Preparing for the study, how and when to take it correctly
Normal indicators of a general blood test in children may differ and depend on the time of day the test is taken and on how full the child is.
It is recommended to take blood in the morning on an empty stomach from a finger (or from a vein), but failure to comply with this recommendation is not critical.
Another thing is important - if during the period of one illness the baby donates blood more than once, then it is advisable to do it the same way - either hungry every time, or well-fed every time, at the same time.
It’s easier to negotiate with a well-fed child.
Blood is taken from a vein using a syringe, and from a finger - either with a scarifier or a lancet.
A scarifier is a specially shaped needle; it must be individually packaged.
A lancet is more complicated and more expensive; when used, pain is minimized, and the likelihood of bringing the baby to the laboratory the next time without hysterics increases many times over.
No matter how difficult it may be to distract yourself from the child and his worries immediately before this procedure, try to do it.
You must be sure that the laboratory technician who works with him uses rubber gloves, which he disinfects after each patient, or, even better, works in disposable gloves.
Should I give immunostimulants to children? Opinions for and against are presented in our review of popular drugs.
An overview of effective vitamins for improving immunity in children is presented in this article.
And here we’ll talk about what vitamins to give a child for growth.
Interpretation of blood test results for CRP
The norm of CRP is not the same in adults and children.
| Patient category | Norm |
| Newborns | 4 mg/l or less |
| Adults | 10 mg/l or less |
| Pregnant | 20 mg/l or less |
A high PSA in a blood test indicates:
- inflammation;
- infection;
- malignant tumor.
Chronic inflammatory conditions are not accompanied by an increase in CRP. If it increases, this indicates an exacerbation of the disease.
A low score has no clinical significance. Even if CRP is negative, this does not mean that the person has any disease. However, a low CRP in the presence of signs of infection or inflammation indirectly indicates liver pathology. The analysis is deciphered only by a doctor. It is impossible to make a diagnosis based on one indicator. All blood parameters and examination data are assessed.
Important figures: UAC data and their meaning
After receiving the material for analysis, certain indicators are examined . The list of these indicators for the UAC is given in a form, the form of which was approved back in 1980 by order of the USSR Ministry of Health.
The analysis demonstrates:
- leukocyte count;
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR);
- hemoglobin content;
- red blood cell count;
- leukocyte formula;
- other indicators.
The components of blood are its liquid part (plasma) and formed elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets).
Red blood cells (RBC) are the “transport” for transporting hemoglobin, the most numerous formed elements.
Hemoglobin (Hb) is a protein that primarily carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues and removes carbon dioxide from the body. The red color of hemoglobin and blood is given by a special component - heme, which contains iron.
Blood color index (BCI) - shows how much hemoglobin is contained in one red blood cell.
Hematocrit (Ht) is an indicator that demonstrates how the volume of plasma and the volume of formed elements relate to each other.
Reticulocytes (RTC) are young red blood cells. If they are present in excess, this indicates an increased need for the formation of new red blood cells due to blood loss or disease.
Platelets (PLT) are the main cells of the system responsible for blood clotting; very important in wound healing.
ESR (ESR) is the erythrocyte sedimentation rate , a litmus test for the course of the disease. The blood that is collected in a test tube soon becomes heterogeneous - due to gravity, colorless plasma remains on top, red blood cells settle.
Not only the gravity of the earth affects this mechanism - outside the body, in the absence of blood movement, red blood cells stick together, and the rate of their sedimentation increases.
When a child has inflammation, substances accumulate in the plasma that accelerate the process of red blood cell clumping.
White blood cells (WBC) are the name of a group of cells of different types (monocytes, lymphocytes, etc.) that make up the immune system. Their role is to protect people from strangers.
The leukocyte formula shows the percentage distribution of different types of leukocytes in the study material.
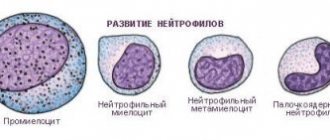
Neutrophils are the most abundant leukocytes. They are united by a common task - to find and destroy bacteria and viruses that can cause disease.
Immediately after its appearance, a neutrophil receives the name myelocyte (still a newborn); as it grows, it becomes a metamyelocyte (immune journeyman), then a band neutrophil (already a fighter), and then a segmented neutrophil (a seasoned warrior).
With an increase in the number of immature forms of neutrophils in the blood, the disease progresses more complexly, and the immune system fights with all its might.
Eosinophils (EOS) - adapted to repel attacks by immune complexes (rather than viruses and bacteria).
Basophils (BAS) are infrequently detected white blood cells. Modern science has not fully studied their purpose; it is only known that they are involved in coagulation processes and allergic reactions.
Lymphocytes (LYM) are active participants in immune reactions. They provide protection against foreign cells that have entered the body.
The number of lymphocytes increases in many childhood diseases , mainly viral ones. The elevated level of leukocytes lasts for up to 2 months.
Monocytes (MON) are large white blood cells that are responsible for clearing foreign particles from the blood. They live in the blood for only about 30 hours, then they move into the tissues and continue to absorb various nasty things already there.
Plasma cells - with their help, antibodies are formed. During viral infections that damage lymphoid tissue (chickenpox, measles, rubella, etc.), their number increases.
People often ask: what should a child take to prevent worms? Let's ask the doctor!
In this article we will look at which vitamins are the best for children over 7 years old.
Our publication and Dr. Komarovsky will tell children about vaccination against pneumococcal infection.
CRP for cancer
In oncology, CRP is a nonspecific indicator. It does not make it possible to determine where exactly the cancer is developing. It increases due to inflammation caused by the growth of a malignant tumor. To determine the location of cancer, you need to take specific tumor markers, do an ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
PSA is determined when diagnosing recurrent ovarian and skin cancer. In colon cancer, protein is a prognostic criterion. The higher the indicator, the lower the survival rate of patients.
Possible reasons for the increase or decrease
Deviation of blood flow levels in children from normal values may mean:
| Index | Some of the possible reasons for the increase | Some of the possible reasons for the decrease in the indicator |
| Hemoglobin | Congenital heart disease, pulmonary fibrosis | Monotonous diet (iron deficiency), dysbiosis, acute bleeding, hepatitis |
| Red blood cells | Second-hand smoke, fever, poor drinking water quality, enzyme deficiencies, dehydration, poor nutrition and starvation | Anemia, iron deficiency, blood loss, vitamin B12 deficiency, overhydration (accumulation of significant amounts of fluid in tissues) |
| Color index | Anemia | Failure to absorb iron into the bone marrow, leading to impaired heme synthesis |
| Hematocrit | Dehydration, hormonal disorders | Anemia and bleeding, kidney failure, excess fluid in the body |
| Reticulocytes | Destruction of red blood cells, bleeding | Anemia, decreased thyroid function, kidney disease, chronic infectious diseases |
| Leukocytes | Great emotional stress, physiological stress, inflammatory processes | Use of certain medications, kidney failure, deficiency of certain B vitamins, infectious diseases (influenza, viral hepatitis, malaria, measles, brucellosis, typhoid fever) |
| Lymphocytes | Increased physical activity, colds and viral infections, vitamin B12 deficiency | Insufficient protein nutrition, tuberculosis, anemia |
| Monocytes | Inflammatory and infectious processes (both chronic and acute), autoimmune diseases, conditions after an infection | Anemia, taking medications (for example, glucocorticoids, cytostatics), shock conditions |
| Eosinophils | Skin diseases (dermatitis, eczema), allergic conditions, parasites, acute periods of certain infectious diseases (infectious mononucleosis, chicken pox, scarlet fever, tuberculosis) | The initial period of the inflammatory process, infectious diseases, helminth infections, allergic reactions and anaphylactic shock, acute appendicitis, severe purulent infections (sepsis, peritonitis, pneumonia, diphtheria) |
| Basophils | Ulcerative colitis, allergic conditions, some infectious diseases (tuberculosis, influenza, chicken pox) | Acute infections, hyperthyroidism, stress |
| Platelets | Inflammation, as well as many viruses and infections, severe bleeding | Autoimmune diseases, use of blood thinners, leukemia, vitamin B12 deficiency |
Note to parents: whether your child should be vaccinated against chickenpox can be found in this article.
The possible consequences of BCG vaccination in newborns are discussed in our material.
You can learn about the side effects of ADSM vaccination for children from this publication.
Factors that increase protein levels
The amount of protein is influenced by cholesterol and lipid levels. In healthy people, the average blood CRP concentration is 0.8 mg/l. In people with cardiovascular diseases, the concentration increases, although it remains within normal limits. Based on the level of CRP, one can assume the risk of developing atherosclerosis, angina, and heart attack. The higher the score, the higher the risk of heart disease.
CRP increases when consuming fatty foods and taking hormonal contraceptives. Its amount is reduced by drugs from the NSAID group, steroids, and statins.
Positive CRP is observed in the following conditions:
- insomnia;
- apnea;
- smoking;
- addiction;
- lack of vitamins A and D;
- chronic stress;
- accommodation in mountainous areas;
- obesity;
- menopause
At the same time, the indicator remains within the normal range, but reaches the upper limit.
CRP is increased in conditions accompanied by tissue damage - burns, trauma, surgery.