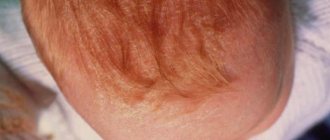
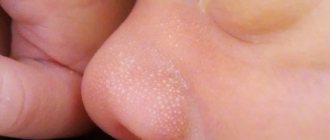
Miliaria in children
Miliaria (miliaria) develops in children in conditions of high humidity and ambient temperature due to the insufficiency of the thermoregulation system and the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
Factors predisposing to the development of heat rash in newborns:
- imperfection of thermoregulation;
- thinness and vulnerability of the epidermis;
- reduced immune defense of the baby's skin;
- well-developed network of skin blood vessels;
- narrowed ducts of the sebaceous glands;
- female gender of the child;
- non-compliance with hygienic rules for caring for infants;
- excessively wrapping children.
There are 3 forms of miliaria:
The prickly heat rash is represented by blisters or nodules (in the red form), the color is pale pink. More often it appears in places of increased overheating of the skin under clothing, in folds. The rashes do not flake or itch. Miliaria quickly goes away even without the use of medicinal ointments, subject to proper hygiene.
Localization of the rash
With allergic contact dermatitis, a rash appears directly at the site of skin contact with the provoking substance. In other cases, it is localized on any other parts of the body: stomach, face (usually cheeks), back, buttocks.
Miliaria never appears on the skin of the face. Favorite localization of rashes: skin folds (armpits, gluteal fold, neck, etc.)
How to distinguish heat rash from allergies in a baby?
The following recommendations will help to correctly diagnose heat rash or allergies in a newborn.
So, you have discovered a rash on your baby’s body.
- Examine the child completely for the presence of rashes, their location and nature.
- Try to remember whether there were predisposing factors for the appearance of heat rash in the baby: overheating, high humidity, excessively warm clothing.
- Risk factors for allergic rashes include recent introduction of new products, use of a different laundry detergent, new skin care products, and medications.
The allergic nature of the rash is indicated by:
- bright widespread rashes on any part of the body;
- characteristic morphological elements of the rash: blisters, papules, vesicles;
- peeling;
- getting wet;
- intense itching;
- recent introduction of new complementary foods;
- use of new cosmetic care products;
- taking medications, especially antibiotics.
The following factors testify in favor of prickly heat
- no rash on the face;
- rash in the form of pale pink blisters;
- elements of the rash are located on areas of the skin covered with clothing;
- the day before, the child could have overheated and was dressed too warmly;
- no itching, peeling, weeping of the skin, or crusts.
How to distinguish skin allergies from prickly heat
With a careful analysis of the rashes, as well as the causes of their occurrence, differences can be found. This is very important, since the treatment of prickly heat involves mainly hygienic measures, and allergies require complex treatment (antihistamines, avoiding contact with the allergen, adjusting the diet).
note
In addition to allergies and prickly heat, skin rashes can be caused by other factors.
Check out the article: Newborn acne or allergies?
To exclude allergies in newborns, you need to know the main factors that can trigger them.
- Introduction of new products into complementary foods.
- Washing baby clothes with new detergent.
- Using clothing made from fabric that is new to the baby.
- Mother's consumption of new foods during breastfeeding.
Here are the main differences between miliaria rashes and allergic reactions, allowing for a differential diagnosis of allergy rashes and prickly heat.
| Allergy | Prickly heat |
| The rash appears on the face, abdomen, limbs (particularly on the folds), buttocks | There is no rash in the face area |
| Allergic rash does not depend on overheating of the child | As a rule, it appears at high indoor temperatures in places that sweat a lot (armpits, neck, buttocks, back, bends of limbs) |
| The rashes are bright red in color and look like bubbles with liquid inside. The rash merges into large spots, and upon healing they become rough to the touch. | The rash is small and pink. The skin does not peel off. |
| The rashes go away if you avoid contact with the allergen and use antiallergic drugs prescribed by your doctor. | If the areas of the rash are dried, the rash goes away within about a day. If you bathe your child more often, wash your child regularly, and change diapers more often, heat rash will disappear without treatment. |
Tips for caring for the skin of infants prone to prickly heat and allergic rashes
If your children often suffer from rashes, these recommendations will help avoid exacerbations.
1. Bathe your baby daily.
Remember that a warm bath is better than a shower. The water temperature should be kept within 37 °C.
It is recommended to stand or boil water for bathing. You can add soft detergents from the Mustella, Topicrem, and Atoderm lines to it.
2. The child’s skin should be treated with moisturizers on the advice of a doctor. It is often necessary to apply up to 4 - 6 applications during the day. The products “Lipikar”, “Mustella StelAtopia”, “Realba”, “Atoderm” have proven themselves well.
3. The baby’s clothes should be cotton; do not use underwear made from synthetic fabrics.
- the baby's skin must breathe;
- It is forbidden to wrap up a child.
4. If you notice that the baby is sweating, then change his clothes.
5. Do not use detergents containing ammonia to clean your apartment. It is better to use special products for people with allergies.
6. Maintain the required level of humidity and temperature.
- use a humidifier;
- recommended air temperature in the apartment is 20 - 22 °C;
- carry out daily wet cleaning;
- use air purifiers.
Useful tips for caring for the skin of children suffering from allergic dermatoses
- remember that creams are water-based, which means they dry out over time;
- ointments moisturize the skin better;
- if the skin gets wet, lotions are used for treatment; if it peels, use fatty ointments;
- soap dries out the skin. Try to use special skin care products from the ReAlba, Lipikar, Physiogel, Atoderm lines;
- a bath with oil additives helps relieve itching and dry skin;
- To calculate the amount of cream required to apply to the area of the rash, you should remember the rule: the amount of cream corresponding to the phalanx of the finger is sufficient to apply to an area of skin the size of the palm.
Let's sum it up
Brief information on the article that will help parents properly help their baby when rashes appear.
- A baby with rashes should be shown to a specialist.
- Miliaria (miliaria) develops in children in conditions of high humidity and ambient temperature due to the insufficiency of the thermoregulation system and the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
- The prickly heat rash is represented by blisters or nodules (in the red form), the color is pale pink.
- Risk factors for the appearance of allergic rashes include the recent introduction of new products, the use of a different washing powder, new care cosmetics, and taking medications.
- The child's skin should be treated with moisturizers on the advice of a doctor. It is often necessary to apply up to 4 - 6 applications during the day.
- If the skin becomes wet, lotions are used for treatment; if it peels, fatty ointments are used.
Thus, in this article we examined the main prerequisites for the appearance of prickly heat in a child, the characteristics of the elements of the rash in miliaria and allergic dermatoses. Issues on proper skin care if you are prone to rashes were also covered.
What is prickly heat?
Irritation on the baby’s skin is a reaction to sweat (hyperfunction of the sweat glands against the background of a slow evaporation process - hyperhidrosis). Bubbles and spots on the child’s body are external signs of prickly heat.
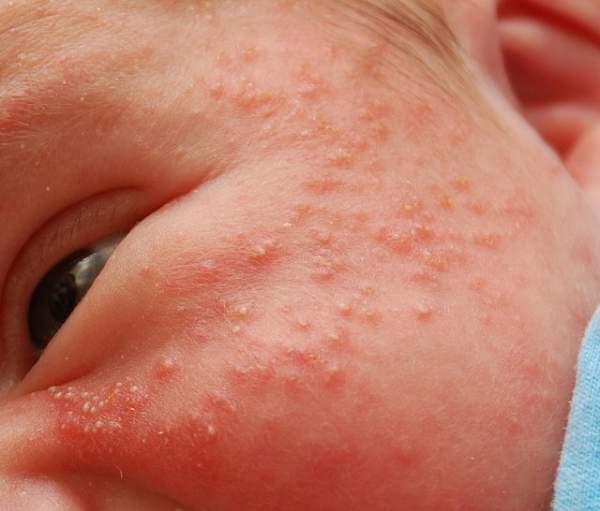
In the first six months of life, the appearance of a rash is explained by poor functioning of glandular cells.
Factors causing prickly heat
The following factors cause the inflammatory process:
- Staying in the sun for a long period of time, while sweating intensively in order to reduce body temperature.
- Stuffiness in transport or indoors.
- Lack of ventilation of skin folds.
- The use of clothing made of thick and synthetic fabrics (wrapping in the warm season).
- High humidity amid hot weather.
- Hyperthermia due to infectious diseases.
- Abuse of children's body care cosmetics (talc and creams), which causes clogged pores.
What are the features of the manifestations of heat rash in infants?
There are the following types of heat rash in newborns:
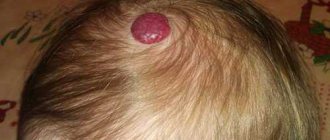
- Crystalline prickly heat. Occurs on the neck, face and chest area. It appears in the form of bubbles or nodules resembling salt crystals, the diameter of which is no more than 2 mm. After 2 hours, the bubbles open, forming a dry crust.
- Miliaria rubra. This type of miliaria can occur in the area of the elbow and the popliteal cap, in the groin area. The size of bubbles with cloudy contents reaches 3 mm. The inflammatory process is accompanied by severe itching.
- Papular miliaria. Occurs in rare cases in conditions of high air humidity. The blistering rash is localized in various parts of the baby’s body, which causes itching. After opening the blisters, peeling of the skin is observed.
Manifestations of prickly heat are typical for children born in the summer. The baby's delicate skin is highly sensitive even to clothes made from natural fabrics.
The use of diapers in the summer also contributes to limited access of air to the skin, which causes the appearance of prickly heat.
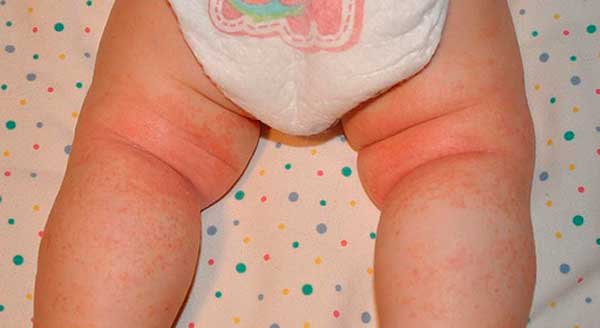
Diagnosing prickly heat in infants
Symptoms of the disease appear almost identically in all children.
Externally, prickly heat looks like spots or blisters filled with clear liquid against the background of reddened skin. This is irritation of the child's skin when sweating is more intense than evaporation. At the same time, you will probably notice that the child behaves restlessly, is capricious, sleeps poorly and constantly spins, which is quite justified, because prickly heat causes a burning sensation of the skin. This serves as a kind of signal from the baby’s body for you to carefully examine him. By the way, the rash rarely appears on the face. This will help you to some extent distinguish heat rash from allergies in an infant.
Types of disease
Based on the type of rash, prickly heat is divided into:
Red miliaria looks like blisters against the background of redness of the skin. The blisters do not merge with each other and cause itching and pain when touched.
In infants, the second type of prickly heat most often manifests itself - crystalline. These are white or pearlescent blisters that are slightly larger in diameter than prickly heat rashes. Elements of the rash can merge with each other, they are easily damaged and the skin in this area peels off.
Miliaria profunda is characterized by flesh-colored rashes measuring 1-3 mm. They can appear and disappear on their own.
Causes of prickly heat
Over the course of the child’s long development, the baby’s skin has become accustomed to one habitat – aquatic (in the mother’s womb). And it is natural that a change in environmental conditions after birth will lead to changes in the baby’s body. A baby’s glands do not function like the glands of an adult, and it takes time for them to normalize their work.
Sweat glands protect the body from overheating; when body temperature rises, they secrete a liquid secretion. If the baby is overly swaddled, warmly dressed, or there is a thick layer of cream on the skin, all this interferes with the normal secretion of sweat and the secretion accumulated in the glands causes redness of the skin and blisters.
The disease can also occur if diapers are not changed in a timely manner or if they spend a long time in a hot room.
Allergies in infants and their manifestations
Unlike prickly heat, allergies cause much more trouble for young parents than prickly heat.
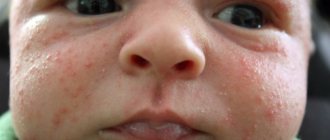
The main thing is to timely and correctly distinguish heat rash from allergies in a baby. Allergies or allergic dermatitis are very similar in appearance to miliaria: a rash appears as a result of the body's reaction to an allergen. These can be food products included in the diet of the mother and/or child, household chemicals, medications and other factors. The reaction appears some time after the allergen enters the body in the form of rashes, spots and redness. Most often, the first type of allergic manifestation occurs. Here you can distinguish prickly heat from allergies in infants: the rash mainly appears on the face, tummy, forearms and buttocks. These types of pimples merge into larger spots after some time and cause severe itching.
Causes of allergies
Allergies in a baby appear due to contact with allergens, which the body mistakes for a foreign substance. In newborns, this reaction occurs due to improper nutrition of the mother. Allergies can be drug, food and contact. Fighting a foreign substance that has entered the body, the child’s immunity exceeds the limits of self-defense, beginning to damage its own tissues.
An allergic reaction is observed on the face, neck, buttocks, back and abdomen. Less commonly, the disease affects the upper and lower extremities. The baby's digestive system is not sufficiently developed, it is not able to digest some foods, which is why particles of undigested food irritate the gastric mucosa and cause the appearance of toxins in the baby's blood. The skin is the first to react to the appearance of toxins and a rash appears.

Types and causes of allergic dermatitis
Depending on the type of allergen that caused the allergic reaction on the baby’s body, there are mainly two types: food and contact dermatitis.
The first type of allergy rarely appears in the first six months of life with breastfeeding, but if it does, it appears in the form of an allergic red ring around the anus. This may be due to some food product. Excluding this product from the diet of the mother or her child will help eliminate this effect. Another reason is calcium deficiency.
Flat red spots or swelling are contact dermatitis and can appear where your baby's skin rubs against clothes or diapers. You can easily determine this, because... other areas of the skin are not affected. The irritant can be various chemicals in powders, soap, water (chlorine), frequent and abundant use of detergents. Synthetic clothing, bedding, toys and furniture can also trigger allergies.
Causes

. Factors that can influence the occurrence of allergies include:
- the presence of a food irritant that has entered the child’s digestive system;
- persistent intolerance to certain medications;
- excessive sensitivity to animal hair or response to plant flowering;
There are a number of factors that determine the predisposition to heat rash in a newborn child and infant:
- vulnerable, thin epidermis;
- increased temperature or humidity in the room;
- the presence of narrowed ducts of the sebaceous glands;
- wrapping the baby tightly;
- excess weight, which determines the presence of deep folds on the body;
- imperfection of thermoregulation;
- an overdeveloped network of skin blood vessels;
- lack of hygiene in caring for toddlers;
- abuse of powder and various creams, which affects the presence of clogged pores;
- synthetic clothing that does not allow the skin to breathe normally;
- the presence of an infectious disease accompanied by high fever.
Manifestation of allergies on the back of an infant
The cause of allergies is the entry of allergens (antigens) into the body. This manifests itself primarily as rashes on the skin.
Breastfed newborns experience mainly food allergies, which can sometimes be confused with prickly heat.
Scaly spots or pimples appear on the child’s thighs, buttocks, head, armpits, and on the folds of the arms and legs. Initially, the allergic rash is localized in several different areas, and after that it can merge into one large one.
In addition to food allergies, skin manifestations are usually accompanied by allergies to medications and sweat.
Miliaria can also easily be confused with a sweat allergy. But these two diseases actually have significant differences. An allergic reaction to sweat occurs in any part of the body and occupies a large area, unlike prickly heat. This type of allergy goes away on its own within a couple of hours.
An allergic reaction is expressed in adults by the following symptoms:
- After excessive sweating, light pink blisters appear on the skin (sometimes they are filled with liquid).
- The rash is accompanied by itching of varying strength.
- Allergies appear in areas of greatest sweating (armpits, neck, natural skin folds.
- Sometimes, in addition to rashes, allergies can be expressed by nausea, vomiting, increased salivation, and stool disorders.
Depending on the type of allergen that caused the allergic reaction on the baby’s body, there are mainly two types: food and contact dermatitis.
The first type of allergy rarely appears in the first six months of life with breastfeeding, but if it does, it appears in the form of an allergic red ring around the anus. This may be due to some food product. Excluding this product from the diet of the mother or her child will help eliminate this effect. Another reason is calcium deficiency.
Flat red spots or swelling are contact dermatitis and can appear where your baby's skin rubs against clothes or diapers. You can easily determine this, because... other areas of the skin are not affected. The irritant can be various chemicals in powders, soap, water (chlorine), frequent and abundant use of detergents. Synthetic clothing, bedding, toys and furniture can also trigger allergies.
Important! Remember that the main danger of allergies lies in a secondary infection, which can occur when a child scratches the places where allergic rashes cause itching.
It is important for young parents to know that in the womb the environment for the child has become familiar within 9 months. An important process took place there - the development of the baby. At birth, a baby’s many functions and systems are underdeveloped; only after a certain time do they achieve full development. But before finishing this process, it is important to go through the process of adaptation to the environment.
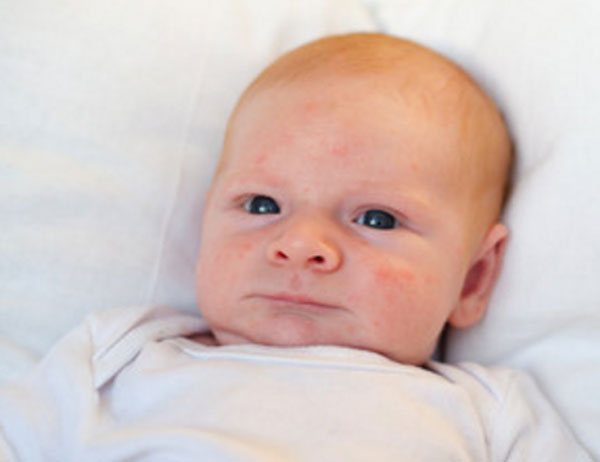

So, at the time of birth, the sweat glands have not gone through the final process of development and are forced to adapt to environmental conditions, because it is so unusual for the skin of a newborn. In this regard, with fluctuations in temperature and air humidity, the sweat glands actively secrete their secretions, which leads to the formation of bubbles. This is also facilitated by:
- Warm clothes. Caring mothers, when the temperature drops outside or at home, put a bunch of clothes on their baby so that he does not freeze. Excessive heat can provoke the formation of this pathology.
- Synthetic clothing. Everyone knows that this type of fabric is not capable of letting air through and absorbing liquids.
- Frequent use of baby cream. Unfortunately, the cream contains substances that are not absorbed, so they clog the pores, as a result of which the outflow of sweat fluid is disrupted.
- Adaptation of both the external and internal environment of the baby’s body. Hormonal adjustment occurs, which also increases sweating.
- Diapers. This is perhaps the most popular cause of heat rash. After all, the diaper does not allow air to pass through at all, although manufacturers guarantee its permeability.
Allergies in newborns can be caused by certain foods and non-food factors. The causes of food allergies are:
- Genetic predisposition. If one of the parents suffers from allergic reactions, then the risk of the child developing this disease increases many times over. Doctors believe that the probability of getting an allergy is about 40% in a child who has only one allergic parent; in a child with two allergic parents, the risk of inheritance increases to 65%.
- Eating allergenic foods during pregnancy. During pregnancy, the expectant mother should not overuse chocolate, brightly colored fruits and vegetables, milk, nuts, chicken eggs, mushrooms and honey. These products affect the formation of an allergenic background in the baby.
- Negative reactions of the body can be caused by intestinal infections and acute respiratory viral infections suffered in infancy. Hypoxia during pregnancy can contribute to the development of allergies.
- This disease affects children who were unjustifiably switched from breast milk to formula. Feeding with cow's milk, frequent changes of formula and consumption of cheap baby food increase the risk of developing food allergies significantly, since in these cases the functioning of the child's gastrointestinal tract cannot improve.
Photos of the symptoms of the disease. May be unpleasant to watch
Infants have poor production of the enzyme that is responsible for digesting food, so new food is either digested with great difficulty or does not do so at all.
This becomes the reason for the rejection of these products in the future.
The culprit of allergies is often not food, but exposure to aggressive elements that the child inhales or touches.
- Excessive cleanliness. The disease can appear due to strong sterilization of the room. The child cannot interact with microorganisms that train his immune system.
- Dust mites and mold. Invisible to the eye, mites often hide on home textiles, open shelves, and hard-to-reach corners where dust accumulates. To combat them, regular wet cleaning is suitable. Mold can form in flower pots, so you need to change the soil in them often and do not overfill them with water.
- Pets. Allergies are usually caused not by animal fur, but by particles of skin or saliva. Sometimes the rash is caused by food. It is necessary to limit the baby’s interaction with the pet. Over time, the body adapts to the allergen, and the child will be able to be friends with the animal.
- Household chemicals. Breasts often suffer from rashes caused by washing powder, detergents and cosmetics. It is recommended to choose only hypoallergenic products.
A common cause of prickly heat is excessive overheating, accompanied by “interference” in normal sweating. Sweat glands begin to accumulate secretions if the child is tightly swaddled, dressed in too warm clothes, or smeared with poorly absorbed cream.
A baby's delicate skin can be susceptible to heat rash if not properly cared for during illness, when heavy sweating is caused by high fever.
To prevent the baby from suffering from heat rash, allergies and other skin problems, parents should take preventive measures. They include:
- maintaining a favorable temperature regime in the child’s room (from 20 to 22°C) and the required humidity;
- using comfortable, moderately warm clothes in which the baby will not sweat;
- daily bathing for children up to 6 months of age and bathing every other day for children up to 1 year of age;
- purchasing bed linen and diapers made from natural fabrics that do not provoke excessive sweating;
- control over the baby’s and mother’s menu, helping to avoid allergenic foods from entering the child’s body.
Treatment
The first thing you need is to correctly distinguish heat rash from allergies in an infant. The method of treatment will depend on this in the future. But no matter what your baby is sick with, the most important rule is hygiene and proper nutrition for you and your baby.
Prickly heat, unlike allergies, can go away on its own, but you still shouldn’t neglect some recommendations. So…
- Ventilate the room where the baby is located more often, and do not wrap the baby too much.
- Clothes should not be synthetic; use only natural fabrics so that the baby’s skin “breathes.”
- Also increase the number of times you bathe your baby, paying special attention to the folds of skin on his body. Most mothers do not neglect herbal decoctions: string, chamomile, celandine. Talc, baby powder, and adding potassium permanganate to the bath when bathing have proven themselves to be effective.
- Do not apply creams to the rash, and to prevent the occurrence of this disease, use only hypoallergenic products.
With allergies, things are much more complicated, because the manifestations of allergic dermatitis will disappear when there is no factor irritating the baby’s body. You can relieve symptoms with antiseptic and antibacterial ointments.
We hope that now you can easily distinguish heat rash from allergies in a baby and choose the right treatment.
Treatment options
The basis of treatment for miliaria is eliminating the cause of the rash and drying the skin. Doctors advise parents:
- Bathe your baby every day without soap, adding to the water decoctions of string, St. John's wort, chamomile, and yarrow. If the rash is profuse, then bathe the child up to 3 times a day.
- After washing, all skin folds and pimples should be treated with powder. Baby powder containing zinc, anesthesin or panthenol is suitable.
- It is necessary to give the baby air baths: for 25 minutes, remove all clothes and diaper from the child.
Pediatricians recommend purchasing medications that will quickly relieve your baby of rashes. Among them:
- Bepanten, which quickly restores damaged skin and eliminates inflammation.
- Sudocrem, which dries the skin, eliminates bacteria. The cream has a greasy consistency, so it is applied pointwise.
- Zinc ointment, which has proven itself as a drying agent.
- Salicylic or boric alcohol, chlophyllipt.
Allergy treatment
Allergies are not easy to cure. The necessary therapy is prescribed by a doctor; antihistamines are usually prescribed: Diprazine, Suprastin, Diazolin, Claritin, Fenistil and others. The mother of the child should refuse to eat foods that could cause the disease: fruits and vegetables of bright colors, seafood, eggs, mushrooms, nuts, sweets, coffee, marinades, spicy foods, semi-finished products, foods with dyes and preservatives.
Traditional medicine also helps to quickly cure dermatitis:
- For 1 liter of boiling water, take 5 bay leaves and a glass of rose hips. Strain and let it brew for two days. Give 4 times/day a tablespoon for two weeks. Store the broth in the refrigerator.
- Tear leaves and branches of black currant, pour 1 liter of boiling water, boil for 10 minutes. Leave for 1.5 hours, strain the broth and add to the bath.
- Mix string, chamomile and oak bark. Pour 3 tbsp. mixture 1 liter of cold water, leave for 12 hours, then boil and strain. The decoction is added during bathing.
There is also a difference in the treatment tactics of diseases. If you treat prickly heat with antihistamines, its symptoms do not disappear. And vice versa, if an allergic rash is smeared with creams, improvement will also not be observed.
For heat rash, medications can be prescribed in the form of ointments, solutions or creams: Panthenol, Bepanten, Drapolen, Zinc ointment. Regular baby powder may also come in handy.
The use of disinfectants is indicated. They dry the skin, relieve irritation and protect the skin from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria. You can treat the miliaria with Chlorophyllipt, salicylic or boric acid.
Allergies are treated with antihistamines (Suprastin, Cetrin, Zyrtec), hormonal (Dexamethasone) drugs for external or oral use. At the same time, sedatives and adsorbents are prescribed.
Miliaria - causes and features
Most often, prickly heat appears on poorly ventilated areas of the skin, which include skin folds:
Photo by Dr Orlena Kerek
- axillary,
- inguinal,
- intergluteal,
- folds on the neck,
- behind the ears,
- under the mammary glands,
- between your fingers.
The disease can also occur on the bends of the knees and elbows, and on areas of the skin that adhere tightly to synthetic fabrics.
There are several types of the disease:
It appears as white or pearlescent bubbles with a diameter of 1-2 mm. In cases where there are too many rashes, the bubbles begin to merge with each other and therefore it seems that the rashes are large.
During friction with the fabric and surface, the bubbles burst and the baby's skin begins to peel off. This type of miliaria in an infant often occurs on the upper half of the body, face and neck.
| View | Characteristic |
| Crystal prickly heat | |
| Miliaria rubra | It looks like uniform nodules or small bubbles in the center of a reddened spot. This type of rash causes itching and pain when touched. Discomfort increases if air humidity rises. |
| Miliaria profuse | This is the name for bubbles up to 3 mm in size, which match the color of the skin. This type of heat rash appears on the arms, legs and torso and goes away within a few hours. |
Crystalline miliaria usually occurs in infants. It does not require any special treatment, does not cause discomfort to the baby and goes away on its own in a couple of days.
Treatment of red and deep miliaria should begin only after the causes of its appearance have been eliminated.
Miliaria is sometimes confused with eczema. But unlike prickly heat, eczema is characterized by dry, red, crusty patches that tend to get larger. This disease occurs in 20% of babies aged 3-4 months.
Features of the manifestation of prickly heat
As a result of increased work of the sweat glands, liquid secretion begins to be produced. If something interferes with the evaporation of moisture from the surface, irritation and redness appear. In infants, spots or even blisters may be found on the body on the affected area.
What is the difference between allergies and heat rash? These two diseases develop due to different unfavorable factors. The most common causes of prickly heat are:
- being in a room where the air is dry and hot;
- prolonged exposure to direct sunlight;
- excess weight, in which the child’s skin folds are deep and sweat cannot evaporate;
- a common cause is clothing that is too warm;
- increased body temperature as a result of infection or teething;
- too frequent use of cosmetics (creams, talcs, lotions).
There are distinctive signs of prickly heat from allergies. Allergy symptoms depend on the type of allergy.
- The crystalline form appears as redness with white rashes. The diameter of one bubble is no more than 1.5 mm, but when drained it can increase in size. After some time, the bubbles open on their own, and a dry crust forms. No special treatment is required. The location is the neck, face, tummy and back.
- Miliaria rubra is recognized by its blisters, which are about 3 mm in diameter. There is redness and swelling around each bubble, and there is a cloudy liquid inside. The affected area is the groin area, elbows and knees. The child feels discomfort, the rash itches and itches. Scratching increases the risk of infection.
- Less common, but still found, is the papular form. Bubbles can reach a diameter of 4 mm. They can go out anywhere. Children become restless and capricious. The area hurts, itches, itches, and the body temperature may rise.
If treatment is not started in time, a secondary infection occurs. The baby's condition is deteriorating, he sleeps and eats poorly. Swelling and redness spread throughout the body. The bubbles contain gray liquid.
Although a rash appears in both cases, with prickly heat it occupies a more limited area on the body than with allergies.