Conjunctivitis in children under one year of age is considered a common pathological condition that often occurs in children in the first year of life.
Conjunctivitis in infants is accompanied by rather unpleasant symptoms and can seriously alarm parents.
How to recognize the disease and what to do if the baby’s conjunctiva is inflamed?
Features of the baby's visual organs

The thing is that even in a full-term baby, not all organs and systems are fully developed, including the eyes.
A baby who has just recently been born practically cannot see; he needs time so that he can focus his gaze on objects and clearly distinguish them.
The baby's visual organs are fully formed only by the age of six months.
Before birth, the fetus has no need for tears, since it is completely in a moist, protective environment. The ducts through which tear fluid should be released are still blocked with special plugs.
In a newborn at 6-12 weeks, the plugs gradually dissolve and the first tear fluid is released - abundantly or very sparingly.
And although tears have appeared, they do not contain enough antibacterial substances capable of absorbing various pathogenic microorganisms and suppressing their development. In addition, the mechanism for washing away tears during blinking is not yet fully functional, so harmful microbes are not completely removed.
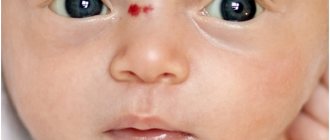
Without good protection, the conjunctiva, the connective membrane of the eyeball, often becomes inflamed in the baby, causing a number of alarming signs. Pediatricians warn that conjunctivitis in infants can provoke complications, so the baby should be shown to a pediatrician and treated according to the prescribed regimen.
Every fifth baby, in the first weeks of life, experiences a blockage (obstruction) of the lacrimal canals - dacryocystitis, causing conjunctivitis. If it is not associated with an infection, then to eliminate the pathology it is enough to do a massage.
General information
To understand the nature of the disease, you need to pay attention to general information about the disease.
What it is?
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye, accompanied by redness and swelling of the eyelids, discharge of mucus and pus from the eyes, burning of the eyes and lacrimation. This pathology occurs much more often than other eye diseases - about 30% of all pathologies.
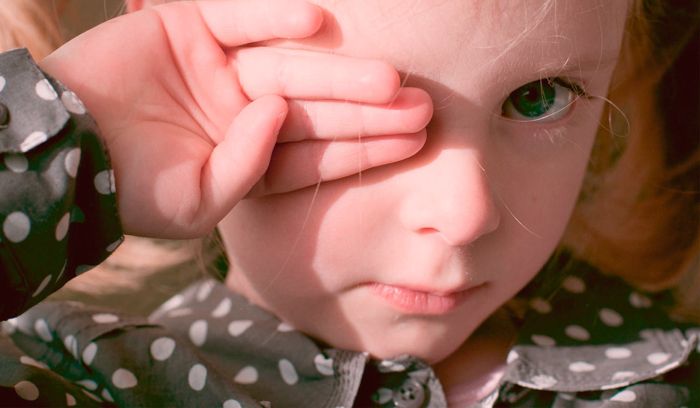

There are several types of conjunctivitis:
- viral is the most common and is a common complication of a cold. The disease is contagious and is transmitted from one person to another through dirty hands, contact with tear fluid or contact with the patient’s hygiene items - towels, napkins, toys;
- bacterial - with this type of infection, the infection is caused by bacteria. Often transmitted between children in kindergartens and schools, it can cause serious complications. Frequent causative agents of the disease are staphylococcus, diphtheria, pneumococcus, streptococcus;
- allergic - inflammation that occurs during an acute reaction of the body to medicinal substances, animal hair, dust, pollen, household chemicals;
- fungal is another name for the disease “ophthalmomycosis,” in which the infection is caused by fungi that affect the mucous membrane of the eye. Often found in contact lens wearers and pool visitors.
Signs of the disease
At the first symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor; self-treatment is not recommended, it can only harm the child.
Main features:
- itching and redness of the eyeball;
- lacrimation;
- burning eyes;
- purulent discharge;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- sensation of a foreign object in the eye.
How many days is the disease contagious?
Typically, the incubation period of a viral disease lasts from 3 to seven days, after which the child is no longer contagious. The bacterial form of quarantine lasts up to five weeks, during which the child is a source of infection. Throughout the quarantine, precautions are taken to prevent infection of other family members.
How is it transmitted?
The infection is transmitted by contact and airborne droplets.
Methods of infection:
- through contaminated toys, hugs and kisses due to a bacterial infection;
- contact with patients with a viral form;
- through dirty hands in viral and bacterial forms;
- if sand, dust, pollen gets into the eyes due to allergic and viral conjunctivitis.
Classification of conjunctivitis in infants
There are several types of disease, which are distinguished based on the cause of occurrence:
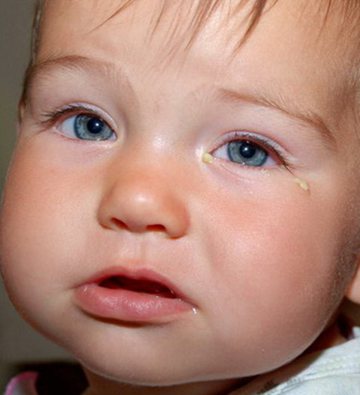
- Bacterial (purulent) inflammation. The causative agents of the disease are pathogenic bacteria, of which there may be several:
- Staphylococcal conjunctivitis. Staphylococcus aureus is detected, which is active against the background of disruption of vital organs or purulent-septic pathologies of newborns - omphalitis (inflammation of the navel), pyoderma (inflammatory lesion of the skin), etc.
- Viral conjunctivitis in infants. The disease is provoked by the herpes virus, its symptoms may appear even before the baby is discharged, then treatment is prescribed in the maternity hospital. Viral conjunctivitis in an infant is sluggish and is accompanied by the appearance of a rash on the eyelids. In most cases, only one eye is infected.
- Gonococcal conjunctivitis of infants (gonoblenorrhea). The pathogen can be transmitted from mother to fetus during labor, then the primary signs of the disease appear on days 2-3. Later development of conjunctivitis suggests that infection occurred after birth. Gonoblenorrhea is a dangerous disease that can lead to the death of the eye. Therefore, the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation issued a law on mandatory preventive measures: a newly born baby wipes its eyes with a swab soaked in a disinfectant and applies 1 drop of a 20% sodium sulfacyl solution to each eye. The procedure is repeated after a few minutes.
- Chlamydial inflammation of the conjunctiva. The causative agent of the disease is chlamydia, an anaerobic microorganism that occupies an intermediate position between bacteria and viruses. With this type of disease, either one or both eyes can be affected. The acute form - with copious purulent discharge, appears in infants 2 weeks of age. Premature babies can vomit as early as 4 days after birth.
- Autoimmune conjunctivitis. It can act as an independent disease or develop against the background of ARVI. Accompanied by severe swelling of the eyelids and conjunctiva and other obvious symptoms.
- Allergic conjunctivitis. In infants, the most common allergens are dust, pollen, contact with fabric, and, less often, food. The course of the pathology is painful.
A quarter of children suffering from allergic conjunctivitis have one or both parents suffering from this disease.
Conjunctivitis at three months: what happens?
Conjunctivitis in a child 3 (or more) months old can occur due to exposure of unfavorable microorganisms to the eyes: viruses, infections, fungi. Sometimes this disease appears against the background of a common cold or flu, but it can occur suddenly, on its own. It happens that parents notice the souring of the baby’s eyes after the introduction of new complementary foods.
In this case, we are often talking about the allergic form of the disease. In some cases, conjunctivitis in a child takes on a specific form - dacryocystitis. This pathology, as a rule, manifests itself already 8-10 days after birth and can acquire a chronic form in the absence of proper treatment.
Dacryocystitis appears against the background of an inflammatory process associated with stagnation of tears. Elements of embryonic tissue that accidentally enter the tear canals during the birth process block the normal outflow of tear fluid, as a result of which it stagnates and microorganisms that enter the palpebral fissure are not removed in a timely manner.
What type of conjunctivitis can a child have:
- Viral. Occurs due to viruses entering the baby’s eyes during ARVI, influenza and other diseases. Often accompanied by a runny nose and fever.
- Bacterial. This type of conjunctivitis is caused by various bacteria. The process is usually accompanied by the appearance of purulent yellow-brown discharge of varying consistency.
- Allergic. Appears due to direct exposure to an allergen (for example, when introducing complementary foods).
- Chronic dacryocystitis associated with obstruction of the lacrimal canals.
Parents should remember that viral or bacterial conjunctivitis has an incubation period that lasts about 5-10 days. The exception is the allergic form of the disease, which manifests itself immediately.
Chlamydial conjunctivitis should be placed in a separate category. Unfortunately, in very young patients this form of the disease is quite difficult to identify, since the baby cannot complain to his parents about pain in the eyes in bright light (increased photosensitivity). The first symptoms of the pathology begin to appear only 2-3 days after chlamydia penetrates the mucous membrane. The child's eyelids swell noticeably, and pus also accumulates in the crease of the lower eyelid.
Provoking factors
Despite the peculiarities of the visual organs in infants, and their vulnerability at first, not all babies develop inflammation. What can trigger the development of pathology?
The risks of conjunctival inflammation increase in the following cases:
- if the child has low immunity;
- a woman in labor suffers from an infectious disease that can be transmitted to the baby when passing through the birth canal;
- the expectant mother has genital or oral herpes;
- the baby is not provided with proper hygienic care;
- It is more difficult for premature infants to resist pathogenic pathogens;
- Dirt particles or foreign bodies enter the newborn's eyes.
Most factors can be eliminated if the expectant mother takes care of her health and, after giving birth, takes care of the baby’s hygiene.
Causes
In newborns, conjunctivitis can occur for a number of reasons, including:
- bacterial infections;
- viruses, including the herpes virus;
- fungal diseases;
- exposure to allergens;
- mechanical eye injuries;
- general diseases.
Also, the causes of conjunctivitis in infants can be genital infections that are transmitted to newborns from the mother when passing through the birth canal. Thus, it is possible for the child to become infected with genital herpes, fungal infection, chlamydia and other conjunctivitis pathogens.
Accompanying phenomena that provoke infection are: reduced immunity, poor diet, insufficient body weight of the child, hypothermia.
How does conjunctivitis manifest in infants?
It is important for parents to identify the disease at the initial stage; in this case, the child can be cured in a short time and complications can be prevented. Symptoms depend on the type of disease.

Viral inflammation of the conjunctiva:
- profuse lacrimation;
- redness of the mucous membrane of the eye;
- Initially, one eye is affected, but later the infection spreads to the second;
- the eyes are covered with a thin whitish film.
Purulent conjunctivitis:
- purulent discharge forms in the eyes;
- after sleep, the baby cannot open his eyes, because the pus causes the eyelids to stick together;
- swelling appears;
- irritation occurs on the mucous membrane;
- hyperemia and increased lacrimation;
- More often the infection affects only one eye.
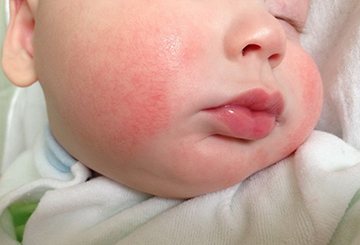
Allergic conjunctivitis:
- the conjunctiva turns red and swells;
- bothered by burning and itching sensations in the eye area;
- because of the pain, the baby may squint and turn away from the light;
- mucous discharge appears;
- allergies are often accompanied by a cough and runny nose.
Any sign of an inflammatory process in the eyes should alert you; you should definitely consult a pediatrician. If necessary, he may recommend visiting an ophthalmologist.
It is not recommended to treat conjunctivitis in an infant on your own, since different types of the disease require different therapy, and, in addition, you can harm the sensitive organ.
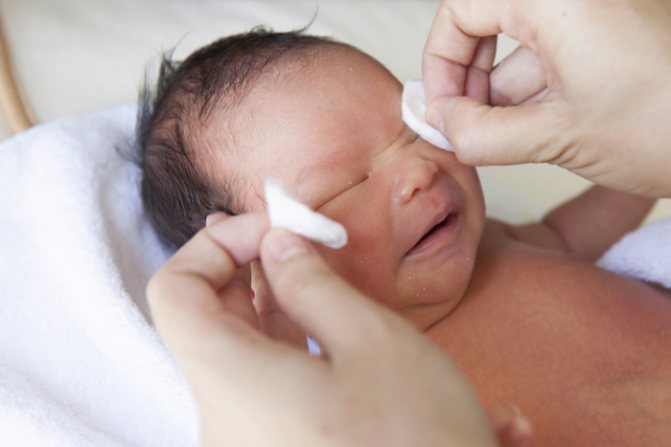
How to wash a baby's eyes with conjunctivitis?
It is necessary to begin treating conjunctivitis by washing the baby's eyes. You should not use antibacterial drugs if the baby’s visual organs have not been cleared of secretions and disinfected. To wash your baby's eyes, you should prepare an antiseptic solution. You can do it yourself. Decoctions of medicinal herbs are suitable for this purpose:
- chamomile;
- calendula;
- sage
Any conjunctivitis - bacterial, viral, allergic - can be treated by rinsing with a solution made from oak bark or aloe. The liquid for cleaning the eyes must be of a weak consistency. The procedure itself should be carried out every two hours during the daytime and 1-2 times at night when the baby wakes up.
Decoctions and solutions must be carefully filtered in advance. At the pharmacy you can purchase a special medicine called “Furacilin” for rinsing. Both the solution itself and tablets for its preparation are available for purchase. Furacilin should be stored in the refrigerator. It must be used within one day. The pharmaceutical solution, supplied ready-made, can be stored in a tightly closed bottle for no more than two weeks.
Treatment of illness in an infant
After examination, the specialist prescribes therapy based on the origin of the pathology, the degree of damage and other related factors.
Therapy for viral inflammation
For diseases caused by adenoviruses or enteroviruses, it is recommended to apply warm lotions to the eyes.
The baby is prescribed complex therapy:
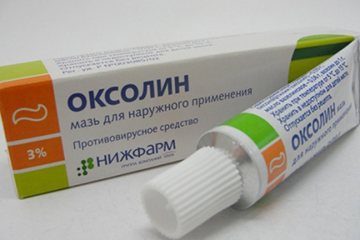
- Interferon drops - used in both eyes and nasal passages;
- antiviral ointments - Oxolinic, Bonafton, Acyclovir;
- drops with antiviral action - Actipol, Trifluridine;
- antiseptic solutions - for treating the affected organ and removing accumulated secretions.
Apply the products to your eyes very carefully, using separate cotton swabs for each.
Therapy for bacterial conjunctivitis
In this case, you cannot do without the use of antibacterial drugs. The baby is prescribed medications that are available in liquid form - a solution or suspension.

Pus should be removed with sterile gauze wipes soaked in chamomile decoction or Furacilin solution.
The process should begin from the outer corners of the eyes, moving towards the inner ones.
The napkin should be changed after each manipulation.
Most often, the drugs Albucid and Levomycetin are prescribed, the dosage and duration of treatment is determined individually . Among the popular remedies is also Oletethrin ointment.
All drugs used should not be cold; the bottles should be warmed in the palms of your hands before use.
Therapy for allergic conjunctivitis
The first thing that is necessary is to identify the allergen and, if possible, eliminate it.
An allergist is involved in the treatment of this pathology, and he decides on the need to prescribe antihistamines.
If we take into account the age of young patients, the range of antihistamines narrows significantly. At an early age, Fenistil or Suprastinex in the form of drops, Suprastin tablets can be prescribed.
Parents should be sure to follow these recommendations. If the disease affects only one eye, both are treated.
As an aid, you can use folk recipes, for example, rinsing the baby’s eyes with boiled water with a few drops of fresh aloe juice or tea leaves.
Early diagnosis and proper treatment make it possible to quickly relieve the baby from unpleasant sensations and possible serious consequences.
Treatment
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor prescribes a number of medications and procedures that help cleanse the newborn’s eyes of accumulated pus and inflammation in the shortest possible time and completely safely. It can be:
- washing with a solution of furatsilin, decoctions of chamomile, calendula and sage;
- instillation of chloramphenicol drops;
- massage of the nasolacrimal duct.
The doctor will write prescriptions and give detailed advice on how to cure conjunctivitis in a baby. If you doubt something, be sure to ask him for advice, but do not rely on your intuition in such an important matter, which will not lead to anything good. Remember: folk remedies in this case are only good for adults. And only a professional should solve problems with a child’s health.
Despite the fact that conjunctivitis is not considered a serious illness, do not forget that a newborn baby is not yet at all adapted to this world, and any little thing can become a serious complication for his fragile body. That is why treatment should be as fast as possible, and most importantly, competent.
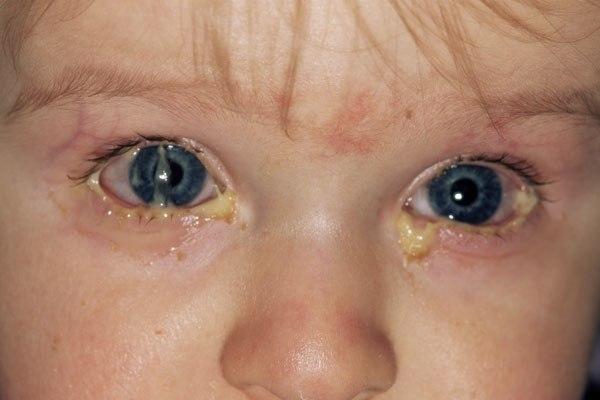
Don't put off visiting a specialist. After all, only an ophthalmologist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment that will quickly help the newborn.
But you can always alleviate your baby’s condition before visiting a doctor, and if the disease strikes you again, you will definitely be fully armed and know what and how to do to effectively treat the disease.
So, how to treat conjunctivitis in newborns if it is not possible to see a doctor?
- Treatment by washing the eyes. A solution of Furacilin will help a newborn get rid of pus, as well as decoctions of herbs such as chamomile, calendula, and sage; Important article on the topic: How to wash a newborn’s eyes?
- Treatment with Levomecithin drops. They should be instilled into the eyes at least 4 times a day;
- Treatment with Tetracycline ointment. It should be carefully placed behind the eyelid of a sleeping newborn.
In addition, read the current article about which drops will help in the treatment of conjunctivitis: Eye drops for newborns
Such measures will help in the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis only. As for the viral one, it will go away after treatment of the underlying disease that caused complications in the child’s eyes. To learn how to raise a healthy child and reduce the number of colds and illnesses to a minimum, see the Healthy Child course
Also, depending on the condition of the newborn, treatment with antibacterial drugs in drops, disinfectant solutions, antiviral drugs and antibiotics is possible.
Important! Such drugs should be prescribed exclusively by an ophthalmologist after examining the newborn and passing certain tests.
And even if you know how to cure your child’s conjunctivitis at home, do not neglect a visit to the doctor. After all, it is better to ask and clarify once again than to carry out belated treatment of conjunctivitis later.
Conjunctivitis in infants is a serious disease. Therefore, you shouldn’t joke with him while self-medicating.
Any treatment should begin with a visit to your pediatrician. This is the only way to most effectively influence the virus that causes conjunctivitis.
A specialist will definitely prescribe drops. He will also select the best dosage for a particular case.
The doctor will recommend cold compresses. With the correct and systematic use of prescribed medications, the child recovers quickly: within a few weeks.
Sometimes it is enough to save the baby from contact with the allergen. For bacterial diseases, ointments and drops containing antibiotics are used.
They eliminate inflammation and have a gentle effect on the child’s body, since the dosage of antibiotics in the drugs is small. When using drops, conjunctivitis quickly disappears.
If a child has conjunctivitis, E. O. Komarovsky recommends giving him the safe drug “Suprastin”. It can be used by babies from the first days of life.
We have figured out what conjunctivitis is, Komarovsky gives some useful recommendations on this matter: it is better for a baby with the disease not to walk on public playgrounds, not to visit crowded places, so as not to add another infection.
There are different types of conjunctivitis. Drops are selected according to the purpose and type of disease.
The bacterial species is treated with drops of Tobrex, Levomycetin and Tsipromed. For a viral type of conjunctivitis, the drug Ciprofloxan is used.
The most important thing to remember is that it is very difficult to cure such a disease in a newborn baby. And if it so happens that the baby does get sick, there is no need to reproach yourself and assume that all the blame falls on the mother. This is possible even with the most careful care. It is important to know exactly how to treat the baby.
Viral and bacterial conjunctivitis is a contagious (infectious) pathology, therefore, during the period of treatment, it is recommended that all other family members adhere to careful hygiene - wash their hands often, do not rub their eyes, and it is advisable to isolate small healthy children at least in the next room.
Conjunctivitis can be successfully treated only with the right therapy. Specialized diagnosis is extremely important, since this disease can be confused with dacryocystitis.
Dacryocystitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the lacrimal sac. The disease is not associated with an infectious factor and develops against the background of obstruction of the lacrimal ducts.
Possible complications

Infants require special care and attention, since any ailment that is easily curable in adults can cause more serious pathological conditions in an infant.
Conjunctivitis, without timely treatment, can lead to:
- abscess of nearby tissues;
- partial or complete loss of vision.
Symptoms
Typical manifestations of conjunctivitis in newborns include:
- increased secretion of tears;
- redness of the eye;
- photophobia;
- sticking of eyelids after sleep;
- purulent discharge (in some forms of the disease), the appearance of dry yellow crusts on the eyes, primarily after sleep.
Conjunctivitis may also be accompanied by loss of appetite and poor sleep. In addition, it provokes such general symptoms as increased fatigue, drowsiness, and anxiety.
The above symptoms may have varying degrees of intensity depending on the level of the child’s immunity, as well as the characteristics of the course of the disease, but in any case they are a significant indication for urgent medical attention. The doctor must conduct a full examination of the child and, based on the data obtained, prescribe treatment.
Preventive measures
So that the baby does not experience all the “beauty” of inflammation of the conjunctiva, parents are required to take care to prevent the disease:
- the baby should be protected from hypothermia and prevent the development of colds;
- keep the house clean, carrying out regular wet cleaning, washing toys and personal hygiene items;
- The baby should be bathed at least 2-3 times a week, washed with boiled water as needed;
- protect the baby from contact with sick guests and family members;
- Take daily walks in the fresh air to strengthen your immune system.
Conjunctivitis is an eye disease that occurs in adults and children at any age. It is important not to self-medicate and entrust therapy to professionals.
Manifestations of conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, an inflammatory process on the mucous membrane of the eyes. Typically, the disease develops in an infant as a result of damage to the developing body by infections: viral, bacterial, fungal, allergens.
Reference! After childbirth, the maternity hospital medical staff carries out prevention of ophthalmic disease: the nurse washes the newborn’s eyelids, puts drops in the eyes, and applies antibacterial ointment. With the development of ophthalmia, the baby’s vision organs begin to water, turn red, and itch.
A negative reaction manifests itself not only due to infection of the body: often the eyes of a newborn baby react sharply to medications, Albucid and other medications used for preventive purposes.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis cannot be missed:
- Hyperemia, adhesion, swelling of the eyelids,
- "Souring", eyes,
- Pinpoint hemorrhages in the conjunctiva,
- Increased tear production
- Exudative discharge from the organs of vision,
- Formation of a grayish-white film on the eyes,
- Photophobia,
- Feeling of “sand” in the eyes
- Itching, burning, stinging,
- The baby is capricious, lethargic, refuses to eat, and sleeps restlessly.
In case of the above manifestations, it is forbidden to self-medicate and it is necessary to urgently show the baby to a doctor, pediatrician, or ophthalmologist.
The symptoms are similar to other ophthalmological diseases, inflammation of the cornea, lacrimal sac (dacryocystitis), non-opening of the nasolacrimal duct and others.
In infants, the clinical picture is much more pronounced than in adults: swelling from the eyes often spreads to the cheeks, and temperature values increase.
Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in infants under one year of age
For each type of pathology, their own medications are used. To diagnose the causative agent of the disease, the doctor takes a smear from the conjunctival cavity and then determines its sensitivity to various antibiotics. Only after this does he prescribe antibacterial drugs for the eyes.
"Albucid"
The most common eye drops for children of any age, starting from birth, which effectively eliminate the symptoms of the disease. They contain sulfonamide, an active antimicrobial substance. "Albucid" is also used to treat blenorrhea and purulent ulcers.
"Tobrex"
The active ingredient is tobramycin. This is a strong antibiotic that suppresses protein synthesis in the cells of microorganisms, disrupting their active functioning. Copes with most pathogens of bacterial conjunctivitis. Adverse reactions such as allergies and urinary disorders are possible. In case of such phenomena, you should consult a doctor to change the medicine.
"Vigamox"
The active ingredient is moxifloxacin 0.5%, which belongs to the fluoroquinolones and has an extended bactericidal effect. If there is severe discharge of pus, you can use an additional antibacterial ointment, for example, Erythromycin 1%. It has proven its effectiveness in forms of the disease that are difficult to treat (fungal, gonococcal, diphtheria and others). The ointment should be used after administering all the drops three times a day for 7-10 days, after which see a doctor.
Doctor Komarovsky about conjunctivitis in a newborn
A popular children's doctor today, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Dr. Komarovsky, warns that if a newborn baby's eyes begin to sour, he needs to be shown to a pediatrician
And, if necessary, he will refer you for a consultation with an ophthalmologist. It is important not to waste time and not to trigger the disease.
If conjunctivitis is caused by a bacterial infection, Komarovsky recommends Tsiprolet solution for instillation into the eye. If there are manifestations of an allergic disease, accompanied by a runny nose, sneezing, he recommends antihistamine drops and mandatory tests to identify the allergen.