According to statistics, leg pain most often occurs in children aged 3 to 10 years. Their causes are often various injuries (bruises, sprains of muscles and ligaments), but it also happens that a child has no visible causes of pain in the legs. In this case, you cannot do without contacting a pediatrician, since pain in the joints or muscles of the legs can indicate many different diseases.
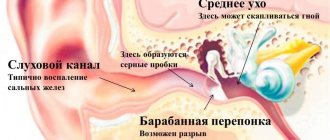
Why do my child's calves hurt?
Few people know that growth until adolescence is achieved mainly through the legs. The most intensive development occurs in the area of the lower leg and foot, where maximum blood flow through the vessels is necessary. It nourishes muscle material and joints that lack elastic fibers. At night, during sleep, saturation decreases, and pain begins in the child’s calves. Regular stroking and light massage alleviate the condition, because due to mechanical action, blood flow increases.
A child’s calves hurt: orthopedics
The second and most common cause of pain may be an orthopedic problem.
- Scoliosis, incorrect posture, neglected flat feet disrupt the center of gravity and the main pressure is focused on the lower limbs.
- After such a load, the legs hurt not only during sleep, but also while awake.
Pain in the joint areas, accompanied by gait disturbances, can also be caused by such ailments as osteochondropathy - diseases of the hip joints, which include: Ostud-Schlatter syndrome - pathology of the tibia and Perthes syndrome - aseptic necrosis of the head of the femoral joint.
Viral and colds: a child’s calves hurt after fever
Parents often complain that their child’s calves hurt after fever, sore throat, or acute respiratory diseases.
- If symptoms are accompanied by loss of appetite, diarrhea, physiological manifestations - swelling, spots, rashes, it is necessary to conduct a full examination of the body, including a general blood test, checking the heart function on an ECG, biochemical blood test, urine test, etc.
- Pain can even be associated with ordinary tonsillitis, caries, and adenoiditis. It would seem that diseases that are easy for us can lead to serious consequences - rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, involving the endocrine system in the process, causing diabetes, kidney diseases.
- The inflammatory process can lead to mineralization of bone material. Pain in the legs may indicate tuberculosis, which is why timely diagnosis and treatment are important.
How to get rid of it?
The process of such treatment is long and complex. And it often costs a lot of money if you do not work independently, but turn to a psychotherapist for help.
Therefore, it is important to know how to reduce the manifestation of symptoms here and now, and relieve muscle fatigue.
There are several ways to reduce psychogenic tremors in the legs, their weakness and the feeling of weakness and helplessness.
Muscle weakness or myasthenia gravis is a decrease in the contractility of one or more muscles. This symptom can be observed in any part of the body. Muscle weakness is more common in the legs and arms.

The causes of muscle weakness can be a variety of diseases - from injuries to neurological pathologies.
Manifestations of muscle weakness can begin to develop from the age of 20. Muscle weakness in children is less common. Most often, myasthenia gravis occurs in women.
Treatment of muscle weakness is medication and physiotherapy.
Advice for parents if their child’s calves hurt
The main responsibility for the health and life of the child lies with the parents.
- From the first days of life, they must be attentive, listen to the complaints or general condition of the baby.
- Children cannot always tell about the problem, so it is necessary to monitor his behavior and appetite.
- It is necessary to enrich the diet with dishes that supply the body with phosphorus and calcium, give up fatty and heavy foods, introduce fruits, vegetables, fish, and dairy products into the diet.
- Often the cause of problems can be uncomfortable shoes without orthopedic insoles.
If you see that your child gets tired quickly, tries to sit or lie down at the first opportunity, or jerks his legs while sleeping, consult a doctor.
Causes of pain
In fact, there are many reasons for the appearance of pain in a child’s lower extremities, from the most harmless bruises to serious diseases. Let's look at them all.
Growing pains . At the age of 5-7 years, the baby “stretches in length” very intensely; sometimes the same growth spurt occurs in adolescence. Moreover, before the onset of puberty, the increase in body length mainly occurs due to the lengthening of the lower limbs. The legs and feet grow fastest at this time. Quite often this is the cause of pain in the calf muscles of the legs. This happens due to the fact that when bone and muscle tissue grow rapidly, they need intensive blood supply. And if during the day, during periods of increased physical activity, blood enters the tissues in sufficient quantities, then at night during the period of rest there is not enough blood. It is for this reason that quite often parents are faced with the fact that their child’s legs hurt at night. To relieve pain, you need to stroke the baby’s legs, this will improve blood supply, the discomfort will go away, and he will be able to continue to sleep peacefully.
Orthopedic pathologies such as flat feet, scoliosis, and incorrect posture can cause pain in the lower extremities. Due to the fact that the center of gravity shifts relative to the axis of the spine, the body weight puts uneven pressure on the legs. As a result of this, the load on one part of the limb (thigh, joint, foot, lower leg) increases many times over. Due to continuous excessive pressure, this part of the leg begins to hurt after a while.
Endocrine diseases such as diabetes, disorders of the adrenal glands or parathyroid glands can cause leg pain. Since they promote demineralization of bone tissue. Pain in the lower extremities can also be a symptom of certain blood diseases.
Neurocircular dystonia is a disease manifested by respiratory and cardiovascular disorders, which leads to intolerance to any physical activity. In this case, most often the legs hurt at night, and quite often the baby complains of a feeling of discomfort in the heart and abdomen, headaches, and sleep disturbances.
Causes of hallux valgus
— Valgus deformity of the feet, abbreviated VDS, accounts for about 18% of all forms of flat feet in children. It differs from classic flat feet in that not only flattening of the foot occurs, but also deformation in the ankle joint, when the inner ankle is located significantly lower than normal, explains orthopedic doctor, candidate of sciences Rustam Mustafin.
Due to this deformation, the joints of the feet, knees and hips suffer. If you do not start treatment for hallux valgus deformity immediately, the consequences will not be long in coming.
The main cause of hallux valgus in children is heredity. Connective tissue dysplasia leads to changes in the foot, but there are other reasons:
- diseases of the nervous system, when foot deformity develops due to problems with innervation;
- damage to the peripheral nervous system due to flaccid paralysis or paresis;
- SUD can develop as a consequence of trauma.
There are also environmental factors that can adversely affect the condition of a child with dysplasia and hallux valgus.
If a child with such problems is sent to a running class, he may develop arthrosis. Treatment of hallux valgus in children depends on the severity of the disease. It has four degrees, the first is the easiest, the fourth is the hardest.
— For grades 1 and 2 of deformity, the child is indicated for conservative treatment, that is, a set of procedures without surgical intervention. There are many conservative methods - first of all, physical therapy, since supporting the muscles for the correct position of the foot and ankle joint is very important. Regular courses of massage and physiotherapy, and orthopedic shoes are also required. All methods of conservative treatment are required only as prescribed by a specialist,” says orthopedic doctor Rustam Mustafin.
If the changes have gone far, for example, to degrees 3 and 4, conservative treatment of hallux valgus may be ineffective. Then the doctor has the right to prescribe surgical correction, but everything, of course, is purely individual.
Orthopedic shoes and insoles are especially needed for children who have the first or second degree of hallux valgus. Of course, you can’t get by with insoles alone; you need shoes to go with them. For VDS, these are special shoes with a rigid side to correct the deformity.
Doctors do not advise buying boots on your own, as this can only make the problem worse. There are many types of orthopedic shoes; a specialist can choose the right shoes for your child.
— I do not recommend choosing shoes and insoles on your own in order to avoid misunderstandings and possible negative consequences due to incorrectly selected shoes. You should choose boots only on the advice of a medical specialist. In this case, this is a pediatric orthopedic doctor,” explains Rustam Mustafin.
Before looking for a massage therapist, you need to consult again. Massage is effective in case of hallux valgus, but this procedure itself has contraindications, so you need to make sure that the child does not have them.
We must not forget that this procedure should be performed by a certified medical professional, a children's massage therapist, and not by a neighbor who has completed express courses.
The milder the degree of foot deformation in a child, the more effective the massage. It best helps children with the first and second degrees.
— For grades 3 and 4, massage is also indicated, as it allows you to normalize muscle tone, improve blood supply to the affected area, and normalize the condition of connective tissue. However, in these cases, massage is considered as an auxiliary procedure with a mandatory comprehensive approach, including possible surgical intervention at the discretion of the doctor, explains orthopedic doctor Rustam Mustafin.
It is impossible to completely cure hallux valgus in children; it is a congenital condition that will accompany him throughout his life. But this does not mean that its degree cannot be reduced. This can be done through physical therapy. In any case, the methodology, complex and regularity of exercise therapy is selected by a specialist with a medical education - an exercise therapy instructor in a medical institution.
Typically, exercises are carried out daily, first in courses in medical institutions, then independently at home or in gyms.

The success of treating hallux valgus in children depends on the parents and their observation. There are a number of symptoms that should alert loved ones and force them to make an appointment with an orthopedist for their child. These signs include:
- trampling of the inside of a child’s shoes;
- The deformation of the foot itself is in the form of valgus, when the inner ankle is located much lower, so the area of the ankle joints, when both feet are located next to each other, begins to resemble the letter X.
If you notice these symptoms, contact your pediatrician.
After the examination, he will give a referral to specialists. (In general, it is better to take your baby to the pediatrician regularly, even if nothing worries you as a parent). - Do not hesitate to confide to the doctor any of your concerns and characteristics that you observe in your child. Since the doctor examines him for only 15-20 minutes, and you monitor him daily and almost constantly. Your timidity and embarrassment are not in your favor, says orthopedic doctor Rustam Mustafin. – The faster the problem is identified, the greater the chances of a good outcome. In addition, do not forget that hallux valgus can be a manifestation of a more severe pathology, for example, neurological.
What to do
To know how to help your baby, you need to find out what causes the pain.
- If these are “growing pains,” then it is necessary to increase blood flow to the extremities. To do this, you can apply a warm heating pad to your feet. A warm bath will also help reduce pain.
- If the cause is fever and general malaise, then to improve the baby’s well-being, give him Panadol or Nurofen, in an age-appropriate dose. These are children's syrups that have analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects.
- In all other cases, the baby must be shown to the pediatrician. So that the doctor examines the child, prescribes tests, and based on their results can promptly diagnose a disease, the symptom of which is pain in the legs.
In conclusion of the article, I would like to tell all parents to listen carefully to their baby and not ignore his complaints about pain in his legs. The child must have shoes that fit, are comfortable and of proper quality. Make sure your baby leads an active lifestyle, moves a lot, and walks outside every day. This will help strengthen the leg muscles and improve blood circulation in the extremities. And, of course, pay attention to the little person’s diet; it should contain a lot of fermented milk products, fruits and vegetables.
Preventive measures
To prevent leg pain that accompanies viral diseases in children, you need to follow the recommendations:
- Monitor the child’s nutrition: he must receive vitamins and minerals necessary for growth and development;
- Treat diseases in a timely manner and under the supervision of a doctor. Always consult a doctor if the child’s well-being suffers or his temperature rises;
- Forbidding your child to endure fever on his feet will only undermine the immune system, delay recovery and lead to complications that can usually be avoided;
- Visit specialized specialists to prevent exacerbation of diseases, in particular, this applies to an orthopedist and neurologist. Many joint problems are not diagnosed in time, and therefore later cause a lot of unpleasant symptoms, which are much more difficult to get rid of. A neurologist evaluates the condition of children's muscles. If necessary, recommends massage of the legs to reduce tone. Excessive overexertion slows down the child’s development and leads to pain;
- Strengthen your baby’s immunity by taking him for walks every day, dressing appropriately for the weather, and introducing him to an active lifestyle.

Walks in the open air
A child's fever and leg pain do not necessarily appear at the same time. Signs of the disease cannot be ignored. During treatment, you need to inform the doctor about all symptoms and changes in the baby’s condition. If the doctor does not see pathologies, he will recommend not to burden the child, maintain bed rest and prescribe medications that relieve inflammation and pain. When discomfort in the legs accompanies a serious illness, consultation with a cardiologist, rheumatologist, orthopedist or neurologist may be required. The sooner the cause is found out, the more effective the patient’s treatment will be, and then complications will be avoided.
Pain in the legs of a child - causes and what to do?

You may notice that your baby does not sleep at night or even complains when walking or running for a relatively long time. Preschool children often experience so-called growing pains , which begin between 2 and 4 years of age. However, there are other more serious reasons that can cause discomfort and pain in the feet, legs and hips.
The main causes of leg pain in children
What to do if your child’s legs hurt? First of all, it is necessary to identify the cause. It can be very different - from a normal physiological process to a serious pathology.
Growing pains
The most common reason is the so-called “growing pains.” They occur spontaneously, usually in the evenings or at night, when the child is at rest. Most often, growing pains bother children aged 2 to 5 years, but they also occur at 6 and 12 years old.
Why do children's legs hurt at night? The reasons for this phenomenon are unknown. The theory that their occurrence is facilitated by the accelerated growth of the child’s bone skeleton, which muscle tissue cannot keep up with, has not received scientific confirmation. There are fast-growing children who do not have these pains, and slow-growing children with pain in the extremities.
Symptoms of growing pains:
- the child’s leg hurts for no apparent reason (there are no dangerous symptoms: redness or swelling, temperature, pain when touched);
- age – from 2 to 12 years (4 or 3 years are the most common cases);
- disturbed in the evening or at night when at rest;
- the day before the baby did not have intense physical activity;
- the pain goes away after 20-30 minutes without any intervention.
Physical activity and injuries
Pain in the legs can be caused by increased physical activity. Carefully examine the child to see if there are any hidden injuries, ask him about what he did the day before. Any excessive muscle tension can cause so-called tension pain, not to mention microtrauma.
The reason may be not only increased sports activity, but also heavy physical work. Long hikes in nature, visiting a museum, or just a long walk around the city can lead to a condition in which a child’s feet hurt.
Microtraumas usually disappear after a few days without any consequences. If for two or three days in a row the pain not only does not go away, but also intensifies, consult a doctor. If you immediately notice an injury (swelling or redness of a limb), you should seek medical help immediately.

Viral infections
Viral infections can also cause leg pain in a child or teenager. Elevated temperature and the inflammatory process occurring in the body provoke general malaise, aches and joint pain.
The child has “pulling legs” and aching muscles, especially at night. Influenza can cause complications on the musculoskeletal system. In this case, it is necessary to treat the root cause - a viral disease.
Orthopedic disorders
Poor posture, flat feet and other orthopedic pathologies are the next possible causes of a condition in which a child often complains of pain in the legs. As a result of poor posture, the center of gravity shifts, the pressure on the legs is distributed incorrectly, which is why joints, muscles and ligaments begin to suffer.
Complaints of pain in the lower legs may be symptoms of developing flat feet. If such pain is regular, and you see that the child walks on the inner surfaces of the feet (an X-shaped gait is formed), contact an orthopedist to establish a diagnosis.
It must be borne in mind that before the age of three or four years it is too early to talk about flat feet in children, since before this age their feet have not yet fully formed. This does not apply to severe congenital pathology of the flat foot, which parents usually find out about in the first month of the child’s life.
To prevent the development of flat feet, you should ensure that your baby actively develops the muscles of the foot: it is useful to walk on uneven surfaces, stand on tiptoes, walk on heels, etc.
To prevent scoliosis and other postural disorders, parents are required to visit an orthopedic doctor in a timely manner and monitor the child’s correct posture and physical activity.
Emotional state and stress
Overly emotional children, as well as those suffering from various nervous or mental disorders, are susceptible to stress. As a result, their gait may be impaired, even to the point of lameness.
At the moment of particularly strong experiences, they begin to limp more and, on the contrary, during a period of normal psychological state, these symptoms may disappear completely. All this can also affect the musculoskeletal system, resulting in pain.
Lack of vitamins and microelements
A lack of vitamins and microelements disrupts the normal functioning of the child’s body. This especially applies to calcium, magnesium, phosphorus and vitamin D.
A growing body must receive all the necessary substances for normal development. With a lack of these microelements, the musculoskeletal system is primarily affected, which can lead to pain in the limbs.
Arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints. For a long time it was believed that this disease affects people only in adulthood. However, now the arthritis is much younger.
The causes of childhood arthritis can be very different: genetic and immune disorders, congenital pathologies, infectious and viral diseases, hormonal imbalances, stress, severe hypothermia, etc.
In the early stages, the disease practically does not manifest itself at all. But attentive parents can pay attention to the first symptoms of the disease: lethargy and inactivity of the baby, reluctance to walk and run, which is explained by pain in the joints.
When to see a doctor?
If you notice an occasional episode of pain in your child's legs, there is nothing to worry about. But if your little one begins to complain of leg pain on a recurring basis, then it is important to contact your pediatrician. There are other signs that may accompany leg pain and indicate a more serious problem:
- bowed legs;
- walking on toes;
- clumsiness/falls;
- arching your toes inward (in-toeing) or outward (out-toeing) when walking;
- refusal to walk;
- foot deformation;
- complaints of back/hip pain.
If your pediatrician suspects there is still a problem, you may want to see a podiatrist for further evaluation and treatment.
Associated symptoms
Fever, rash and cough in a child - what is it?
Symptoms that may appear with leg pain include:
- The baby complains when trying to walk and cannot stand on his heel. He shifts from foot to foot, stepping on the toe or side of the foot;
- When palpating the limbs, especially from the back, from the knee and below, the complaints intensify;
- During palpation, compactions are detected;
- The skin turns red and becomes hot to the touch;
- Body temperature is slightly elevated, ranging from 37.5 to 38.0 degrees.
Important! If the pain intensifies when walking, and in the morning the baby cannot step on his foot, while he has a fever without signs of a cold, you should not hesitate to visit the doctor. Losing time can lead to serious complications.

Doctor's appointment
If a child is less than a year old and does not walk, parents notice something is wrong the moment they put the baby on his feet. He begins to press them in, refuses to lean on them, whereas before he calmly moved around the support. Any changes in behavior should alert you. This is especially true for young children who are unable to talk about what worries them.
What can you do to help?
Sometimes children can suffer from overworked muscles, which is why they are quite active during the day. Here are some tips that may help:
- Buy durable shoes . Babies' feet are still developing and growing. In the early stages of walking, they need durable boots to help support their leg muscles and bones. Take your little one to the shoe store and get the right size. Remember that children's feet grow quickly, so the size changes several times a year.
- Give your child a warm bath . You can try a warm bath for your baby in the evening after a long day of running, jumping and playing. This will help tired muscles relax and help your baby sleep better. After the bath, give him a foot massage using baby lotion.
- Encourage drinking fluids . During digestive problems or hot days, make sure your baby takes in enough fluids. Limit sugary drinks, try to force them to drink only clean water.
- Prevent anemia . Feed your baby foods high in iron to avoid developing anemia. Examples include iron-fortified grains, eggs, lean meats, and leafy green vegetables.
These are examples of what you can do for your child if he or she is experiencing leg pain when the doctor has found no serious underlying cause that requires treatment.
Causes of pain in calves
Pain in the calf of the right or left leg is one of the most common clinical manifestations. Sometimes it is caused by overwork of a muscle after intense or prolonged physical activity. However, this symptom does not always indicate such innocent reasons. It is often caused by serious diseases such as diabetes, atherosclerosis or spinal tumors.
Quite often, the causes of calf pain lie in thrombosis and varicose veins. Suspicion of these vein pathologies should arise if, in addition to the main symptom, the leg is pulled or the heels hurt when walking. This happens because with severe circulatory impairment in the venous vessels of the leg, swelling of the leg occurs, which manifests itself in pain. As a rule, such pain is dull in nature and is accompanied by heaviness in the limbs. If these processes become chronic, there is a decrease in the supply of nutrients to the tissues, leading to the accumulation of waste and toxins, and also causes inflammatory processes.
Provoking factors
The causes of painful symptoms in the legs in childhood can be quite different, ranging from a simple bruise and injury to the development of severe pathological diseases.
Experts identify the most common factors contributing to the development of this condition:
- one of these reasons is intensive growth, in medicine classified as “growing pains”, which manifests itself in children from 5 to 7 years old. In this case, rapid body growth (before puberty) is noted due to elongation of the lower limbs;
- children may complain of pain if they have orthopedic problems (flat feet, scoliosis, poor posture, etc.). As such conditions progress, there is a shift in load, which leads to increased body pressure on the legs. In addition, pain in the legs can occur with pathological changes in the hip joint of a hereditary nature;
- The cause of leg pain in a child may be a chronic infection, for example, caries, adenoids or tonsillitis. Therefore, timely sanitation of lesions, especially in the oral cavity, is extremely important;
- a child may suffer from leg pain if the endocrine system is disrupted, which may manifest itself, for example, in the form of diabetes. The provocateur of the development of this disease is impaired function of the parathyroid gland and adrenal glands, which is manifested by demineralization of bone tissue;
- Children after 3 years of age often experience pain in the calf muscles, which is caused by insufficient intake of phosphorus, calcium and potassium into the body. In addition, an extremely unpleasant disease that accompanies any physical activity (even minimal) is neurocircular dystonia, in which the child complains of pain in the legs, appearing most often at night. In this case, the baby may complain of discomfort in the heart and abdomen;
- Painful symptoms in the legs of children are possible as a result of pathological disorders of the circulatory system, characterized by causeless falls of the baby and the presence of discomfort. In addition, during active sports, a child may experience pain in the legs, which requires a review of the training regimen and a reduction in load.
Schlatter's disease is very common in children, which causes acute pain in the front of the knee joint.
In all cases of pain in the lower extremities in children, it is necessary to contact a medical institution to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe further therapeutic measures. Consulting a doctor is especially important when the knee hurts and unpleasant symptoms appear at night, accompanied by a deterioration in the child’s general condition. This condition may signal leukemia, Still's disease, or malignant neoplasms. In addition, the baby should be shown to a doctor if swelling appears in the leg area.
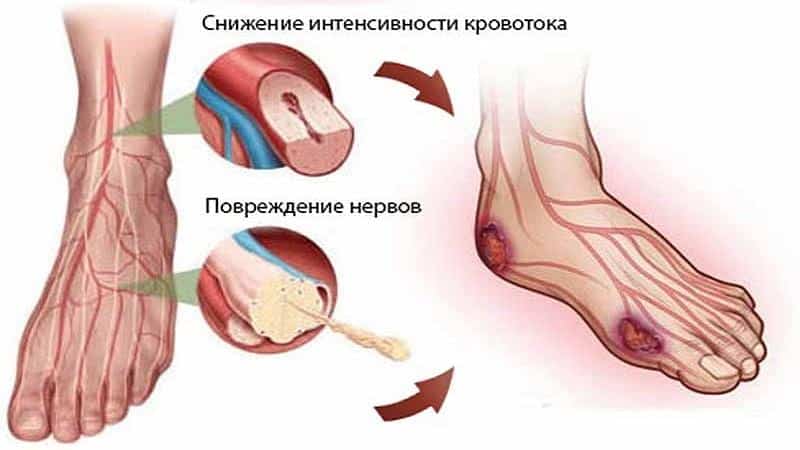
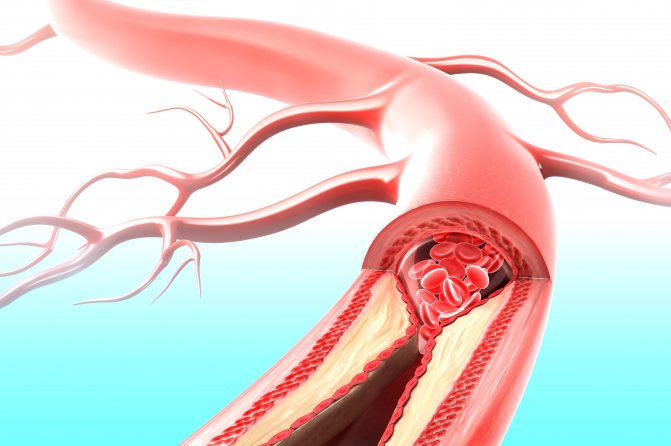
Calf pain due to arterial insufficiency
This diagnosis is characterized by very severe pain associated with insufficient blood supply, which is the main source of oxygen and nutrients. Such processes can cause very serious consequences, including gangrene.
Atherosclerosis causes hardening of the vessel walls, which causes pain in the patient's calf. The pain is of a compressive nature and is localized directly in the area of the lower leg muscles. When walking, the load on the muscle increases, which leads to increased pain. The main manifestation of atherosclerosis is cold feet syndrome, which occurs regardless of air temperature.
Symptoms
In advanced cases, X-shaped legs in a child can be noticed immediately by the special shape of the limbs. Clinicians also identify false deformities, when the bone structure is not disturbed, but the shape of the muscles and subcutaneous tissue causes the appearance of curvature. At the initial stages, the symptoms are mild, but when the child begins to walk independently, some signs are immediately noticeable. These include:
- Fatigue quickly when walking – this shape of the legs is unnatural; the muscles have to put in more effort to contract than normal. All this leads to the child’s fatigue even during normal walking,
- Gait instability – gradually the disease leads to sprained ligaments and the development of instability in the knee joints. As a result, under the weight of the baby’s own body, the gait becomes shaky and unstable. In severe cases, subluxations in the knees and hip joints may develop,
- Curvature of the lower limbs - with age, when the child grows and the limbs stretch - the deformation becomes clearly noticeable,
- The appearance of convulsions - with curvature and gait disturbances, hypertonicity and muscle fatigue appear, which leads to convulsions,
- Leg pain develops several years after the onset of the disease, when a persistent curvature has formed, forcing the baby to change his gait and physical activity.
If correction is not carried out, then over time the child will develop deformation of the feet and the appearance of curvature of the spinal column.
Over time, normal walking is disrupted - the baby begins to tuck his leg in such a way that the load falls on the outer edge of the foot. If in a normal state it is evenly distributed over the foot, then with this pathology the line of support shifts to the side. All this leads to bone deformation and the development of flat feet. The ankle joints gradually become bent, and the redistribution of the axial load disrupts posture and leads to scoliosis or kyphosis of the spine.
Spinal diseases and peripheral nerve diseases
The spine is connected to almost every organ, so its pathologies can manifest themselves in any part of the body. Thus, disorders in the intervertebral discs often radiate to the legs, and the back itself may not hurt. This category includes sciatica - inflammation of the sciatic nerve, in which pain is localized in the lower extremities.
If your calf muscles hurt, this may indicate peripheral nerve disease. An additional symptom is that the pain has a paroxysmal appearance. Such attacks can last from several seconds to several minutes, and between these waves there is practically no pain.
Causes of muscle weakness
The main cause of muscle weakness is damage to the junction of nerve endings with muscles (synapses). As a result, the root cause of the disease is a disorder of innervation, all other factors are its consequences.
Innervation of muscles is provided by a special substance – acetylcholine. In myasthenia gravis, acetylcholine is perceived by the patient's immune system as a foreign substance, and therefore it begins to produce antibodies to it. The conduction of nerve impulses to the muscle is disrupted, which leads to the development of weakness in the muscles. But at the same time, the muscles continue to retain their capabilities, since alternative life support systems are launched in the human body, compensating to some extent for this deficiency.
Muscle weakness can be a symptom of various diseases. In some cases it simply indicates fatigue, and in others it indicates damage to tendons, muscles, joints, bones, and diseases of the nervous system. Some muscle weakness always occurs during illness and, as a rule, is one of the signs of aging.
The immediate causes of muscle weakness include:
- Neurological diseases: multiple sclerosis, stroke, cerebral palsy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Guillain-Barre syndrome, nerve damage, Bell's palsy;
- Diseases of the endocrine system: Addison's disease, thyrotoxicosis, low levels of calcium or potassium in the body, hyperparathyroidism, diabetes mellitus;
- Various intoxications: poisoning with organophosphorus compounds, botulism;
- Muscle diseases: muscular dystrophies, polymyositis, mitochondrial myopathies;
- Other causes: polio, anemia, emotional overload, stress, asthenic syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis.
Muscle weakness in the legs can also occur with varicose veins, arthritis, scoliosis, and intervertebral hernia.
Muscle weakness in a child is most often caused by pathologies of the nervous system. Decreased muscle tone in newborns is usually a consequence of birth injuries.
Inflammation and infectious diseases as a cause of pain in the calves
An inflamed calf muscle causes very severe pain. Myositis - inflammation of skeletal muscles - requires immediate treatment and constant medical supervision. As a rule, they occur as a result of injuries to the leg muscles or complications from influenza and other diseases.
If the calf muscles hurt and the pain is aching, it is highly likely that purulent myositis can be diagnosed. It is also indicated by chills, increased body temperature, and the presence of dense nodules and muscle compactions.
Often, calf pain is caused by osteomyelitis, a bone infectious disease that manifests itself in acute and prolonged pain. Their cause lies in the bones themselves, so eliminating such pain is quite difficult.
Diagnosis of the causes of calf pain
Diagnosing the cause of pain in the lower extremities is extremely difficult. This is primarily due to the huge number of pathologies that can cause such reactions.
If you have severe pain in your calves for a long time, you should immediately tell your doctor so that he can diagnose the cause of the pain.
If pain occurs in the calf of the left or right leg, you should contact the following specialists:
- angiosurgeon;
- traumatologist;
- phlebologist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- neurologist.
Making the final diagnosis and prescribing treatment are carried out not only based on the patient’s complaints, because many people have pain in their legs below the knees. To determine an accurate diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- a general blood test allows you to identify what elements are missing in the body for the normal functioning of the leg muscles;
- X-ray of the spine, hip joint, sacral joints;
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography are the most modern and informative diagnostic methods.
Sometimes anamnesis data is used to increase the efficiency of diagnosis.
Timely diagnosis is especially important for pregnant women, because pain in the calves when walking can be a symptom of very serious diseases and significantly worsen the condition of the fetus.
What vitamins are missing if your calves hurt?
Skeletal muscles suffer due to the resulting calcium deficiency. The macroelement takes part in biochemical reactions aimed at contracting and relaxing its fibers. It catalyzes the production of bioactive substances - the main building material of skeletal muscle cells.
There are often situations when calcium enters the body in sufficient quantities. But it is not fully absorbed due to a lack of fat-soluble vitamin D3.
Its reserves are replenished in three ways:
- Air baths. Frequent exposure to direct sunlight stimulates D3 production in the skin.
- Taking medications. Therapeutic regimens include Calcium D3 Nycomed and Natekal D3 complexes. Improves the functioning of the entire musculoskeletal system by taking a course of fish oil in an oil solution or capsules, and ergocalciferol in various dosage forms.
- Correction of diet. The fat-soluble vitamin is especially abundant in fatty sea fish - salmon, herring, mackerel. All vegetable oils are saturated with it: olive, sunflower, corn, flaxseed, sesame.
A common cause of muscle aches in the cold season is a deficiency of B vitamins. Bioactive substances stimulate adequate blood supply and muscle trophism, improve the transmission of nerve impulses.
Against the background of vitamin deficiency, severe weakness occurs, especially pronounced in the limbs. It is impossible to perform usual physical activities. A person suffers from tremors, aches, crawling sensations, and loss of sensitivity.
How to eliminate the deficiency of riboflavin, thiamine, cyanocobalamin, pyridoxine, folic acid:
- introduce into the diet more fresh vegetables, fruits, berries, cereals made from rice, buckwheat, millet, corn, fish and lean meat, seeds, mushrooms;
- exclude drinks with a diuretic effect from the daily menu - alcohol, coffee, strong tea;
- additionally take balanced vitamin and mineral complexes - Centrum, Vitrum, Complivit, Supradin, Multitabs;
- as prescribed by a doctor, use medications with B vitamins - Milgamma, Combilipen, Neurobion.
Fat-soluble vitamin E is available in capsules and oil solution. It has pronounced antioxidant and regenerative properties, prevents the destruction of muscle tissue by free radicals.
Its lack also often causes pain in the calves. This is also true for ascorbic acid, an integral participant in regenerative biochemical reactions.
Before prescribing medications, the doctor determines why the body lacks a certain vitamin. There is a possibility of developing severe pathology requiring pathogenetic therapy.
For example, the absorption of biologically active substances is disrupted due to endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism).
↑