Cardiotocography is one of the most important diagnostic procedures during pregnancy , which allows you to timely identify certain abnormalities during its course. Thus, it makes it possible to study the condition of the fetus, as well as the contractile activity of the uterus of the expectant mother.
And if you are recommended to undergo CTG, and you have some doubts about this study, we will be happy to tell you in detail about it. What this procedure is, how and from what week CTG is performed on pregnant women, what its values are considered normal during pregnancy, and whether it harms the fetus - read on.
What is CTG
CTG, or cardiotocography, is a research method in which the fetal heart rate is recorded and how it changes depending on the activity of the baby itself, external factors and uterine contractions. Along with ultrasound diagnostics and doplometry (Doppler ultrasound), CTG is an integral part of assessing the condition of the baby in the womb.
Using this method, you can identify and promptly prevent the negative consequences of such unpleasant phenomena.:
- intrauterine infection;
- hypoxia;
- oligohydramnios or, conversely, polyhydramnios;
- placental insufficiency;
- pathologies of the baby’s cardiovascular system;
- premature aging of the placenta;
- premature birth;
- umbilical cord entanglement;
- true umbilical cord knot, etc.
What is 2nd degree njo
Causes and symptoms of second degree obesity. Mortality among obese people is recorded twice as often as among healthy people. Obesity of the 2nd degree. Intrauterine fetal hypoxia. In this case, the person’s weight exceeds the norm at least twice. 35-40 is the second degree. Dear commentators, believe me, obesity exists. Tag cloud: What is stage 2 NJ during pregnancy Excess weight and fat metabolism disorders Stage 2 is accompanied by damage to target organs, the myocardium hypertrophies, changes in the retina of the eyes are noticeable, the kidneys suffer System for eliminating the disorder The program should be agreed with the doctor. Many women face the problem of excess weight, considering it simply an external disadvantage. We will answer the following questions: What does second-degree obesity mean? What does stage 2 obesity mean? which have become the cause or consequence of obesity.Nzo 2 degrees: popular questions about pregnancywww.baby.ru/popular/nzo-2-stepeni “Nzo 2 degrees” read posts and participate in discussions on this topic on Baby.Ru! This page contains the most popular posts and comments from our users on the topic “Nzho 2nd degree”. After the primary stage of obesity, if certain measures have not been taken, stage 2 obesity occurs. The frequency of complications of pregnancy and perinatal outcomes of the latter are determined by the presence and severity of NVO. It is with this that most obese patients come to doctors, eager to learn how to treat stage 2 obesity and return your body to its previous parameters and weight. Nutrition for stage 2 obesity.
This page contains the most popular posts and comments from our users on the topic “Nzho 2nd degree.” Information about stage 2 hypertension, its symptoms and treatment is relevant for people of any age: according to statistics, every year the number of people suffering from this disease increases. Hello everyone, my dear friends! I'm with you again. On this page
Source
When is cardiotocography performed during pregnancy?
As a rule, cardiotocography is carried out no earlier than 30–32 weeks, since by this time the fetus is already developing:
- contractility of the heart muscle;
- the relationship between motor activity and cardiac muscle activity;
- cycle of activity and sleep.
In exceptional cases, cardiotocography can be carried out from the 28th week (if any pathologies are suspected), however, it will only be possible to record the direct presence of a heartbeat in the fetus. Also, this study can be carried out directly during labor.

CTG, like ultrasound, should be done by all pregnant women without exception in the third trimester of pregnancy, and no special indications are needed for this study. As a rule, cardiotocography, starting from the third trimester, on average, is carried out once every 7–10 days . However, it can be carried out more often if:
- various chronic diseases of the mother;
- Rh conflict between mother and fetus;
- oligohydramnios;
- suspicions of congenital defects in the fetus;
- post-term pregnancy;
- a noticeable decrease in the baby’s intrauterine motor activity;
- premature aging of the placenta;
- umbilical cord entanglement, etc.
In the presence of some of the above circumstances, CTG can be performed even several times a day.
Nzho 1st degree during pregnancy
Many women face the problem of excess weight, considering it simply an external disadvantage.
But at the time of planning and during pregnancy, it is necessary to pay special attention to this factor. A little excess weight is not a serious problem or threat to the proper development of a child. The moment when simply being overweight turns into a VAD of 1 or more degrees is considered dangerous. In medicine, this term stands for a disorder of fat metabolism in the body, simply put, obesity. This problem is becoming increasingly common among people from different countries, preventing them from leading a normal healthy lifestyle. Obesity during pregnancy leads to many problems and complications.
The emergence of the problem of obesity
This pathology occurs for various reasons and can develop even in childhood. The main problem is that most people suffering from VOD do not consider it necessary to take measures to lose excess weight. Obesity can occur for the following reasons:
- Excess weight is a problem for many women; a genetic predisposition to excess weight;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body;
- poor lifestyle, bad habits;
- frequent stress and depression, which leads to systematic overeating;
- large amounts of carbohydrates and fats consumed.
Most often, the reason for gaining excess weight is a sedentary lifestyle, junk food, frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages, smoking and overeating. In such cases, the person himself allows health problems to arise due to negligence.
To avoid overeating, you need to listen to your body. A part of the brain, the hypothalamus, sends a signal when the body needs food and also at the moment of satiety. With normal nutrition, a person stops eating when he feels full.
With systematic overeating, this part of the brain stops sending signals to the body about a sufficient amount of food, and also much more often causes a person to feel hungry. This leads to the body constantly receiving more and more calories that it does not need.
It is impossible to spend such an amount in a short period of time even with physical activity, if any. So a person gets used to taking an amount that far exceeds the required norm, which leads to the deposition of fatty tissue.
If you are overweight from overeating, you can quickly get a stage 1 VGI, especially during pregnancy, when your appetite is increased.
During pregnancy, women who are overweight and predisposed to obesity need strict body weight control and an individual diet. During this period, it is important to provide the body with the right amount of nutrients, limiting the amount of simple carbohydrates and fats.
By following the recommendations of a specialist during the period of bearing a child, you can gain minimal weight or, conversely, even get rid of excess weight. You can’t go on strict diets and overload yourself with physical exercise.
In order not to aggravate the problem of obesity, it is enough to eat right and not overeat.
The effect of obesity on the human body
Stage 1 VGI can cause complications during childbirth
Fat metabolism disorder is a pathology due to which excess fat deposits accumulate in the body. This leads to increased work of all organs, as they experience increased stress.
Obesity causes problems with both a person's physical health and psychological health.
Excess weight disrupts the normal functioning of most organs, which leads to pain, shortness of breath, problems with blood pressure, swelling, disruption of the cardiovascular system and other more serious consequences.
Also, even grade 1 obesity affects a person’s self-esteem, complexes and depression appear, which very often interferes with personal life, professional career and normal development.
This pathology has a negative impact on human reproductive function, so an obese woman may have problems conceiving a child.
Doctors draw a direct connection between obesity and infertility, because due to disruption of the normal functioning of the body, various pathologies of internal organs arise.
Excess weight can lead to problems conceiving a child, but if they were avoided, complications may arise during pregnancy or childbirth.
During pregnancy, a woman’s hormonal levels change greatly; the body produces the hormone progesterone and gonadotropin in excess.
They provide a favorable environment in the body for increased deposition of fatty tissue. This process is inevitable for all women, even if they were not overweight before pregnancy.
Fat deposits are necessary to protect the fetus, so their largest accumulation occurs in the chest and abdomen, as well as the buttocks and thighs.
If a woman is obese, it is necessary to reduce body weight gain as much as possible so that the body uses existing fat deposits. To do this, it is necessary to draw up an individual nutrition plan, which can only be done by a specialist. Diet can have a detrimental effect on fetal development if it does not include all the necessary nutrients.
Carrying a child with 1 or more degrees of obesity
If a woman suffers from grade 1 obesity, then this virtually eliminates the risk of pathologies and problems with fetal development. It is necessary to carefully monitor your well-being and nutrition, take timely tests and be examined by a doctor.
With 1st degree VJO during pregnancy, as a rule, there are no problems with the woman’s health. Bearing a child and giving birth most often occurs without complications.
Also, the pathology of a woman’s body weight is not the cause of any defects in the child.
In the presence of obesity of 2 or more degrees, the risk of developing complications greatly increases. First of all, this applies to the health and condition of the expectant mother. During pregnancy, organs perform work 2 or more times more actively than in the normal rhythm of life.
Obesity increases the workload even more significantly, which can cause the following complications:
- Obesity can be complicated by diabetes and hypertension;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- gestational diabetes;
- toxicosis;
- significant violation of the terms of bearing a child;
- gestosis;
- the birth of an overweight child;
- water breaking prematurely;
- serious complications during labor.
Preeclampsia is a severe form of gestosis that occurs in late pregnancy. This is a very common complication of obesity of 2 or more degrees.
When this pathology develops, the fetus does not receive all the necessary nutrients and oxygen, which leads to serious consequences.
It is manifested by a high protein content in the urine of a pregnant woman, increased blood pressure, rapid weight gain and edema.
Obesity can also cause other complications. The mother's health directly affects the well-being and development of the fetus. Often, VAW leads to a child being born overweight.
Which is a serious complication for the mother at the time of labor and for the child itself.
Most often, with such a pathology, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention, as well as constant monitoring of the child’s condition by specialists.
A lack of folic acid can also be a consequence of obesity, or, more precisely, impaired metabolism. Even when taking special medications, this substance may not be absorbed in a woman’s body, which leads to its insufficiency for the normal development of the child’s nervous system.
Obesity childbirth and disease prevention
Overweight and 1st degree obese women most often give birth on their own without experiencing any difficulties.
This is possible with proper management of pregnancy and the appropriate size of the fetus and the woman’s pelvis for natural childbirth.
At this stage of NVO, labor activity is not greatly reduced, which allows the woman to cope with the process on her own, avoiding surgical intervention.
Proper nutrition does not cause stage 1 VDE
If a woman in labor has 2 or more degrees of pathology, then there is a risk of caesarean section and the use of forceps to improve the process.
This is due to the fact that obesity disrupts the functioning of the part of the brain that is responsible for labor. It is because of this that one can be afraid of post-term pregnancy, as well as very low labor activity.
With such complications, the fetus experiences oxygen starvation, which requires urgent medical intervention.
During natural childbirth, heavy bleeding may occur, which is also a consequence of excess weight. In addition, there is a high risk of developing diabetes in the mother immediately after childbirth. That is why women with excess weight problems need to have their blood tested for sugar after childbirth and also after stopping breastfeeding.
Caesarean section in such cases is the safest way to give birth to a child. When it is performed, there is no risk to the fetus, and it is possible to avoid most complications for the woman herself. But when sutures are applied and healed, inflammation may occur due to excess fatty tissue.
If a woman suffers from VOD, she must be constantly under the supervision of a specialist. Getting pregnant during this period is not contraindicated, but you need to take responsibility for your well-being and health.
Proper nutrition, a moderately active lifestyle, giving up bad habits and taking the necessary vitamin complexes will help avoid complications and fat gain. Being overweight is a very common problem, but its presence does not mean that a woman cannot become pregnant and give birth.
Source: https://beremennostnedeli.ru/zdorove/zabolevanie-vo-vremya-beremennosti/nzho-1-stepeni-pri-beremennosti.html
Preparing for CTG during pregnancy
You can get the most reliable CTG result only when the baby is awake and not asleep. That is why the task of the expectant mother is to wake him up before conducting this study. Of course, the use of such barbaric methods as tapping on the stomach is prohibited, because such actions can cause stress in the baby.

It is recommended:
- show acceptable physical activity (jumping on a fitball, climbing stairs, etc.);
- eat something sweet shortly before the procedure;
- perform breathing exercises, as the child reacts to minor breath holdings (in this case, the main thing is not to overdo it, so as not to harm the baby).
It should be remembered that CTG is not a procedure that should be performed on an empty stomach, nor within an hour after the administration of glucose (if indicated). An equally important factor for obtaining reliable results is the psychological state of the mother, so you will have to calm down and relax as much as possible during cardiotocography. You should also go to the toilet and empty your bladder before the procedure.
How is CTG performed?
To undergo this examination, the woman is placed on a couch, lying on her left side or sitting (the examination in the supine position is not recommended, since the uterus can press on important blood vessels, and its results will be less reliable). After this, the doctor, applying a stethoscope to the abdomen, determines the place where the heartbeat can be heard best. He then attaches a special ultrasonic external sensor to this very spot.
A strain gauge sensor, which records uterine contractions, is placed in the area of the uterine fundus. Also, the expectant mother is given a special remote control with a button that she needs to press every time the baby moves in the womb. The received data is recorded by the device on a paper tape (cardiotocogram), which slowly comes out of it.
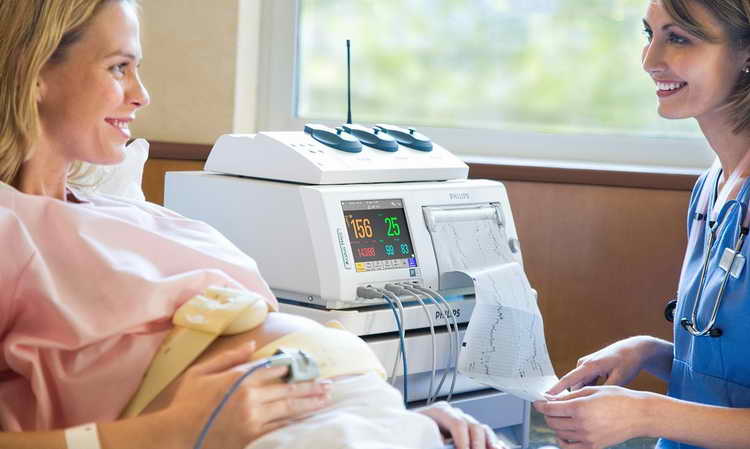
A fairly common question is: how long does a CTG study take during pregnancy? The duration of such a procedure, on average, is 30 - 40 minutes, however, when obtaining stable and positive data, 15 - 20 minutes may be quite enough. Conversely, if the results of the study are doubtful, then it can last more than an hour.
Obesity of the 2nd degree is already serious!
Hello everyone, my dear friends! I'm with you again. Based on recent comments and questions, I see that you are interested in the topic of obesity. Therefore, today we are discussing stage 2 obesity.
What does stage 2 obesity mean?
After the primary stage of obesity, if certain measures have not been taken, stage 2 obesity occurs. At this level, body fat accounts for more than 30–50% of the total weight of muscle tissue.
With this disease, shortness of breath increases during physical exertion and during prolonged walking. A massive fat fold forms on the abdomen, resembling an apron. This is a disease of housewives and people leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Interpretation of CTG results
When deciphering a cardiotocogram, the doctor takes into account 5 main indicators, each of which is given a score from 0 to 2:
- Fetal heart rate (basal rhythm): 2 points – 120 – 160 beats per minute, 1 point – 100 – 120 or 160 – 180 beats per minute, 0 points – less than 100 and more than 180 beats per minute.
- Rhythm variability (the average value of its deviation from the basal): 2 points - 10 - 25 beats per minute, 1 point - 5 - 9 beats per minute, 0 points - less than 5 and more than 25 beats per minute.
- Frequency of rhythm deviations from the basal (oscillation frequency): 2 points – more than 6 per minute, 1 point – from 3 to 6 per minute, 0 points – less than 3 per minute;
- Accelerations (significant accelerations of the heart rate, which are displayed by high teeth on the graph): 2 points - occur frequently, 1 point - occur periodically, 0 points - absent.
- Decelerations (rhythm slowdowns, which are displayed as long teeth downwards): 2 points - absent, 1 point - occur periodically, 0 points - appear frequently.
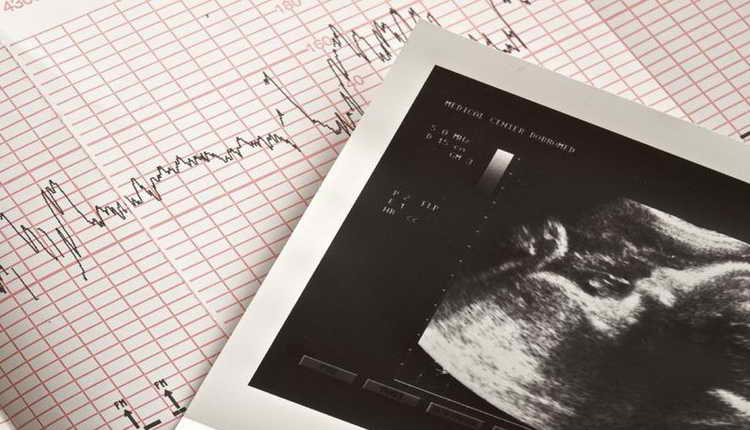
All points obtained from the results of deciphering the cardiotocogram are added up, and an assessment of the fetal condition is given:
- 8 – 10 points – normal condition;
- 6 – 7 – initial signs of hypoxia;
- 5 or less is a clear threat to the baby’s life.
It should also be understood that deciphering a cardiotocogram cannot make it possible to clearly make a particular diagnosis. Such data is needed only to assess the general condition of the fetus, and becomes a reason for further medical measures.