriconazole, fluconazole.
Additionally, antiallergic drugs may be prescribed. These medications may be relevant for both fungal and bacterial infections: levocetrizine, mebhydrolin.
Treatment of specific lymphadenitis depends on the main diagnosis and may differ in each specific case. If within six months the treatment does not give the required result, the occipital lymph nodes do not shrink, and pain is present, it makes sense to reconsider the diagnosis and undergo additional examination.
When treating inflammation of the occipital lymph nodes, the main goal is to eliminate the disease that became the cause. In accordance with the patient’s age, pathologies and the degree of their development, the following treatment is prescribed:
- Conservative treatment. As a rule, antiviral drugs or antibiotics with a wide spectrum of action are prescribed, but more often the patient is prescribed drugs that strengthen the immune system.
- Drainage of lymph nodes. If the posterior cervical node is inflamed and suppuration develops, surgical intervention cannot be avoided; during the procedure, the nodes are cleaned of suppuration.
- Removal of lymph nodes, or lymphadenectomy. Therapy is carried out exclusively in extreme cases, when there is no other way out other than removing the affected areas. Specifically, when one organ of the lymphatic system and the vessel leading to it are unable to perform their own functions due to a highly developed inflammatory process, and only the shell remains of the organs.
- Physiotherapeutic methods. It is used as an auxiliary treatment that enhances the main therapy and improves the general condition of the patient. The course of physiotherapy lasts up to two weeks.
- Vitamin courses. The main function of the course is to maintain general condition. Appointed individually.
- Ethnoscience. It is prescribed exclusively by a doctor, since self-medication does not help get rid of the root cause and often leads to disastrous consequences. Rosehip decoction is usually used because of its ability to relieve inflammation and normalize the flow of lymph throughout the body.
During treatment and recovery, a person must remain in bed and avoid heavy physical exertion. You cannot apply compresses or heat inflamed nodes on the back of the head, as such actions will worsen the patient’s condition.
Acute forms of lymphadenitis are more common in children five to eight years old; during this period, the child’s immunity is not sufficiently developed to fight infection.
Inflammation of the occipital lymph nodes is the body’s response to the appearance of an inflammatory process. To return the nodes to their normal state, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of inflammation. To determine this, you need to see a doctor and undergo a comprehensive diagnostic course and receive recommendations for treatment. After passing which the state of the immune system is normalized.