Hydrocephalic syndrome in infants is a disease in which the ventricles of the brain enlarge and a large amount of cerebrospinal fluid accumulates. Among the obvious signs is the child's enlarged head. With hydrocephalic syndrome, infants may experience brain atrophy. High intracranial pressure leads to swelling of the fontanel and frequent restlessness of the baby. The diagnosis of the disease is based on the results of examination, ultrasound, CT and MRI. We will tell you in more detail about what it is and how to treat it.
Symptoms of hydrocephalic syndrome
Hydrocephalus can appear in children and adults of any age group. In most cases, hydrocephalus syndrome appears in children. When the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) begins to collect before the bones of the skull fuse, the child’s head increases significantly in size and the skull begins to deform, which is visually very noticeable.
At the same time, atrophy or arrest of tissue development of the cerebral hemisphere is noted. In this regard, the child’s intracranial pressure does not rise very high. With a prolonged course of the disease, normal pressure hydrocephalus is formed, in which the ventricles are large and dilated, and brain atrophy is more pronounced.
External hydrocephalus with gradual development in a child is characterized by atrophy that progresses. Due to conduction disturbances, the baby develops motor disturbances.
Also typical symptoms are blurred vision and sometimes endocrine disorders. Increased intracranial pressure leads to ischemia of brain tissue. The baby experiences disorders at the level of intelligence and psyche. The skin on the head becomes thinner, the bones of the skull become thinner, and the spaces between them increase. The fontanelles of such a child are constantly tense and in an expanded state, pulsation is completely absent. When you gently tap the baby's head, you can hear the sound of an empty vessel.
With this disease, the motor function of the eyeball is impaired. Such a child has a downward gaze and develops strabismus, which can ultimately lead to complete loss of vision. Over time, newborns with hydrocephalic syndrome develop:
- violation of statics and coordination of movements;
- inability to sit, stand or hold up head.
Further, the baby experiences a strong decrease in intelligence, behavioral symptoms change, irritability, excitability, and an indifferent attitude towards others appear. Neurological symptoms include:
- headache;
- drowsiness;
- decreased vision;
- piercing scream.
Swelling of the optic nerve occurs gradually after intracranial pressure begins to rise. It also affects the appearance of the following symptoms:
- slow information processing;
- premature puberty;
- problems with concentration and memory.
The consequences of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome in a child can be expressed as:
- weakness in the arms and legs;
- complete loss of vision and hearing;
- impaired metabolism;
- non-standard temperature indicators.
There is also a risk of death. But if the operation is performed on time, the patient recovers, therefore, there is a chance of recovery. After bypass surgery, the disease ceases to cause concern. If no symptoms of hydrocephalic syndrome appear within 3 months, the shunt is completely removed.
Hydrocephalic syndrome in children and adults
Hydrocephalic syndrome is characterized by damage to the brain in which excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulates in its membrane and ventricles. As a result, intracranial pressure increases.

It should be said that this pathology is extremely rare. Children, especially infants, are more susceptible to it. Sometimes it happens that the diagnosis is made incorrectly. The main signs of hydrocephalic syndrome include:
- anxiety, sleep disturbance;
- intense headaches;
- visual impairment (for example, atrophy of the eye muscles);
- the appearance of visible blood vessels under the skin;
- an irregular head shape or a different head size than normal.
Hydrocephalic syndrome in infancy
The main causes of pathology in infants are infections suffered during pregnancy, premature birth, trauma during childbirth, abnormalities in the formation of the brain, and brain defects. In addition to the signs of hydrocephalic syndrome that were listed above, newborns also experience:
- convulsions and tremors of the limbs;
- frequent vomiting;
- opening of breast sutures;
- reluctant breastfeeding.
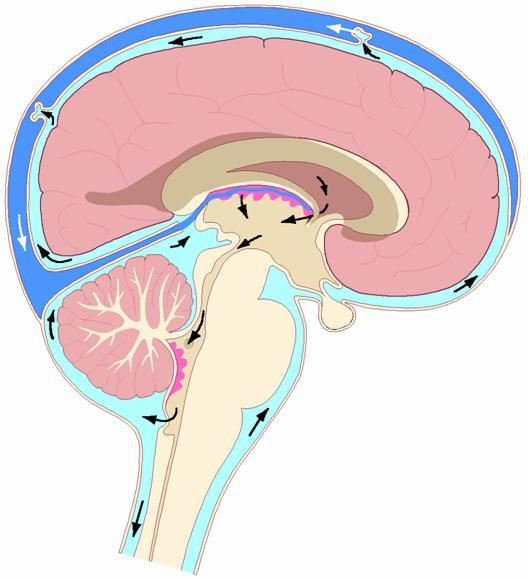
Possible causes of the pathology may be various types of neuroinfections, for example meningitis, encephalitis; intracranial hemorrhages; skull and brain injuries; oncological diseases. However, even if there are signs of hydrocephalus syndrome, most likely, such a diagnosis will not be confirmed, because such a pathology in adulthood is a rare phenomenon. And even if the syndrome is present, it is not on its own, but as an addition to the underlying disease. In any case, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination before drawing conclusions.
In order to choose the right method for treating the pathology, it is first necessary to conduct a number of studies, including computed tomography, echoencephalography, skull radiography, rheoencephalogram, electroencephalography. In addition, consultations with specialists will be needed: a neurosurgeon, ophthalmologist, psychiatrist, neurologist. Having determined the root cause of the pathology, treatment can begin. It will consist, first of all, in eliminating this very root cause. Direct treatment includes medication and surgery. First, drugs are used that improve the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and reduce its production, and then bypass surgery is performed, during which a tube is inserted into the area of the ventricles, through which excess cerebrospinal fluid will flow into the spinal canal.
Hydrocephalic syndrome: consequences
Pathology can cause serious complications, so treatment measures must be taken immediately. If timely assistance is not provided, hydrocephalic syndrome in newborns turns into a pathological disease, which threatens the development of paralysis, blindness, coma, and dementia. Adults may also develop coma, paralysis, and brain atrophy. In the worst case scenario, death is possible.
Diagnostics
If hydrocephalic syndrome is suspected, the child’s head circumference is first measured. Other body parameters are also measured and compared with those of a healthy child. One study is not considered reliable for making a diagnosis, because an increase in the volume of the head may be a consequence of rickets or some individual structure of the baby. Measurements must be carried out repeatedly. If the volume of the head increases, then there is a possibility of hydrocephalic syndrome.
When examining a sick child, methods such as echoencephalography and neurosonography are used. A slightly increased or slowed rate of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is considered as an indicator of normality. Minor changes in the parameters of the cerebral ventricle. All signs of the disease should be examined several times. Also during diagnosis, a lumbar puncture is performed to measure fluid pressure in the spinal cord.
Treatment of hydrocephalic syndrome in a child
The treatment method will completely depend on the causes of the disease and the intensity of the development of hydrocephalic syndrome. If necessary, pathogenic or symptomatic therapy is practiced, the main goal of which is to eliminate intracranial pressure. Conservative treatment for this disease is ineffective, but it can be used at the initial stage or as dehydration therapy.
The basis of all effective methods is surgical intervention. It is used in the absence of inflammation of the meninges or in case of progression of the syndrome. The operation consists of creating a path through which cerebrospinal fluid can be removed to one of the parts of the body, where it can be utilized.
In the case of open hydrocephalic syndrome, it is necessary to constantly remove excess cerebrospinal fluid from the cranial cavity. Bypass surgery connecting the lumbar cistern and the abdominal cavity can be used.
Today, shunting of the cavity of the lateral ventricle with disposal of cerebrospinal fluid into the cavity of the right atrium is considered the most acceptable. The shunt is carried out over a long distance under the skin. Shunting is performed in children with progressive hydrocephalic syndrome. With any type of bypass surgery there is a possibility of an infectious complication, so periodic examinations are carried out using ultrasound and computed tomography.
Treatment of hydrocephalic syndrome
Treatment of hydrocephalic syndrome is carried out by neurologists and neurosurgeons with the involvement of ophthalmologists. Patients with HGS need to be observed and treated in a specialized neurological center.
Treatment in newborns
Children under 6 months of age require outpatient treatment.
Main therapeutic measures:
- prescription of a diuretic drug – diacarb (reduces the production of cerebrospinal fluid and removes fluid from the body),
- taking nootropics – improve blood circulation in the brain (piracetam, actovegin, asparkam),
- sedatives are also indicated (diazepam, tazepam)
- massage
Treatment for infants is quite long, lasting several months.
Treatment of HGS in older children and adults
In adults and older children, therapy depends on the cause of hydrocephalic syndrome.
If it is the result of a neuroinfection, then appropriate antiviral or antibacterial therapy is carried out.
In case of traumatic brain injuries and tumors, surgical intervention is indicated.
Complications in the treatment of hydrocephalic syndrome
After bypass surgery, some complications may appear in the form of:
- hyperdrainage state;
- shunt occlusion at different levels;
- seizures of epilepsy;
- infection of the shunt with the further development of certain diseases, etc.
Today, in case of occlusive hydrocephalus, endoscopic surgery is used to restore the patency of the cerebrospinal fluid. Removal of shunts occurs very rarely.
Preventive measures for hydrocephalic syndrome If a child is diagnosed with infections such as syphilis, meningitis, encephalitis, after treatment, preventive measures should be aimed at them. It is also advisable to eliminate stress and overwork from a child’s life. In case of suspicious behavior of a child, seek advice from a pediatrician, neurologist, surgeon, or neonatologist.
Causes
Etiological factors that can lead to the development of hydrocephalic syndrome in a child under one year old can affect the fetus during the intrauterine period, during childbirth, and also affect the child in the early postpartum period.
The risk of developing HS increases in the presence of risk factors on the part of the mother of the newborn during pregnancy and childbirth:
- toxicosis of pregnancy (preeclampsia, eclampsia);
- delayed or premature birth;
- pathological course of labor (abruption and placenta previa);
- multiple pregnancy;
- long anhydrous period (12 hours or more);
- somatic and infectious diseases of the pregnant woman (diabetes, cytomegalovirus infection);
- mother's age at birth (under 20 years, over 40 years).
The following article will be useful to young parents:. Migraine in a child - symptoms and possible complications of the disease.