Mechanism of appearance in children
Moles are formed under the influence of the following factors:
- Prolonged exposure to the sun provokes the development of nevi. The skin contains special cells - melanocytes. The latter secrete a pigment called melanin. It provides color to the neoplasms.
- Frequent visits to solariums lead to active proliferation of melanocytes.
- The appearance of pigmented spots is associated with a hereditary predisposition to neoplasms. A typical example is harmless pigmented spots that are inherited. The baby receives markings from its mother or father.
- Radiation and X-rays provoke the appearance of formations.
- Growths can appear in adolescents due to hormonal changes in the body. During this period, many pigmented formations appear on the child’s body. After hormone levels normalize, the nevus disappears.
- Pigmented neoplasms appear in the prenatal period. After birth, the baby's moles are scattered throughout the body. They do not protrude above the skin level and rarely become malignant. Convex formations occur in adolescents and older children.
Pigmented neoplasms in children rarely degenerate. Proper care of moles and periodic inspection of growths will prevent possible problems in the future.
Causes of age spots in teenagers
The reasons for the appearance of many age spots on the body of a teenage child:
- excessive sun exposure;
- genetic predisposition;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- X-ray and radiation exposure;
- stress.
It is necessary to monitor the time spent in the sun. The World Health Organization has developed an international standard - ultraviolet index, the degree of ultraviolet radiation. Depending on it, the maximum time spent in direct sunlight is calculated. In mid-latitudes you should not be in the sun for more than 15 minutes.
Prolonged exposure to the sun has a detrimental effect on the skin and eyes. During the daytime, you need to hide in the shade, cover your body as much as possible, wear glasses and hats.
The peak appearance of pigment spots occurs during puberty (puberty), when the growth of the body is activated. In the blood, the concentration of hormones increases, increasing the intensity of cell division and differentiation, and anabolic processes intensify. Melanin metabolism is influenced by the melanotropic hormone of the pituitary gland, the content of which in the blood also increases. As a result, melanin synthesis and its accumulation are enhanced.
All processes are strictly dependent on genetic factors.
Many teenagers are susceptible to stress. This is influenced by many factors: unfavorable living conditions, problems with peers, pressure from parents, confusion and fear of future problems. In a stressful situation, the sympathetic system is activated in the body. As a result, the level of stress hormones - glucocorticoids, which indirectly increase the formation of melanin, increases.
At what age do they appear?
A small percentage of newborns are endowed with pigmented spots from birth. Other children develop different types of nevi throughout their lives. The growth and activation of melanocytes is directly related to the following reasons: prolonged exposure to the sun (especially during a sea holiday), hormone levels, frequent visits to solariums). Gradually, the number of tumors on the skin increases.
It is difficult to talk about the exact timing of the appearance of moles in childhood. The period of melanocyte activity ranges from 6 months to 1 year. Second wave – 5-6 years. It is associated with the active development of a small organism and is called a growth spurt. The third is adolescence. Hormonal imbalance is a favorable factor for the development of tumors. According to scientific data, moles can appear up to 25 years of age.

Features of children's moles
Moles are dark spots that appear on the skin of the face and body in newborns. For some they disappear, while for others they become numerous over the years. They are formed due to the accumulation in certain places of a dark pigment - melanin.
At one time it was believed that they arise due to harmful environmental influences, but now they are more often blamed on genetics. Being benign, in some cases they degenerate into malignant, causing skin cancer .
Is it normal for a child to have no
Attentive and caring parents are interested in the important question of whether it is normal for moles to be absent on a child’s body. Clean skin without pigmented spots should not cause concern. This phenomenon is considered a normal condition in childhood.
Nevi are divided into congenital and acquired. If a baby inherits moles from his parents, they are present on the body from birth. Other children have clear skin for a long time. Under the influence of sunlight, hormones, and liver diseases, melanocytes are activated. They accumulate inside the dermis and, under the influence of melanin, color the skin dark. The fewer pigmented formations, the better for the child.
What is dangerous when children have too many of them?
If parents are worried about spots that have appeared on the baby’s body, they should definitely contact a dermatologist or pediatrician. The doctor will conduct an examination and determine how dangerous it is for the child’s health. Malignant pigment spots at a young age are not a common occurrence. But, it is important to ensure that the moles do not become even larger.
It is also important to take into account the child's reaction to such education. Often nevi appear on the skin due to decreased immune defense. This can also cause changes in the size and color of moles.
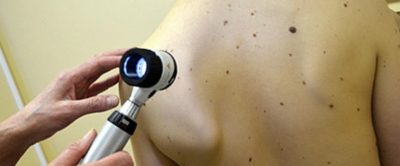
Often, inflammatory processes can bother a child when birthmarks degenerate. Taking this information into account, we can say that even barely noticeable nevi can be very dangerous.
But don’t sound the alarm ahead of time. Degeneration of moles is quite rare. Moreover, this does not depend on the number of spots that occur on the baby’s body.
In medicine, there is a special classification of nevi. They can be vascular or regular. The former differ in their structure, since they contain blood vessels.
Their color can take on different shades - from pink to red. Red moles are not dangerous, but in some cases they are removed because such formations do not look aesthetically pleasing.
The second type of moles is considered common. They often have a smooth surface. They take on a light brown or black tint. and their appearance can be observed in the first years of a child’s life. When hair grows in this area, it is considered a good sign. You need to worry about moles that are located on the palms or soles of your feet.
How to distinguish dangerous from non-dangerous moles
Every skin growth poses a danger to the child's health. Any nevi can eventually degenerate from a benign tumor to a malignant one. There are the following types of harmless moles:
- Red spots are observed in babies up to one year old. Their typical location is the forehead, the back of the head, and the nose. The mechanism of appearance of these neoplasms is associated with friction against the maternal bones. The baby's head is large in the womb. When passing through the birth canal, the protruding parts of the skull rub against the pelvic bones for a long time. Red spots do not require treatment. In a one-year-old child they completely disappear.
- Flat brown formations do not protrude above the skin level. They rarely get injured. Brown spots may disappear without a trace over time. Sometimes they last for the rest of your life. The formations do not malignize and do not pose a serious threat to the health and life of the patient.
- Strawberry hemangioma is a convex pigmented growth of red or burgundy color. Soft to the touch. Strawberry hemangioma appears in the first weeks of life. It may be congenital. The pathology brings discomfort during movement if it is located on the palms or heels. Dermatologists and oncologists do not recommend removing the formation using known methods. Minor injuries can cause hemangioma to transform into cancer.
- Cavernous hemangioma is formed by blood vessels. It has unclear boundaries and an uneven shape. The growth disappears on its own during puberty.
Dangerous moles include:
- Setton's nevus is a small red nodule. The neoplasm differs from other growths in the presence of depigmented light skin around it. It has an oval shape with clear boundaries. It often degenerates into melanoma. Sometimes the tumor disappears on its own. Typical locations are arms, back, abdomen, feet, fingers, navel, lips.
- Papillomatous nevus visually looks like a malignant tumor. It is characterized by an irregular shape, blurred edges, dark color, and large size. The growth is localized on the head. Hair grows on it. One type of papillomatous nevus is verrucous. On its surface there are cracks and pigmented inclusions.
- Fibroepithelial nevus is characterized by slow growth. It has a dark brown, blue color. On the surface of the mole there is stubble or vellus hair. Several formations appear on the skin at once. Fibroepithelial growth should be differentiated from borderline growth. The latter is distinguished by smooth borders and dull coloring.
- An intradermal nevus is a formation that looks like a birthmark.
- An atypical nevus grows more than 1 cm. It is characterized by typical signs of malignancy: irregular shape, unclear boundaries, black color.
- The Mongolian spot comes in blue and brown colors. The typical location is in the spine. Education disappears during adolescence.
Any skin growths can degenerate. Symptoms of malignancy include:
- The growth began to grow rapidly.
- The shape of the growth has changed.
- The mole has become asymmetrical.
- It has blurred boundaries.
- The color of the growth has changed. It can be black or white.
- Vesicles with transparent contents appeared around the neoplasm.
- The mole has festered.
- Benign neoplasms do not hurt or itch. The appearance of unpleasant symptoms indicates degeneration. If the lump begins to itch terribly, seek medical help immediately.
- Crusts, peeling, ulcerative defects, bulges on the mole indicate malignancy of the formation.
- Location in frequently traumatized areas can lead to the development of melanoma.
- An increase in the number of nevi indicates pathology.

Red and black birthmarks on a child's face
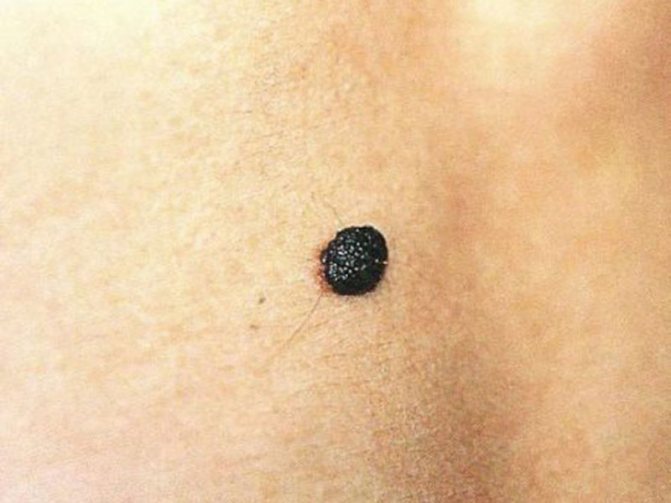
Nevi can vary greatly in color, but the most common are brown or black pigment spots. If new birthmarks begin to appear on the child’s face, it is important to regularly examine them and it is advisable to have this done by an experienced doctor. After all, only through timely control can undesirable consequences be avoided.
If we consider the size of nevi in children, they can be either miniature - from a few millimeters, or huge, more than 10 cm in diameter. From the results obtained in the process of laboratory research, the degeneration of medium- and large-sized moles in half of the cases leads to the appearance of a malignant tumor.
Congenital nevi of gigantic size are quite rare. At the same time, girls are more predisposed to pathology. The mole grows together with the child's body and stabilizes in size as the person matures.
Most often, red spots may appear on the face of children, which are located on the bridge of the nose or forehead. This is a congenital phenomenon that occurs due to friction of the baby's skin against the mother's pelvic bones during pregnancy. In most cases, such red spots go away on their own. One-year-old children have practically no such spots.
The second most common ones are flat nevi, or port-wine stains as they are called. They are most often observed on the face and scalp. The growth of port-wine birthmarks continues even after the child reaches adulthood without any changes in color. Such formations are removed with a laser.
Not too common are standard brown spots, which sometimes have a dark, almost black tint. They appear both on the face and on other parts of the body of children and are absolutely harmless to health.
The following neoplasms can be found most rarely on the skin:
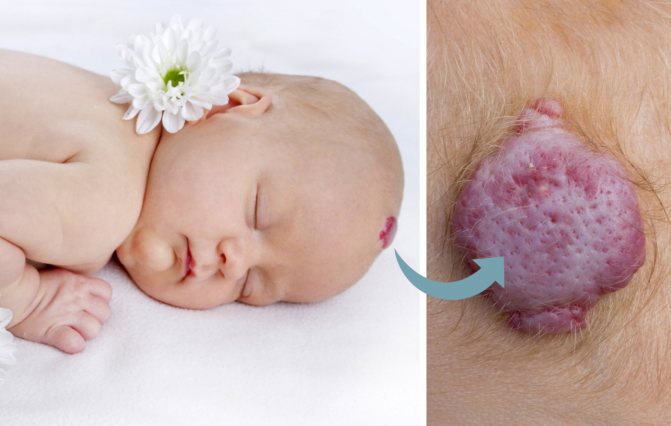
“Strawberry” hemangiomas are spots that look like bulges with a red tint and are quite soft to the touch. This pigmentation is observed in the first weeks of a baby’s life, although in rare cases it can be congenital. With age, the spot becomes pale and changes in size. This mole is absolutely harmless and does not require treatment.- “Cavernous” nevi, which are large birthmarks with vascular elements. This type of hemangioma penetrates into the deep layers of the skin. The color of the new growth is bluish-gray, and the contours are blurred. This pathology also cannot be treated. Usually, when a child reaches 12 years of age, it disappears on its own.
It is important to understand that the presence of large birthmarks on a baby’s skin can lead to their degeneration into a malignant tumor and, as a consequence, skin cancer.
Which nevi should be removed and at what age
Dangerous formations (hanging, modified) should be removed. Treatment is carried out at any age in a hospital setting. Home remedies and Dr. Komarovsky’s advice are ineffective in this case. There are a huge number of effective ways to eliminate moles:
- Cryodestruction is a method of getting rid of skin growths using liquid nitrogen. During the procedure, mobile children may experience thermal burns. Cryodestruction is rarely used in childhood. It is suitable for adults and children over 14 years of age.
- Electrocoagulation is a medical procedure in which a high-frequency current is applied to the pathological area. Using a heated loop, the tumor is removed.
- Laser destruction is a harmless and painless way to treat skin growths. The formations disappear in one session of the procedure.
- Radio wave removal is carried out using a special device - a radio knife. The electrode heats the atypical tissue. They evaporate and the disease recedes. Radio wave surgery is widely used in therapeutic and pediatric practice. The manipulation does not leave any marks on the body.
- Drug therapy is selected individually in each case.
The division of neoplasms into dangerous and non-dangerous is a controversial concept. Any moles can degenerate. Pathology has a risk of death.
Should I delete it if the quantity starts to bother me?
Many children develop moles at a very young age. This phenomenon is absolutely normal. You can only be wary if many moles appear in 2-3 months. In this case, it is better to visit a dermatologist or oncologist.
The doctor will examine the moles on the baby’s body and tell you about the reason for their multiple appearance. Often, nevi appear as a reaction to tanning and other external factors. In rare cases, they can talk about pathologies associated with the immune system and diseases of the internal organs.
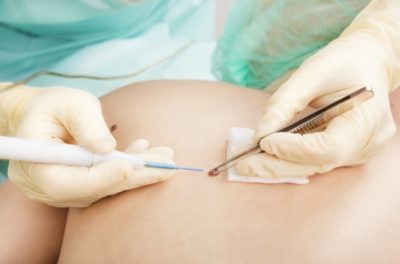
But often they appear in places where a child can catch them with clothes or shoes. Removing nevi is in some cases a simple necessity. But even after a minor operation, a number of complications associated with bleeding and allergies to anesthesia can occur.
Nowadays, the most popular methods of getting rid of moles are:
- surgical.
- Laser cleaning.
- Use of liquid nitrogen.
- Cauterization with electric current.
- Radio wave.
The choice of method is made by a doctor , as he takes into account the properties of moles. Often, tumors similar to cancer are removed with a scalpel in order to completely rid the body of infections. In other cases, cryodestruction and laser cleaning have become extremely popular. Such methods are considered the safest.
After removing a mole, pain may occur after some time. It is associated with a violation of the integrity of the skin. If desired, it can be stopped using painkillers. The best of them should be prescribed by a doctor.
The wound at the site of the mole should be treated until complete healing. Using ointments you can speed up this process. To prevent infection from getting into the wound, you need to take into account the following tips:
- You can’t get the crust wet and tear it off.
- It is important to ensure that the wound does not get exposed to the sun. Before your child goes out into the sun, cover it with a plaster.
If a mole has been removed surgically, its complete healing can be observed after 2 weeks. As for the other methods, they are less painful and the unpleasant sensations will not last more than 7 days.
It is very rare to observe wound inflammation due to infection. In this case, healing may be delayed, and scars may remain after it.
Possible complications
The main and dangerous complication of moles is melanoma. This tumor is malignant, a formation that consists of atypical melanocytes. Pathologically altered cells quickly proliferate and grow into the underlying layers of the dermis. They enter the bloodstream and are carried by the blood to all internal organs. Tumor metastases occur in the bones, lungs, kidneys, and brain. Fighting diseases takes several years. Even after the patient has fully recovered, this insidious pathology can recur.
Vigilance and health care help stop the growth and degeneration of nevus in children and adults. At the first signs of pathology, you should consult a dermatologist-oncologist to confirm or refute your concerns.
The formations degenerate with constant trauma and prolonged exposure to the sun. Teach your children to take care of their skin from an early age. Handling nevi carefully can help prevent a serious disaster.
Parents should monitor children's large moles in order to promptly identify a malignant process. To prevent the development of melanomas, seek medical help promptly!
Classification of formations
There are several types of moles in children:
- Vascular. Many blood vessels form such nevi; their color is pink, red or bright red; with a smooth or convex surface. These nevi are classified as benign moles that are not dangerous to health if they do not change or become damaged. At the same time, if the red nevus is non-congenital, then pathological processes associated with the work of visceral organs can occur in the body: the colon or pancreas; causing disruption of metabolic processes, for example, lipid metabolism; causing skin diseases.
- Non-vascular moles are formed from clusters of melanocytes and come in different sizes (from 0.5 to 10 cm) and colors (from yellow to brown or black). It is these nevi that look like warts. It is dangerous if they are placed on the soles or palms, as they can be torn off or damaged.
- Hanging moles are a combination of nevus and papilloma. Almost always, in the presence of such formations, the body is parasitized by HPV - the human papillomavirus. These formations are also highly susceptible to damage.
Spontaneous disappearance of moles is also a cause for concern
Even if a child has many moles on his body, but they are small, with smooth edges and uniform coloring, then this is not dangerous. If a child has many moles on the body, some of which are pedunculated, others have an uneven color, a tendency to grow unevenly, or a size of more than 1.5 cm, etc., then you should consult a qualified specialist and remove the dubious formations. The spontaneous disappearance of moles is also a cause for concern: the appearance of a pale spot at the site of a nevus may be a sign of a skin disease.
When do newborns develop moles and is it worth paying attention to?
Moles are a common phenomenon for everyone and appear throughout life. As a rule, they do not threaten health, but when they appear in newborn babies, they raise many questions and concerns among parents.
A mole (or nevus) is a skin growth characterized by pronounced pigmentation.
The appearance is possible on any part of the body, both on the limbs, head, torso, and on the mucous membranes.
They can be of different colors, depths and shapes.
There are several classifications of moles depending on size, origin and impact.
Moles are:
- pigmented (they are also called ordinary);
- vascular.
Common moles appear in the first years of a child's life. Their color ranges from light brown to black. Pigmented moles have a smooth surface and can be convex or flat. They arise under the influence of melanin. If this pigment is not enough, then the birthmark will be lighter than the skin; if there is an excess of it, on the contrary, it will be darker.
In newborns, there are moles of a non-standard color, blue or light blue. This is a blue nevus. It may go away on its own or remain for life. Experts recommend examining this type of nevus as early as possible from the moment of birth.
Vascular consists of a large number of blood vessels, so they are usually pink or red in color. These moles are benign and do not pose a danger in themselves.
Vascular moles in children are also divided into:
- Hemangiomas. This tumor can appear several weeks or months after the birth of the child on any part of the body. The main period of growth occurs between the ages of six and twelve months. The hemangioma increases in size, but becomes lighter over the years and usually disappears completely by the age of ten.
- "Stork bite." It looks like a pink spot and is usually found on the neck, back of the head, or bridge of the nose. Appears due to dilation of blood vessels during development in the womb. Interestingly, the color of the “stork bite” is influenced by the condition of the newborn. If the baby cries, the spot turns red; if he sleeps or is hypothermic, the spot turns pale. Usually, when a child reaches two years of age, the tumor disappears.
- Flaming nevus, or port-wine stain. Unlike the two previous types, this mole is permanent and does not disappear with age. It has a very bright, rich pink color and is located on the face, usually on one side. Over the years, it becomes even more intense in color, and after ten years it looks like a tumor. In addition to the psychological problem, depending on the location, this nevus can cause, for example, glaucoma. To exclude this, it is necessary to start treatment at an early age, preferably before three years of age, before everything turns into a serious problem.
- "Mongolian Spot" Mostly such spots are localized on the legs, tailbone and hips. May occur due to difficult childbirth. In appearance they resemble large gray bruises with a bluish tint. They usually go away by the age of two. This birthmark never develops into a malignant one. In 90% of cases it occurs in the Mongoloid race, hence the characteristic name.
Depending on the layer of the skin in which birthmarks are located, they can also be divided into:
- Borderline is a type where all cells are located in the epidermis;
- Intradermal - formed from the dermis;
- Mixed - can simultaneously be in both the dermis and epidermis; they are also called complex.
Moles in newborns: causes
Moles can be either congenital, which formed in the womb and appeared in the first month after birth, or acquired. Therefore, there are several reasons for this:
- Heredity. For example, if mom or dad has birthmarks, the baby may have them in the same places. This is a manifestation of genetic predisposition.
- Stress during pregnancy. Sudden changes in blood pressure in the child's mother can lead to vasoconstriction and impaired blood circulation. Bursted blood vessels can form a vascular nevus in a baby.
- Ultra-violet rays. Prolonged exposure to the sun can cause new nevi to appear.
Who is most likely to have birthmarks at birth?
The following group is most likely to get congenital nevi:
- Children with very fair skin.
- Girls. According to statistics, birthmarks are four times more common in girls than in boys. Scientists explain this by natural hormonal levels.
- Children born before their due date.
Precautionary measures
Newborn birthmarks must be carefully monitored and limited from damage to prevent the transition of a benign neoplasm to a malignant one.
- Do not expose skin areas with birthmarks to prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays; they can both lead to the appearance of new moles and irradiate existing ones. Mothers often go to the beach with their children, in which case it is necessary to use special sunscreens with a high level of protection, cover moles with clothing, and also wear a hat. You must be in the shade from 11 a.m. to 4 p.m. You can use a beach umbrella to provide shade for your child. Some people believe that if you tan well, the birthmark will not be so noticeable, but in fact this opinion is wrong, because the neoplasm will also darken.
- Avoid damaging the nevus. To do this, you need to choose comfortable clothes and make sure that the child does not cause harm himself. If the mole is located in such a place that friction cannot be prevented, and it is periodically injured, it is better to remove it.
- Avoid interaction of acids and alkalis with the skin.
- Monitor visual changes in birthmarks.
- Treat dermatitis.
- Do not cover nevi with adhesive tape, thereby creating a greenhouse effect.
- If there are hairs on the birthmark, do not pull them out.
It is desirable that the SPF index for children's sunscreen be 50 or more, and the PPD index be 42. The first indicator indicates the degree of protection against ultraviolet rays, and the second indicates the degree of protection after exposure to the sun.
The child needs to be seen by a doctor if the following changes in the nevus become noticeable:
- the color has changed completely or partially;
- increased size;
- itching appeared;
- a crust formed and liquid began to secrete;
- a glossy shine appeared that was not previously noticeable;
- the color around the nevus has changed (red or white skin around);
- growths appeared;
- the boundaries have become blurred;
- the mole began to bleed;
- the nevus has broken off or fallen off.
Under no circumstances should you attempt to remove a child’s mole yourself or resort to folk remedies. This can cause irreparable harm to the baby, even death.
Removal of birthmarks in children is carried out for cosmetic (on the face) or oncological indications.
In modern medicine, there are many different ways to treat birthmarks: medication, surgery, laser, and cryotherapy. The doctor chooses the most suitable option for the newborn.
During drug treatment, hormonal drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets or ointments, which slow down the development of formations.
The advantage of laser removal is that this method does not leave scars and is carried out quite quickly.
Removing moles with liquid nitrogen is rarely used for children, this is due to the fact that one procedure may not be enough, and repeated use may leave a burn on the child’s skin.
In most cases, birthmarks in newborns are not dangerous. With proper precautions and careful monitoring, there should be no cause for concern for parents.
But do not forget that a benign spot can degenerate into a malignant one due to a number of factors, so if any changes occur, you should contact an oncologist; timely treatment can prevent an unfavorable outcome.
Source: https://momjournal.ru/razvitie-detej/kogda-u-novorozhdennyx-poyavlyayutsya-rodinki.html
Red moles in newborns: causes, types and possible consequences
Moles in infants are formations that can appear immediately after birth or appear during the first year of the baby’s life. Age spots are caused by multiple factors and are not a sign of disease, but can cause concern for parents. A nevus consists of melanocyte cells, which are formed in utero and are prone to multiply within the epidermis under the influence of environmental factors or the developmental and growth characteristics of a child’s body.

Types of nevi
Categories of stains are differentiated according to the following indicators:
- pigment color – brown or red. Depending on the color, a mole or a vascular hemangioma is distinguished. A white or black nevus may appear (a type of brown pigment of varying intensity of coloring of the formation), blue or blue-gray (the level of pinching of the vessel, the type of damage to the veins, capillaries or arterioles);
- by size: small dots with a diameter of up to 1.5 cm, medium ones up to 10 cm; large - more than 10 cm in diameter. Large ones - rarely found in a baby, they are a cause for concern and require histological examination;
- vascular disorders: anemic red nevus (strawberry angioma), cavernous gray-blue hemangioma. Red moles in infants are common, due to the peculiarities of pregnancy and the passage of the fetus through the birth canal (compression during cephalic presentation, ischemic-hypoxic effects of pushing on unformed vascular formations);
- in shape: from oval, round, angular, to spots in the shape of animals, any object that surrounds us in everyday life;
- rising above the surface of the skin: hanging, pointed, mushroom-shaped, warty;
- depending on the depth of location: borderline (protrude slightly above the skin), intradermal spherical, hanging and convex;
- congenital and acquired.