Cobbler's chest, or concave chest, is a common developmental anomaly of the thoracic skeleton. In most cases it is congenital. Therefore, from birth it is recommended to carefully monitor the baby’s health. In case of the first signs of pathology, you should immediately seek help from an orthopedic doctor.
The older the child gets, the faster the abnormal development of the chest progresses. The pathological process affects the functioning of adjacent organs. As a result, normal blood circulation, the location and rhythm of the heart, and respiratory functions are disrupted, which can negatively affect well-being.
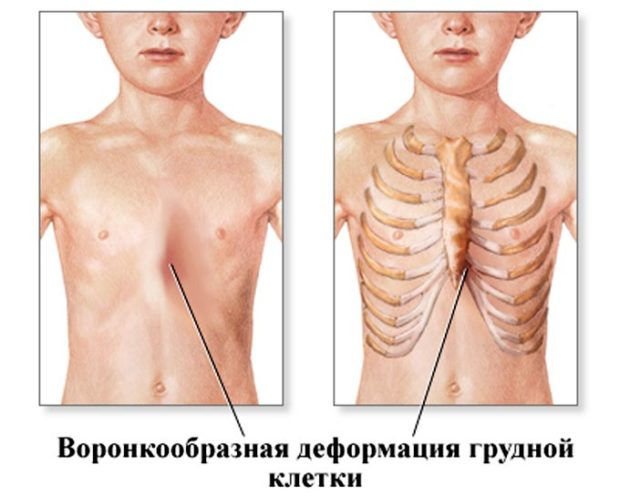
Funnel chest deformity
Chest deformation is a disturbance in its development in the form of a funnel-shaped retraction of the sternum, which is marked by disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
This anomalous development was first described in 1600. The first corrective operation was performed in 1899 in Europe.
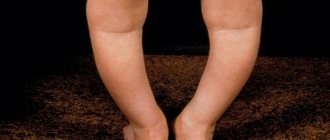
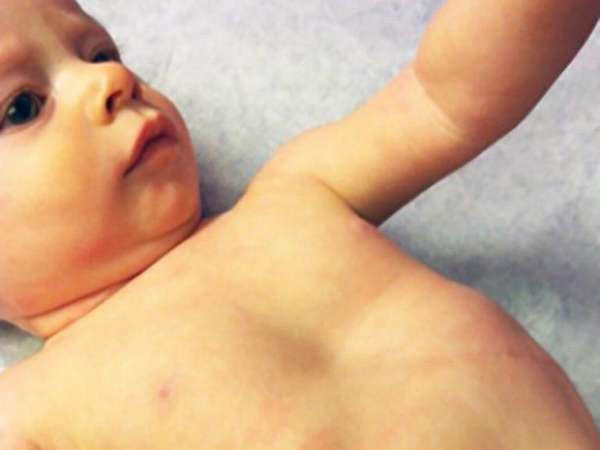
The photograph shows a congenital funnel-shaped curvature of the chest in a child.
Sunken chest in a child: causes
In fact, the exact reason has not yet been established. Some scientists argue that this defect is toxic and infectious in nature. This theory suggests that improper development of the sternum is associated with past or hereditary diseases of the mother.
Another theory is that the cause of the development of the defect may be the unfortunate position of the fetus in the womb, when too much pressure was placed on the unborn baby's chest.
If we talk about neurology, then there are no compelling reasons for the development of this pathology. Ultimately, we came to the conclusion that this problem arises due to a violation of the development of the fetus, or rather, the uneven formation of the bone and cartilaginous structure of the sternum and ribs.
excavatum may not necessarily be congenital; it can also be acquired. Most often, deformation occurs as a result of previous diseases, such as rickets, bone tuberculosis, scoliosis, and chronic lung disease. Injuries or severe burns in the chest area can lead to deformation.
Consequences of a sunken chest in a child
There are three degrees of severity of this pathology, which, to a greater or lesser extent, can lead to disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
- First degree. At this stage, the pathology manifests itself in the form of a small funnel, no more than 2 cm in size. This degree is considered the mildest; at this stage, the deformation of the chest does not displace the heart. The problem has more of an external, aesthetic side.
- Second degree. The funnel in this case can reach a depth of up to 4 cm. At the same time, the heart can shift by 2-3 cm, which already leads to disturbances in the body, in particular in the functioning of the heart and lungs.
- Third degree. And finally, the most dangerous degree of funnel chest is when the depth of the funnel itself is more than 4 cm. With this pathology, the heart is greatly displaced. Of course, in this case the patient experiences extensive disturbances in the functioning of the internal organs.
Causes of pathology
This type of disorder is most often congenital. Scientists agree on four options for the development of the disease, based on disturbances in the development of the embryo. Let us list the reasons for funnel-shaped breasts in infants:
- Defective formation of cartilage and bone tissue (ribs, sternum) in the embryo. Disturbances occur in areas where bones grow. Then there is a lag in the development of skeletal bones.
- Abnormal development of the diaphragm, especially in areas where the ribs are attached. As a result, the rib cage takes on an irregular shape: the muscular layer of the chest is pulled into a funnel. This process subsequently disrupts the physiologically correct structure of the body.
- Incorrect position of the fetus during pregnancy, which causes pressure on the chest. The reason is usually low water.
- Infections, harmful substances or abscesses in the womb, due to which destructive disorders occur in the fetal skeleton.
Deformation degrees
The degree of complexity of the disease depends on the depth of the cavity and disturbances in the position of the heart. According to the classification created by N. Kondratin, there are 3 degrees:
- I degree is characterized by a depth of less than 2 cm, without changing the correct position of the heart,
- Grade II is indicated when there is a depression up to 4 cm in size, while the heart is displaced by several centimeters,
- Grade III is diagnosed when a depression of more than 4 cm is formed with a displacement of the heart of 3 cm or more.
The photo shows VDGK of the 1st degree.
Pathology of the shape of the chest (PDHA) is classified by specialists according to its nature, shape, and effect on adjacent organs.
According to the form of VDGK it is:
- symmetrical,
- asymmetrical,
- flat or flat-funnel.
According to the nature of deformation it is divided into:
- typical,
- saddle-shaped
- helical.
Based on the presence of damage to adjacent organs or systems:
- compensated,
- decompensated,
- subcompensated.
To evaluate the treatment performed, Russian specialists use the Giżycka index. It is obtained by dividing the minimum distance between the back of the spine and the back contours of the sternum by the largest indicator of such a segment.
As a result, we get: an indicator of less than one corresponds to the first degree of the disease, an indicator from 0.5 to 0.7 - the second, and less than 0.5 - the third degree of the disease. It is possible to develop the fourth degree of the disease with the lowest or negative indicator.
One of the most common and complete classifications for determining the scale of the problem and its treatment:
- Type 1A is a typical symmetrical depression.
- Type 1B – flat, symmetrical with a wide contour.
- Type 2A (1) – helical type with an asymmetrical recess.
- Type 2A (2) – asymmetrical type with a wide contour.
- Type 2A (3) is an asymmetrical pathology with a wide and deep depression with a large area, extending from the collarbone.
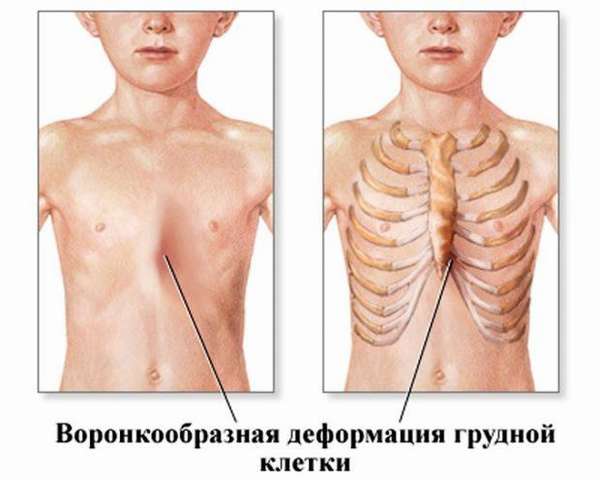
Pectus excavatum (Funnel chest, Sunken chest)
Treatment can be carried out by orthopedic traumatologists and thoracic surgeons. Conservative therapy for this pathology is ineffective. Indications for surgical treatment are increasing disturbances in the functioning of the circulatory and respiratory organs. In addition, sometimes surgery is performed to eliminate a cosmetic defect. Surgeries (except cosmetic ones) are recommended to be performed at an early age, the optimal period is 4-6 years. This approach allows us to provide conditions for the correct formation of the chest, prevent the development of secondary spinal deformities and the appearance of functional disorders. In addition, children tolerate surgical interventions better, their chest is more elastic, and the correction is less traumatic.
Currently, about 50 types of surgical interventions are used. All techniques are divided into two groups: palliative and radical. The goal of radical methods is to increase the volume of the chest; they all involve sternotomy (dissection of the sternum) and chondrotomy (dissection of the cartilaginous part of the ribs). During the operation, part of the bone is removed, and the anterior parts of the chest are fixed using special sutures and various fixators (wires, plates, allo- and autografts). Palliative interventions involve masking the defect without correcting the volume of the chest cavity. In this case, extrathoracic silicone prostheses are sewn into the subfascial space.
An absolute indication for radical surgical treatment is grade 3 deformity, grade 2 deformity in the stage of subcompensation and decompensation, pronounced scoliosis, flat back syndrome, adhesive pericarditis, cardiopulmonary failure and hypertrophy of the right ventricle of the heart. Before the operation, a comprehensive examination is required and treatment of chronic infectious diseases (bronchitis, sinusitis, chronic pneumonia, etc.) is carried out.
Indications for palliative intervention are grades 1 and 2 of deformity. Palliative operations are performed only on adults, since as the child grows, the silicone prosthesis may visually “peel off” and the cosmetic effect of the surgical intervention will be lost. Patients over 13 years of age with minor deformities can undergo correction of the location of the costal arches - an operation in which the arches are cut off and fixed crosswise on the anterior surface of the sternum.
To create the most favorable conditions in the postoperative period, the patient is placed in the intensive care unit, where he is in a state of medicated sleep. At the same time, careful monitoring of the condition of the chest organs and the function of the respiratory system is carried out. To prevent hypoxia, oxygen is inhaled through a nasal catheter. From 2-3 days breathing exercises begin. A week later, exercise therapy and massage are prescribed.
Symptoms
The most noticeable symptom of developing a pectus excavatum defect is a depression in the chest. This pathology does not always manifest itself immediately as soon as the newborn is born.
The following are symptoms that indicate the development of abnormalities in the bone and cartilage tissue of the chest:
- The appearance of a hernia in the diaphragm.
- Weak immune system.
- Circulatory problems and arrhythmia.
- Deviations in the functioning of the heart muscle and lungs.
- Bronchial spasms.
- Changes in normal mental state.
Important . If one or more signs appear, you should consult a doctor for advice.
Types and classification
Funnel chest is classified according to several criteria. It can be symmetrical or one-sided, flat and classic. The funnel configuration can be saddle, helical or typical.
There are also 3 degrees of deformation:
- 1st degree of VDHA - the depth of the cavity is no more than 2 cm, there is no displacement of the heart, the function of the internal organs is normal;
- 2nd degree – the depth of the funnel is 2-4 cm, the heart is shifted by 2-3 cm, minor deviations in the functioning of the heart and lungs are possible;
- 3rd degree – the depth of the funnel is more than 4 cm, the displacement of the heart is more than 3 cm, significant dysfunction of the chest organs is observed.
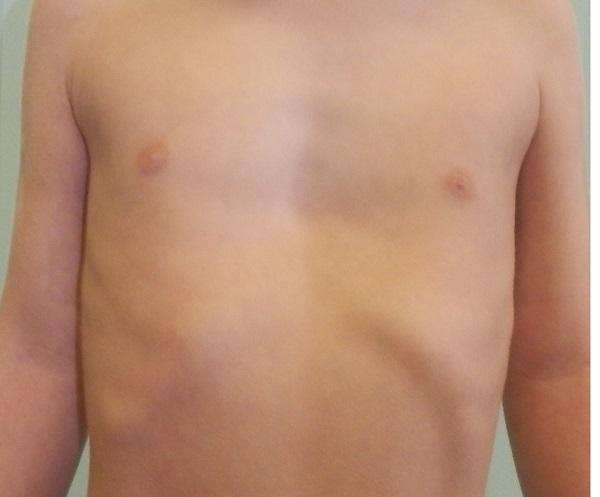
Left-sided deformity - asymmetrical type of chest
To classify by degree, the Giżycka index is used, which is calculated from x-rays. To determine it, measurements are made of the smallest (S1) and largest (S2) distances from the inner surface of the chest to the outer surface of the spine. Ratio N1/N2 – Gizycka deformation coefficient:
- 0.7 – 0.9 – corresponds to 1st degree;
- 0.5 – 0.7 – corresponds to degree 2;
- 0 – 0.5 – corresponds to grade 3 VDHA.
The most important criterion is the Heller index - the ratio of the width and anterior-posterior size of the chest. Normally it is 2.5. An increase in this indicator to 3.2 - 3.5 serves as an indication for surgery.
Methods for diagnosing VDHA
To carry out correct and effective treatment, patients with a chest defect undergo diagnostics. This is necessary to determine the degree and type of deformation, localization of pathology and disturbances in the functioning of organs adjacent to this area.
Thoracometry is required. During the diagnosis, the parameters of the cavity are determined and the chest change index is calculated.
In addition, specialists prescribe MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and x-rays . With their help, the condition of organs, their location, and disorders due to pathology are checked.
If there are significant deformations of the internal organs, the patient is referred to a cardiologist and pulmonologist. Specialists conduct a number of studies, including an electrocardiogram, to identify the degree of organ dysfunction and minimize complications.
Ultrasound is used to diagnose defects in organs and cartilage and bone structures. To complete the picture, longitudinal and transverse scans of the body are performed.
Important . It is important to evaluate vital capacity (vital capacity), since most patients suffer from respiratory problems. This makes you feel worse and lowers your immune system. About half of all patients with severe curvature of the chest have significant deviations from the norm of vital capacity.
Diagnostics
Chest deformities may be obvious in infancy, but often also develop or become more obvious as one grows. Abnormalities are usually noted by parents, but may only be obvious to a doctor and discovered during an examination. Other deformities may be noted by the patient because the rib cage develops over time, becoming less flexible after infancy.
The diagnosis is confirmed with X-rays and sometimes an assessment of your child's lung function and exercise capacity. Sometimes associated with other diseases, and your child will need to be evaluated for such diseases.
Treatment of pathology
In medical practice, there are two approaches to the treatment of VDHA.

Non-surgical method
Treatment involves physical exercise, a massage course, swimming, physiotherapy, procedures to enrich the body's cells with oxygen (drinking cocktails, being in a special pressure chamber). Such measures are carried out to strengthen muscles, prevent further deformation, improve posture and increase vital capacity.
At the first signs of the disease or suspicion of the presence of pathology, it is possible to treat funnel chest deformity in children without surgery. Infants are prescribed a course of massage in the first year of their life. To improve the result, 10-12 courses of such therapy are necessary.
For older children, light physical activity is recommended. Among the most effective exercises are the “bridge”, other exercises with deflections of the spine, “bicycle”, you can use a fitness ball, or a gymnastic stick.
Surgical method
In most situations requiring surgical intervention, operations are performed on patients under 10 years of age, so that over the years the chest takes on the correct shape and proportions. In addition, surgery helps prevent the development of spinal disorders later in life, such as kyphosis, scoliosis, etc.
Indications for urgent intervention are an increase in organ deformation and disturbances in the functioning of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. In other cases, surgery is performed to eliminate an external cosmetic defect. In this case, it is important to calculate in advance all the risks associated with intervention in the body.
Operations to eliminate VDHA are divided into two categories:
- palliative _ To maintain the chest in the correct position, the patient is sewn with silicone prostheses. This method is prescribed to adult children with degree I or II curvature in order to exclude the possibility of detachment of the prosthesis,
- radical _ This type of intervention is prescribed for pathologies of II, III degrees, also due to obvious scoliosis. A fixator is installed in the chest, after making an incision in the area of the ribs.
A child has a sunken chest: what to do?
As soon as the doctor has made a diagnosis, it is necessary to urgently begin treatment for this disease. While the baby is small and his ribs and chest are mostly cartilage and not bones, then there is a chance to be cured using conservative methods:
- Special therapeutic massage;
- Special breathing exercises;
- Swimming, active exercises in water;
- Wearing a corset.
Of course, the course of treatment will be selected individually, based on the degree of pathology and the patient’s condition. A massage course is prescribed to strengthen muscle tissue, improve blood circulation and accelerate metabolic processes.
One of the most important roles in the treatment of a sunken chest in a baby is played by breathing exercises. It is very important to teach a child of a conscious age to take a “tense breath” (a specialist will teach you how to do it correctly). The child also needs to create aerobic exercise; swimming is suitable for small children; running and cycling are suitable for older children. All this physical activity helps to expand the chest and increase the intercostal spaces.
But if the doctor sees that the disease is developing too quickly and seriously threatens the health and life of the patient, then surgery is prescribed. There are cases when only surgical intervention can help restore the natural position of the chest and prevent further development of the pathology.
There are a number of other indications for surgery:
This is when the deformation is of the third degree, as already mentioned, in this case the obligatory accompanying symptom will be a displacement of the heart and disturbances in the functioning of the internal organs.
A deformation that does not provoke serious disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, but leads to serious psychological disorders of the patient.
With Poland syndrome, when the frame and protective properties of the osteochondral structure of the chest decrease due to deformation.
Congenital clefts in the chest area in children of different ages.
When surgery is contraindicated:
If deformations of the ribs and sternum are accompanied by very severe pathologies of the cardiac, vascular and respiratory systems. The patient has moderate to severe mental retardation.
Surgery is a great chance for recovery. In 95% of cases, children get rid of this disease, and only a small percentage of children require repeated surgery.
Complications and consequences
After the completion of the surgical operation, the patient is transferred to intensive care. There they put you into medicated sleep. At first, respiratory failure is observed. Complications often occur in the form of tongue retraction, accumulation of blood and air in the pleural cavity. Sometimes the airways fill with mucus.
To alleviate the patient's condition and prevent more severe consequences, inhalations are prescribed. Next, they are sent to physical therapy, a course of massage and breathing exercises.
Important . With any complex operation there is a possibility of relapses. Chest pathology is no exception. The manifestation of complications is associated with age, the degree of VDHA and concomitant diseases.
Symptoms of ongoing pathological changes in the chest
The most important symptom indicating the development of an anomaly is a funnel in the chest.
Sometimes this symptom does not appear immediately. This is due to the fact that in newborn children no changes are visible in the chest area. Therefore, it is so important to know those moments that can indicate the beginning of the emerging deformation of the sternum. This manifests itself in the following:
- the immune system weakens;
- blood circulation in the body is disrupted;
- arrhythmia is observed;
- hernias occur in the diaphragm;
- the functioning of the heart and lungs is disrupted;
- changes occur in the mental state;
- spasms in the bronchi.
If you detect at least one of the above signs, you should definitely consult a specialist, since timely diagnosis allows you to begin treating a child or adult patient at the very beginning of the development of pectus excavatum.