Headache in a child is quite common. About 80% of children have experienced this disease at least once in their lives. The causes of headaches can be both neurological and psychological. Children never just complain about pain. Either the pain is very severe, or the child has headaches very often. Complaints should never be ignored. Timely treatment and diagnosis will help eliminate the risk of developing complications in the future. Why a child often has a headache and how to cope with pain, we will find out further.
The main causes of headaches in children
The causes of unpleasant sensations in the head include a number of pathological processes, mental disorders and constant overwork of the child. It is important to establish the correct cause in order to select a rational treatment. Without diagnostic measures, it is impossible to make a diagnosis yourself.
The main causes of headaches in children:
- Migraine (childhood or teenage).
- VSD syndrome (vegetative-vascular dystonia).
- Tension headache.
- Tumor-like processes in the brain and its membranes.
- Diseases of ENT organs and eyes.
- Meningitis and encephalitis.
- Violation of intracranial pressure.
- Infectious and viral pathologies.
- Poisoning.
- Inflammatory process in the trigeminal nerve.
- Head and brain injuries.
If a child complains of a headache, do not try to drown out the illness with analgesics. First, find out what the nature of the pain is, how long it torments the child, and the frequency of occurrence. If accompanying symptoms occur, such as nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, call an ambulance immediately. Before the ambulance arrives, it is better to refrain from taking any medications, as the clinical picture may be blurred, which makes it much more difficult to make a diagnosis.
Why does a child feel dizzy?
If, based on the listed signs, parents suspect that their child has dizziness, the question of their origin arises. Vertigo itself is only a symptom of trouble, and to find out the cause, a medical examination is required.
For reference. But medical help is not always necessary: often illness is a consequence of physiological factors that are not dangerous to life and health.
For example, dizziness in teenage boys or girls is in most cases due to the natural process of puberty. Therefore, before contacting a doctor, you should pay attention to the nature of the attacks (frequency, duration), accompanying symptoms, and also take into account the circumstances in which the child suddenly became dizzy.
Physiological reasons
Dizziness in most cases is associated with dysfunction of the vestibular analyzer. If the sensitive cells of the labyrinth of the inner ear become intensely irritated, one begins to feel sick, dizzy, and loses balance.
This occurs when swinging on a swing, fast linear movement (driving a car, train), or rotation. After eliminating the irritating factor, the pathological symptoms disappear quite quickly.
In active, active children, physiological dizziness is a common occurrence, and in this case there is no reason to worry. The baby, due to insufficient training of the vestibular apparatus, may also get motion sickness in transport. If at the end of the trip the discomfort goes away, there is no need to worry either.
For reference. In a healthy elementary school student, attacks of vertigo may be caused by overwork. The combination of studying at school with visiting clubs and sections creates an increased load on the child’s body.
In addition, the head may feel dizzy due to long breaks between meals and lack of fluid. For high school students, their health may worsen with the onset of puberty. Hormonal fluctuations in boys and girls during puberty affect vascular tone, causing spasms and ischemia of brain tissue.
Dizziness in teenage girls can also occur due to heavy blood loss with the onset of menstruation until the cycle stabilizes.
Pathological causes
Dizziness in a girl or boy in the first year of life may be a consequence of intrauterine hypoxia or birth injuries. As a rule, disorders of this kind become known immediately after birth, and treatment is prescribed immediately.
Among other causes of vertigo paroxysms, the following are most often identified:
- Vestibulopathy is inflammation, injury or dysfunction of the vestibular analyzer. Diseases such as benign paroxysmal positional vertigo or Meniere's disease are quite rare in children. But inflammatory processes in the inner ear are not uncommon (labyrinthitis, neuronitis).
- Neurological disorders such as epilepsy or severe central nervous system infections (encephalitis, meningitis).
- Acquired or congenital diseases of the endocrine system, for example, hypothyroidism or adrenal hyperplasia.
- Cerebrovascular disorders, trauma or brain tumors.
- Hematological diseases of varying severity, from iron deficiency anemia to cancer.
- Intoxication as a result of colds, bacterial infections, food poisoning, medications, snake or insect bites.
- Allergies and helminthiasis.
All these pathologies pose a serious threat to the health and sometimes the life of the child, so they need to be treated in a timely manner. The doctor will prescribe consultations with specialized specialists and a comprehensive examination using laboratory and instrumental methods for the boy or girl.
Clinical picture and nature of pain
So, if a child has a headache, first of all, we provide him with complete rest and find out the main clinic, based on the complaints. Children 10 years old can quite clearly describe their condition. The nature of headaches in a 5-year-old child is more difficult to determine; usually children either turn to the wall, not wanting to communicate, or cry loudly, which further increases the intensity of the pain.
Headache in children can be:
- piercing;
- pulsating;
- pressing;
- bursting;
- aching.
Localization can be observed in the occipital, parietal, frontal, and temporal lobes. It may hurt in the eye area or throb in the temples. If you managed to find out the nature of the child’s headache, this is already good. All that remains is to figure out how headaches occur in pathological conditions.
A child’s eyes hurt, causes, symptoms, how to treat
Vision problems can begin at almost any age; many preschool children already wear glasses. Advanced ophthalmological diseases often lead to vision deterioration. The reasons why a child’s eyes hurt can be either completely innocent or require immediate treatment.
Parents need to listen to any children's complaints and respond to them in a timely manner. What to do if a child has a sore eye? To determine the cause of the pain and prescribe adequate treatment, you must consult a doctor.
Causes of eye pain in children
If a child has eye pain, the causes of this discomfort are very diverse. The most common:
- Passage through the birth canal . Even babies often suffer from eye pain. A child passing through the birth canal can become infected from the mother if she has not previously undergone preventive treatment. Therefore, after birth, all children’s eyes are treated with special drops.
- Obstruction of the lacrimal canal . Not all babies born have developed lacrimal glands. Obstruction of the tear duct leads to suppuration and pain. A pediatric ophthalmologist may prescribe probing, a special procedure for clearing the tear duct. Probing is usually carried out at the age of 2-3 months.
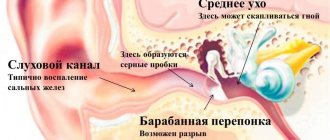
- Colds . A child’s complaints of pain in the eyes often occur with a severe cold, accompanied by inflammation of the nasal sinuses - sinusitis. With untreated colds, the infection can spread to the ears, causing otitis media. To exclude diseases of other organs, the course of treatment should always be completed.
- Overwork . Sometimes a child often complains of pain in the eyes due to their overstrain. This is especially typical for schoolchildren who spend at least 5-6 hours at their desks, and upon returning home sit down at the computer and TV. Eye fatigue is accompanied by dull pain. Chronic overexertion leads to a decrease in visual acuity, which can be restored with the help of glasses or surgical correction.
- Bacterial or infectious disease . Bacteria and viruses can cause blepharitis - inflammatory processes in the eyelids, keratitis - damage to the cornea, neuritis - inflammation of the optic nerve, dacryocystitis - inflammation of the lacrimal sac.
Any eye disease in children requires immediate treatment by a qualified specialist. It is necessary to show the child to an ophthalmologist, because pain is always caused by some reason and will not go away on its own.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis
Often, children with complaints of discomfort in the organs of vision experience conjunctivitis, an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye caused by infection. It is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Swelling, redness of the eyelids, itching.
- Presence of purulent discharge.
- Sensitivity to light, sensation as if sand had been poured into the eyes.
Important! The severity of symptoms may differ depending on the nature of conjunctivitis - allergic, viral or bacterial.
If the disease is caused by an allergy, it is recommended to consult an allergist-immunologist; based on the research results, the irritant will be identified. It must be excluded to eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Foreign body in the eye
Often a child complains of pain in the eyes as a result of a foreign body. Any crumb can cause sensations that are very unpleasant, since the mucous membranes are very delicate and vulnerable.
Important! When a child’s eyes hurt due to a foreign body, under no circumstances should they be rubbed. The retina can be damaged.
Even a speck of dirt that gets on the mucous membrane can cause severe inflammation. It must be rinsed with plenty of clean running water and gently wiped inside with a sterile cotton swab. If this does not help, you should definitely seek medical help.
Migraine
The disease most often affects children from 7 to 11 years of age. Migraine pain is characterized by:
- Pulsation in the area of the eye or temple, on one side.
- Irritation and increased pain from bright light and noise.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Reaction to odors.
The condition improves after the child vomits and falls asleep.
A 10-year-old child, as a rule, has less intense pain than a seven-year-old child. The older the patient, the richer the vessels. This is why teenage migraines usually subside by age 18.
Migraine headaches in children have their own characteristics, in contrast to the course of the disease in adults:
- paroxysmal pain lasts from 30 minutes to 5 hours;
- cephalalgia is directly related to fatigue and psychological stress;
- may be accompanied by fainting and severe dizziness;
- The child will definitely have a stomach ache, diarrhea and vomiting.
If a child often has a headache and the cause is migraine, it is important to eliminate the provoking factors. The child should not get tired; nutrition and rest should be observed and adjusted. Mental stress should be distributed, and physical stress should be supervised by parents.
VSD syndrome (vegetative-vascular dystonia)
Frequent headaches in a child aged 7–10 years are often associated with changes in vascular tone. The reasons may lie in brain hypoxia, a clear sign of which is constant yawning. In addition to oxygen starvation, the development of VSD syndrome can be influenced by diseases associated with dysfunction:
- Of cardio-vascular system.
- Kidney.
- Liver.
Medical statistics claim that VSD affects children exposed to constant stress and overwork. The atmosphere in the family plays an important role in the development of the disease. With constant scandals in the house, the child gets a severe headache. VSD syndrome resolves when the underlying disease is eliminated and the patient’s emotional background is stabilized.
Head pain is accompanied by disturbances in heart rate and blood pressure. Such children are subject to frequent mood swings and excessive irritability.
TTH (tension headaches)
The peak of such pain occurs between the ages of 7 and 10 years. Approximately 75% of cephalgia are the result of tension headaches.
The problem happens with children:
- spending a lot of time at the computer and watching TV;
- with crooked posture;
- with tension in the neck muscles.
The main complaint is localization of pain in the frontal or parietal region. Pressing pain that calms down after the patient rests. Children have severe headaches, but by the time they reach adulthood, the disease goes away.
Pain due to pathological processes of ENT organs and eye diseases
Chronic and acute diseases of the sinuses, throat and ears are often accompanied by pain in the head. Children react especially acutely to sinusitis and sinusitis. Toxic effects on the membranes of the brain lead to attacks of headaches and vascular disorders. Cephalgia will go away only after successful treatment of the underlying disease.
Headaches that occur in a 6-year-old child are usually associated with prolonged eye strain. When reading books, drawing and watching TV, the optic nerve receives a large load that the child’s body is unable to cope with. The headache is accompanied by pain in the eyes, tearing and blush on the cheeks. The trouble can be easily eliminated if you rationally distribute the child’s work and rest schedule. If your child cannot live even an hour without a book, teach him to relax. Eye exercises will help relieve tension and eliminate headaches.
My child’s eyes hurt – what should I do?
A child’s eyes hurt – this situation is well known to parents.
Most often, a child's eyes hurt when conjunctivitis or a common viral infection begins. But there may be other reasons: allergies, foreign bodies in the eye. Finally, the cause of pain in a child’s eyes may be the consequences of a birth injury. Pain in the eyes of a child due to colds
Colds in children are associated with a temporary decrease in immunity. This situation occurs, for example, during hypothermia. Against the background of decreased immunity, the child develops an acute respiratory disease (ARI), caused either by an infection that came from outside (a viral or bacterial infection that he contracted from another patient), or by his own opportunistic microflora, which constantly lives in the respiratory tract and is activated against the background decreased immunity.
A peculiarity of a child’s body is that any acute respiratory infections in him are prone to generalization, that is, to damage the entire organism. If an adult suffers from a cold in the form of a runny nose, then the child will most often develop a fever, cough, runny nose, headache, joint pain. Joint pain - how to figure out what is happening? and muscles. Headache is often accompanied by eye pain. The eyes become red, watery, and the child rubs them with his hands, which can contribute to infection. If purulent conjunctivitis does not develop, then eye pain goes away on its own as the child recovers and does not require special treatment.
If a child’s eyes hurt, but there are no signs of a cold, then he should be shown to an otolaryngologist - perhaps he has some kind of permanent source of infection in the form of chronic tonsillitis. Chronic tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils, sinusitis or adenoiditis. In this case, the child’s eyes may also hurt.
Pain in the eyes of a child with conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is a very common disease in children. It can develop when a speck gets into the eye - a child rubs his eyes with dirty hands, injures the conjunctiva, and an infection takes root in micro-abrasions. In children's groups, acute viral and bacterial conjunctivitis is transmitted from a sick child to healthy children, sometimes entire groups get sick. The younger the children in the group, the higher the risk of spreading the infection.
Acute conjunctivitis begins with a feeling of speck in the eye, the child rubs his eyes, the conjunctiva turns red, the eyelids swell, and purulent discharge appears. Such a child must be isolated from the team and treated until complete recovery. For the treatment of purulent conjunctivitis, eye drops and ointments with an antibacterial effect with chloramphenicol, ofloxocin, and sulfonamides are used. To treat viral conjunctivitis, eye drops with an antiviral effect, for example, Ophthalmoferon, are used.
Pain in the eyes of a child due to eye injury
Most often, the eyes are injured when a speck hits them. This creates a threat of developing conjunctivitis and even an erosive-ulcerative process in the cornea. The first aid in this case may be to carefully rinse the eye with boiled water so that the speck moves to the inner corner of the eye, from where it can be easily removed. You can also apply any antibacterial eye drops to your eyes. If you cannot remove the speck yourself, you should urgently consult an ophthalmologist.
Pain in a child's eyes caused by allergies
When asked why the eyes hurt Why do the eyes hurt – the reasons are infectious in a child, the doctor will best answer. Therefore, if your baby’s eyes constantly hurt and are watery, he needs to be shown to an ophthalmologist. Very often, the cause of eye pain is an allergy - an inappropriately high reaction of the immune system to some substance. Allergic conjunctivitis in children is often caused by pollen from flowering plants and is seasonal.
But they can also be year-round. Such conjunctivitis is often caused by body fluids and pet hair, fish scales, and so on. An allergist will help you figure out what exactly caused allergic conjunctivitis in a child. He will prescribe the necessary treatment.
Pain in the eyes of a child not associated with infection or allergies
When the eyes hurt If the eyes hurt: folk remedies for various eye diseases in a child, this is not always associated with infection. Sometimes pain in the eyes appears due to severe eye strain. A small child should not watch TV for a long time, play games on the computer, or even look at pictures in a book for a long time. All these activities need to be combined with outdoor games.
Long-term eye strain can lead not only to eye pain, but also to headaches. Prolonged visual strain is especially dangerous for children with perinatal lesions (during pregnancy, childbirth and in the first weeks after birth) of the brain. Mild lesions of this kind can manifest themselves in the form of minor symptoms, which parents do not always pay attention to. But if the child is not treated and allowed to constantly strain his vision, this can have negative consequences. Therefore, children with eye pain of unknown origin should be consulted by a pediatric neurologist.
If a child’s eyes hurt, he should be seen by a doctor.
Galina Romanenko
Article tags:
- eyes
|
|
Related articles If your eyes are watery - the problem and its solution
If your eyes itch, this is a possible onset of conjunctivitis.
Probing the tear duct in newborns - opening the tear ducts
The eyes of a newborn are festering - a reason to contact an ophthalmologist
Intracranial pressure disorder
The concept of intracranial pressure disorder refers to hypertension, that is, a change in pressure in the vessels of the brain. This disease usually affects young children. Vascular incompetence and a sharp drop in pressure causes activation of pain receptors. The accumulation of intercellular fluid puts pressure on the vessels and pain occurs. The danger of hypertension lies in the possible development of convulsive syndrome.
With increased intracranial pressure, the baby constantly has a headache when the weather changes or overwork. By the age of five, the disease usually subsides. Bursting pain may be accompanied by vomiting, in some cases uncontrollable.
Intracranial pressure can be not only increased, but also decreased. Fluid deficiency leads to tension in the membranes of the brain. It is stretching that leads to increased pain. The unpleasant feeling goes away when you change the position of the head and body.
What to do if a child has a sore eye and develops a fever or other symptoms?
A falling eyelash, mechanical damage, or overexertion from spending a long time at the computer
cause eye pain At the same time, there is a risk of developing an ophthalmological disease.
Childhood diseases of the visual organ in 85% of cases are characterized by an inflammatory process . As a result, conjunctivitis, chorioretinitis, and chalazion develop.
Myopia, astigmatism, and macular degeneration are associated with impaired visual acuity.
Various causes of pain and treatment recommendations
Visual function involves the eyeballs, muscles, nerves, blood vessels and brain.
Only the coordinated interaction of the components ensures normal vision.
The final formation of the eye organ is completed by 3-4 years . Binocular vision begins to function, completing three-dimensional vision of images.
Any change in visual acuity or manifestation of symptoms of an ophthalmological disease requires consultation with an ophthalmologist.
A child may complain of eye pain for various reasons.
Overwork
The child feels discomfort behind the eyeball , accompanied by dryness and pain.
Symptoms in 95% of cases occur in children who spend a long time playing computer games , tablets or TV.
There is a gradual decrease in visual acuity as a result of fatigue of the eye muscles.
As a conservative treatment, the ophthalmologist prescribes conservative treatment - wearing glasses and contact lenses.
Bacterial infection
There are situations in which limiting the time spent on the computer has no effect . The child continues to feel pain and cry.
The appearance of symptoms is due to the development of an infectious process.
The risk of infection with pathogenic bacteria is higher in children than in adults. Rubbing your eyes with dirty hands is enough to introduce microorganisms.
Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and determine further treatment , so self-medication is not allowed.
An itchy sensation (itchy eyes) in the inner corner of the eye is a warning sign of conjunctivitis . The mucous membrane of the eyes becomes inflamed, causing symptoms:
- redness of the sclera;
- pain in the eyes;
- photophobia;
- purulent discharge;
- tearfulness;
- spasm of the orbicularis oculi muscle.
In the morning the child wakes up with his eyelids glued together. To remove dried discharge, you have to rub your eyelids with your hands.
If timely treatment is not provided , conjunctivitis can be complicated by inflammation of the lacrimal sac (dacryocystitis).
Presence of a foreign body
Prolonged presence of a solid in the eye contributes to damage to the cornea, which is accompanied by an inflammatory process.
What should I do to extract?
You must try to remove the foreign object yourself - by rinsing with plenty of warm water.
An effective remedy is also to remove the object with a sterile cotton swab.
Cotton can be moistened with a herbal solution (oak bark, chamomile, green or black tea) and wiped from the outer edge to the inner.
If a speck gets into a child's eye, then it is necessary to limit the child's movements . Especially if pain continues after removal of the foreign body.
Do not rub or touch the injured eye with your hands , as there is a possibility of damaging the retina or reducing visual acuity.
Viral diseases with fever
High temperature is a sign of a viral disease.
If the temperature persists for a long time, then this is a sign of a bacterial infection in the body.
A viral attack reduces immunity, resulting in eye diseases .
When complications occur, the temperature rises higher.
An increase in t after 38 degrees indicates an increase in eye pressure.
The latter can increase due to stress, emotional tension, as well as against the background of diseases of the urinary, cardiovascular, and endocrine systems.
Allergic reactions
Hypersensitivity to a certain substance causes pain in the orbital area. The child begins to scratch the eyelids under the eyeball.
Signs of allergies are caused by increased vascular permeability.
Soft tissues are affected by the mediators of the allergic reaction - prostaglandins, serotonin, histamine.
If a child begins to choke or his throat swells (signs of anaphylactic shock, angioedema), you must immediately call an ambulance.
Eye injuries
In case of mechanical damage, the cornea is the first to suffer . Dirt and debris can damage soft tissues.
The child begins to rub his eyes with his hands, which can increase the injury.
It is possible to get a foreign object using a handkerchief. You need to move the object to the inner corner of the eye to make it easier to pull out.
If it is not possible to remove the speck, it is recommended to rinse the eye with boiled water or herbal infusion (chamomile solution, tea leaves).
After successful extraction, the eyes must be treated to prevent an infectious or inflammatory process.
If you experience problems with vision, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist.
Headache
A feeling of discomfort in the eyes against the background of a headache indicates a spasm of blood vessels .
“Flies” or sparks begin to float before your eyes To get rid of the unpleasant consequences of narrowing of the vascular lumen, the child begins to hold his temples and close his eyes.
The causes of spasm are considered to be climate change, changes in blood pressure, and overwork.
Pain in only one eye sometimes a symptom of migraine. At the same time , children feel nauseous and are afraid of light and sounds .
If a child feels a bursting dull pain or heaviness in the eye sockets, these are signs of increased intracranial pressure . It is caused by excess accumulated fluid in the ventricles of the brain.
From this video you will learn what to do if your child gets something in his eye:
The causes of pain in the orbital area may vary.
When the temperature rises, irritability appears, or when visual acuity decreases, it is dangerous to self-medicate.
You need to seek help from an ophthalmologist.
The visual organ stops recovering by the age of 18, so mechanical damage and infectious diseases provoke a final impairment of visual function.
It is necessary to begin treatment immediately so as not to resort to surgical intervention.
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material and the author!
( 1 5.00
Source: https://zrenie1.com/bolezni/simptomy/bolyat-glaza/reben-bol-glaz.html
Viral and infectious diseases
Any viral and infectious diseases begin with pain in the head. Intoxication is the main cause of the disease. Toxic substances formed during the life of viruses and microbes poison the child’s body. Common symptoms of intoxication also include:
- Weakness.
- Fatigue.
- Drowsiness.
- Nausea.
Along with the above symptoms, body temperature increases, body aches and muscle pain appear. Therefore, if a child has a severe headache and is shivering, it is likely that he has an acute respiratory viral infection or acute respiratory infection. A pediatrician can make a diagnosis when examining a small patient.
Meningeal headaches
Inflammation of the membranes of the brain caused by viruses and bacteria is always accompanied by pain in the head.
Meningitis is characterized by:
- severe pain in the head;
- vomit;
- fear of light and sounds;
- increased sensitivity of the skin;
- forced position of the patient in bed.
A patient with meningitis lies on his side, his head thrown back, and his legs tucked to his stomach. If you try to bring your head to your chest, muscle spasm occurs (stiff neck). It is dangerous to treat such a patient at home; only timely help from doctors will help relieve inflammation from the membranes of the brain.
Poisoning
Acute food poisoning is characterized by severe headaches in children. This symptom is a consequence of intoxication of the body. If a child complains of soreness in the head, nausea and weakness, it is important to find out what he ate at school or at a party. Later, vomiting and diarrhea occur. The worst thing about poisoning is dehydration. Only replenishing lost fluid will help you recover quickly. Give the patient food often and in small portions. You must tell your doctor about what happened.
Diagnostic measures
If a child has a severe headache, what should you do? The very first step parents take is going to the doctor. Diagnostics will reveal the true cause of the disease.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following will be prescribed:
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- X-ray of the cervical spine.
- Angiography.
- Duplex of cerebral vessels.
- REG.
If meningitis is suspected, the patient is indicated for a spinal puncture, with examination of the cerebrospinal fluid for the presence of pathogens.
Only after diagnosis will the doctor announce the verdict on why the headache hurts and how to deal with it.
When to sound the alarm
Calling an ambulance or going to the doctor is urgent if your child has:
- severe and sudden headache;
- unusual, shooting pains, accompanied by noise in the ears and head;
- when changing body position, the pain intensifies;
- pain is observed in the morning;
- during an attack, consciousness becomes confused;
- severe pain after a previous injury.
There are many types and forms of headaches in children; only a doctor can identify the true cause. It is very difficult to recognize what is bothering a child if he is still very young. Infants react to discomfort in the head with anxiety, refusal to eat, insomnia, and frequent regurgitation. With intracranial hypertension, “fountain” vomiting may occur. The fontanel pulsates and bulges.
Older children complain of fatigue, holding their heads and trying to lie down. Some people try to distract themselves from discomfort by fiddling with their hair or scratching their face.
Children 7 years old suffer from cephalgia differently. They lie down more and can casually tell their mother that their head hurts. When the pain is unbearable, tearfulness and fear appear.
At the age of 10, the child will clearly voice his condition, when the changes occurred and where it hurts. Treatment of cephalalgia in adult children proceeds faster due to the clear clinical picture.
The main causes of eye pain in children
Let's look at what causes eye pain and what can be done to eliminate it. The provoking factors in children and adults are the same, but children suffer from infectious diseases much more often.
Overwork
If a child constantly sits at a tablet, computer, or plays on the phone, his eyes are under severe strain. Pain in this case is a natural result of improper visual hygiene and is often accompanied by a decrease in the acuity of visual function.
Watch what your child is doing, do not allow him to constantly be in front of the monitor.
To avoid strong protests, come up with an alternative activity that will be interesting to your daughter or son - in this case, they will not whine about being bored and interfere with your work and household chores.
You cannot leave things to chance, because the visual system in childhood is just developing, and it is in your best interests that the child does not start wearing glasses. Constant overexertion is not only painful, but also myopia, which cannot be completely eliminated.

Diseases
Children are active, play around in playgrounds, with sand, and don’t really like to wash their hands. The contact of bacteria on the mucous membranes is fraught with the development of various unpleasant pathologies, which can also cause pain.
To get conjunctivitis with redness, pain, pain, purulent discharge, just rub your eyes with dirty hands. There are many diseases, the clinical picture of most of them includes discomfort and pain.
If you notice alarming symptoms, contact an ophthalmologist so that he can conduct a comprehensive examination and prescribe effective treatment.
You cannot select medications on your own, since they have certain features of action and are effective for some pathologies and not effective for others.
Conjunctivitis in childhood is much more common than other diseases and causes inflammation, redness, and purulent discharge. Treatment should be medicinal; washing with saline solution, furatsilin, and tea leaves helps a lot.
Folk remedies are also effective, but they may not be enough - consult a specialist so as not to waste time. With improper treatment or its complete absence, conjunctivitis begins to become chronic, which is quite difficult to cure.
Children do not always play carefully and safely. If your eye hurts, it may be that a foreign body has entered it. A characteristic sign is complaints of discomfort in only one eye, and not in both. You need to try to get the speck, and as soon as possible.
If you cannot cope with the task yourself, or a sharp, dangerous, or large object gets into your eye, consult a doctor.
If a foreign body enters, friction is contraindicated - there is a risk of damage to the retina and, as a result, loss or simply deterioration of vision.
Other diseases
A child’s eyes may hurt due to injuries to the head, brain, surges in intraocular, intracranial, and blood pressure. Pain also occurs with certain dental pathologies, acute respiratory viral infections, sinusitis, sinusitis, and cysts in the maxillary sinuses.
First you need to be examined by an ophthalmologist, but if he does not suspect anything wrong, contact specialized specialists - a neurologist, a dentist, an ENT specialist. Rule out the presence of seasonal allergies, for example, to pollen - a common cause of corresponding unpleasant symptoms.
Children, especially very young ones, cannot always accurately and clearly say what hurts them, where, how much. Listen to your baby's complaints and pass them on to the doctor. Do not draw hasty conclusions yourself and do not prescribe treatment.
First aid for a child
Treatment of headaches in children at home begins with creating complete peace. Television and other external irritants must be eliminated immediately. Place the patient in bed, soak a towel in cool water and apply for 5 - 7 minutes. The room should be well ventilated. Very often, children suffer from pain due to stuffiness in the room.
Offer the patient a warm drink, especially if vomiting occurs. Ascorbic acid relieves cephalalgia well. You can give 2 - 3 tablets of ascorbic acid or tea with lemon. Decoctions of soothing herbs - motherwort, valerian - will relax the blood vessels and help the child fall asleep. Do not give chocolate under any circumstances - this product provokes even greater pain.
If rest and sleep do not help, it would be a good idea to consult a doctor. Children can only take Paracetamol and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Ibuprofen.
Do not overuse medications. The only thing that differentiates a medicine from a poison is the dose. Failure to comply with the frequency and exactly specified dosage can cause significant harm to health.
Create the most comfortable conditions if the pain is not frequent and is associated with overload at school. If attacks are repeated with a certain frequency, and the child turns pale, loses consciousness, or does not remember the events taking place, call an ambulance immediately.
Replacing lenses
Often during summer vacations, parents replace their children’s glasses for vision correction with contact lenses. Firstly, with the lenses the child will be able to wear sunglasses. Secondly, the older the child, the more often he is embarrassed by poor vision and, as a result, does not like to wear glasses. In such cases, parents should know that under no circumstances should they swim with contact lenses. The water can harbor microorganisms that will settle on the contact lens and cause serious keratitis. Often even contact lens solutions cannot cope with such microorganisms. Therefore, if your child loves to swim, then you can buy him special glasses for the pool with diopters, in which he can admire the wonders of the underwater world. But under no circumstances should children be allowed to swim wearing contact lenses.
It is surprising for parents that in the summer, many children’s vision declines, sometimes significantly. It would seem that the child spends a lot of time in the fresh air, eats well, eats fruits and berries, and does not experience the stress that he had during his studies. But not only visual stress affects the progression of myopia. In the body of a myopic child, biochemical processes occur that lead to the growth of the eyeball. Increased visual load only increases the progression of myopia, but is not the main cause. Therefore, in the summer it is also necessary to visit a pediatric ophthalmologist in order to prescribe the necessary treatment for the child in a timely manner. Moreover, the child will not be busy with school activities and clubs, so he can easily set aside 10 days to undergo a course of treatment to stabilize myopia.
Preventive actions
To reduce the intensity of pain and protect as much as possible from relapses, follow simple rules that are very easy to follow:
- The child must have a clear daily routine.
- Meals are timely and rich in microelements.
- Regular walks in the fresh air.
- Protecting the child from stress and overwork.
- Ventilation of the children's room.
- The family environment should be as comfortable as possible for children.
- Communication and participation in the life of a small family member.
- Active lifestyle.
- Limitation on computer games and hours of sitting in front of the TV.
If your child suffers from frequent cephalgia, you should be regularly monitored by a neurologist. This is especially true for children aged seven. Primary school completely changes the daily routine, mental and emotional state of the student. Excessive mental stress should be corrected by the attending physician and distributed in a rational manner.
Source
Unnoticeable injury
Summer is a time for active outdoor games. And microtraumas to the eyes in children are a common occurrence during the holidays. Sometimes the damage can be more serious than you think.
Parents need to be quite vigilant in such situations.
The first option is blunt trauma or so-called contusion of the eyeball. For example, struck with a fist or a ball. Contusion can be divided into several degrees of severity. From a small subconjunctival hemorrhage (a simple bruise) to severe complications up to retinal detachment. These complications arise due to deformation of the eyeball upon impact. Even through closed eyelids. The danger of such an injury is that immediately after it, changes inside the eye may not be noticeable. Even in the absence of visible damage to the eyes, it is better to go to an ophthalmologist as a preventative measure to check your vision and fundus.
It is also important to remember that you need to contact an ophthalmologist not only in case of direct eye injury, but also in case of head injury! Because when the eyeball is concussed, there may be damage that is not noticeable without examination.
The second option is when you get hit in the eye with a branch or stick. This type of injury often causes corneal erosion. In other words, a scratch. The cornea (the transparent layer of our eye) is a very sensitive organ. Even a light touch causes pain, not to mention a scratch. Therefore, a person experiences severe discomfort: pain, lacrimation, inability to open eyelids, redness.

Strabismus test. An ophthalmologist talks about what diseases 3D cinema can reveal Read more
Fortunately, with proper treatment, the cornea regenerates very quickly.
Place a clean napkin on the damaged eye and see a doctor so that he can rule out a penetrating wound, assess the depth of the scratch and prescribe treatment.
Injuries that damage the cornea often lead to astigmatism, which reduces vision. Or they can cause persistent clouding of the cornea: a cataract.