Prevalence of giardiasis among children
It is believed that around the world, about 20% of the population and about 25% of children suffer from giardiasis. In the Russian Federation, about 130 thousand cases of the disease are registered annually, which is 95.0 per 100 thousand. The incidence of giardiasis in children is 3.7 times higher than that in adults and amounts to 350.0 per 100 thousand population. Among all cases of giardiasis, children under 14 years of age account for about 70%. Among them, up to 70% are children 3–4 years old. Boys get sick 2-3 times more often than girls.
Young children are most susceptible to the disease.
Rice. 2. Up to 200 million cases of giardiasis per year are registered in the countries of Africa, Asia and Latin America.
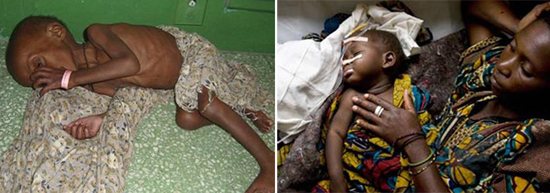
Rice. 3. Giardiasis in Africa, Asia, and South America is the cause of chronic diarrhea, leading to malnutrition, immunosuppression and nervous system disorders.
Epidemiology
Giardia is spread by patients and carriers. Parasites in the form of cysts with feces are released into the external environment. The infection is transmitted through dirty hands, water, food (usually vegetables and fruits), soil, and household items. The infection is spread by flies, cockroaches and ants.
In institutions where preschool children live, as well as in families, Giardia is transmitted through the dirty hands of parents, relatives, staff and the children themselves, toys, furniture, carpets, door handles, pots and toiletries. The habit of holding fingers in the mouth, biting nails, pencils and pens contributes to the spread of infection.
Factors for the spread of giardiasis are:
- unfiltered water (from open reservoirs and pools),
- soil contaminated or fertilized with human feces,
- poorly washed greens grown in soil fertilized with human feces,
- dishes that are not subject to heat treatment (for example, salads, puddings, etc.).
The incidence of giardiasis in children increases in the warm season - spring, summer and autumn.
Poor sanitary standards and non-compliance with basic hygiene rules contribute to the spread of giardiasis among children and adults.

Rice. 4. The most common outbreaks of giardiasis are waterborne.

Rice. 5. Water from open reservoirs and swimming pools is a factor in the transmission of infection in children.

Rice. 6. The habit of keeping your fingers in your mouth, biting your nails, pencils and pens contributes to the spread of infection.
Prevention of lambiasis
If you want to protect your child from such an unpleasant disease as giardiasis, then you should pay maximum attention to parasitic prevention. To do this, tell and teach your baby some rules:
- Personal hygiene. It's the most important. Teach your child to wash their hands thoroughly before eating, after using the toilet, and after walking outside. Regularly monitor the length of your nails; children tend to bite their nails. Explain that chewing on foreign objects (ballpoint pens, pencils, etc.) is also unsafe. They may have Giardia cysts.
- Purity of products. Fruits and vegetables must be washed before consumption. “You can’t eat something unwashed” - your baby should not only know this rule, but also apply it.
- Eating out. It is not advisable to buy prepared food for your child at fast food establishments. What are the sanitary and hygienic conditions there?
- Sandboxes. This is a fairly pressing problem. Any child, seeing a sandbox, will run to play in it; in kindergartens it is an integral part of children’s games. Therefore, teach your child to wash his hands thoroughly after using the sandbox. Try to protect it as much as possible from city sandboxes and parks. Solve the problem differently by installing a sandbox in your yard that will be covered from animals and their feces.
- Water. You cannot drink tap water. It must be processed. Children should only be given boiled water.
- Reservoirs. You should not swallow water in fresh water bodies. It is not advisable for children to dive. After swimming, it is recommended to take a shower. No parasites can survive in salt water.
Following these rules will help you and your child reduce the risk of contracting Giardia by 50%. But, if you notice the manifestation of symptoms of giardiasis, consult a doctor for diagnostic examinations.
Giardia - the causative agent of giardiasis
Giardia are single-celled flagellated protozoan parasites. There are 6 species of Giardia, but only one of them, Lamblia intestinalis, is dangerous to humans. Among this species, 7 subtypes are distinguished, each of which causes a special type of giardiasis. The parasite exists as a cyst and a vegetative form (trophozoite).
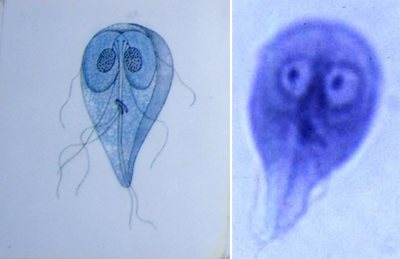
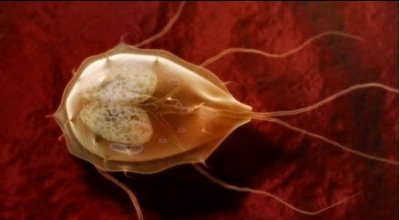
Rice. 7. Giardia are pear-shaped, 4 pairs of flagella, 2 nuclei. The axial rod divides the cell into two parts.
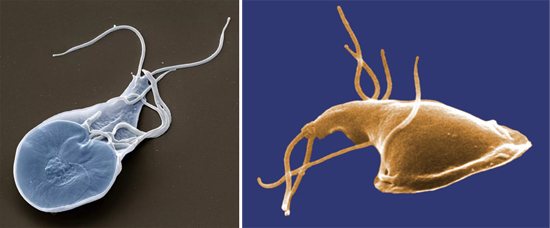
Rice. 8. With the help of a suction disk, lamblia attaches to the epithelial cells of the villi of the small intestine.
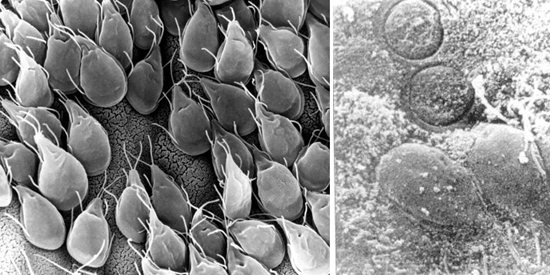
Rice. 9. Giardia moves with the help of 4 pairs of flagella.
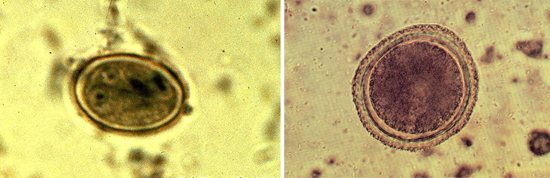
Rice. 10. Giardia cysts are round in shape, have 2 nuclei (immature forms) and 4 nuclei (mature forms), a thick outer shell, as if peeled off from the cell. Sufficiently stable in the external environment.
Giardia life cycle
Giardia lives in the upper parts of the child’s small intestine, where it enters in the form of cysts. The low acidity of the child's stomach promotes the survival of cysts, as a result of which they quickly penetrate the small intestine, where within 10 - 15 minutes they turn into vegetative forms (trophozoites). In the intestine, trophozoites feed and multiply intensively by dividing in two. There are about 1 million parasites per 1 cm2 at a time. After 10 - 15 days, Giardia descends into the lower sections of the large intestine, where it turns into cysts and is released into the external environment with feces. A patient excretes up to 18 billion cysts per day through bowel movements.
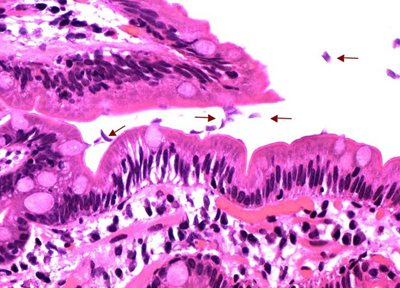
Rice. 11. Vegetative forms of parasites rush to the villi of the intestinal wall (indicated by arrows).
Types and routes of transmission of giardiasis
Giardiasis at its core is nothing more than a banal parasitic infection. The causative agent of the disease is the simplest microscopic unicellular parasite – Giardia. In a child's body, Giardia lives in the liver and small intestine, disrupting their normal functioning. Giardia is divided into two types:
- Vegetative (mobile) form.
Giardia of this species is pear-shaped, its front end is rounded, and its tail, on the contrary, is pointed. Its length is approximately half a millimeter. Giardia has four pairs of flagella and one disc, with which it is firmly fixed to the intestinal mucosa.
- Cysts.
If Giardia from the small intestine enters the large intestine, they are modified, since the conditions there are extremely unfavorable for them. Giardia transforms into oval-shaped cysts, about a millimeter in size. Cysts lack any mobility.
However, cysts are extremely important for the reproduction of Giardia. Cysts from the large intestine enter the feces and are excreted from the body. Once in the external environment, Giardia can remain there for a long time, exposing others to the risk of infection. At an ambient temperature of approximately 18 degrees, the viability of Giardia remains for 40 days, under the rays of the scorching sun - up to 7 days, and in ice water - up to three days. Once in the human body, Giardia cysts are again freed from their membranes and acquire mobility.
The most popular habitats for Giardia are wastewater, natural reservoirs with wastewater, dirty hands of children already infected with giardiasis, unwashed fruits and vegetables, as well as sand in children's sandboxes, especially if there are cats in your yard and the sandbox is not closed at night with a lid. . Doctors identify three main routes of transmission of Giardia cysts:
- Water route of infection. In the case of waterborne infection, Giardia cysts enter the child’s body when he or she consumes contaminated tap water. Unfortunately, very often and in many cities, tap water does not undergo the necessary thorough cleaning, and the risk that a child will become infected with Giardia by simply drinking tap water is very, very high. The same can happen if a child accidentally swallows water while swimming in an open pond. However, in fairness, it should be noted that Giardia cysts live only in fresh water and never in salty sea water;
- Contact - household route of infection. With this type of infection, the transmission of Giardia from one child to another occurs through toys, dishes, towels, and utensils contaminated with cysts. The risk of contracting Giardia is especially high in those children who have the habit of chewing toys, pens, pencils, and nails. As a rule, almost one hundred percent of such children are diagnosed with Giardia during examination;
- Food route of infection. If a child eats unwashed fruits and vegetables, and even more so meat that has not undergone the necessary heat treatment, there is a fairly high risk of infection with Giardia.
How does giardiasis develop in a child?
The development of giardiasis depends on the number of pathogens, virulence factors and the state of the child’s immune system. Giardia sticks to the villi of the small intestine and, after finishing feeding, detaches and reattaches in a new place. 10 parasites can simultaneously attach to one villus. In this case, epithelial cells are damaged and the villi are shortened, resulting in:
- The absorption of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals and vitamins is impaired. Malabsorption syndrome develops.
- Synthesis is disrupted and the release of enzymes is hampered, which leads to disruption of food digestion.
- As a result of the toxic effects of metabolites, intestinal motility and secretion of fluid and electrolytes by mucosal cells increases.
- The composition of the intestinal microflora changes. Dysbacteriosis develops.
- Metabolic products of parasites, absorbed into the blood, lead to the development of toxicosis and astheno-neurotic conditions.
- Toxic substances released during the death of Giardia and inflammatory mediators released during inflammation of the intestinal wall induce the development of allergic reactions.
- During their life, Giardia metabolizes the substance arginine, which is used by enterocytes to synthesize nitric oxide (nitric oxide slows down the process of transformation of cysts into vegetative forms and damages trophozoids). The synthesis of immunoglobulins is disrupted, which reduces the effectiveness of preventive vaccinations and increases the incidence of bacterial infections - bronchitis, pneumonia, tonsillitis, otitis, etc.
- The aggressive environment of the biliary tract is destructive for parasites. Dyskinesia of the biliary tract with giardiasis is of a reflex nature.
- With the development of inflammation in the duodenum, the pressure in the main pancreatic duct increases. Increased activity of proteolytic enzymes leads to inflammation of the organ.
- Giardiasis often occurs under the guise of various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and allergies, the course of which becomes aggravated without adequate antiparasitic treatment and acquires a chronic, relapsing course.
Rice. 12. Giardia on the surface of the villi of the small intestine (photo on the left). In the photo at the top right you can see traces of Giardia attachment, below - the parasites have attached in a new place.
What is Giardia in children
Giardia are parasites that inhabit the small intestine, gallbladder, and duodenum, which lead to disruption of the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. Such microscopic helminths are especially dangerous for the liver, as they contribute to the gradual destruction of this valuable organ. If a child has Giardia, they can be detected in the stool, with which they are partially excreted. Externally, cysts (protozoa) look like small white worms and are characterized by increased activity. If the parasites are not killed in time, the symptoms manifest themselves with double intensity.
Articles on the topic
- Discomfort in the abdomen
- How to care for ficus at home
- How to make papier-mâché step by step
What causes lamblia in children?
The cause of the disease may be an environmental or social factor, and infection occurs more often in people with weakened immunity and a tendency to pathological processes in the digestive system. Giardia appears in children in the intestines through the oral cavity, and moves all the way to the stomach. There they feel a favorable environment for further development and spread - giardiasis progresses. The routes of transmission of pathogenic infection are as follows:
- upon contact with toys, contaminated dishes, and everyday items;
- in case of eating unwashed berries, fruits, vegetables;
- in the absence of boiling water;
- with earth, sand;
- through mother's milk during breastfeeding.

Signs and symptoms of giardiasis in children
Giardiasis in children manifests itself in the form of dyspepsia, pain, astheno-neurotic reactions and allergies. In 50% of cases, giardiasis manifests itself simultaneously with dyspeptic, pain and astheno-neurotic syndromes.
Pain (in 81% of cases) and dyspepsia (in 77% of cases) are the leaders in the clinical picture of the disease. In 64% of cases, asthenoneurotic syndrome develops, in 32% - allergies.
Giardiasis in children can be secretive, asymptomatic, or have a manifest course. The disease manifests itself in the intestinal form, but extraintestinal forms of the disease are sometimes recorded.
Sometimes giardiasis in children occurs in an acute form, similar to food poisoning. Vomiting, diarrhea and fever are the main symptoms of this form of giardiasis. There is dehydration and rapid weight loss.
Giardiasis occurs in stages, has an incubation period, a period of manifest manifestations, a period of chronicity and convalescence (recovery). Intestinal manifestations have a wave-like course, and symptoms of intoxication and allergic manifestations are constantly increasing.
Children and adults remain at high risk of re-infection.
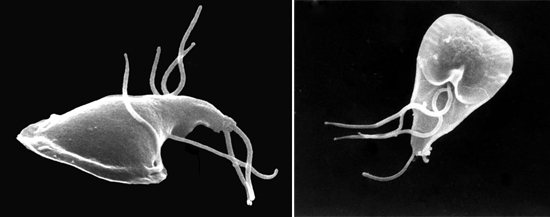
Rice. 13. Giardia (photo taken using a scanning microscope).
Giardia in children - symptoms
- Why do women and men dream about snakes?
- Cervical biopsy
- Chicken liver fried with onions in sour cream: recipes
The incubation period is characterized by its short duration. Then the acute stage of the disease begins with frequent relapses. Differentiating a characteristic illness is as easy as shelling pears; a presumptive diagnosis of giardiasis is made after collecting anamnesis data and a detailed study of the clinical patient’s complaints. So, the signs of Giardia in children have the following varieties, most often prevailing in the complex:
- attacks of nausea, less often vomiting;
- dizziness, headache;
- pain in the upper abdomen;
- chronic constipation, diarrhea;
- belching after eating;
- bloating, flatulence;
- yellow stool with the consistency of porridge;
- sudden weight loss;
- decreased appetite;
- general weakness, increased fatigue;
- signs of dyspepsia, unpleasant rumbling;
- recurrent skin rash (atopic dermatitis);
- poor sleep, excessive irritability;
- feces with mucus admixtures;
- temperature jump above 38 degrees;
- teeth grinding at night;
- redness in the navel area.
Intestinal damage
Giardia parasitizes the small intestine, so enteral disorders are the leading cause of the disease in the clinic. As a result of damage to the small intestine in children, the absorption of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, microelements and vitamins is impaired (malabsorption syndrome). Unreasonable nausea, loss of appetite, diarrhea, abdominal pain and increased gas formation are the main symptoms of giardiasis in children. Sleep and mood worsen, tearfulness and irritability appear. In severe cases, the child's weight decreases. After a week, the severity of the symptoms of enteritis decreases and the disease becomes chronic. At the same time, the symptoms of intoxication and allergic manifestations increase, which significantly impedes cure.
Symptoms of giardiasis in children at different ages manifest themselves differently:
- In children 2–3 years old, dyspeptic and allergy symptoms come to the fore. Asthenoneurotic syndrome is recorded extremely rarely.
- In children aged 4 to 7 years, dyspeptic disorders also come to the fore; pain syndrome is registered in 70% of cases; reactive pancreatitis is registered in half of children of this age; in 38% of cases, pathology of the gastroduodenal zone develops.
- In children 8–12 years old, the above-described symptoms are accompanied by biliary dyskinesia. Reactive pancreatitis is most often recorded (70%). The dominant pathology is the gastroduodenal zone.
- In children aged 13 - 15 years, pain syndrome occupies the leading place against the background of dyspeptic disorders.
Symptoms of giardiasis in children under one year of age
With giardiasis, children under one year of age experience bloating and difficulty passing gas. Fecal matter has a foamy character and a sour odor. The stool contains copious mucus and “white lumps” of bile salts. As a result of constant irritation by liquid, acidic stool, swelling and redness appear around the anus. The child screams, worries, twitches his legs. Then there is an alternation of constipation and diarrhea. The feces have a fetid odor, splashing and foamy. Putrefactive microflora in feces indicates the development of dysbacteriosis. Despite diarrhea, children often develop normally and gain weight.
Disorders in the functioning of other digestive organs
- With giardiasis intoxication, the liver enlarges. Its edge protrudes from under the costal arch from 2 to 4 cm, elastic and painless. By the end of 5 - 7 days, the size of the liver is normalized.
- Biliary dyskinesia (insufficient or excessive supply of bile) with giardiasis is of a reflex nature.
- With the development of inflammation in the duodenum, the pressure in the main pancreatic duct increases. Increased activity of proteolytic enzymes leads to inflammation of the organ.
- Stomach upsets are functional in nature.
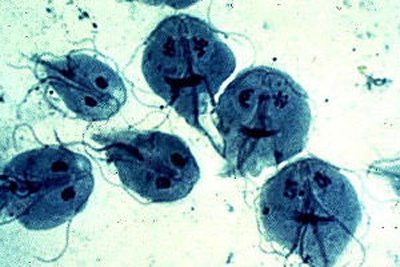
Rice. 14. Giardia under a microscope.
Intoxication syndrome
The degree of manifestation of intoxication depends on the massiveness and virulence of the parasites.
- In some cases, the liver and spleen become enlarged (hepatolienal syndrome).
- Lymph nodes enlarge.
- With long-term giardiasis, neurological symptoms appear: bruxism (teeth grinding) and tics.
- The waste products of parasites inhibit the functioning of the central nervous system, which is manifested by the development of astheno-neurotic syndrome.

Rice. 15. Intoxication is a characteristic sign of an infectious disease.
Astheno-neurotic syndrome
In more than half of the cases of giardiasis in children, asthenoneurotic cider develops along with dyspeptic syndrome. Vitality decreases, the child gets tired quickly, headaches and dizziness appear, small children become tearful, and sleep is disturbed. Professor D. F. Lambl, who described the microorganism in 1859, called Giardia “a parasite of melancholy and sadness.”
In 50% of cases in children with giardiasis, three main clinical syndromes are simultaneously determined: dyspeptic, pain and asthenoneurotic.

Rice. 16. Headaches and tearfulness are symptoms of astheno-neurotic syndrome.
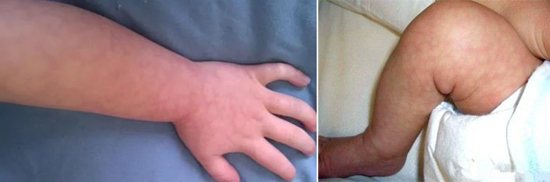
Rice. 17. The “marble” pattern of the skin indicates the reaction of the autonomic nervous system to the development of the infectious process.
Allergy
Allergic reactions in children appear regardless of the severity and severity of the infectious process. This is confirmed by an increase in the level of immunoglobulins IgE and IgM, as well as eosinophils in the patient’s blood. Skin lesions in the form of atopic dermatitis are most often recorded with giardiasis (70% of cases), less often with enterobiasis (16% of cases) and ascariasis (3% of cases). In children under one year of age, allergic manifestations are very diverse - from an itchy rash to eczematous lesions.
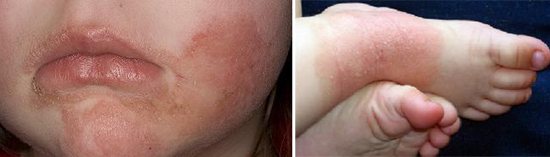
Rice. 18. Atopic dermatitis can be a manifestation of giardiasis in children.
Traditional treatment
Traditional medicine has proven in practice that it is a good auxiliary method for treating many diseases. It is auxiliary, so it is clearly not worth completely replacing full-fledged drug therapy with traditional recipes.
Here is an approximate list of possible recipes effective for giardiasis in children:
- Garlic and horseradish . We will need the same amount of garlic and horseradish (about 30 grams). We pass the ingredients through a meat grinder, and then pour half a liter of vodka. You need to insist for at least ten days in the dark, shaking the container periodically. Then you need to strain the tincture, after which you take a tablespoon half an hour before meals. The tincture is quite strong, so it needs to be diluted with water.
- Birch leaves and cognac. We will need birch leaves, which are poured with half a liter of cognac. The tincture should stand for three weeks, after which it is filtered. To remove bitterness, add carrot and beet juice, as well as a small amount of honey. You need to take three tablespoons before meals, i.e. three times a day.
- Iodine. We will need an alcohol solution of 1 percent iodine in an amount of 5 ml. Mix it with 30 ml of water, then take 15 drops before meals three times a day.
- Rowan. A teaspoon of rowan is poured into one glass of boiling water. The mixture should steep for at least a couple of hours, after which it is divided into three doses.
- Celandine . We need one tablespoon of celandine, which is poured with 200 ml of boiling water. The mixture is infused for 30 minutes, after which it is taken three times a day for 14 days.
- Meadowsweet . One teaspoon of meadowsweet is poured into 200 ml of boiling water. The mixture should be boiled for 15 minutes in a water bath, after which it should brew for about half an hour. The water that has boiled away must be replenished with a new portion of boiled water. You need to take two tablespoons immediately before meals.
Skin lesions
In chronic forms of giardiasis in children and adults, the skin is often affected:
- It manifests itself as pallor of the skin, especially the face, with normal hemoglobin levels, which is probably due to spasm of blood vessels.
- In the first years of the disease, uneven coloration of the skin is noted.
- In children and adolescents, the red border of the lips is affected to varying degrees of severity. There is peeling and dryness, in severe cases - cheilitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane and red border). With cheilitis, cracks, jams and peeling of the area around the mouth appear.
- Hair becomes thinner, its growth slows down, and it takes on different colors.
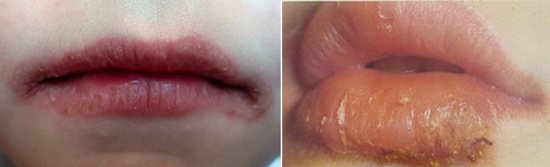
Rice. 19. Cheilitis often occurs in children and adolescents with giardiasis.
Diagnosis of giardiasis in children
The absence of pathogonic symptoms significantly complicates the diagnosis of giardiasis. Subject to examination:
- children with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, prone to chronicity, moderately severe and frequent exacerbations;
- children with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and neurocirculatory dysfunction;
- children with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and persistent eosinophilia;
- children with gastrointestinal diseases and allergic reactions.
Immunological methods
Immunological methods (detection of antibodies to parasites) are specific and highly sensitive. Immunoglobulins IgM and IgG appear in the blood from 12 to 14 days of illness. After sanitation, IgM disappears, and IgG persists for up to two months. However, one cannot rely only on immunological methods for diagnosing giardiasis in children for the following reasons:
- insufficient study of the pathogenic properties of Giardia;
- not all children have antibodies (antibodies are rarely detected in children with lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis);
- antibodies may not be detected in children with ineffective humoral defense mechanisms, in whom giardiasis often takes a protracted course.
The diagnosis of giardiasis is based on the detection of vegetative forms of Giardia in duodenal contents or cysts in liquid or formed feces.
Giardia in children - treatment
If the disease is established, antiparasitic therapy takes place, aimed at the speedy extermination of the parasitic flora. Treatment of Giardia in a child should be prescribed exclusively by a knowledgeable doctor, taking into account the patient’s age category. Otherwise, you can only increase the signs of intoxication in the body and cause complications dangerous to health. In the photo on the World Wide Web you can actually see what Giardia can look like, but using dubious advice from incompetent people in terms of treatment is strictly contraindicated.
- The normal level of leukocytes in the blood of women
- Henna tattoo at home. How to paint mehendi on hands and feet using a stencil
- Cleansing the body at home
How to treat giardiasis in children
If the germs are not removed, the symptoms of the characteristic disease only intensify. However, before removing Giardia from a child, it is necessary to find out to which synthetic components of drugs the hypersensitivity predominates in the little patient’s body. For example, a baby’s immunity is not fully formed, so the pediatrician advises to abandon “chemistry” altogether and use mainly folk remedies. In general, the treatment regimen for lamblia in children is as follows:
- antiparasitic therapy to kill microbes;
- symptomatic treatment based on symptoms;
- taking antihistamines to treat rashes;
- enzyme therapy to restore intestinal microflora;
- therapeutic diet to reduce the activity of pathogenic flora;
- vitamin course.
How to treat Giardia in children
Taking medications involves the presence of several pharmacological groups at once, which only enhance the therapeutic effect and ensure a speedy recovery. Photos of parasites are shocking; parents are even more frightened by the complications they can provoke. Therefore, it is important to treat lamblia in children in a timely manner. Otherwise, the first to be “under attack” is the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, followed by the liver, and biliary dyskinesia should not be ruled out. Effective treatment of giardiasis in children includes the use of the following medications:
- Antiparasitic drugs for helminths: Trichopolum, Tiberal, Nemozol, Furazolidone, Metronidazole, Ornidazole, Albendazole, Macrimore, Mepacrine, Tinidazole.
- Enterosorbents for removing Giardia waste products: Polysorb, Enterosgel, Smecta.
- Antihistamines against itchy skin rashes and signs of allergies: Fenistil, Tavegil, Suprastin.
- Bifidobacteria: Simbiter, Biogaya, Bifidumbacterin, Linex, Biovestin, homemade live yoghurts.

Giardia in children - treatment with folk remedies
It’s one thing to see in a photo what Giardia can look like, and quite another to experience unpleasant body symptoms. Alternative medicine recipes implemented at home can enhance the effect of medications. If Giardia is diagnosed in the feces of children, treatment with folk remedies is possible using the following methods, according to the prevailing symptoms:
- Tampons with vegetable oil at night are an effective method that reduces the activity of helminths and paralyzes them. Supplement such treatment with diet (for example, eat more dried fruits), antihistamines.
- If it is possible to recognize Giardia in children, the symptoms and treatment are interrelated. If you prepare an aspen decoction (2 tablespoons of raw material per 500 ml of boiling water) and give it to your baby for 10 days, the signs of giardiasis quickly disappear.
- To eliminate symptoms, you can give tea from birch buds, pre-infused in a water bath. The treatment is safe at any age; the patient soon forgets what the symptoms of Giardia look like.