Essence of the question
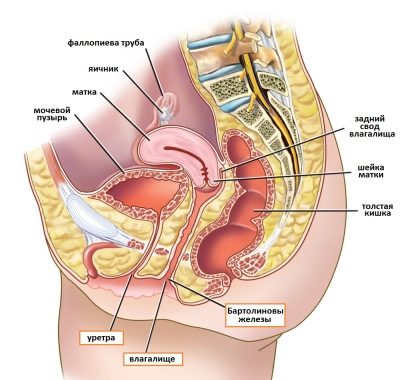
The cervix is the lower part of the organ. It is a tunnel connecting the uterine cavity with the vagina. Inside it is the cervical canal. During the examination, the doctor visually and by touch assesses the condition of the vaginal part of the cervix.
This part has the shape of a protruding hemisphere, the diameter of which is about 2.5 cm. It is surrounded by the walls of the upper vaginal area. The hemisphere is covered with a smooth and shiny mucous membrane, uniformly colored light pink.
The external opening (pharynx) of the neck is located in the center of the hemisphere. It looks like a round depression. In nulliparous women, the pharynx is small and round, after childbirth it looks like a slit. Inside it, the mucous membrane has a loose consistency. Outwardly, it resembles bright pink velvet.
The cervical canal is tightly closed and clogged with mucus. The substance secreted by the cervix serves as a biological filter that prevents the penetration of bacterial flora from the vagina into the overlying parts of the reproductive system.
Sperm can only overcome it during ovulation, when the mucus thins. During this period, the area of the uterus rises slightly and softens.
The external opening of the cervical canal becomes slightly wider during menstruation. This allows the rejected tissues of the inner surface of the uterus to freely come out along with the blood.
The length of the lower part of the uterus is approximately 3-4 cm. In a non-pregnant woman, the cervix is firm to the touch. Its dense structure has the same elasticity as the wings of the nose.
Color after conception
Immediately after fertilization, the body begins to create all the necessary conditions for bearing a child. In the early stages of pregnancy, the uterus rapidly increases in size. The growth of her body occurs due to the intensive growth of the mucous membrane (endometrium) and muscle layer (myometrium).
Along with the growth of layers, the area of the network of blood vessels penetrating the body of the organ increases. The vessels fill with blood and dilate. Blood circulation in the uterus is significantly enhanced. The body prepares to supply nutrients and oxygen to the growing fetus.
An increase in uterine blood flow causes a change in the color of the cervix. From light pink it turns into bluish-purple. Increased blood circulation causes swelling and darkening of the mucous membrane of a woman’s external genitalia. Swelling of the labia, vaginal walls and the surface of the vaginal part of the cervix may also be observed.
enlargement of the uterus during early pregnancy
This amazing organ is formed and functions only during pregnancy; immediately after the birth of the baby, the child’s place leaves the mother’s body. From Latin “placenta” is translated as “cake”. This name is given to the placenta for its appearance, because in appearance it resembles a large round cake or disk, to the center of which the umbilical cord is attached.
The placenta, or baby's place, begins to form almost from the moment the egg attaches to the wall of the uterus, or, as doctors say, from the moment the egg is implanted into the uterine cavity. First, from the 9th day after conception until the 13-16th week of pregnancy, the precursor of the placenta, the villous chorion, develops. The trophoblast cells that surround the embryo rapidly divide, and a branched sheath of villi forms around the embryo. Vessels of the embryo grow into each similar villi.
At 16 weeks, the chorion turns into the placenta, which has 2 surfaces: one facing the baby and called fetal, the other, called maternal, towards the inner wall of the uterus. The umbilical cord of the future baby is attached to the fetal side, and the baby’s blood flows inside its villi. On the outside, these villi are washed with the mother's blood. The maternal side of the placenta is divided into 15-20 lobules, separated from each other by partitions.
Thus, there are 2 systems of blood vessels in the placenta - the baby's and the mother's. And it is here that a constant exchange of substances occurs between the mother and her unborn child. At the same time, the blood of the mother and child does not mix anywhere, since the two vascular systems are separated by the placental barrier - a special membrane that allows some substances to pass through and prevents the penetration of others. The placental barrier begins to function fully by 15-16 weeks.
The structure of the placenta is finally formed by the end of the first trimester, but its structure continues to change depending on the development of the baby and the growth of his needs. Moreover, at first the placenta grows faster than the baby. For example, at 12 weeks of pregnancy, the future baby weighs 4 g, and the placenta weighs up to 30 g. By the end of pregnancy, the baby's place becomes more compact, dense and takes the shape of a disk. From 22 to 36 weeks of pregnancy, the weight of the placenta constantly increases, and closer to the time of birth, the diameter of the placenta will be about 15-18 cm, thickness - 2-3 cm, and it will weigh 500-600 g, that is, 1/6 of the baby’s weight. After 36-37 weeks, the growth of the placenta stops, its thickness decreases slightly or remains at the same level.
WHAT IS THE PLACENTA NEEDED FOR?
As we have already said, in the placenta there is a constant exchange of substances between the expectant mother and her child. Oxygen and nutrients come from the woman’s blood, and the baby “returns” metabolic products and carbon dioxide, which must be removed from the body.
The placenta also protects the baby from adverse effects: the placental barrier retains bacteria contained in the mother’s blood, some viruses, and the mother’s antibodies produced during Rh conflict, but freely allows oxygen, nutrients and protective proteins from the mother to the baby. But the protective function of the placenta is selective. The same substances overcome the barrier in different ways towards the baby and towards the mother. For example, fluoride passes perfectly from mother to baby, but does not penetrate at all in the opposite direction. Bromine penetrates to the baby much faster than back.
In addition, the baby's place plays the role of an endocrine gland, producing hormones that support pregnancy, prepare the breasts for lactation, and the mother's body for successful childbirth.
WHAT DOES THE DOCTOR PAY ATTENTION TO?
When performing an ultrasound at different stages of pregnancy, the doctor carefully monitors the condition of the placenta. Important for him:
1. Location and attachment of the placenta, as well as its accretion
In a normal pregnancy, the placenta is most often located in the mucous membrane of the anterior or posterior wall of the uterus. In the early stages of pregnancy, the baby's place often reaches the exit from the uterus. And then the woman hears the term “low placental attachment.”
But it is premature to worry: we must take into account that in most women, as the size of the uterus increases, the placenta rises upward. There is even a term “placental migration”. The movement occurs due to the fact that the lower segment of the uterus changes its structure during pregnancy, and the placenta grows towards the bottom of the uterus (its upper segment), because this part of the uterus is better supplied with blood. “Migration” of the placenta occurs over 6-10 weeks and ends by 33-34 weeks of pregnancy. For this reason, the diagnosis of “low placement (attachment) of the placenta” should not be scary. This position remains in only 5% of women until the 32nd week, and in only a third of these 5% the placenta remains in the same position by the 37th week. In the latter case, doctors decide on the tactics of labor management and the method of delivery. After all, a low position of the baby's seat is fraught with placental abruption before the baby is born, which is dangerous for both mother and baby. With such a complication, the woman is hospitalized. If the abruption is minor, the symptoms are mild, in order to slow it down or stop it, the amniotic sac is opened during childbirth. If internal bleeding begins and its symptoms (increased heart rate, decreased blood pressure, severe pain in the uterus) increase, resort to cesarean section.
If the placenta reaches the internal os of the uterus (the exit from the uterus) or blocks it, they say placenta previa. Most often, this occurs in women who have repeatedly become pregnant and have given birth. Contribute to placenta previa and uterine development abnormalities. But placenta previa determined by ultrasound in the early stages may not be confirmed in later stages. However, doctors are wary of this situation, as it can cause bleeding and premature birth. For this reason, in order not to miss such a complication, the expectant mother will undergo an ultrasound scan at intervals of 3-4 weeks throughout the entire pregnancy, as well as before childbirth. The tactics for managing pregnancy and childbirth with placenta previa are the same as with placenta previa.
The chorionic villi (the precursor of the placenta) “grow” into the mucous membrane of the uterus—the endometrium—during the formation of the baby’s place. In very rare cases, it happens that villi grow into the muscle layer or into the thickness of the uterine wall. In this case, they talk about placenta accreta, which is fraught with bleeding after the birth of the child. If this happens, you have to undergo surgery to remove the placenta along with the uterus.
If the chorionic villi have not grown so deeply, they speak of a tight attachment of the placenta. It usually occurs with a low-lying placenta or placenta previa. Alas, it is possible to recognize placenta accreta or dense attachment only during childbirth. In the latter case, the doctor delivering the baby will separate the placenta manually.
2. Degree of maturity of the placenta
The placenta grows and develops along with the baby. Using an ultrasound, the doctor determines the degree of maturity - the structure at a certain stage of pregnancy. This is necessary to understand whether the child has enough nutrients and how the placenta copes with its tasks.
There are 4 degrees of placental maturity: zero, first, second and third. When pregnancy proceeds normally and without complications, until the 30th week the placenta is at zero degree of maturity. During this period, its membrane is smooth and its structure is homogeneous. At 27-34 weeks, the placenta reaches the first degree of maturity. The membrane becomes slightly wavy, the structure becomes heterogeneous. At 34-37 weeks of pregnancy they already speak of the second degree of maturity. In some places, this organ becomes thinner and begins to become covered with lime (salt) deposits, but this does not prevent the placenta from coping with its functions. From the 37th week of pregnancy until the moment of birth, the placenta should remain in the third degree of maturity. During this period, the placenta divides into lobules, and noticeable depressions appear in the membrane.
If the degree of maturity changes ahead of time, this may indicate premature maturation (aging) of the placenta. It may occur due to disruption of blood flow in the placenta. The cause of the latter is, for example, serious pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia and anemia. At the same time, such a process may also be an individual feature of the mother’s body. So don't get upset ahead of time. Typically, in such a situation, the woman undergoes Doppler testing and monitors the uteroplacental blood flow and the development of the child. If the baby is not suffering, then everything is fine. The woman will be recommended only preventive treatment. When alarming symptoms appear, the expectant mother is sent to the hospital. There, doctors reduce the tone of the uterus, which makes it easier for the baby to receive nutrients. In addition, doctors are trying to improve blood circulation in the expectant mother and her baby.
Rapid aging of the placenta can also be the result of infectious diseases suffered during pregnancy (for example, intrauterine infection) or bad habits, for example, smoking. Also, a similar situation arises if a woman has chronic diseases, such as diabetes, or pregnancy is complicated by Rh conflict.
In very rare cases, we may be talking about late maturation of the placenta. Sometimes this may indirectly indicate congenital malformations of the fetus.
3. Thickness of the placenta and its dimensions
Thickness can be determined after 20 weeks of pregnancy. If the pregnancy proceeds normally, this parameter increases all the time until the 36th week. At week 7 it will be 10-11 mm, at week 36 - a maximum of 35 mm. After this, the growth of the placenta stops and its thickness not only does not change, but may even decrease. The latter will be the first symptom of aging. At the 40th week, the aging placenta is an indication for stimulation of labor that has not yet occurred.
The placenta is said to be thin if the thickness is less than 20 mm in the third trimester. A similar situation is typical for preeclampsia (increased blood pressure, swelling and protein in the urine). In this case, there is a threat of miscarriage and fetal malnutrition (growth retardation). When a hemolytic disease of the fetus occurs during an Rh conflict (the body of a Rh-negative mother produces antibodies to the Rh-positive red blood cells of the child, and the latter are destroyed), a thick placenta (thickness 50 mm or more) indicates a violation. Similar symptoms occur with diabetes mellitus. Both situations require treatment.
The size of the placenta may also not reach the norm or exceed it. In the first case, with normal thickness, the area of the placenta is less than normal. This may be due to genetic disorders (such as Down syndrome), preeclampsia and other complications. Due to the fact that the small placenta cannot fully supply the baby with oxygen and nutrients and remove metabolic products from the body, the child is stunted in height and weight. This complication is called placental insufficiency. Hyperplasia (increase in size) of the placenta has the same consequences. Timely treatment allows you to correct the baby’s development.
POST PERIOD OF CHILDREN
Once the baby is born and the midwife cuts the umbilical cord, the placenta finishes its job. Within 30 minutes it comes out along with the membranes. In this case, they say that the afterbirth is born. The doctor first of all carefully examines the placenta, measures and weighs it. All data is recorded in the birth history. Thanks to this, doctors receive valuable information about how the pregnancy went and how the baby is feeling. If the indicators differ from the norm, the pediatrician is informed about this.
The main thing is that the placenta and fetal membranes must completely leave the woman’s body. If, after a thorough examination of the placenta, doctors have doubts about this, a manual examination of the uterine cavity is performed. After all, particles of the placenta remaining in the uterus can cause bleeding or inflammation. This examination and removal of remaining particles are carried out under anesthesia.
After this, doctors are no longer interested in the placenta. It is either destroyed or used for scientific or medicinal purposes.
Change location
After conception, the cervix lowers slightly and deviates towards the back wall. This position of the lower part of the organ helps reduce the likelihood of spontaneous abortion.
Based on the height of the cervix, the doctor determines whether the pregnancy is progressing normally. Its high location is an alarming signal. It may indicate increased tone of the organ. A relaxed state is favorable for bearing a child. Tension of muscle fibers can cause fetal rejection. If the position is high, the doctor recommends that the pregnant woman go to the hospital.
However, in some cases, the high position of the lower uterus is an individual feature of the body. It is possible to reliably determine whether there is a threat of early termination of pregnancy using an ultrasound examination.
In early pregnancy, the cervix moves easily. Its mobility is caused by softening of the tissues of the isthmus.
Immediately after conception, intensive production of mucus in the cervical canal occurs. It has a thick consistency and tightly clogs the entrance to the organ. This helps protect the developing fetus from pathogenic microorganisms.
Active treatment of a weakened neck - cerclage
{module direct4}
Whether a child is born premature as a result of premature birth or due to a weakened cervix, the result is the same - neonatal intervention is necessary for the child to cope with this. Premature birth is already a warning, but a weakened cervix is a surprise if the child is the first. (In subsequent pregnancies, doctors will already know this.) Of course, if there is a history of cryotherapy or laser treatment for the cervix, this will cause your doctor to check it at the initial examination and at the beginning of the second trimester. If it is too short, surgery will be required, and the second trimester is considered the best time for surgery. The procedure, called cerclage, is actually simply placing a loop of tape around the perimeter of the cervix to keep it closed. At the appropriate time it is removed so that birth can occur. This is done vaginally and usually works well. If the neck is so weakened that the cerclage extends into it, thereby negating the benefit of this operation, then prolonged bed rest for months, possibly even in hospital, may be required. In such cases, there is another way out. Conventional cerclage is done through the vagina, but when there is nothing left of the cervix to work with, an abdominal surgical approach is possible, in which a thread tightens the part of the cervix that expands from the inside at the side of the wall that is the back of the vagina (inside the pelvis). This so-called internal cerclage involves an incision in the abdomen and is better done before conception than after, because any surgery during pregnancy, especially abdominal surgery, risks bleeding due to the additional growth of blood vessels that accompanies pregnancy. As for internal cerclage, even before pregnancy it can be assumed that the patient will not benefit from cerclage done vaginally in the second trimester, so the first one should be done in advance. Internal cerclage creates other problems. Because it is applied through surgery through the abdomen, it blocks the vaginal birth path. This means that because the cerclage is internal, your doctor will not be able to cut it later through the vagina, and so the birth must be by Caesarean section. And since the cerclage needs to be left for subsequent pregnancies, then we are, accordingly, talking about subsequent cesarean sections too. In fact, not many obstetricians perform internal cerclage, and although it is a simple operation, doctors are uncomfortable when they have to learn how to do it on their own patients. Even in my practice, I have done less than 5 of them in 20 years. It's a really simple operation, but it's still an operation. Unlike permanent internal cerclage, vaginal cerclage is done while you are already pregnant and removed before the end of each pregnancy—simply an outpatient procedure that allows for a vaginal birth soon after in the hospital. It is structurally more dangerous, as statistics show. An internal cerclage is more reliable, but it requires surgery, a caesarean section for each additional child, and excellent ability to predict when a magic crystal may be necessary. Although there is something barbaric about preventing premature birth by “tying the bag,” cerclage is a life-saving remedy and an intuitive solution to the problem of a weakened cervix.
Lower organ
Under the influence of hormones at the beginning of pregnancy, the tissues of the uterus become loose and soft like lips. However, the vaginal part of the organ has a denser consistency than its other areas. During pregnancy, the cervix becomes more dense than during ovulation. It plays the role of a “shutter” that protects the organ cavity and the fertilized egg from external pathogens.
The external cervical os closes tightly, blocking access to the uterine cavity. It becomes smaller, the lumen of the cervical canal narrows. The fossa of the external pharynx is practically not palpable. Even the tip of your finger should not be immersed in it.
Cervical elongation is observed until the 25th week of pregnancy. During this period, the length of the cervical canal may increase by 5-7 mm. It must be large enough to withstand the pressure of an expanding fetus. After 25 weeks, the length of the cervical canal begins to decrease. The shortening of the cervix is caused by pressure exerted by the growing baby.
Normally, the external os of the cervical canal remains tightly closed and sealed until birth. Sometimes the neck becomes so dense that it is called “oak”. The dense structure of the lower part of the organ does not affect pregnancy in any way, but during childbirth there may be problems with expulsion of the fetus.
Determining pregnancy by touch
To determine the presence of pregnancy by touch, a woman needs to lie on her back and spread her legs bent at the knees to the side. The doctor inserts the fingers of his right hand into the vagina. At the same time, his thumb remains pointed upward. The palm is pressed tightly against the perineum.
The doctor determines the degree of loosening of the tissues of the vagina and the vaginal part of the cervix. He evaluates the length, shape, consistency of the cervical canal and external pharynx. By touch you can determine whether the throat is open or closed, whether it is round or slit-like. The height of the cervix and its location are also determined.
A lump that is too soft and wet, or a lump that is too hard and dry, will not indicate pregnancy. After conception, it will become soft but elastic.
To confirm the presence of pregnancy, a two-manual examination is performed. The fingers of the right hand remain in the anterior fornix of the vagina, and the fingers of the left hand are placed on the abdomen just below the navel. They gently press on the abdominal wall in the direction of the right hand. A two-handed examination allows you to assess the condition of the walls of the uterus, the shape and consistency of its lower segment.
The organ in which the developing embryo is embedded has a soft consistency. The softening in the area of the uterine isthmus is more pronounced. This sign (Horwitz-Geghar symptom) is a reliable way to determine pregnancy at 6-8 weeks from the start of the last menstruation.
Two-handed examination also makes it possible to establish high mobility of the uterus (Gubarev and Gaus sign).
It is not recommended to independently determine the condition of the genital organs by touch. Incorrect mechanical action can injure a pregnant woman. Its mucous membranes are very sensitive and vulnerable. They are easy to damage. In this case, the tissues quickly become infected, which poses a great threat to the developing embryo. Self-examination can cause organ contraction and fetal rejection.
The first signs of pregnancy are the cervix
11. 08. 2013 —
Every pregnant woman will have many visits to the antenatal clinic during her nine-month period. However, the most often remembered is the first visit, during which, based on the results of a gynecological examination, the doctor determines the fact of pregnancy and calculates the period after conception. At the same time, the first signs of pregnancy are revealed - the cervix and its general condition.
It is known that after conception, the cervix undergoes certain changes, the presence of which is used by an experienced gynecologist to determine pregnancy. Let's look at what transformations are characteristic of the cervix during this period.
What is the cervix?
The cervix is the lower part of the uterus, in the form of a tube connecting the vagina and the uterine cavity itself. The length of this tube is approximately 4 cm, and the diameter is 2.5 cm. During examination, the gynecologist can see only the vaginal part of the cervix, which is located “neighborhood” to the vagina.
The cervix as the first sign of pregnancy - what changes?
| Color changes | If the cervix in the “ordinary” state is pink, then after conception the organ acquires a bluish tint. The reason for this “metamorphosis” is increased blood circulation and intensive “proliferation” of the vessels of the cervix. |
| Surface softening | The “non-pregnant” cervix feels firmer to the touch (for comparison, let’s take the hardness of the nose). After conception occurs, this organ can be compared to the softness of lips. |
| The situation is changing | During the process of ovulation, the cervix is raised up and its canal is open. Immediately after conception occurs, under the influence of the hormone progesterone, the cervix lowers. |
| Changing shape | Based on the shape of this organ, the doctor will “read” all the information about the woman’s past. In nulliparous women, the cervix is wide and flat and has a cylindrical shape. The cone shape is typical for women who have had childbirth experience. Vaccination against cervical cancer - sterilization of women... |
Taking into account all these changes, it is possible to determine the presence of pregnancy within a few weeks. The first examination examines the shape, size, consistency and location of the cervix. Then, based on the results obtained, a conclusion is made about the gestational age.
We take tests
If pregnancy is confirmed and the first signs of pregnancy are detected, the cervix should be “subjected” to periodic examination in order to avoid various pathologies and diseases.
During the examination, the gynecologist will definitely take the following tests:
- Flora smear. This analysis will identify the following types of infections (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, candidiasis, fungus)
- Cytology analysis. It is necessary to study the structure of cervical cells in order to identify cases of oncology in the initial stage.
As a rule, such examinations are not isolated and throughout the entire pregnancy the doctor can prescribe similar tests 4 times. The timing of these procedures is “distributed” throughout the entire pregnancy. This allows you to minimize the risk of possible pathological cases, as well as take appropriate measures in a timely manner.
Thus, it should be remembered that the first sign of pregnancy is that the cervix changes its color, consistency and location. Therefore, it is better to contact an experienced doctor who can “organize” monitoring of the condition of the cervix throughout the entire period. After all, the cervix performs an important function not only during conception, but also throughout pregnancy. It acts as a “guide” during the ovulation process, protects the uterus from infections and “gives a way” to the baby during childbirth. Therefore, the health of this organ is very important for the expectant mother.
Rate the article: Average rating: 4.4 out of 5 (Ratings: 29)
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency
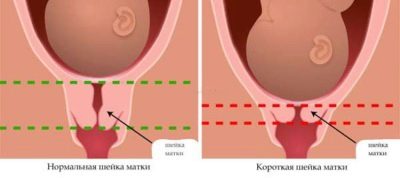
Examination of the cervix can detect pathological conditions. An alarming sign is a shortened section. The length of the cervical canal 3 cm is dangerous. In this case, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination to determine the degree of threat to the pregnant woman.
If the length of the cervical canal is 2 cm, a diagnosis of isthmic-cervical insufficiency is made. A cervix that is too short and soft cannot support the weight of a developing baby. As it grows, the external pharynx will expand and infection will penetrate into it. Pathogenic microorganisms can cause disruption of the integrity of the amniotic sac and rupture of amniotic fluid. If the opening of the external pharynx occurs rapidly, the fertilized egg may fall out.
Signs of cervical opening during pregnancy
Disclosure does not always occur at the right time. In some cases it occurs much earlier. This is ICI or isthmic-cervical insufficiency. The pathology is dangerous because it causes miscarriage or premature birth. Therefore, the woman needs treatment.
ICI is diagnosed during examination - gynecological examination, ultrasound.
Symptoms of an open cervix during pregnancy are as follows:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- bloody issues;
- length discrepancy relative to normal indicators;
- the amniotic sac is visible upon examination;
- feeling of spasms in the vagina.
In some cases there are no characteristic signs. Therefore, the woman does not feel that the cervix is open.
Polyp of the cervical canal
During an examination of a pregnant woman, polyps of the external pharynx may be detected. They often protrude beyond the cervical canal. Therefore, they can be seen by a doctor during a gynecological examination. A polyp is a growth formed as a result of pathological proliferation of mucosal tissue. The defect can cause isthmic-cervical insufficiency and premature opening of the external pharynx. Polyp tissues often become infected. The presence of a focus of inflammation in the genital organs of a pregnant woman poses a threat to the development of pregnancy and the health of the fetus.
In cases where the polyp quickly increases in size or causes bleeding, it is removed. The operation to excise the growth is performed at 12-14 weeks.
If the polyp does not threaten pregnancy, it is not touched. In some cases, the growth disappears on its own after childbirth.
Cervicitis in pregnant women
During examination of the cervix in early pregnancy, acute or chronic inflammation of its mucous membrane (endocervicitis) may be detected. If the mucous membrane of the cervical canal is simultaneously affected, cervicitis is diagnosed.
The inflammatory reaction is caused by pathogenic microorganisms that have settled on the mucous membrane of the cervix. The presence of inflammation is indicated by severe redness and swelling. There may be an ulcer and serous-purulent discharge on the surface. Smears from the vagina and cervical canal help identify the causative agent of the disease.
Cervicitis causes uterine tone, loose membranes, spontaneous abortion, premature birth, purulent-septic complications, as well as the development of oxygen starvation of the fetus and its intrauterine infection.
When diagnosing cervicitis, a pregnant woman is prescribed therapy directed against the causative agent of the disease (antibacterial or antifungal).
- The role of cervicitis in obstetric and gynecological pathology, Candidate of Medical Sciences Yu.I Tirskaya, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, E.B. Rudakova, I.A. Shakina, O.Yu Tsygankova, Omsk State Medical Academy, Omsk, BUZOO “KMHC-MZOO”, Omsk, magazine “Attending Doctor”, No. 10, 2009.
- Isthmic - cervical insufficiency with various risk factors, L.I. Kokh, I.V. Satysheva, journal “Siberian Medical Review”, No. 2, 2008.
Healthy intrauterine development of a baby is impossible if the expectant mother has any pathologies of the female genital organs. During pregnancy, doctors regularly evaluate the condition of the cervix. It is especially important to carry out such diagnostics at the earliest stages of pregnancy.
What reasons
Dilation of the cervix prematurely, that is, in the early stages of gestation, often leads to miscarriage. An open throat cannot hold the fetus inside.
There are 2 types of isthmic-cervical insufficiency:
- Organic.
- Functional.
The first occurs as a consequence of injury as a result of:
- miscarriages, history of abortions;
- treatment of erosion, polyps;
- diagnostic curettage.
Due to such manipulations, the cervical tissue loses its elasticity and scars appear on it. The organ loses its ability to contract, as a result the fetus cannot stay in the uterus.
Causes of functional ICN:
- pathology of the uterus;
- polyhydramnios;
- hormonal imbalance.
Women with diagnosed deficiency are at increased risk.
On the video about changing the length
Physiology
The cervix is a kind of entrance to the uterus. This organ is a continuation of the cervical canal. Normal cervical dimensions are very important. Deviations from the norm can lead to various pathologies occurring in a woman and her baby.
The location of the uterus and cervical canal is determined during an extended gynecological examination , which is performed on the expectant mother in a chair.
The size of the cervix in most healthy women ranges from 3 to 4.5 cm. A change in this indicator is a very important clinical sign of the development of many pathologies.
Unstable hormonal levels cause the size of the cervix to change. This is especially clear in the second half of pregnancy.
If, when carrying a baby, a woman’s cervix is shortened in size, this is a manifestation of a pathology that requires correction.
State before ovulation
The cervix is adjacent to the vagina in its lower part. In non-pregnant women, this area is hard. Already in the first weeks of pregnancy, it becomes loose and softens. The position of the vaginal part of the uterus before menstruation may change slightly. This condition is usually detected by a gynecologist during a gynecological examination.
During different periods of a woman's menstrual cycle, the cervix is different. In the period before ovulation, its hardness is maximum. The cervical canal is narrowed as much as possible. This condition is physiological.
Severe narrowing of the cervical canal is necessary at this stage of the female cycle in order to prevent conception.
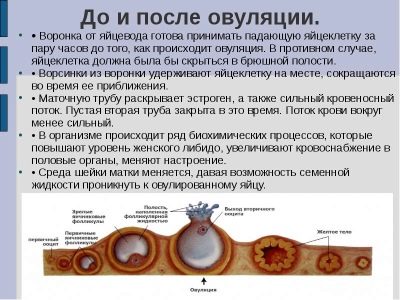
During ovulation
During this period of the female cycle, the condition of the cervix changes. It becomes more loose and soft. If a gynecologist conducts an examination during such a period, he will also detect closure of the internal os of the uterus. Doctors call this emerging condition a symptom or sign of the pupil.
The cervix also rises slightly during this period. If the location of the reproductive organ is non-physiological, then this situation can lead to the woman experiencing adverse symptoms. Usually in this case, a nagging pain appears, and white discharge from the genital tract begins to appear.
During this period of the female cycle, the secretion of cervical mucus increases. It is necessary for successful conception to occur. It is thanks to this secretion that sperm can penetrate the uterus and the egg.
If the fusion of the sex cells of a man and a woman does not occur, then the next stage of the menstrual cycle begins.
After ovulation
During this period of the female cycle, the position of the cervix changes. This organ begins to shift downward. During a gynecological examination, the doctor determines that the cervix becomes dry and somewhat dense to the touch. The diameter of the cervical canal is insignificant.
This period is characterized by the fact that the cervix is not ready for sperm penetration . Changing hormonal levels contribute to the appearance of such changes. Female sex hormones affect epithelial cells, which leads to the development of their specific changes.
In early pregnancy
During a gynecological examination, the doctor evaluates several clinical indicators. It determines the location, tone, color, shape and density of the cervix.
In the first weeks of pregnancy, the color of the mucous membranes of this organ changes. This zone changes its color from pale pink to dark burgundy. The density of the cervix before a missed period is also different. All clinical indicators change as pregnancy progresses.
During a gynecological examination, doctors already in the first days of pregnancy detect congestion of blood vessels. The tone of the uterus also changes during this period.

If it is too pronounced, then this situation is already a manifestation of pathology - hypertonicity. In this case, more careful monitoring of the expectant mother is required throughout pregnancy.
Characteristic changes in the cervix begin to occur already in the first half of pregnancy. Even in the earliest periods from the moment of conception, the density of the organ changes. The cervix becomes softer.
The lumen of this organ also changes. At first, the cervix is slightly open. As pregnancy progresses, the diameter of the cervical canal gradually decreases.
This physiological reaction is necessary to ensure that a woman does not experience premature birth.

The location of the uterus in the pelvis is a very important clinical sign. It may be tilted too far forward or to the side. In this case, the course of pregnancy may be pathological. In such a situation, a woman requires more careful monitoring throughout the entire period of bearing her baby.
In the early weeks of pregnancy, the cervical mucosa appears smooth. This is due to the large amount of cervical mucus produced by the epithelial cells of the cervical canal. Such a biological secretion is necessary in order to protect the pelvic organs and the developing baby from infection.
As pregnancy progresses, the mucous membranes of the cervix become looser. Typically, this situation develops by the third trimester of pregnancy. If the cervix becomes too soft or loose, the expectant mother may even need to be hospitalized in a hospital.
Uterus in early pregnancy
The uterus undergoes a large number of modifications in the early stages of pregnancy . First, changes occur in the innermost layer of the uterus - the endometrium - thickening and hyperplasia are observed, and they are not visible to the naked eye, and as pregnancy progresses, these changes affect all layers of the uterus, which becomes visible externally.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the uterus swells and softens, especially in the isthmus area, and as a result it acquires some mobility. The uterine mucosa takes on a cyanotic (bluish) color, which is explained by intense blood flow and an increase in the number of blood vessels.
Enlargement of the uterus in the early stages can be observed from the fifth to sixth week of pregnancy in the anterior-posterior direction, and then in the transverse direction. At the same time, a modification of the shape of the uterus from pear-shaped to spherical is observed.
- At the end of the fourth week of pregnancy, the size of the uterus is comparable to the size of a chicken egg.
- At the end of the twelfth week of pregnancy, the size of the uterus can be compared to the size of a goose egg.
- At the end of the sixteenth week of pregnancy, the volume of the uterus is comparable to the volume of the average man’s fist.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the uterus is located in the pelvic area and external signs of pregnancy are not yet noticeable; the abdominal circumference may increase slightly, especially in first-time mothers.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the body of the uterus softens, and its cervix remains dense, which makes it possible to bring the fingers of both hands closer to each other during a two-handed vaginal examination - this is a sign of Horwitz-Hegar pregnancy. Also, when conducting a gynecological examination in early pregnancy:
- The uterus contracts slightly and becomes denser, and after the examination stops it becomes soft again - this is an early sign of Snegirev’s pregnancy;
- A dome-shaped protrusion is noted in one of the corners of the uterus, which is caused by the implantation of the fertilized egg; as a result, the uterus looks asymmetrical - this is also an early sign of Piskacek’s pregnancy.
- Characterized by slight mobility of the cervix, due to softening of the isthmus of the uterus - this is an early sign of pregnancy by Gubarev and Gauss.
- There is a slight bend of the uterus anteriorly due to softening of its isthmus; in addition, it is possible to detect, but not always, a comb-like thickening along the anterior surface of the uterus along its midline - this is Genter’s sign.
Clinically, in the early stages of pregnancy, a woman may feel minor nagging pain, discomfort in the lower abdomen and/or lower back, which can be observed normally and is associated with:
- implantation of the fertilized egg into the endometrium,
- changes in the hormonal sphere of a pregnant woman,
- changes in the osseous-ligamentous apparatus, due to the preparation of the body for the upcoming labor - secretion in the pregnant body of the hormone relaxin, under the influence of which the connective tissues become extensible and become loose, as a result - the pelvic bones become mobile;
- an intense increase in the body weight of a pregnant woman, which creates an increased load on the spinal column, especially if there is a pathology in it - osteochondrosis, scoliosis.
If pain of this nature is not intense, does not increase and is not accompanied by pronounced bloody or other discharge, then there is no need to worry.
But if there is an increase in the intensity of pain, the occurrence of heavy bloody or brown discharge, or a feeling that the uterus is “stony” or heavy, it is necessary to urgently seek help from an obstetrician-gynecologist, as this may indicate increased tone (hypertonicity) of the uterus and a threat miscarriage.
Uterine hypertonicity may result from:
- hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body,
- inflammatory changes in the pelvic organs,
- abnormalities of the uterus,
How to determine the condition of the cervix in the early stages?
To identify cervical pathologies, a gynecological examination is not always necessary. Usually the doctor conducts such studies only when indicated. More often, to monitor developing disorders, doctors resort to prescribing transvaginal ultrasound.
If a woman has a long cervix and no shortening, frequent gynecological examinations are not required. It should be noted that the appearance of cervical pathologies occurs in the very early stages of pregnancy.
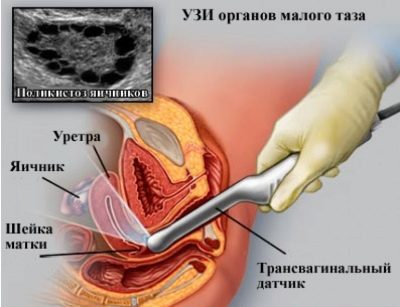
It is no coincidence that several clinical examinations are performed during pregnancy. Until the 20th week, the cervix should be the same as before in the first days after conceiving the baby. No significant changes in this organ are observed. This is due to a gradual change in hormonal levels.
In this case, both pharynx of the cervix remain completely closed. The dimensions of this organ range from 4 to 4.5 cm. If in a woman this figure decreases to 2 cm, then in this case doctors talk about shortening.
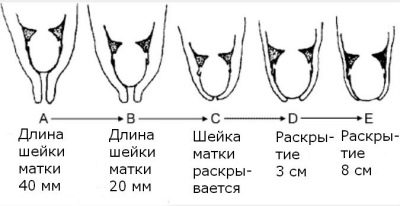
Normally, the length of the uterus should be within normal limits. Only after 20 weeks does a slight physiological shortening of this organ begin to occur. This condition develops almost before the 28th week of pregnancy.
Subsequently, the size of the cervix continues to decrease. This situation is necessary for natural childbirth.

Cervix in early pregnancy
The cervix (cervix) is a transitional, lower segment of this organ, connecting it to the vagina. The normal length of the cervical canal is about 4 centimeters. A gynecological examination involves examining the vaginal portion of the cervix, assessing its density, shade, and position.
The cervical canal itself is clogged with mucus, which is produced by the cells lining the cervix. The properties of the mucous secretion change somewhat throughout the cycle - during the ovulatory period it thins out and becomes permeable to sperm.
Characteristic features of the cervix at different stages of the menstrual cycle
Features of the structure of the cervix during the menstrual cycle
Just before menstrual bleeding, the cervix is hard to the touch. During the ovulatory period, the cervix becomes loose, the pharynx opens somewhat to ensure that sperm enter the uterus. During menstruation, the pharynx is dilated, which is necessary for the release of blood clots from the uterine cavity.
This feature can provoke the entry of pathogens into the organ; for this reason, during menstrual bleeding, you should not swim in the pool or open water, or have an active sex life. During menstruation, it is necessary to follow the rules of hygiene, wash twice a day. After menstruation, the cervix narrows and its structure becomes denser.
Functions of the cervix during pregnancy
The first weeks of pregnancy are the beginning of serious changes in a woman’s body.
The cervix plays an important role in the process of bearing a child from the earliest stages of pregnancy.
At this time, the cervix undergoes significant changes: its density, size, shade, shape and position become different.
In addition, the glands in the mucous lining of the cervical canal expand and branch even more.
The role of the cervix in the process of bearing a child is to ensure retention of the fetus in the uterus and prevent the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the uterine cavity.
If an infectious-inflammatory process nevertheless begins, the structure of the cervix changes significantly, the cervix acquires pathological uneven looseness. Such changes are a signal to the doctor about the need to prescribe additional diagnostic procedures and a course of therapeutic correction acceptable to the pregnant woman.
How to use indomethacin suppositories during pregnancy
Diagnostic role of cervical changes during pregnancy
Dynamics of changes in the cervix in primiparous and multiparous women
Changes in the cervix during gestation are so pronounced that it becomes possible to determine pregnancy by the cervix. The most significant signs include:
- Color change. The cyanosis of the cervix is completely physiological and is explained by increased blood supply. In healthy, non-pregnant women, the cervix is pink.
- Change in position relative to the uterus. The cervix descends during pregnancy.
- Change in consistency. The cervix becomes less dense to the touch as pregnancy progresses.
Interesting fact! The way the cervix looks depends on whether the woman has had childbirth before or not. In nulliparous women, the cervix is cylindrical in shape, while in those who have already given birth, the shape is cone-shaped.
Changing the position of the cervix
During pregnancy, regular medical consultations are required.
The cervix in the early stages of pregnancy is located lower than usual. The cervix descends after conception to retain the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. This process is ensured by the action of progesterone. If the cervix is located high, then this may confirm the high tone of the uterus and be a threat to pregnancy.
However, the high location of the neck can also be an anatomical feature of the body. The risk to pregnancy must be assessed by a doctor: perhaps a change in the position of the cervix will cause the woman to be hospitalized in order to maintain the pregnancy.
Changes in the consistency of the cervix
A looser cervix during pregnancy is due to the growth of the vascular network, swelling and an increase in the number of glands that produce mucous secretion. Also, the cervix becomes looser due to the effects of progesterone.
Note! In the early stages, the cervical structure retains its density. The Horwitz-Geghar sign of pregnancy indicates the preservation of the elasticity of the cervix, which makes it possible to approach the fingers during a two-handed gynecological examination.
During early pregnancy, the cervix narrows, the elasticity of the tissues remains, and they are difficult to stretch. The density changes with increasing age, but there is no need to fear that if the cervix is loose to the touch, it will not be able to hold the fetus.
Papaverine hydrochloride suppositories during pregnancy: benefit or harm
During pregnancy, a more active production of mucous secretion by glandular cells occurs. The mucus itself becomes thicker, its viscosity is higher than in the absence of pregnancy. The cervical canal is closed during pregnancy by a mucous plug, which performs the following functions:
- preventing pathogens from entering the uterine cavity;
- maintaining optimal vaginal microflora;
- ensuring the normal functioning of the organs of the reproductive system.
Insufficient mucus production can cause the progression of infectious diseases.
Pathologies of cervix consistency
If the cervix is hard during pregnancy, this may indicate excessive tension in the organ (hypertonicity). This condition is quite dangerous, so when it is detected, the doctor must prescribe therapeutic correction measures, in some situations deciding whether the pregnant woman needs to be hospitalized in a hospital.
It is impossible to determine on your own, at home, that something is wrong with the cervix. You should regularly visit a specialist who is managing your pregnancy. Only a doctor can determine the pathological or normal condition of the cervix in the early stages of pregnancy.
Excessive looseness of the cervix at the beginning of pregnancy is also an alarming sign. This, combined with a short cervical length and loose closure of the cervical canal, may indicate a risk of spontaneous miscarriage.
The discovery of large loose areas in the cervical canal most often indicates the presence of an infectious-inflammatory process, the causative agents of which can be the following microorganisms:
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasma;
- gonococci;
- adenoviruses;
- cytomegalovirus.
If your stomach hurts early, you should immediately consult a doctor!
Usually the pathological process is accompanied by nagging pain, vaginal discharge, and upon examination, ulcerations are revealed on the mucous lining. Such symptoms indicate the need for additional diagnostic methods to identify the pathogen and determine the optimal measures to eliminate it.
Physiological role of cervix softening
During the process of bearing a child, the cervix remains dense for up to 32 weeks, its external os is closed. After this period, an uneven softening of the structure of the cervix occurs; it gradually “ripens” for opening during delivery. The cervix softens in the peripheral areas, the cervical canal itself remains closed, which is confirmed by ultrasound examination data.
When is Ginipral prescribed for pregnant women?
By the 36th week of pregnancy, the external pharynx allows the tip of the gynecologist’s finger to pass through during an examination in first-time mothers, and in women who become mothers again, the pharynx may be somewhat weaker, which is why it can allow the doctor’s entire finger to pass deeper.
From the 37th week, the cervix is already in a mature stage - it becomes soft, shortens, and during a medical examination the pharynx allows one or two fingers of the gynecologist to pass through. One of the reasons for such changes is that the fruit puts more pressure on the neck, which accelerates the process of its ripening.
Immediately before delivery, the cervix softens to such an extent that it is “smoothed” during labor to ensure the passage of the baby through the birth canal.
Conclusion
Do not hesitate to ask questions to the doctor - this will help dispel any doubts
If all of the above changes are detected, the gynecologist can confirm the fact of pregnancy before the delay or a little later, at a very short time, but, of course, not in the first days. The doctor should examine the color, size, density and position of the cervix. Analysis of the examination results allows you to both determine pregnancy by the cervix and draw a conclusion about its duration.
Monitoring the parameters of the cervical canal should be carried out throughout the process of bearing a child. The specialist knows what the cervix should look like at different stages, this allows timely detection of pathological changes and taking corrective measures if necessary.
Regular monitoring and compliance with all recommendations will allow you to carry the pregnancy to term with minimal risk of pathologies for mother and child.
You need to be aware of what the cervix is like in the early stages of pregnancy, which of its changes are physiological, and which are confirmation of some pathology. The doctor should talk about all this during regular consultations with the pregnant woman.
Compliance with all medical recommendations, contacting a specialist for any alarming symptoms - all these are necessary conditions for ensuring the normal course of pregnancy and timely detection of any abnormalities.
Source: https://shejka-matki.ru/shejka-matki-pri-beremennosti/shejka-matki-na-oshhup.html
How do pathologies manifest themselves?
Doctors identify several risk groups, which include women with certain pathologies. In order to assess this risk, anamnesis is very important. If a woman had abortions, especially complicated ones, before conceiving a baby, then in this case more careful monitoring of her pregnancy is required.
The use of obstetric forceps and other auxiliary medical instruments during previous pregnancy contributes to the fact that the cervix may be damaged.
Hormonal imbalance only contributes to the fact that a woman’s progesterone level significantly decreases. In this situation, doctors, as a rule, prescribe special hormonal drugs to pregnant women.
Expectant mothers carrying twins or triplets also have a higher risk of developing various cervical pathologies. Such pathological conditions appear during multiple pregnancy already in its earliest stages.
Low placenta previa very often leads to the development of various pathologies of the cervix. Typically, this pathology develops towards the end of the first trimester of pregnancy.
The lack of full medical control over the development of this condition can contribute to the development of extremely dangerous pathologies for both the expectant mother and her baby.
Women in whom doctors have identified cervical erosion before or in the early stages of pregnancy are at increased risk for the development of various pathologies. In this case, careful monitoring and selection of monitoring tactics for the expectant mother is necessary.
If by the end of the first trimester a woman’s doctors suspect isthmic-cervical insufficiency, she is referred for additional examination. For this purpose, she undergoes an ultrasound examination. In some cases, this may lead to the doctor referring the woman to hospitalization.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency can be suspected already in the very early stages of pregnancy. In this case, the cervix opens too early. Usually it opens significantly by 8-12 weeks of pregnancy. This pathology is fraught with the possibility of spontaneous miscarriage.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency can also lead to infection of the fetus and internal female genital organs. hormonal therapy is usually prescribed More invasive procedures are used somewhat later.
If the pathological condition is severe, then sutures may be required. This procedure is already carried out in a hospital setting. In this case, sutures are placed on the cervix. They are removed closer to childbirth.
It is important to note that isthmic-cervical insufficiency is not an absolute contraindication for natural childbirth. If the stitches are placed on time and the treatment tactics are chosen correctly, then a woman can give birth to a baby on her own without a cesarean section.
Even cervical pathologies that occur early in pregnancy and are detected in a timely manner can be controlled and effectively prevented.
For information on the norms for cervical length during pregnancy, see the following video.
Many girls are interested in what signs gynecologists use to determine pregnancy during an examination, and how this can be done at home. To have an idea of the processes occurring in the female body after fertilization, it is necessary to know the features of the location and functioning of the reproductive system.
Bishop's degree of cervical maturity
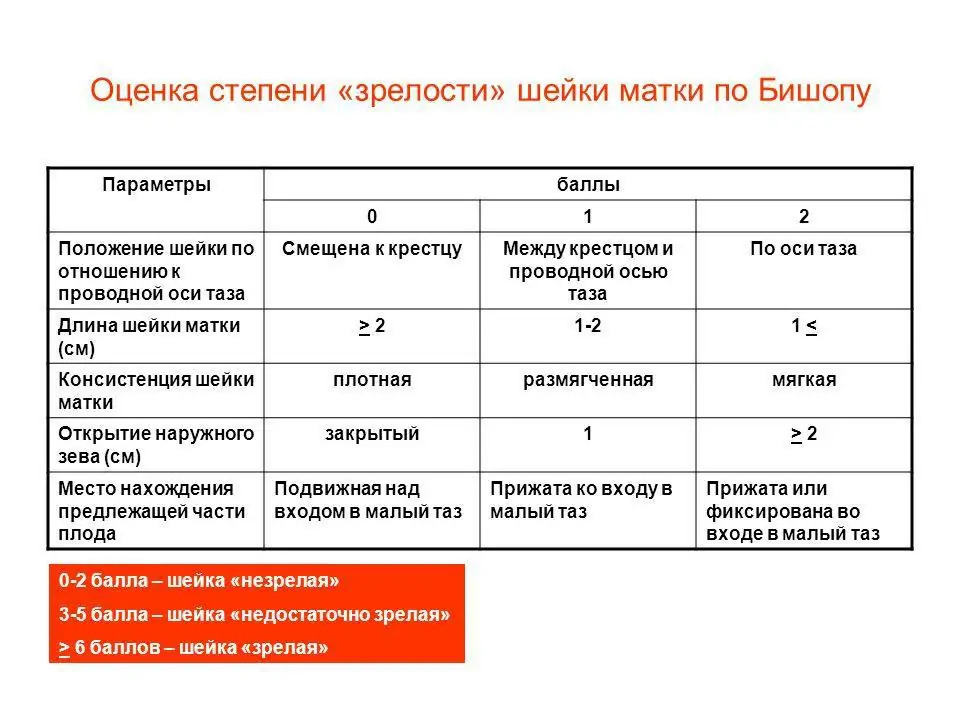
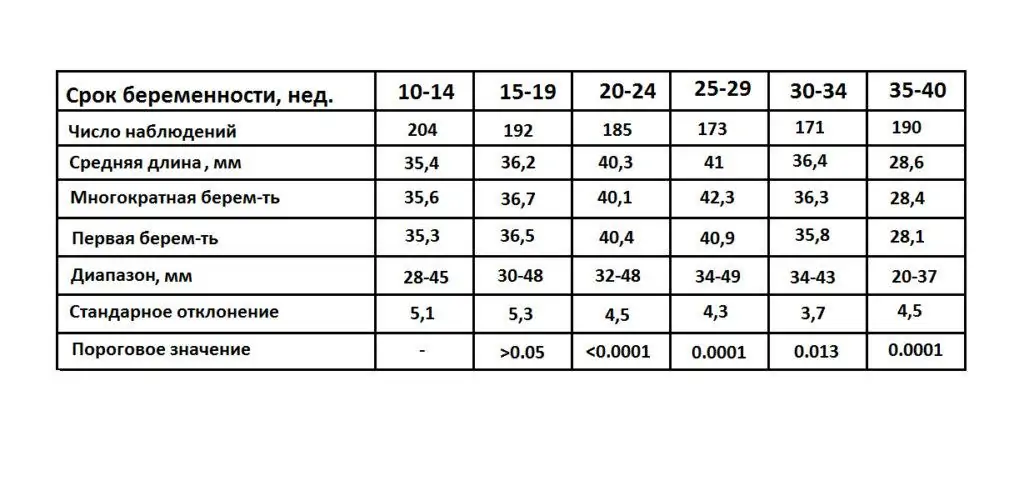
Table “Cervical length during pregnancy by week”
The organ matures rapidly during the last two prenatal weeks. Its length is reduced to one centimeter, and the cervical canal, closed by a mucous plug throughout the entire gestation period to protect the fetus from various infections, opens and forms an exit from the uterus to the vagina. This is how the body should prepare for the birth process; all deviations have their own reasons and require mandatory correction.
Position of the cervix before pregnancy
The cervix (cervix) is the lower segment of the organ connecting the uterine cavity to the vagina, which is divided into two main parts:
- The vaginal zone has a convex shape, protruding into the vagina. It is covered with a smooth mucous membrane.
- The supravaginal zone includes 2/3 of the organ and is connected by the isthmus to the body of the uterus.
The cervix is a muscular tube about 4 cm long. Inside it is the cervical canal, which has an internal and external os. The first is part of the muscular ring, directed towards the uterine cavity. The second is located between the vagina and the internal os.
During a gynecological examination, the external pharynx looks like a round depression. In nulliparous women, it is narrow (no more than 2.5 cm in diameter). This section of the tube is lined with bright pink squamous epithelium, which has a loose surface.
Inside the cervical canal there is a large amount of mucus containing bactericidal substances. It serves as a kind of biological filter that prevents infections from the external environment from entering the uterine cavity.
During the period of ovulation, the mucus becomes more liquid, and the area of the uterus rises slightly so that sperm can easily penetrate to the mature egg. Liquefaction of the contents of the cervical canal is also observed during menstruation. When the upper layer of the endometrium peels off and is excreted from the body along with the blood, a slight expansion of the external pharynx occurs. At the beginning of a new menstrual cycle, the cervix closes completely.
Changes in the cervix in early pregnancy
Pregnancy shows signs of the presence of a fertilized egg from the very beginning. The changes concern primarily the reproductive organs. Therefore, it is natural that in the early stages of pregnancy the cervix is made different than before. So the changes happening to her are one of the many symptoms of the event awaiting the woman.
Cervix: where is it?
Not all women will be able to explain, if necessary, what this segment of the reproductive system is, where it is located and what its significance is. This is logical; it is impossible to monitor the health or problems of the cervix on your own. Its examination and assessment is the responsibility of the examining gynecologist.
The cervix is the part of this organ visible during visual examination, which is transitional to the vagina and connects them to each other. It produces mucus at all stages of the menstrual cycle.
The role of the cervix during pregnancy cannot be underestimated; it largely ensures that the fertilized egg is kept in its proper place. During examination, only its vaginal part can be detected, but this is often enough to assess the state of gynecological health.
Upon examination, it looks like a round, protruding formation, covered with a mucous membrane and having a small hole in the middle.
The usual size of the organ is 4 cm in length and 2.5 in circumference, the consistency is hard, the pharynx is closed, it becomes slightly wider on critical days for the release of secretions.
Changes in the cervix in early pregnancy are quite noticeable to a specialist, which makes it possible to detect this condition. It is considered one of the important signs, along with the cessation of menstruation.
Signs of changes in the area of the uterus after conception
The uterus itself begins to change noticeably from about 4 weeks of pregnancy, when the grown fertilized egg causes protrusion of its wall, an increase in the size of the organ and asymmetry. A specialist can also detect this.
What kind of cervix is in the early stages of pregnancy depends on the length of time from its beginning. But the increase in progesterone, which is observed immediately after fertilization of the egg, leads to the fact that the organ changes purely visually. This is easy to notice during a gynecological examination.
An experienced doctor can accurately determine the period from the moment of conception.
During early pregnancy, the cervix acquires the following differences from its previous state:
- The color of her mucous membrane becomes bluish, and before fertilization it was pink. Do not be afraid of these changes; they are caused by the proliferation of blood vessels and the activation of metabolic processes. This is necessary to improve blood supply in this area, since the formation of the membranes of the fetus and its nutrition require a large amount of oxygen;
- Its position changes relative to the main part of the organ;
- When palpated during examination, the tissues become different in consistency.
How the location of the vaginal part of the cervix changes
When the embryo appears, the reproductive organs adapt to it in such a way as to ensure normal development, comfort and protect it from possible dangers. This dictates the new position of the cervix in the early stages of pregnancy.
It is not constant even before it, changing at different stages of the cycle. But in general, this part of the organ is located quite high relative to the vagina.
This is especially noticeable during ovulation, when the body strives to facilitate the penetration of sperm into the female reproductive cell as much as possible.
The position of the cervix in early pregnancy becomes lower than usual. It lowers under the influence of progesterone, preventing the fertilized egg from slipping out. The course of the process depends on the level at which the cervix is located in the early stages of pregnancy, high or low.
If the cervix is high, this may mean increased tone of the organ itself, which creates a risk of interruption. Because of this circumstance, some women have to spend almost the entire period in a horizontal position. But the doctor will also take into account and evaluate other existing signs. Perhaps the high position of the cervix is a feature of a particular organism that does not threaten the fetus in any way.
Cervix consistency
The cervix feels quite soft to the touch during early pregnancy compared to its previous state. This is due to the dilation of its blood vessels, swelling and more active functioning of the glands.
The indispensable companion of pregnancy, progesterone, also plays its role, making the uterus itself and the endometrium lining it also looser and thicker. But in comparison with the consistency of the walls of the organ, the cervix is denser.
It is like a castle protecting the approaches to the fetus. That does not prevent her from being more mobile than before conception.
Many people are afraid that if the cervix feels soft to the touch during early pregnancy, it will not hold the fertilized egg.
The fears are unfounded, since its channel narrows significantly, but the tissues normally still remain elastic and difficult to stretch for a certain time.
The glands begin to more actively produce mucus, which becomes thicker and more viscous. A large clot of secretions called a plug forms in the cervical canal. It performs several functions at once:
- does not allow foreign bacteria to enter the uterine cavity;
- helps maintain the balance of microorganisms in the vagina;
- creates comfortable conditions for the functioning of the reproductive organs.
If the cervix in the early stages of pregnancy feels too hard to the touch, this may indicate excessive tension in the organ itself, called hypertonicity. This condition threatens the rejection of the fertilized egg. It is unrealistic to independently assess the consistency of the cervix without being a specialist.
Therefore, you should not “wind up” yourself if it seems too soft or hard during self-examination. Regular visits to the gynecologist are a guarantee that the pathology will be detected before it is too late to correct it.
What is a short neck
Not many women experience pregnancy without any problems. And one of the most serious is the threat of interruption, which is caused by various reasons.
Fetal development and weight gain increase pressure on the cervix. In extreme cases, it shrinks in size and can no longer serve as full protection for the fetus.
This condition of the cervix in the early stages of pregnancy is most often caused by hormonal reasons, but it can occur with injuries to the organ in the past, multiple pregnancy and polyhydramnios.
This phenomenon is referred to as isthmic-cervical insufficiency and requires constant medical supervision and subsequent treatment. Symptoms of shortening of the cervix during pregnancy, detected by a specialist:
- The consistency of its tissues is too soft;
- Excessive mobility of this part of the organ;
- Expanded lumen of the cervical canal.
In some women, these signs are mild, but in any case, she herself will not notice the problem, especially in the first weeks. It is important that the doctor has the opportunity to see the anomaly, both visually and using ultrasound. This requires timely registration and a lot of examinations.
Why is shortening the cervix dangerous?
In early pregnancy, shortening the cervix is dangerous because it increases the likelihood of miscarriage.
Instead of a dense ring that protects the embryo from falling out of the cavity, isthmic-cervical insufficiency leads to the appearance of an element that provokes bleeding next to it.
This part of the organ is unable to contain the increasing pressure, which leads to uterine tone. It becomes hard, tense, and its muscles can begin to actively clench and unclench at any moment, trying to reject the fertilized egg.
At an early stage, this is dangerous because the symptoms of cervical contraction during pregnancy are not always noticeable to the woman herself. Shortening of an organ area is also detected using transvaginal ultrasound, which is prescribed at different times. Some women experience:
- The appearance of watery discharge. They are present in this state and are normal, but usually thick and not in such large quantities;
- Mixing drops of blood into clear mucus;
- Frequent need to urinate;
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, unpleasant sensations in the form of tingling in the vagina.
Sometimes the short length of this part of the organ is congenital, in more common cases it is acquired. But in order not to provoke shortening of the cervix and not create a threat to the baby, a woman needs to take care of this even before pregnancy, that is:
- avoid abortion;
- do not smoke, as a bad habit provokes hormonal disorders;
- do not be nervous and do not overwork during pregnancy itself.
How to examine the cervix at the beginning of pregnancy
In addition to a gynecological examination using speculum and two-handed examination, the doctor will refer the woman to undergo a microflora analysis. It is necessary to make sure that there are no sexually transmitted infections or fungi in the body that can harm the fetus. We are talking about the microflora of the vagina, but it directly affects the condition of the cervix.
Another cytology study examines the structure of the cells in this part of the organ. The cervix during pregnancy in the early stages is not at all immune from their degeneration into malignant ones. Two more problems that are sometimes discovered at the beginning:
- Endocervicitis. Infectious inflammation of the cervix can lead to the penetration of bacteria into the organ cavity, infection of the fetus, weakening of muscles and, as a result, miscarriage. Therefore, treatment must be carried out immediately. The disease manifests itself in the fact that in the early stages of pregnancy, the infected cervix produces purulent discharge instead of mucous;
- Erosion. Its formation can be caused by pregnancy or provoked by other reasons. But in any case, treatment is carried out after childbirth, and before it the condition of the epithelium is monitored. Erosion looks like redness or an ulcer on the surface of the mucosa.
In the early stages of pregnancy, a changed cervix is not only one of the symptoms of an “interesting position”.
In addition to its protective functions for the fetus, it informs about possible problems that, if adequate measures are not taken, can lead to the worst.
Therefore, women should not be afraid and avoid gynecological examination and intravaginal ultrasound, especially if there is a history of abortion, miscarriage, or premature birth.
Source: https://7mam.ru/izmenenie-shejki-matki-na-rannix-srokax-beremennosti/
What happens to the cervix after fertilization?
If conception occurs during ovulation, serious changes begin to occur in the woman’s genitals. Experienced specialists determine the presence of pregnancy by a change in the position of the cervix, which can be felt with a finger. A characteristic sign of fertilization is a change in the shape of the external pharynx and the color of the epithelium.
In the first days after conception
After conception has occurred, the production of the hormone progesterone in a woman’s body increases significantly. This promotes the dilation of blood vessels in the genital organs, resulting in softening of the endometrial tissue. In the first days of pregnancy until the missed period, the cervix retains firmness and elasticity for successful implantation of the fertilized egg. Subsequently, the cervix becomes softer.
The development of the embryo in the uterine cavity activates the glands that produce cervical mucus. The secreted secretion becomes very thick and accumulates in the supravaginal area. The resulting clot is called a “plug” in gynecology and performs several functions in the expectant mother’s body:
- protects the reproductive organ from infection from the outside;
- helps create optimal conditions for the formation of the fertilized egg;
- maintains the balance of vaginal microflora.
If the consistency of the cervix remains hard to the touch for a long period after fertilization of the egg, this indicates hypertonicity of the reproductive organ. This pathological condition is observed with a lack of progesterone.