Ovarian function during pregnancy
Before pregnancy occurs, the ovaries perform two functions - reproductive and hormonal.
The first is to ensure the monthly maturation of the eggs located in the follicles and their subsequent release. This period is called ovulation and is considered a favorable time for conception. The hormonal function is to produce sex hormones that support the monthly cycle. During gestation, the ovaries suspend reproductive function, but continue to produce sex hormones.

The corpus luteum formed after the release of the egg produces progesterone, which promotes reliable attachment of the fetus to the uterine epithelium and its further development. Its production by the ovaries continues in an intensive mode for up to 12 weeks. At this stage, the placenta forms, begins the production of hormones, and the corpus luteum gradually dies.
The reproductive function of the ovaries returns after childbirth, the frequency of the menstrual cycle is normalized after breastfeeding is stopped.
The volume of the ovaries during pregnancy increases slightly, which is associated with increased local blood circulation. Their position changes - they are forced out by the gradually growing uterus and are located outside the pelvis. This is why the ovaries can hurt - this is one of the causes of discomfort in women carrying a baby.
Ectopic pregnancy
In an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants and develops outside the uterine cavity.
In the vast majority of cases (98%), the fertilized egg attaches to the walls of the fallopian tube. During the growth of the embryo, some pregnant women may experience minor pain in the ovary area. However, many women are not bothered by pain. Further development of pregnancy can lead to tubal abortion or rupture of the fallopian tube.
In a tubal abortion, the fertilized egg is peeled off from the walls of the fallopian tube and expelled into the abdominal cavity. At this moment, pregnant women experience severe cramping pain in the ovary area. They can radiate to the leg, rectum or thigh. The pain may stop for a while, then return with renewed vigor. Tubal abortion is accompanied by bleeding, dizziness and fainting.
Also read: Symptoms of chronic fissure
Rupture of the fallopian tube occurs due to the destruction of the thin walls of the passage by the villi of the fertilized egg. Symptoms of a breakup appear unexpectedly and severely. Severe pain occurs in the ovarian area and bleeding appears. The woman feels weak and dizzy. She might faint.
Tubal abortion or rupture of the fallopian tube occurs at 5–6 weeks of pregnancy. This condition requires immediate medical attention. It poses a danger to a woman's life.
Why do the ovaries hurt during pregnancy?
During gestation, the presence of unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen is noted. The cause of their appearance is determined by the location of the pain, its intensity and frequency of occurrence. Usually they are not considered a deviation and mark the correct course of pregnancy.
Non-dangerous pain
They occur in both the right and left organs. Most often, the ovaries hurt during pregnancy in the early stages.
Physiological causes of pain:
- Attachment of the fertilized egg. At the moment of conception, the pain is similar to the pain from the implantation of the embryo into the uterine cavity. These sensations are easily confused due to the close proximity of the organs. They appear periodically in the form of nagging or mild tingling pain in the area of the ovaries or uterus, marking the beginning of pregnancy.
- Growth of the uterus. Causes stretching of the ligaments holding the organ. Pain occurs on the sides and is similar to discomfort in the ovaries. Increased sensations occur with a sudden change of position, physical activity, or uncomfortable posture.
- Hormonal changes. They contribute to the occurrence of nagging pain in the lower abdomen, often caused by dysfunction of the intestines. The intense production of estrogen and progesterone increases the peristalsis of the latter, causing bloating and other unpleasant sensations in the pelvis.
- Physical exercise. The growing uterus changes the position of the organs, which is accompanied by the appearance of discomfort in the lower abdomen after physical exertion or sudden movements.
- First pregnancy. Before the age of 25, conception provokes discomfort in the genitals. With repeated gestation, the muscles become more elastic and discomfort is less present.
- Corpus luteum cyst. A common pathology, the pain is localized in the right ovary during pregnancy, less often in the left. This formation goes away on its own and does not require treatment.
- First month of pregnancy. The first weeks after conception, the production of the hormone relaxin contributes to the occurrence of pain in the lower abdomen, accompanied by toxicosis - nausea, weakness, drowsiness.
- Stimulation of ovulation and IVF. When artificial insemination or taking drugs to induce ovulation in the early stages of pregnancy, the ovary, which is susceptible to medical intervention, pricks.
Do the ovaries hurt in the early stages of pregnancy (before the delay)?
| About everything that worries us in this important and joyful period. Moderator: Girls, I apologize if this topic has already been raised, but I have already looked through many pages - and no. Yes, and the Internet is barely crawling. And then there is such fear... My husband and I wanted a baby, and then finally, in my opinion, it happened. I'm 5 days pregnant and my pregnancy symptoms are very similar. There is only one BUT: with more sudden movements, my right ovary will start to stab (I think so in it). Not that intolerable, but very unpleasant. Very rarely there is a slight tingling in the left one, but compared to the right one it’s like flowers... Dear girls, tell me what it could be??? I am very worried |
- cysts of various origins.
The ovaries during pregnancy simply do not bother you.
Pain in the ovaries can be isolated or be a chronic problem, so during pregnancy it is important that the expectant mother independently listens to the signals of her body.
If you begin to feel suspicious symptoms in critical areas, you should immediately consult a doctor
Causes of discomfort in the ovaries
If a woman is pregnant for the first time, then the origin of the pain will be quite difficult to determine, that is, to understand whether the ovaries actually hurt during pregnancy or whether their cause is located elsewhere, but in the same area. During the first pregnancy, with complaints of nagging pain in the right or left ovary, it often happens that these sensations are symptoms of other diseases, such as:
- stones in the kidneys;
- infections and inflammation in the gallbladder area;
- constipation;
- bladder inflammation or urinary tract infection;
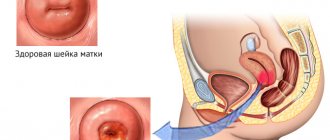
- ovarian cyst;
- bacterial infections in the intestines;
- dysbiosis.
The listed painful sensations are very easy to confuse with pathologies of other reproductive organs, which are located in the abdominal and pelvic areas.
Is pain after ovulation dangerous or not?
If your stomach hurts after ovulation and the cutting, cramping or stabbing sensation persists, this is considered a common occurrence and can last from 2 hours to 2 days.
The appearance of discomfort after ovulation may mean the onset of pregnancy with some complications that can cause miscarriage, interrupted pregnancy, increased uterine tone or health problems. These pains require close monitoring by a doctor.
The ovaries during pregnancy must be protected from all sorts of negative influences. After 8-12 weeks of gestation, women may often experience aching pain in the lower abdomen.
If after ovulation the ovary hurts and premenstrual cramps occur, this only means that the woman’s body, by inertia, is preparing for the arrival of menstruation. As long as there are no symptoms of bleeding, unusual discharge or cramping, there is no cause for great concern. After ovulation, the uterus expands, so pain is the body’s reaction to the processes occurring.
Why do pain appear on the right and left sides of the abdomen?
When the second trimester begins, many women begin to feel that their left ovary, then the right, hurts. The pain comes from the upper side of the uterus and is clearly felt in the groin.
Women tend to feel pain after walking or driving for very long periods of time, or after standing up abruptly from a chair. On this occasion, doctors reassure patients and ask them to just be careful.
Why does pain occur? During long walks or bicycle walks, as well as when abruptly jumping up from a chair, the uterus leans forward and strains the ligaments. The same phenomenon occurs when a woman lies on her side. If a woman lies on her right side for a long time during pregnancy, she may assume that her left ovary hurts.
If he sleeps on his left side, he may think that his right ovary hurts. Pain of this origin most often disappears after 24 weeks of pregnancy. If the left ovary constantly hurts during pregnancy, this may indicate the possible formation of a benign tumor - a cyst. However, with such a diagnosis there is no need to be scared.
This formation is most often a cavity that is filled with liquid. During pregnancy, the tumor often disappears and does not cause the woman any problems. It is worth sounding the alarm only when the cyst leg becomes twisted, dies and can cause peritonitis.
Why does pain occur at the end of pregnancy?
Towards the end of gestation, the woman’s body begins to intensively produce the hormone relaxin, which helps the woman’s body prepare for childbirth and makes the ligaments more elastic. Very often, relaxin can weaken the joints of the pelvis and even lead to inflammation. Against the background of these changes, many women begin to assume that their ovaries hurt again during pregnancy.
This is an extremely erroneous opinion. If during this period the expectant mother feels, along with abdominal pain, discomfort in the pubic bone area and is wary of unsteady legs, then it is time to wear a pelvic support bandage. Only this device in the later stages of gestation can stabilize the critical zone.
Pain associated with chronic constipation is also a concern for expectant mothers. Constipation is common during pregnancy. It causes pelvic pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen. Hormones produced during pregnancy slow down the digestive tract.
Therefore, to eliminate the problem, the doctor may recommend consuming foods rich in iron and fiber during pregnancy, such as raw vegetables, fruits and berries, and drinking more water.
Severe pelvic pain during pregnancy
Some women during pregnancy with an abnormal course often experience serious complications that provoke pain after ovulation and in the pelvic area.
If a mother-to-be experiences persistent back pain, this could be a sign of preterm labor.
Along with pain, such pain is accompanied by fever, bleeding, and various discharges. These are obvious symptoms of miscarriage, which can be rhythmic and similar to menstrual pain.
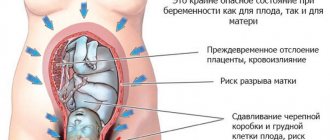
An ectopic or tubal pregnancy also causes very severe pain. If you experience severe pain and bleeding between 6 and 10 weeks of pregnancy, this may be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy. It requires immediate surgical treatment.
In this situation, doctors have from a few minutes to 4 hours to correct the situation. In this situation, you should immediately consult a doctor.
In obstetric practice, along with the described cases that provoke pain, there are many other types of pain, which are often compared to pain after ovulation. If you experience any pain or deviation from the norm, do not neglect consulting a doctor.
Source: https://maa-maa.ru/beremennost/6-nedel-bolit-levyj-yaichnik.html
Relieving pain at home
To reduce pain, you must follow the recommendations of specialists. If they are followed, the intensity of the sensations decreases, and their attacks occur less frequently.
First half of pregnancy
In the first 20-25 weeks of gestation, if pain occurs, it is necessary to undergo examination by specialists. In the absence of pathologies, you are allowed to use methods to alleviate your own condition:
- organization of daily proper rest - pregnant women need more rest, daytime sleep is useful - in a horizontal position and in a comfortable position the pain recedes;
- using a bandage - this is relevant from the 20th week of pregnancy to ease the load on the back, prevent stretch marks and give the stomach the correct position;
- light physical activity – regular attendance at fitness and yoga courses for pregnant women is optimal;
- a varied and balanced diet - if the rules of nutrition are followed, the well-being of the expectant mother will noticeably improve;
- prohibition on lifting weights and physical activity that strains the abdominal muscles.
When you need specialist help
You should call a specialist at home or visit your doctor if the following conditions occur:
- persistent or increasing pain in the lower abdomen;
- the appearance of discharge mixed with blood or complete bleeding;
- increased body temperature above 38 degrees;
- change in the nature of discharge, appearance of odor;
- hardening of the abdomen.
For these symptoms, gynecologists recommend undergoing preventive therapy in a hospital or treatment in a hospital setting to maintain pregnancy. In the absence of severe pathologies, the doctor issues a sick leave for rest and restoration of the body at home.
Why do the appendages hurt during pregnancy?
Many women are interested in the question of why the appendages hurt during pregnancy and what is the reason for this. Yes, pain during pregnancy is considered a certain inevitability.
But you should be attentive to your health and listen to the symptoms that appear, since pain in the appendages can mean a normal pregnancy process, or they can be signs of the onset of a serious pathology
1. Adnexitis
During pregnancy, pain in the appendages causes adnexitis. The disease is an inflammation of the ovaries, which worries not only expectant mothers, but also many women.
© shutterstock
Signs of illness
Adnexitis manifests itself:
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- Pain in the sacrum, coccyx and perineum;
- Increase in temperature;
- Feeling tired.
If symptoms are severe, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Treatment options
Therapy for adnexitis, which causes pain in the appendages during pregnancy, is carried out:
- Antibacterial drugs;
- Antispasmodics;
- Drugs that reduce uterine tone;
- Drugs that improve blood flow;
- Medicines that restore biocenosis.
All medications, in strict order, must be prescribed by the attending physician.
2. Cyst
Pain in the appendages in pregnant women can be caused by a cyst - a benign neoplasm filled with fluid. When making such a diagnosis, a pregnant woman should not worry too much, because this disease is treatable with medication.
© shutterstock
3. Apoplexy
Another cause of pain during pregnancy is apoplexy - rupture of the right appendage or left ovary. The disease is a very dangerous disease that requires urgent medical intervention.
© shutterstock
4. Miscarriage
The reason that the appendages hurt in the early stages may be a miscarriage.
© shutterstock
Preparing for childbirth
Often, pain in the appendage area in the last stages of pregnancy is associated with the body’s preparation for childbirth.
© shutterstock
Signs
Due to the increased activity of the hormone relaxin, cartilage and ligaments soften, the pelvic bones diverge, all this leads to significant discomfort in the appendages.
Awkward movements
Sometimes, during pregnancy, the appendages hurt due to the awkward movements of the expectant mother.
© shutterstock
Doctors treating pain of the appendages during pregnancy
The only specialist who can help eliminate discomfort is a gynecologist. The doctor will diagnose and prescribe appropriate treatment.
In rare cases, consultation with a urologist or surgeon may be necessary.
Less popular causes of appendage pain during pregnancy
There are many reasons why the appendages hurt during pregnancy.:
- Sprain;
- Various inflammatory processes;
- Kidney diseases;
- Cholecystitis;
- Bladder problems;
- Appendicitis;
- Pyelonephritis.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for pain in the ovaries are sometimes the only method of therapy. With their help, a woman’s well-being is facilitated. Popular folk recipes:
- for inflammation of the ovaries - infusion of blueberries, linden decoction;
- severe pain - a decoction of yarrow, lemon balm;
- high temperature - taking decoctions of rose hips, chamomile, linden;
- aching pain - daily intake of 4-10 juniper berries or a decoction with their addition, goose cinquefoil tea.
The use of folk remedies should be agreed upon with a gynecologist.
Prevention of pain
Prevention is carried out in the absence of pathologies of the genital organs and the physiological nature of the pain. It consists of following the recommendations:
- regular observation by a gynecologist, testing;
- avoiding nervous tension and stress;
- moderate physical activity;
- daily rest;
- refusal of any diets, salt and heavy foods;
- eating large amounts of vegetables and fruits;
- drinking plenty of fluids.
Typically, pain in the ovaries during pregnancy is not considered dangerous and is caused by physiological changes in the body. To alleviate them, you should lead a healthy lifestyle, rest and avoid excessive physical activity. If the pain is intense or worsens, you should consult a doctor.
Today, starting from lunch, the left ovary began to shoot, slightly, but unpleasantly ((I’m worried that this could be. I don’t have any ovarian cysts, cystitis or inflammation either. I read that organs are displaced due to the growth of the uterus and therefore can hurt in area of the ovaries... I just don’t understand why exactly it shoots, about once every 15 minutes, when I was lying down, it all went away for about an hour. What do you say? Has anyone had this and is it serious? Is it worth sounding the alarm? Thanks in advance for answers and advice

Pain in the ovaries during pregnancy is not uncommon. Moreover, it can be a completely natural process or indicate pathology. In the first case, expectant mothers should not worry, but in the second, this symptom, or rather, the disease with which it is accompanied, poses a threat. This phenomenon requires urgent medical attention.
The specialist will conduct a diagnosis and determine its cause. If necessary, treatment will be prescribed. You should not put off visiting the doctor, as discomfort may indicate the presence of a serious pathology that threatens the unborn baby.
The ovaries hurt during pregnancy in the early and late stages: why are they drawn and how to relieve the pain?
Diseases of the genitourinary system lie in wait for women of all ages. Pregnant women often complain of discomfort in the lower abdomen. Pain in the ovaries is characteristic of both early and late pregnancy. What are the causes of pain? How to get rid of them?
Why do the ovaries hurt in pregnant women?
Often, pain in the female reproductive glands occurs due to the development of an inflammatory process. However, there are a number of other factors that provoke the appearance of pain in the early stages and in the second trimester of pregnancy. They are divided into three groups - physiological, pathological, and non-obstetric.
Physiological pain
READ ALSO: What are the dangers of an ovarian cyst in early pregnancy?
Physiological pain appears due to hormonal changes and pressure on connective tissue structures, which is caused by the displacement of organs due to the active growth of the uterus. Unpleasant sensations may appear after an unsuccessful bend, careless movement, or prolonged rest in a position on your side. In addition, pain appears under the following circumstances:
- Advancement and attachment of a fertilized egg to the uterine wall. A pregnant woman feels discomfort a week after fertilization of the egg; the pulling sensation is somewhat similar to menstrual pain.
- Problem with the digestive tract. Exacerbations of chronic diseases or malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract occur due to an increase in the amount of progesterone.
- It has been noted that most often discomfort is experienced by young mothers aged 18-25 who are bearing a child for the first time. In subsequent pregnancies, symptoms occur much less frequently.
- A large hollow tumor on the corpus luteum of the gland. A cyst forms at the site where the reproductive cell exits the follicle. As the formation develops, the pain increases. The hollow tumor does not require treatment and disappears along with the corpus luteum before the beginning of the twelfth week of pregnancy.
- A side effect resulting from undergoing hormonal treatment to stimulate ovulation. Women's complaints of tingling pain after artificial fertilization of an egg are quite common.
- A high concentration of relaxin is observed at 14-39 weeks. Under the influence of the hormone, the pelvic bones move apart, and the pregnant woman feels the lower back being pulled.
Pathological pain of the ovaries
Severe pain near the gonads, which increases over time, is most likely pathological in nature. Often the discomfort is especially noticeable during urination.
Inflammatory process in the glands is a common occurrence in young women. The cause of its occurrence is hypothermia, a viral or fungal disease. Pain also appears due to pathologies:
- Ectopic pregnancy, when the egg with the embryo is fixed not in the uterus, but in its cervix, tube or abdominal cavity. A woman may complain of pain and tingling; in addition, bleeding is a sign of abnormal localization of the embryo. Ectopic pregnancy poses a serious danger to a woman.
- Neurosis, depression or other mental disorder. Severe stress combined with changes in the endocrine system can lead to a feeling of discomfort.
- Apoplexy (rupture) of the ovary due to too high pressure in it. This occurs due to injury, treatment with anticoagulants, and hematopoietic diseases.
- A cyst that often forms in women carrying a child. Pregnant women feel tingling and intense pain in the area where the hollow tumor has formed. With the dynamic growth of the formation, it will rupture, and the woman will feel sick and feverish.
- Polycystic gonads, which is a benign growth inside and outside the glands. This disease is found in 10 percent of women. Depending on the location of the formation, the expectant mother may feel pain in the left ovary during pregnancy or, on the contrary, a pull in the right one. If growths are present on both sides, both sex glands ache.
- Spontaneous abortion.
Non-obstetric pain
Pain may occur due to:
- Cystitis - pregnant women complain of aching, spasmodic sensations (for more details, see the article: symptoms and treatment of cystitis in pregnant women in the early and late stages). During urination, women feel a burning sensation and characteristic cramps, while, despite the frequent urge, very little urine is released.
- Renal failure and kidney disease - in addition to pain, characteristic symptoms are swelling, pallor of the skin, and increased blood pressure. In addition, the expectant mother may notice that when urinating, less or, on the contrary, more urine is released, it happens that urine is not released at all or urination is painful.
- Tumors or cysts on organs in the pelvic area - the larger the formation, the stronger the pain. Often, neoplasms are benign and are treated with conservative methods. To diagnose a tumor, it is enough to undergo an ultrasound.
- Cholecystitis - pathology is characterized by pain in the upper right corner of the abdomen. In some cases, patients experience fever, chills and nausea. The inflammatory process with cholecystitis appears suddenly and develops rapidly.
- Appendicitis - it is characterized by sharp, severe pain from the right ovary. The hallmark of appendicitis is a hard abdomen. If such symptoms are present, immediate medical attention is required, as there is a risk of appendix rupture.
What to do if pain occurs?
When the right, left, or both appendages hurt, you should not guess what caused the discomfort. The only reasonable solution would be to visit a medical facility.
The gynecologist will determine the root cause that caused the pain and, if necessary, refer you for examination to exclude possible pathologies. Only after receiving test results can something be done to eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
It is worth remembering that ignoring pain during pregnancy poses a threat not only to the pregnant woman, but also to her child.
In early pregnancy
If a woman did not have problems with the gonads and genitourinary system before conception, the likelihood of them appearing during pregnancy is low. Pregnant women need to protect themselves as much as possible from physical and mental fatigue; they should not lift heavy objects.
If discomfort appears, the first thing the expectant mother needs to do is lie down and relax. However, as soon as you feel a little better, you should consult a gynecologist. In case of increasing pain or bleeding, you cannot hesitate; you must immediately call emergency help. These symptoms may indicate the onset of spontaneous abortion.
In the later stages
If you experience minor pain in the pelvic area at the end of the third trimester, the main thing is not to panic.
In the later stages of pregnancy, the body is actively preparing for the upcoming birth; under the influence of the hormone relaxin, the cervix, ligaments and cartilage become softer, and the pelvic bones gradually move apart.
Against the background of hormonal changes, a pregnant woman feels discomfort in the gonads, but such pain does not pose any threat, does not require therapy and is considered a physiological norm. If the doctor has ruled out the presence of pathology, it is recommended to adhere to the following recommendations:
- to eliminate discomfort due to stretching of the uterine ligaments, you can apply a slightly warm compress;
- to maintain the tone of the whole body, physical exercises for pregnant women are recommended;
- maintain sexual rest until the pain stops;
- adhere to the principles of healthy eating - exclude fried, canned, unhealthy foods and carbonated drinks from your menu;
- get as much rest as possible;
- Taking painkillers is allowed only after approval from a doctor.
If a slight dull pain develops into a tingling sensation, it is better to immediately contact a medical facility. You should not hesitate to visit a specialist in the following cases:
- the pain intensifies and does not go away for a long time;
- the temperature has risen;
- spotting with ichor appeared;
- the stomach seemed to be “petrified”;
- bleeding began;
- The discharge has a foul, unpleasant odor.
Preventive actions
Prevention of ovarian pain involves paying close attention to your health, both before and during pregnancy. A timely gynecological examination will detect pathology at an early stage and prevent it from developing into a chronic form.
If you have any ailments, it is recommended to treat them before becoming pregnant. It is important to get rid of bad habits: smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages is unacceptable.
It is recommended to observe sexual intercourse during pregnancy before conception and during the first month of pregnancy. In addition, expectant mothers should adhere to the following recommendations:
- avoid physical fatigue;
- do not delay registration;
- get enough sleep;
- take daily walks;
- undergo all examinations prescribed by the gynecologist;
- be sure to take blood and urine tests;
- avoid stressful situations;
- adhere to the principles of healthy eating.
Source: https://www.OldLekar.ru/beremennost/jenskoe-zdorove/bolyat-yaichniki-pri-beremennosti.html
Why does a woman's ovaries hurt during pregnancy?

In addition, the uterus rises a little along with them, that is, the usual localization of the organs changes, which means that they are no longer at their previous location and, quite possibly, pain in this area is caused by other reasons.
The nagging pain that the woman attributes to the ovaries is caused by the ligaments that hold the uterus and are located on both sides of the lower abdomen. The uterus gradually increases in size, accordingly, the ligaments become tense and the same discomfort occurs, and the woman thinks that it is the ovaries that hurt during pregnancy. This condition is not dangerous and is also temporary. In this case, the sensations are compared with unpleasant feelings during menstruation.
Why does pain occur at the end of pregnancy?
Towards the end of gestation, the woman’s body begins to intensively produce the hormone relaxin, which helps the woman’s body prepare for childbirth and makes the ligaments more elastic. Very often, relaxin can weaken the joints of the pelvis and even lead to inflammation.
Against the background of these changes, many women begin to assume that their ovaries hurt again during pregnancy. This is an extremely erroneous opinion. If during this period the expectant mother feels, along with abdominal pain, discomfort in the pubic bone area and is wary of unsteady legs, then it is time to wear a pelvic support bandage.
Only this device in the later stages of gestation can stabilize the critical zone. Pain associated with chronic constipation is also a concern for expectant mothers. Constipation is common during pregnancy. It causes pelvic pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Hormones produced during pregnancy slow down the digestive tract. Therefore, to eliminate the problem, the doctor may recommend consuming foods rich in iron and fiber during pregnancy, such as raw vegetables, fruits and berries, and drinking more water.