Definition of lesion
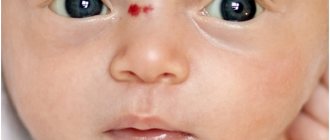
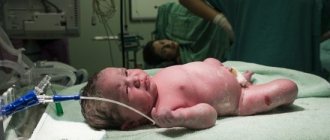
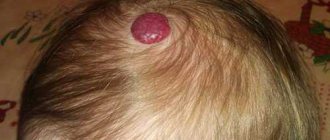
A photo of port-wine stains on a newborn is shown below.
A port-wine stain usually refers to one of the types of dysplasia of the superficial vessels of the skin in a child. The disease begins to affect the human body even during development in the womb, which is why skin lesions are usually called newborn spots. This disease has a second name - flaming nevus.
Port-wine stain in newborns - what is it? The peculiarity of such formations lies in their special bright red color, which continues to persist throughout life. In appearance, such areas of the body are more reminiscent of hemangiomas; they cannot transform into a chronic form, but can be localized in any part of the body. The main cause of port-wine stains in newborns is dilation of the capillaries. The disease can occur in both girls and boys.
Skin rash in children. The faint of heart should not look at the pictures!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Vascular spots on the skin of a child in most cases appear if disorders of the circulatory or vascular systems are diagnosed. They can have a variety of shapes and sizes depending on the reasons for their appearance. The rashes can be single or multiple, convex and flat, homogeneous or differ in texture. Pigmentation can spread throughout the body or be localized in small areas. Most often, children have red spots; the pigments have a bright red tint, but dark purple is also considered the norm.
There are many examples in the photo of what vascular spots look like in infants. The cause of the appearance of vascular formations is a violation of the blood supply.
Therefore, the child has vascular spots on the body. If a vascular spot appears in a newborn, you need to visit a pediatrician to examine the baby. Rashes in children are divided into several types. Taking into account the type of pigmentation and the level of danger, the doctor selects adequate treatment. Their color ranges from bluish to scarlet. They protrude slightly above areas of the skin. Pigmentation does not require removal.
By the age of 7 it goes away on its own. These are flat-shaped formations, which in color resemble wine-purple spots due to the pronounced vasodilation in this place.
They resemble several mature, slightly dilated blood capillaries, which are located asymmetrically to each other. The formations slightly rise above healthy areas of the skin. They have clearly defined boundaries and a dense texture. They are hard to the touch. The formation resembles a small nodule the size of a match head.
Small blood vessels branch out from it in various directions in the form of peculiar rays. The location is the ears, the surface of the face, the upper part of the body, and the inside of the hands.
The disease is observed in the child from the first days of birth and goes away on its own within a year without therapy. This hemangioma looks like a tumor that rises above healthy skin. Vascular spots in newborns are localized on the face, on the buttocks, and rarely in the oral cavity.
The plaques have a lumpy structure with blood-filled cavities. They are soft on palpation. They have brown or bluish tints. The disease is associated with a defect in the proper development of blood vessels.
The pigments have a variety of shades from light pink to bluish. The surface of the formations is smooth and even. Vascular spots may appear on the legs, arms and other places on the skin. The appearance of formations is provoked by disturbances in the quality of the hematopoietic system.
Nodules protruding above healthy skin acquire a light shade when lightly pressing on them. When injured, they can transform into ulcers that must be urgently removed due to the risk of infection. Often in children, red vascular spots on the legs, arms and other parts of the body indicate the presence of cavernous hemangioma. Their appearance is associated with malfunctions of internal organs due to lack of blood circulation.
After diagnostic procedures, the doctor can determine the name of the disease. Only after this is the question of choosing a therapeutic treatment or method of removing plaques. Vascular lesions do not always require treatment. If a child has flat angiomas, they are monitored. If they do not change in size, removal is not necessary. Over the years, such rashes go away on their own. If the color, shape and size of the plaques change, the doctor prescribes removal, selecting an effective method.
Laser therapy is most often used. This is a safe method of therapy in which a beam of laser beams is applied to the plaque without damaging the structure of healthy areas of the skin. This prevents the appearance of wounds, and prevents the occurrence of inflammatory processes and infection. Laser beams burn out the plaque and after a week it disappears.
After the procedure, scars and cicatrices do not appear. After removing the pigmentation, a wound remains, which heals on its own within weeks. Removal is possible using the coagulation method. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
An electric current is applied to the plaque, cutting out the root. After the procedure, a wound remains, which is treated with antiseptic drugs for days. After removal there is a possibility of scarring.
If a newborn has a vascular spot on the leg or other areas of the skin, cryodestruction is resorted to. The removal method involves exposing the plaque to liquid nitrogen.
The procedure lasts a maximum of 3 minutes. The doctor treats the surface of the skin using a special apparatus with ultra-low temperature nitrogen. The rash itself and the intercellular fluid are frozen, which is why the vital activity of cells stops. The plaque tissues are gradually destroyed and over time replaced by new, healthy ones. After the procedure, small scars remain, which will disappear on their own over time. It does not matter what type of vascular rash the child has pigmentation.
Parents independently constantly monitor the size and color of the hemangioma, so that in case of minor deviations or other changes, contact their pediatrician in a timely manner. Do not forget that this type of pigmentation is a tumor, which will lead to negative consequences if injured and damaged.
Doctors warn! Worms cause enormous harm to the body, and the first to suffer is our immune system, which should protect the body from various diseases.
The head of the Institute of Parasitology shared the secret of how to quickly get rid of them and cleanse your skin, it turns out that it is enough Read more You should not resort to self-medication. Ointments and traditional medicine recipes will not help get rid of hemangiomas. By cauterizing them, there is a risk of causing injury and introducing infection into the wound.
For this reason, the pigmented plaque is likely to degenerate into a malignant tumor. Therefore, treatment and removal are carried out only under the supervision of a doctor. Your email will not be published. Skip to content.
The main reasons for the appearance
The main causes of port-wine stains in newborns include:
- intoxication of a woman’s body during pregnancy;
- negative effect of radiation on a child developing in the womb;
- change in the amount of progesterone in the body of a pregnant woman;
- infectious processes in the genitourinary system;
- acute infectious diseases in women during pregnancy.
All of these factors can lead to the appearance of a nevus in a child. The main cause of port-wine stains in newborns is the lack of contact between nerve endings and capillaries. When nerve impulses are damaged, the vessels stop contracting fully, resulting in red or purple spots on the skin.

Experts attribute disturbances in the functioning of nerve endings to a gene mutation; such a process was identified not so long ago. In this case, the development of the lesion begins almost immediately after conception. But the exact reasons for this mutation have not yet been determined.
Symptoms of a flaming nevus
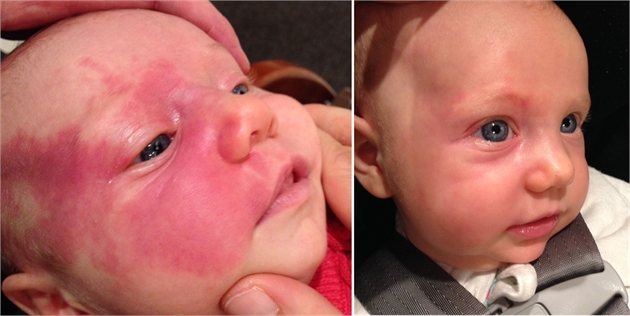
Immediately after the birth of a child, a flaming nevus is a slightly pinkish spot of irregular shape with fuzzy edges; there may be areas of normal skin in the center of the spot. When crying
or the cry of a baby, the port-wine stain
becomes brighter
and more saturated, which is associated with blood flow to the head and an increase in its content in the capillary bed.
As the child grows older, the appearance of the nevus also changes. It becomes darker in color and may take on a red, violet or purple hue. Sometimes nodules appear on its surface, its thickness increases, which leads to an elevation of the formation above the skin level.
Apart from external manifestations, flaming nevus is devoid of any symptoms and manifestations. As the child grows, it increases in proportion to height
its
body
, does not cause pain, itching, inflammation or other reactions.
Sometimes it can spontaneously decrease until it disappears completely. Photo 2. It is known that children with fair skin are more likely to develop nevi. The spots may go away on their own before puberty. Source: Flickr (Andrew Sweeney)
Common symptoms
Port-wine stains are multiple spots that are distinguished by their clear boundaries and an unusual light pink or purplish-red color that stands out against the rest of the skin. The number of spots on a newborn's body may vary.
In some cases, neoplasms spread to large areas of the body, which brings significant discomfort in aesthetic terms. Most often, you can notice port-wine stains on a newborn’s face, neck, and scalp. In rare cases, the formation is diagnosed in the mucous membrane.
Treatment of nevus of Unna
Treatment of port-wine stains has long been used in medicine and cosmetology. It is effective and eliminates the problem. The sooner the necessary measures are taken, the more effective. Darkening of the nevus reduces the likelihood of its complete removal. There are different methods used in therapy, which only a doctor can choose correctly. You can get rid of pigmentation in a hospital or in a beauty salon, but after differential diagnosis.
Nevus of Unna is a congenital benign formation on the skin caused by a disorder in the development of skin vessels. Most often it occurs on the forehead, bridge of the nose, eyelids and the back of the head.
Nevus of Unna is often located on the back of the newborn's head
Unna's nevus is called differently: angel's kiss, flaming nevus, fiery nevus, wine formation. Nevus is found in almost 50% of newborn children, and by two years, in 80% it goes away on its own. It can remain in some areas of the body for life. The spot does not itch or become inflamed. If the stain does not disappear over time, it becomes cyanotic. Such spots do not belong to malignant tumors, but are only dilated vessels without changes in the cells themselves.
Possible negative consequences
Such a spot can appear after the child is born or during several months of his life. If education does not take place for a long time, then, as a rule, it remains for the rest of life.
The formation can change in size and progress as the baby grows. The shade of a port-wine stain may also fade or become brighter. In some cases, the spot thickens, specific areas become enlarged, and nodes form.
A port-wine stain is primarily an aesthetic defect and no treatment is required unless it becomes larger or changes color.
Also, such a formation can indicate the presence of a certain genetic disease in the child’s body, for example, Sturge-Weber syndrome. In this case, it is important to see an ophthalmologist and have your eyes examined to identify possible glaucoma. If you do not start timely treatment of the disease, there is a high risk of simply losing your vision.
It is also additionally important to undergo an MRI or ultrasound. Since with this disease the child may have cramps in the limbs, he should also consult a neurologist.
This disease is considered a type of vascular benign tumor, which can cause problems with the musculoskeletal system.
What does a birthmark on the buttock mean?
Humanity has been collecting signs about birthmarks for centuries; facts about a person can be guessed based on the location of the birthmark on the butt.
- If located at the top of the right buttock, this indicates the man’s irresponsibility, unwillingness to be responsible for words and actions. People don't strive for development. They are open to communication and make friends easily. Many people use friendship as an advantage and lose loved ones. Women with a birthmark on the top of the right buttock are frivolous, it is difficult for them to save money, the funds are spent on entertainment and shopping.
- When the formation is located at the bottom of the right buttock (right, left) - the man is kind, charming, an excellent friend, interlocutor. People are lucky with money, they know how to earn money and save money. Women are lazy, calculating, cunning, marry for money, cheat on their husbands.
- Women who have a spot at the top of the left buttock are sincere, independent, trusting, love to work hard at work, at home - ideal wives and mothers. Men are characterized by seriousness and tenderness, they make excellent friends and husbands. A man will not take risks if he is not sure of success.
- The meaning of a nevus located at the bottom of the left buttock for men speaks of a love of popularity and hard work. Women are careerists, it is difficult for them to find their ideal, to enter into a successful marriage.
Interpretations are popular among esotericists. Applicable to almost every owner of pigmentation on the butt.

Possible diseases
If a port-wine stain in a newborn is localized in the area of a limb, then there is a risk that Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome is progressing in his body. In this case, an ultrasound scan is mandatory. In this condition, the nevus joins and varicose veins of the superficial veins develop.
As a result of this process, the structure of the limbs is disrupted and gigantism of the affected leg or arm begins. In addition, as a result of increased blood flow in the diseased area, lameness may appear, and the healthy leg will become shorter than the diseased leg by a couple of centimeters. If port-wine stains are located on a limb, it is important to visit a vascular surgeon.
A port-wine stain on the back of the head in newborns can provoke epilepsy, since this disease negatively affects the condition of the blood vessels in the brain. Thickening of the skin in the area of the spots prevents the child from moving normally and disrupts the condition of the motor system.
If the formation is localized in the cheek area, it may even prevent the child from chewing food normally. By examining the vascular bed, the doctor can determine all blood supply disorders and prevent the development of pathological processes.
Diagnosis of nevus port wine stain
Diagnosis, as a rule, does not present any particular difficulties due to the fairly characteristic external manifestations of this formation. One of the diagnostic criteria is vitropression
(pressure on the nevus with a glass slide, under which it will somewhat lose its color), another - increasing the brightness of the spot against the background of a child screaming or crying.
, dermatoscopy may be performed
and
biopsies
, which will help to finally determine the pathology.
In rare cases, Unna's nevus is combined with damage to the brain and visual apparatus. In this regard, it is recommended
undergo
examination
by
a neurologist and ophthalmologist
.
If a hemangioma, which is a benign tumor of vascular origin, is detected, it is necessary to consult with a number of specialists to exclude damage to internal organs. An important factor is that in the absence of damage to internal organs, hemangioma can go away spontaneously
.
Are therapeutic therapies important?
It is important to treat the disease only in cases where it progresses, develops rapidly, and poses a danger to the person’s condition. Sometimes such a cosmetic defect must be removed, as it simply does not allow the child to lead a full life.

The following physiotherapy is used in treatment: cryotherapy, surgery, laser coagulation. In this case, a positive effect can also be achieved using traditional medicine.
A child's port-wine stains will not go away on their own, so a specialized vascular laser may be needed to change their color. Many specialists prescribe treatment for a child in the first months of his life.
The main methods of treating education
Previously, the treatment of port-wine stains in a newborn was carried out through skin transplantation, that is, with the help of a very dangerous and risky operation, which, among other things, brought severe pain. After it was carried out, unsightly and noticeable scars could remain on the child’s body.
With an incorrect diagnosis of the disease and unprofessional surgery, the remaining nevus cells changed to malignant.
Now in modern medicine, such errors no longer occur due to accurate diagnostic methods. Spots of this type are excised through surgery. Along with this, modern medical procedures became widespread.

These include: infrared radiation, radiation therapy, cryodestruction. These methods of treating neoplasms help improve the appearance of the spot and make it less noticeable. When they are carried out, the walls of blood vessels are destroyed, but the condition of the tissues is preserved.
Recently, laser treatment of various tumors on the body is considered the most effective and high-quality method. This method does not damage healthy tissue on the body, which helps prevent various complications, such as burns, unpleasant scars and pigmentation.
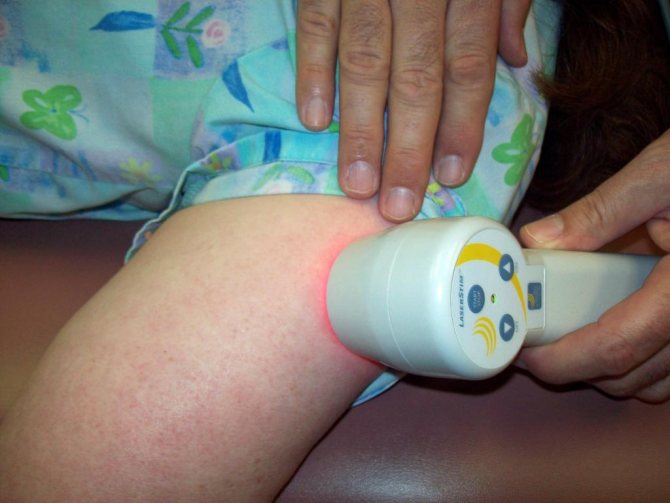
Laser coagulation helps to treat the disease without anesthesia, and also protects against the appearance of scarring on the surface of the skin.
Laser treatment is a safe method that is well suited for both newborns and older children. At the same time, the depth of the vessels and their shade do not have any special significance on the indications for the procedure.
Type of vascular spots
There are several types of spots that occur in newborns. Depending on this type, a decision is made about the level of danger of the disease and how to treat it.
Types of vascular spots:
- Flat angioma . The disease manifests itself in the form of crimson dots, which can be located on any part of the body. During childbirth they are invisible and appear during the first month of the child’s life. This type of hemangioma occurs quite often in children.
The likelihood of such spread increases with a large number of hemangiomas that are located on the face or upper body. Please note that the hemangioma grows with the child, so during the first six months it increases significantly in size, which often frightens parents.
- Capillary hemangiomas . The disease occurs as a result of deformation of the capillaries and is characterized by the appearance of a collection of them in one place, which thus form a spot. They appear on the surface of the skin even before birth and are immediately visible. Capillary hemangiomas themselves do not go away; they require treatment and consultation with a doctor. This type of disease most often has a purely cosmetic nature. Sometimes cases arise in which hemangiomas can cause more complex diseases that require further treatment. For example, the location of such a spot near the eyes can lead to the development of glaucoma. Therefore, it is imperative to visit a pediatrician to control this spot: its size, location and nature.
- Angiodysplasia . The disease is considered a malformation of blood vessels. The spots have a different color shade: from soft pink to cherry purple. They have a smooth surface, do not protrude on the skin, tend to darken and are a significant cosmetic drawback.
- Cavernous hemangioma . The disease occurs due to a disturbance in the structure of blood vessels . The structure is nodular, protrudes above the surface of the skin, and can lighten when pressed. The size of the spot can change both larger and smaller. Such hemangiomas can cause the development of infectious ulcers, so their removal or treatment is an urgent need, because such ulcers can directly interfere with the full functioning and development of internal organs.
Treating port-wine stains with folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies can give good results if you want to reduce the brightness of the spots. However, it is not possible to completely eliminate the nevus using such methods.

Basic methods of treatment with folk remedies:
- Fresh juice of the celandine herb is infused, placed on the affected area and fixed with a simple band-aid. The procedure lasts from 7 to 10 days. As a result of this effect, the stain becomes lighter and loses its expression over time.
- Apply garlic juice to the affected area, and after 2-3 minutes add lemon juice. Such procedures are repeated 5-6 times a day for seven days. In this case, the reaction of the spot may vary depending on its shape and brightness.
- Experts also advise lubricating the formation with the juice of unripe figs once a day.
- Apply hemp oil and chalk to the formation three times a day (in a ratio of 4 to 1). The result is a fairly long-lasting whitening effect. The procedure is carried out within a week.
- Take 2 cloves of garlic and infuse it in 250 ml of apple cider vinegar for 14 days. The finished product is applied to the stain in the form of a lotion.
Experts' forecast
Experts note that in the absence of a progressive process, such a formation does not pose a particular threat to the child’s health and may not be treated. But at the same time, it is important for the baby to be regularly observed by the attending physician in order to prevent possible pathological processes.
In adolescence, you can try to hide such formations, if they cause psychological discomfort, through cosmetics. When a spot begins to develop, it is important to seek help from a dermatologist or oncologist, who will help identify possible complications and prescribe effective treatment.
Types of vascular spots in newborns
In order to understand whether a particular stain is dangerous, it is imperative to show the child to a doctor. The pediatrician will refer you to a dermatologist, who, in turn, will take all the necessary tests and samples and tell you whether this spot needs to be smeared with something, treated or removed somehow, whether it is dangerous or not.
Vascular spots on the body of newborns are divided into several types:
- A vascular nevus is an irregularly shaped pink, red, lilac or purple spot. This spot is also sometimes called a “flaming nevus.” This stain does not resolve on its own; over time, this stain darkens and turns pale. This is what is called a birthmark. It can grow up to several centimeters. A sign of a vascular nevus is that it does not protrude above the skin, that is, it is impossible to find this spot by touch.
- Capillary hemangioma - appears due to problems with the capillaries. Such capillary hemangiomas in newborns are visible on ultrasound even before the child is born. Accordingly, when the child is born, the doctor already knows about this problem and begins observation. Such spots do not go away on their own and do not resolve; this problem must be treated. As a rule, this issue is eventually resolved through cosmetic surgery.
- Cavernous hemangioma is a small benign tumor that can be found on the mucous membranes, internal organs, in the brain, and simply on the skin. Such a hemangioma sits very deep, and it is quite difficult to get it out, as well as to treat it. The doctor is constantly and very closely monitoring this spot.
- Mixed hemangioma is when, along with a capillary neoplasm, tumor cells of nerve, connective or any other tissues have been added.
Any hemangiomas located near the eyes, ears or nose in newborns become a source of problems with vision, hearing and breathing.